iGCSE Edexcel Physics Electricity
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
115 Terms
conductor
a material that allows current/electric charge to move through it freely and fairly quickly
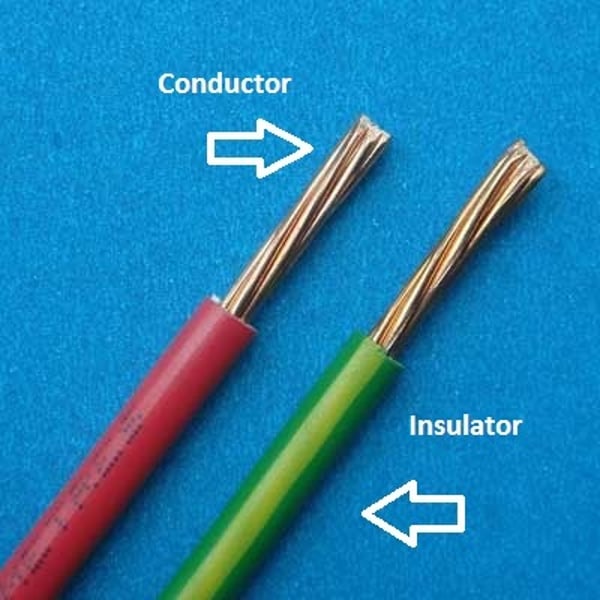
insulator
a material that does not allow current/electric charge to move through it

electric current
the rate of flow of charge
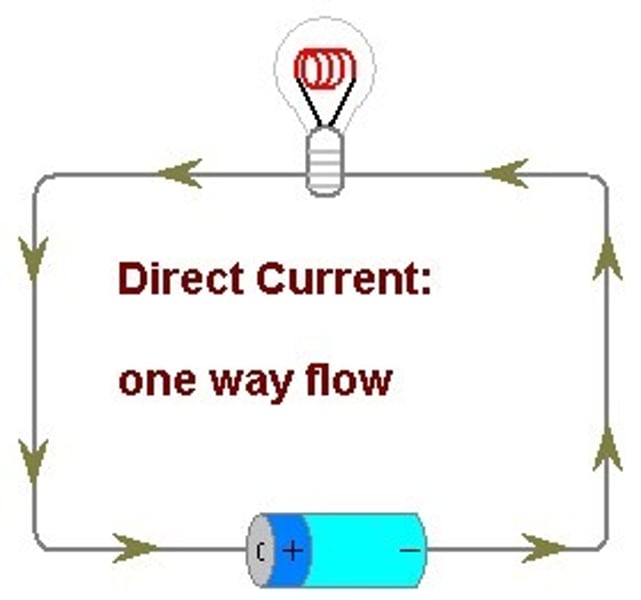
direct current
the current only flows in one direction
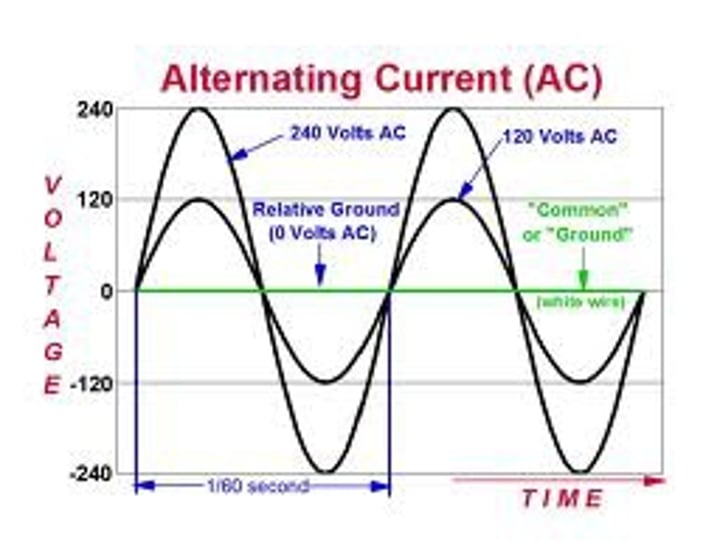
alternating current
the current repeatedly reverses direction
voltage
the energy transferred per unit charge passed

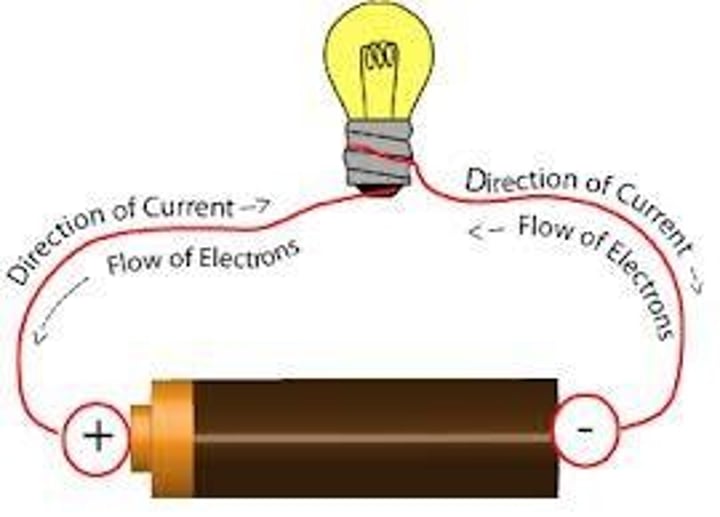
conventional current
flows out of the positive terminal of the cell and back into the negative terminal
electrical power
the electrical work done (electrical energy transferred) per second

resistance
a measure of how difficult it is for the current to flow through something
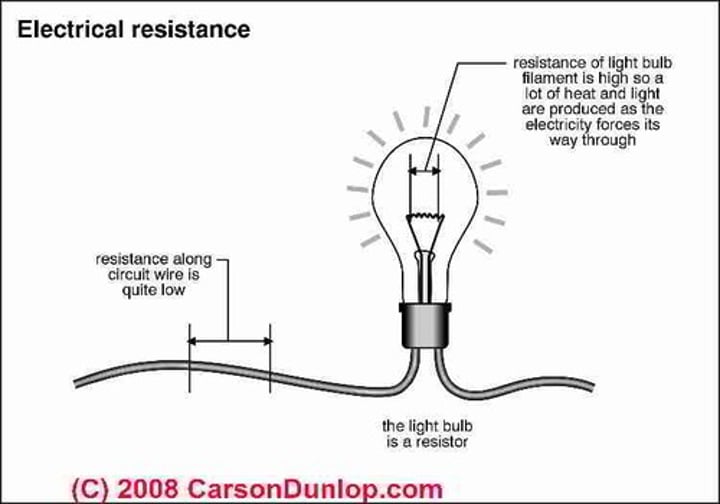
ohm's law
the current in a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage across its end, provided its temperature remains constant
calculation of current
electric charge/time
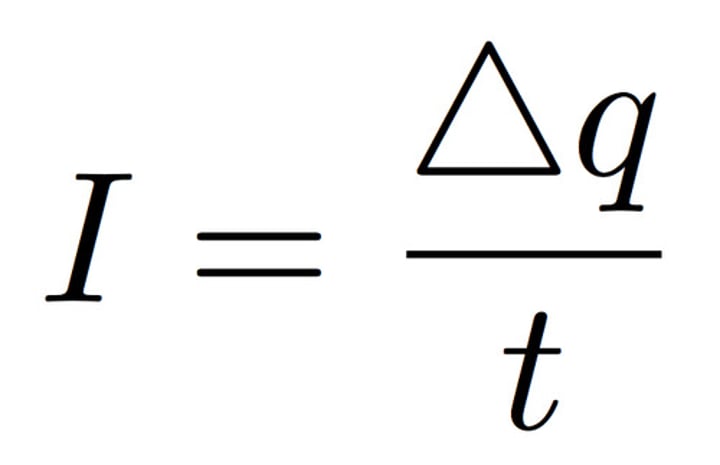
D.C. sources
cells, batteries, solar cells, dynamo
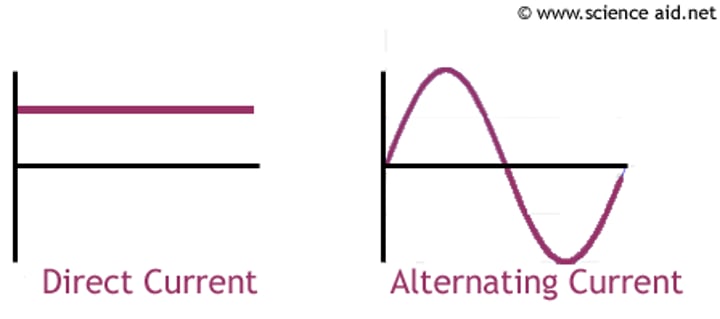
A.C. sources
UK mains, generators
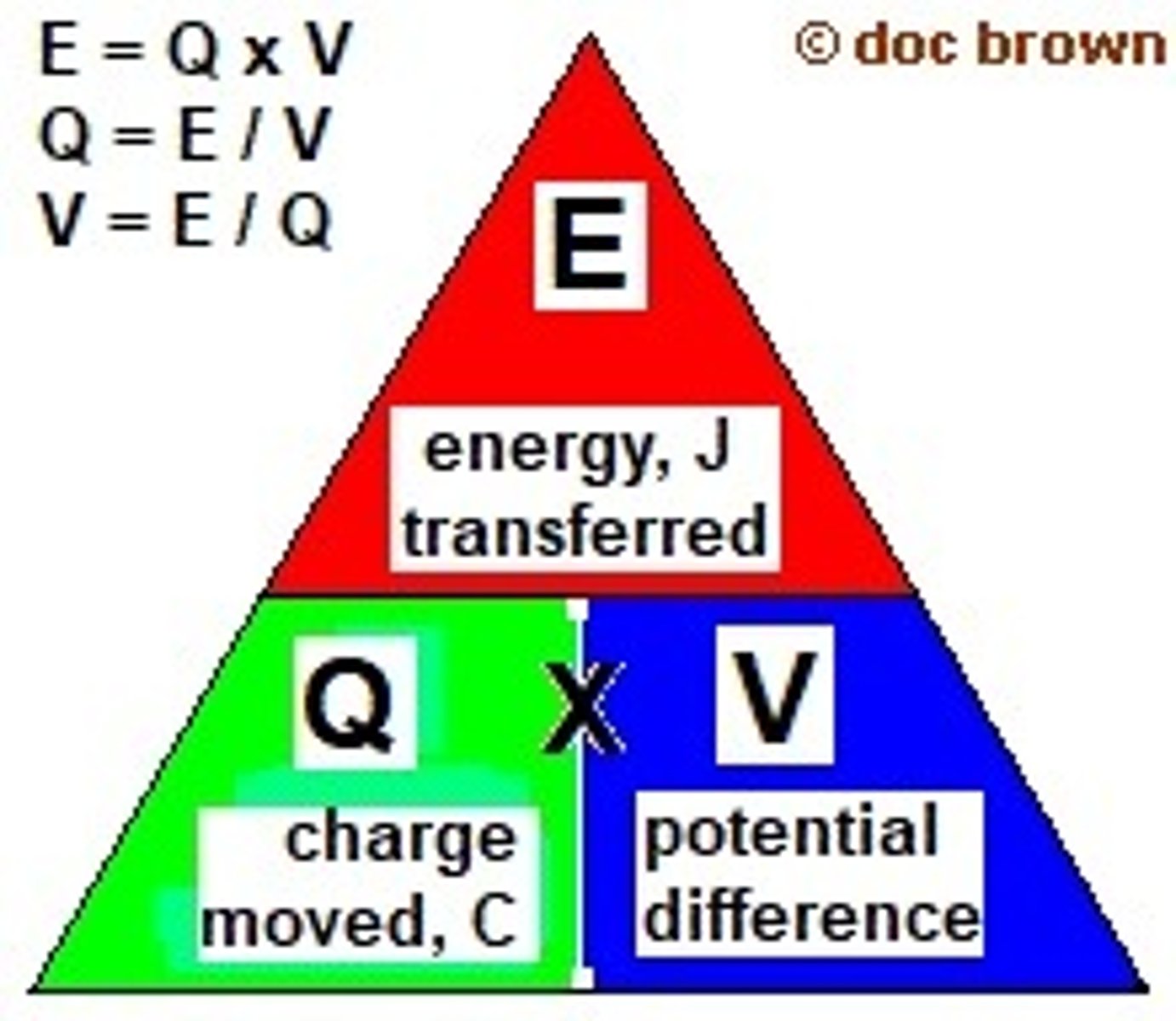
calculation of voltage
energy/charge
calculation of power
voltage×current
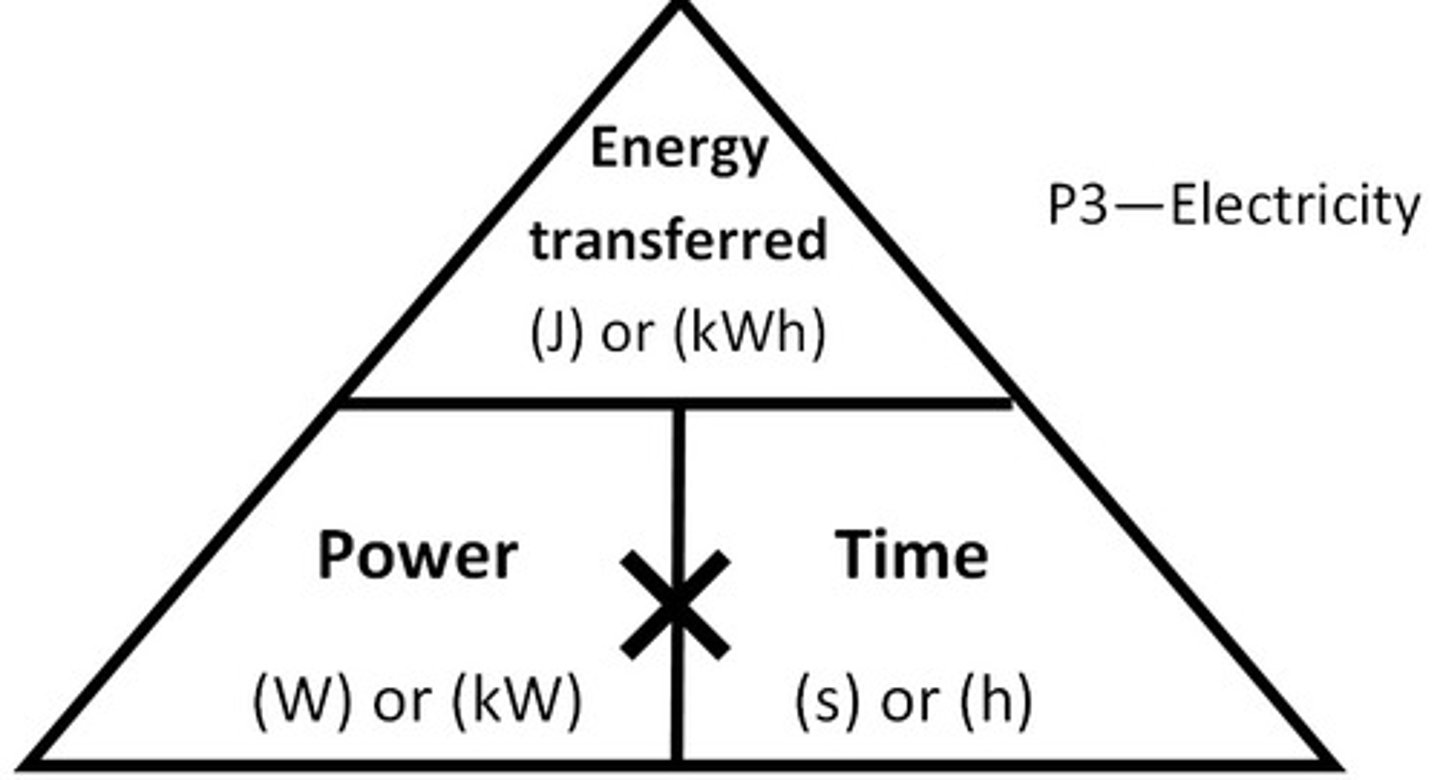
calculation of energy transferred
voltage×current×time
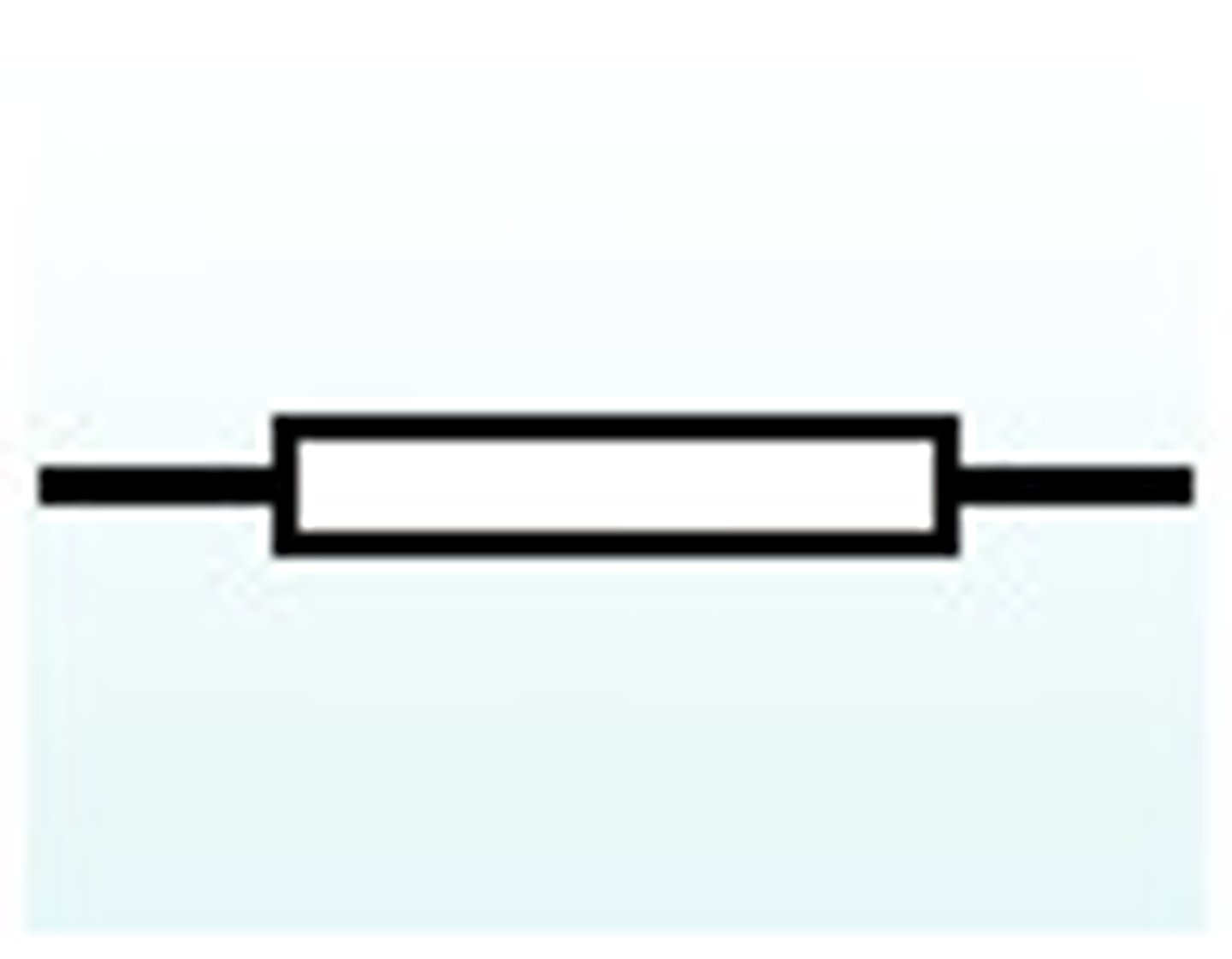
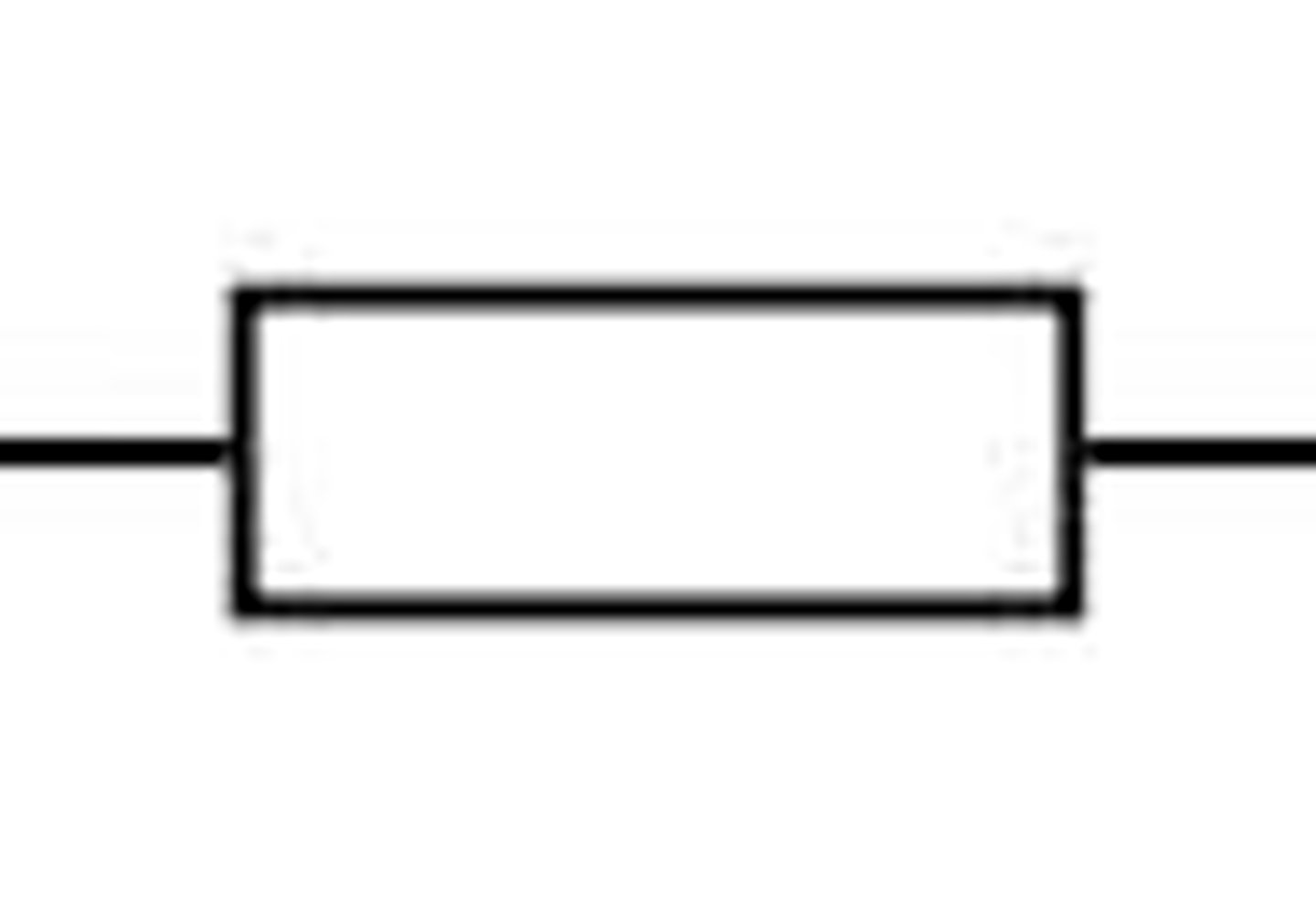
resistor
an electrical component that restricts the flow of electric current
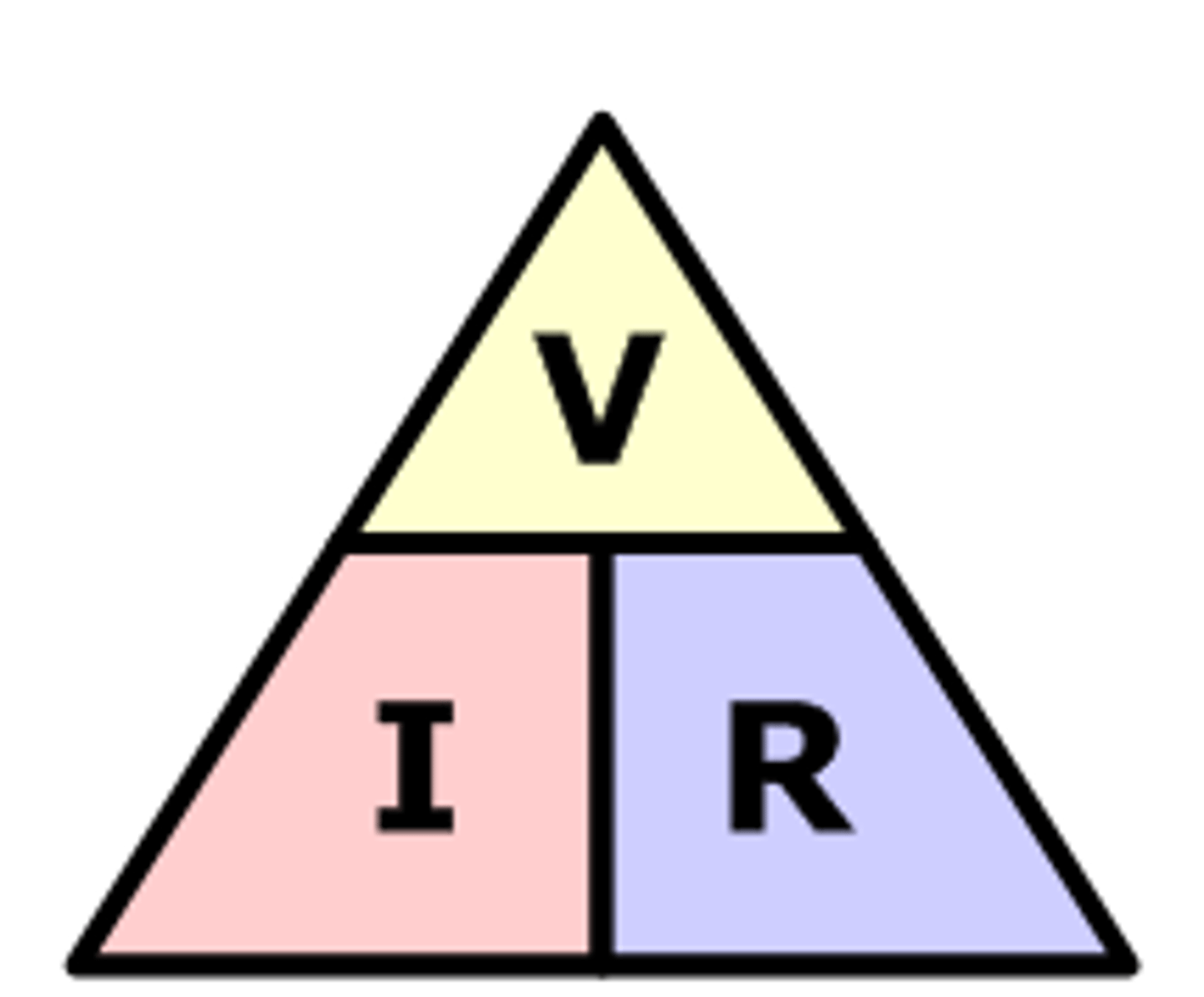
calculation of resistance
voltage/current
uses of LDRs
-sensors that turn car and street light on/off automatically
-security alarms
-digital cameras
-street lights
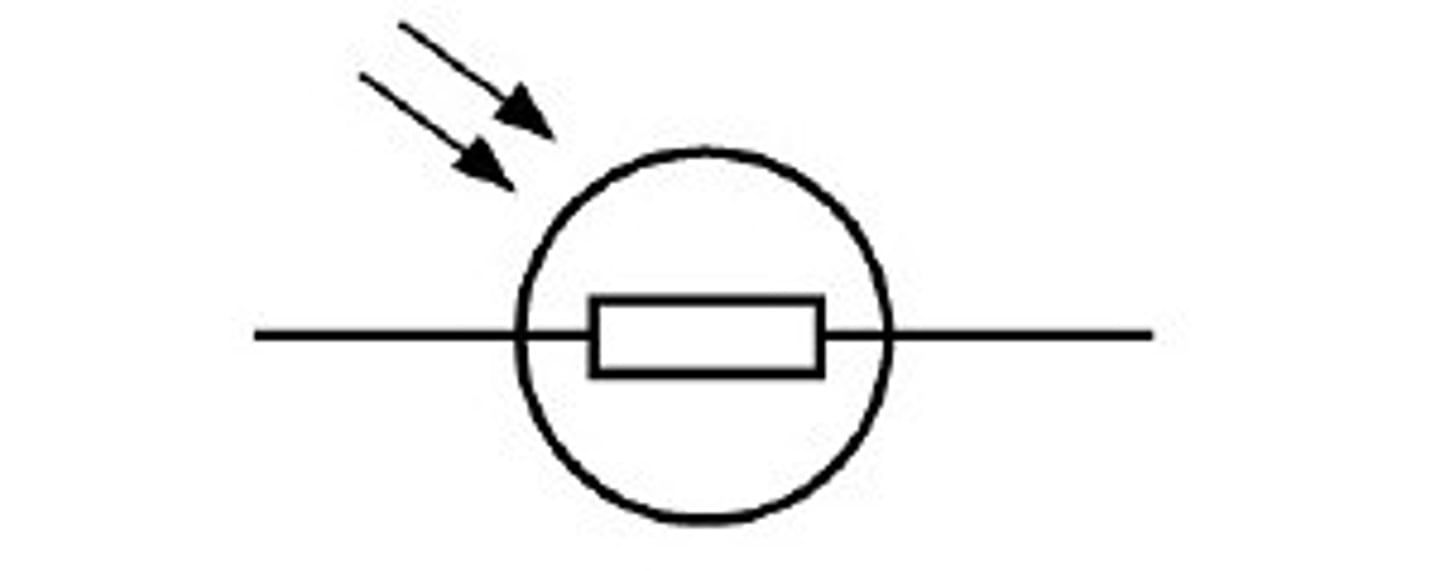
LDR
a type of resistor that responds to changes in light intensity
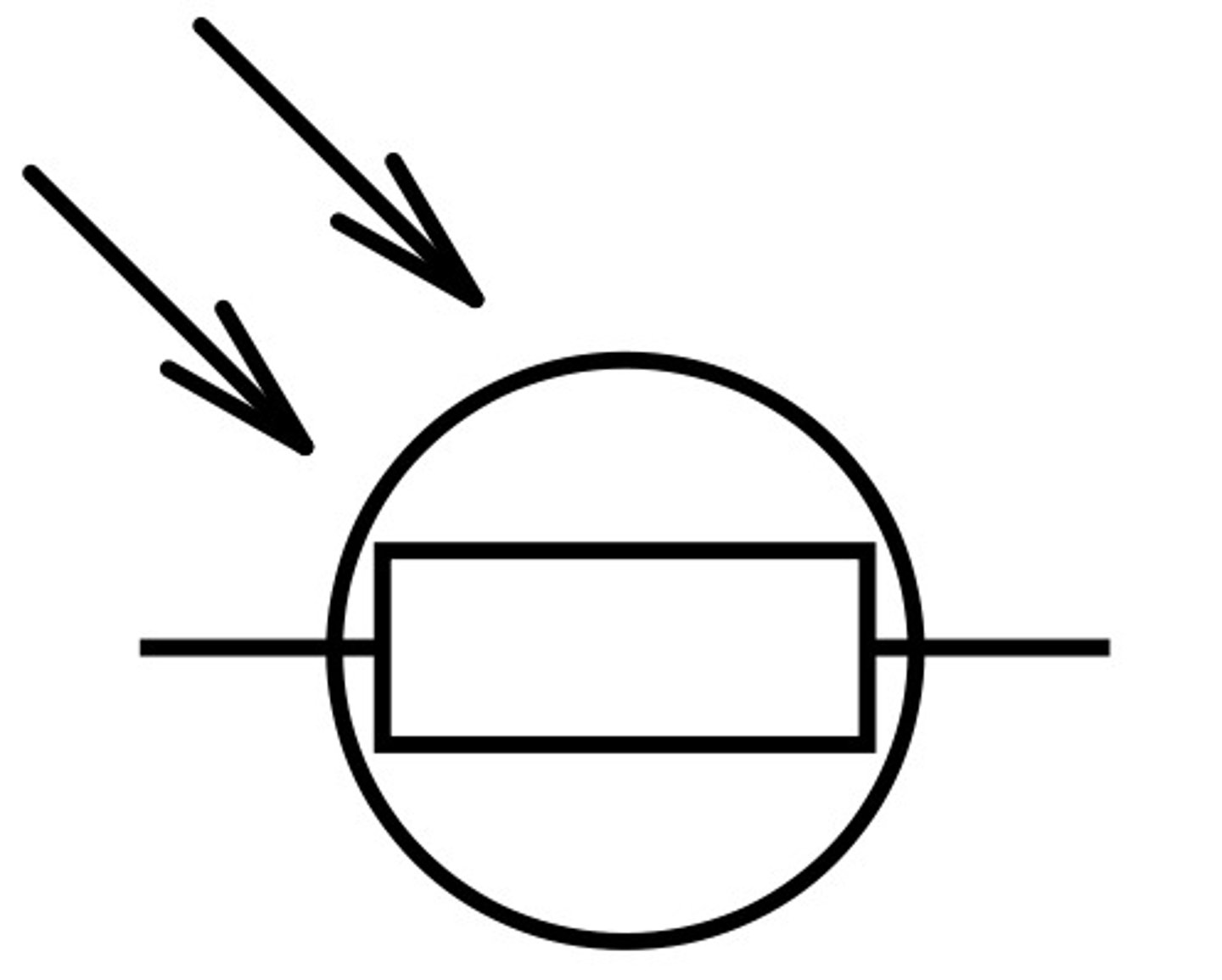
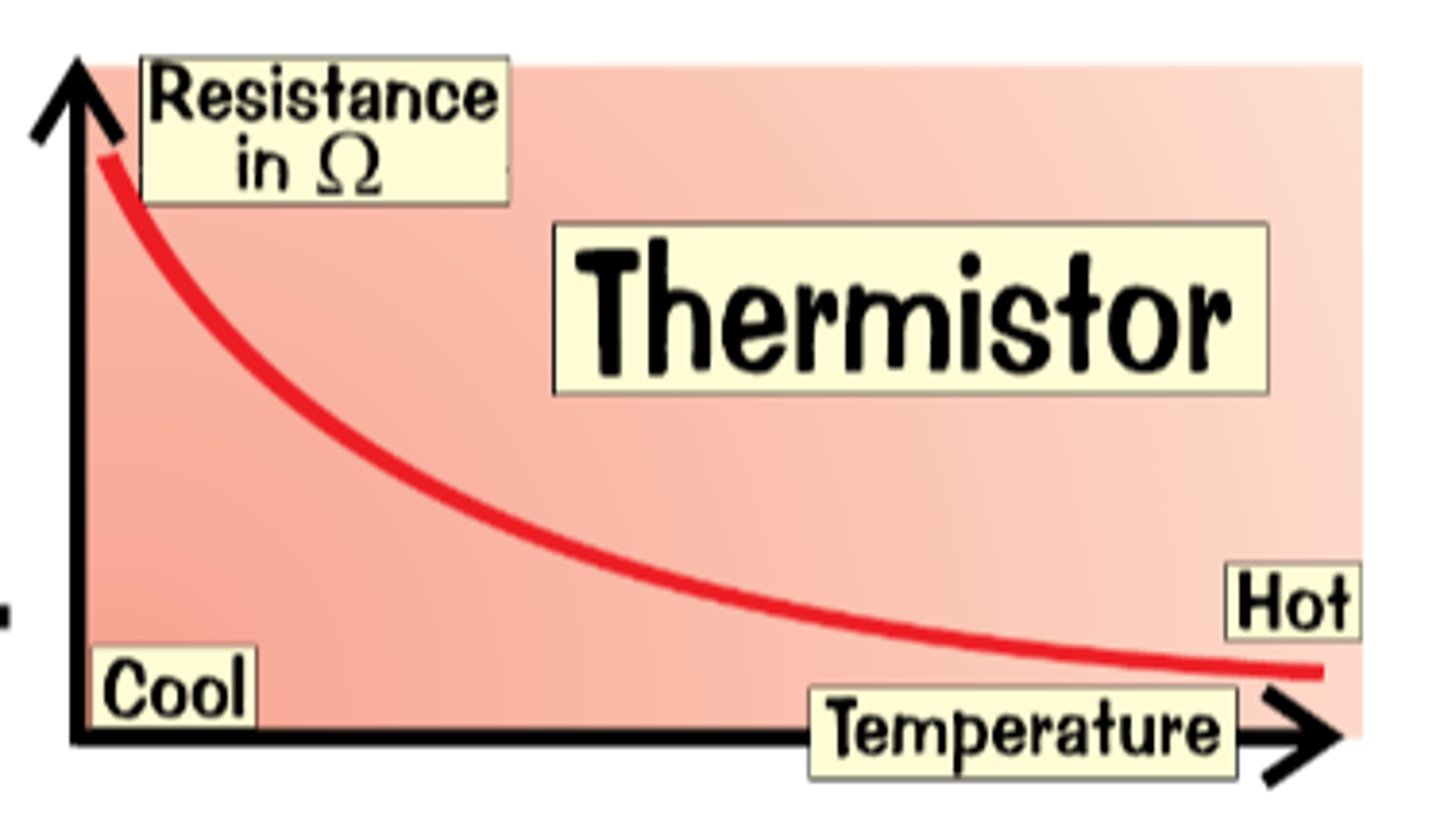
thermistor
a type of resistor that responds to changes in temperature
uses of thermistors
-digital thermometers
-thermostats
-keeping fridges cold
-keeping swimming pools warm
-automatic ventilation of
-greenhouses
-security alarms (burglar detectors)

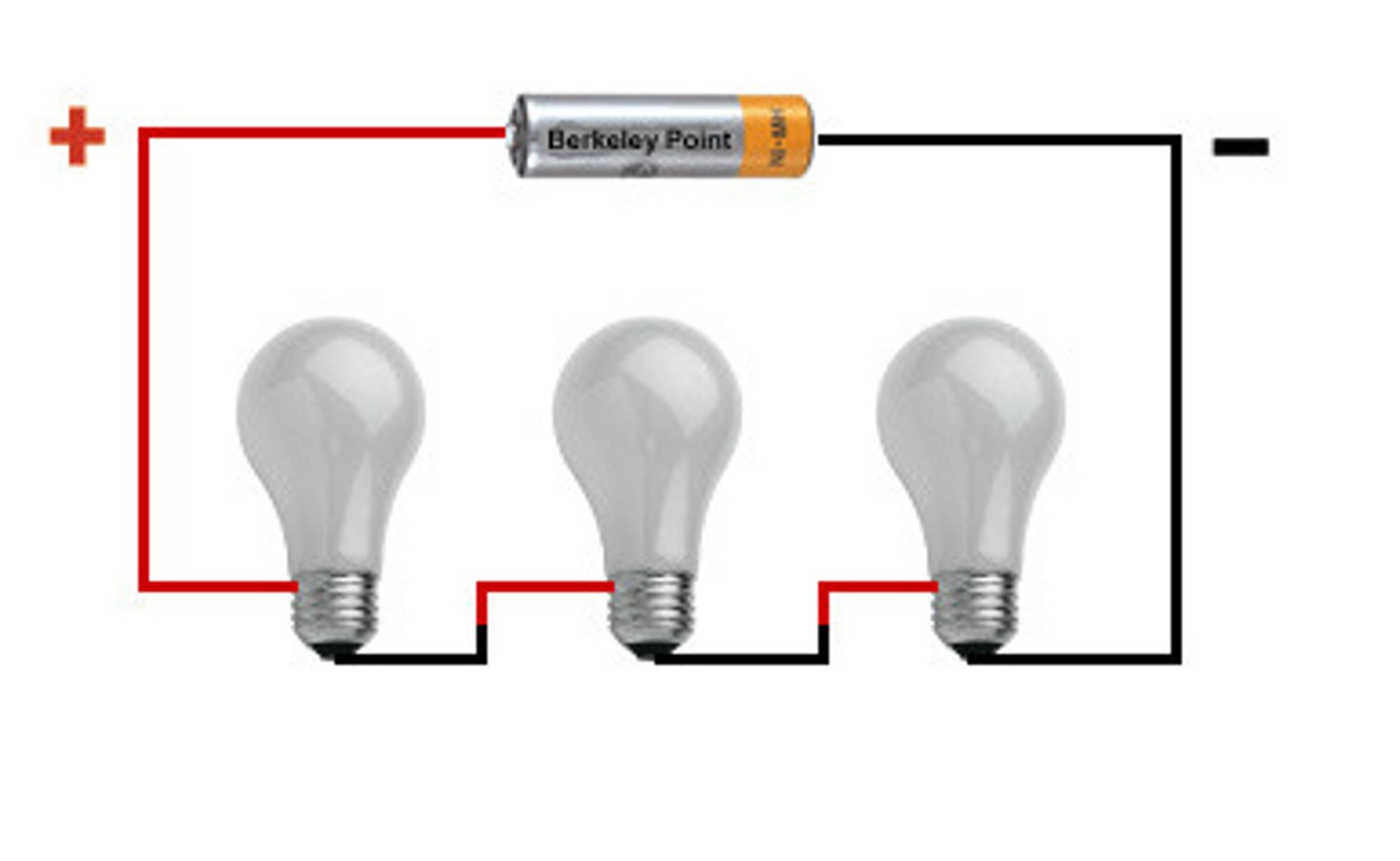
series circuit
one loop, only one route the current can take
no junctions
each component is connected one after the other
parallel circuit
more than one loop, there are junctions - the circuit is branched or split
more than one route that current can take
components are in different loops
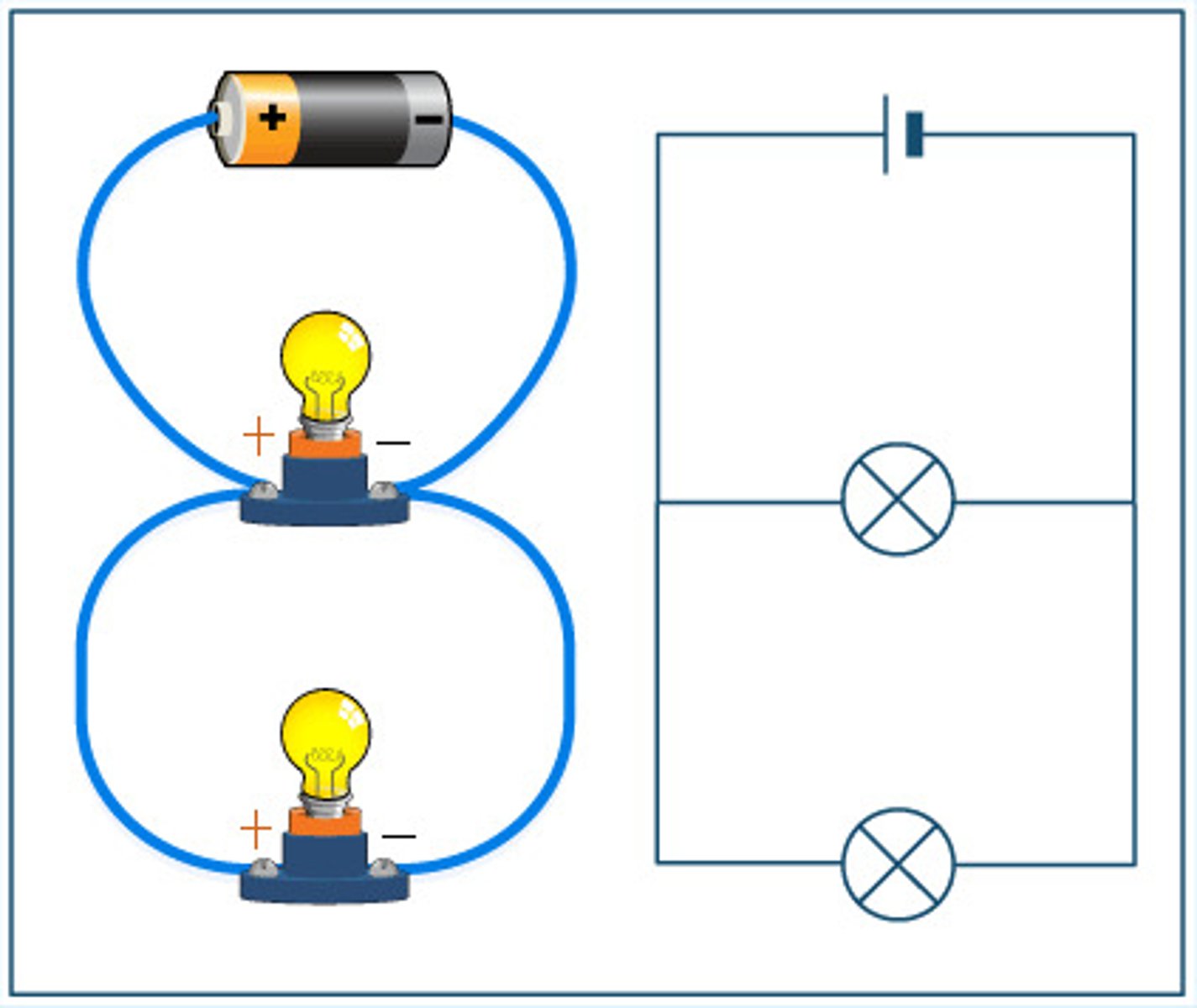
measuring current in a series circuit
the current is the same at any point in the series circuit
what happens if one bulb breaks in a series circuit?
the circuit is broken, no current flows

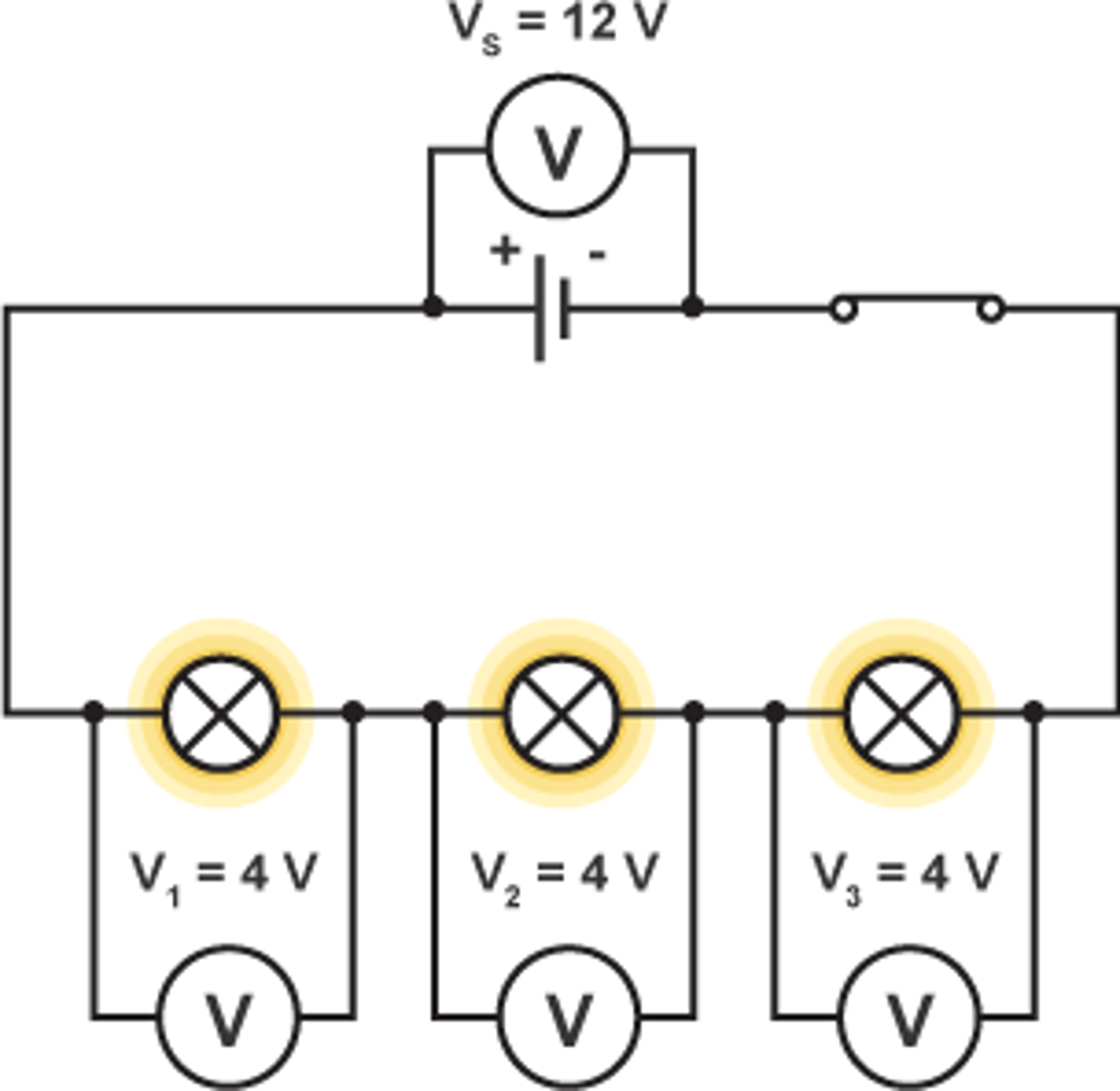
measuring voltage in a series circuit
the sum of the voltage for each component is equal to the voltage across the cell/battery
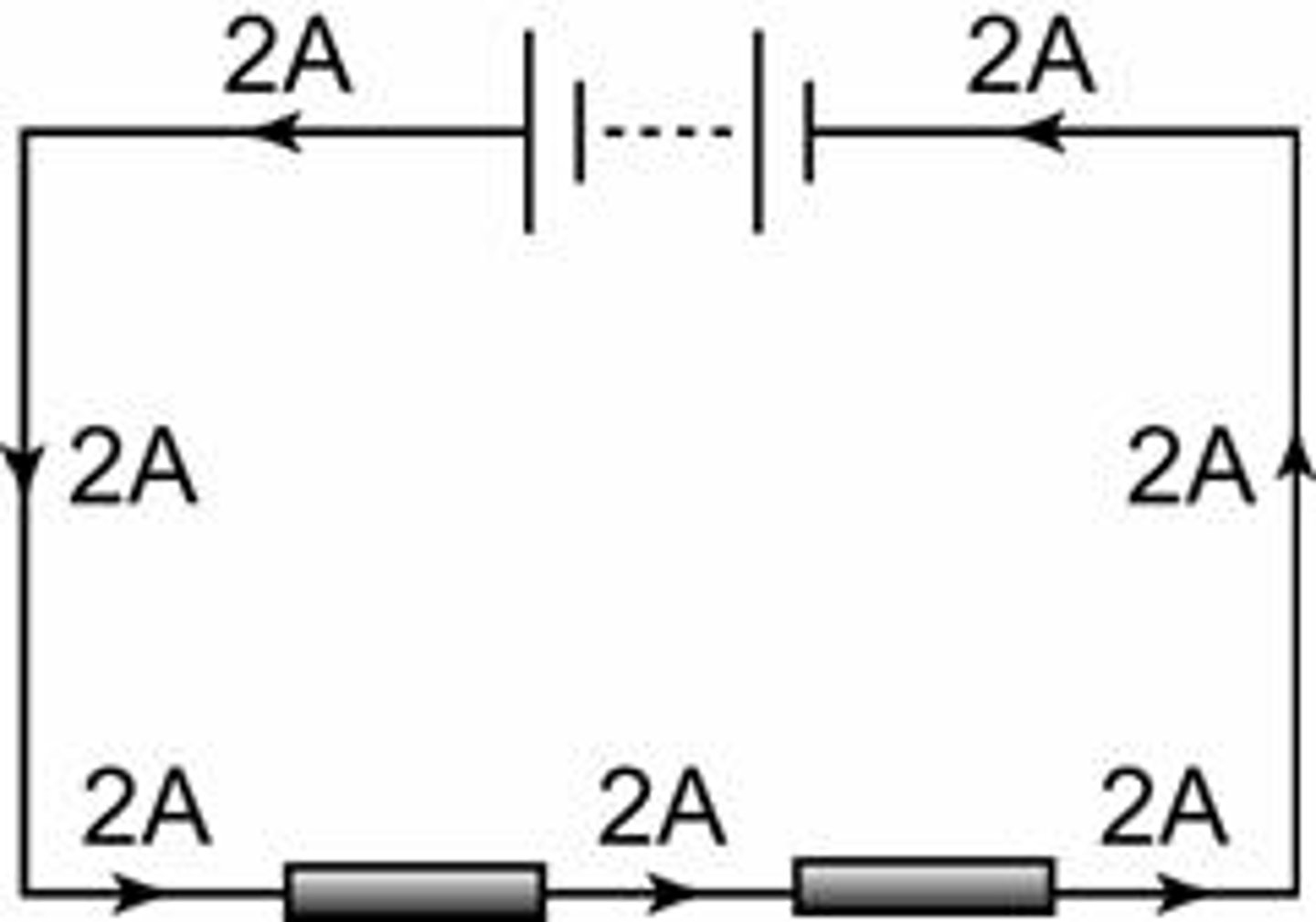
rules of series circuit
the electric current is the same at any point in a series circuit
the voltage of the cell/battery splits up in between the components
the more components are added to the circuit the higher the total resistance is, and so the flow of electric current decreases
what happens if one bulb breaks in a parallel circuit?
the others are still on as current flows in their loops

rules of parallel circuits
the electric current of the main loop splits up in between all the loops
the voltage is the same across any component
the total resistance of the circuit decreases by adding more components and so the flow of electric current increases

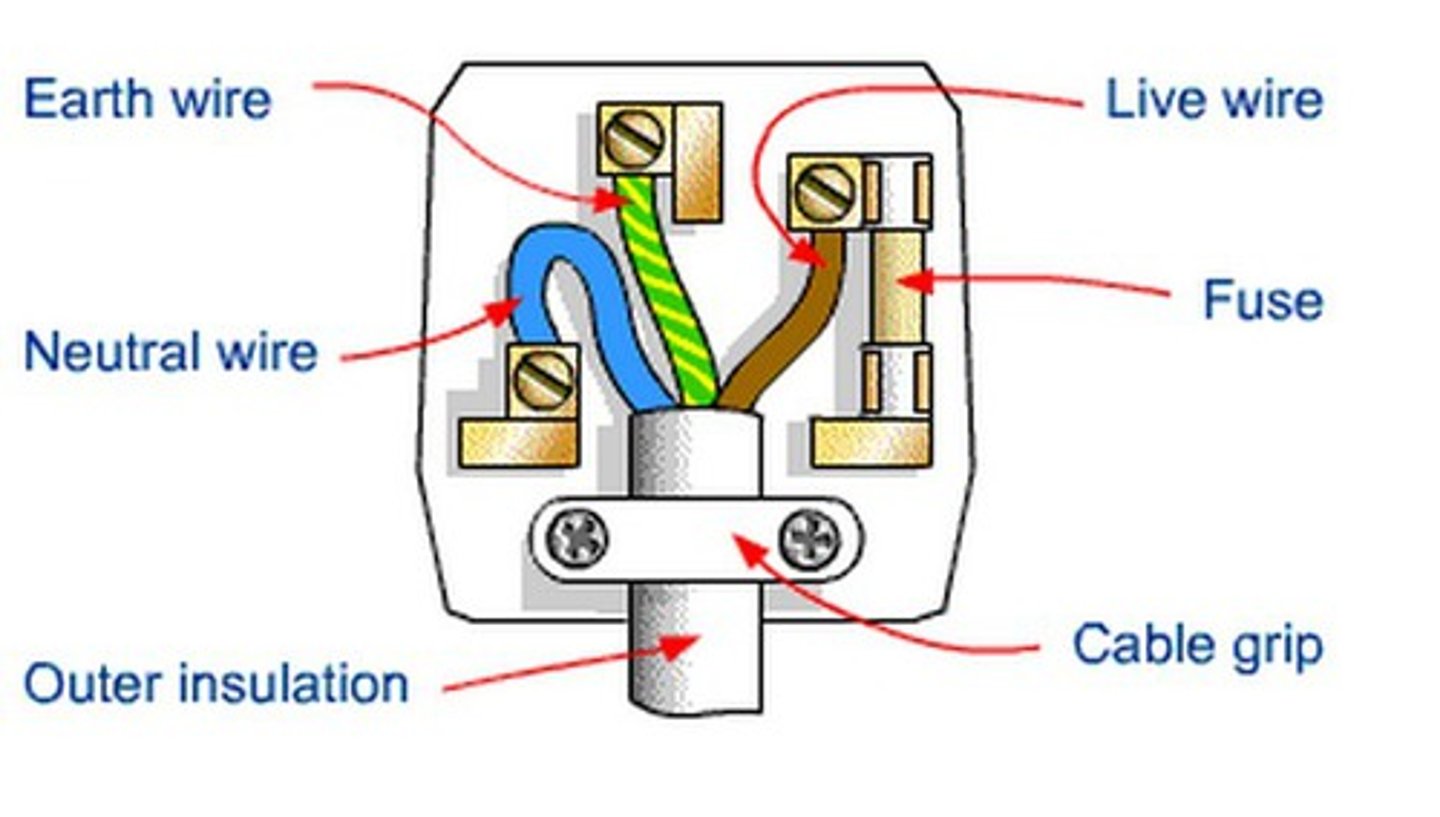
earth wire
low resistance wire, offering a path for the current to earth in case the live wire touches the metal case of the appliance. no electrocution (green & yellow)
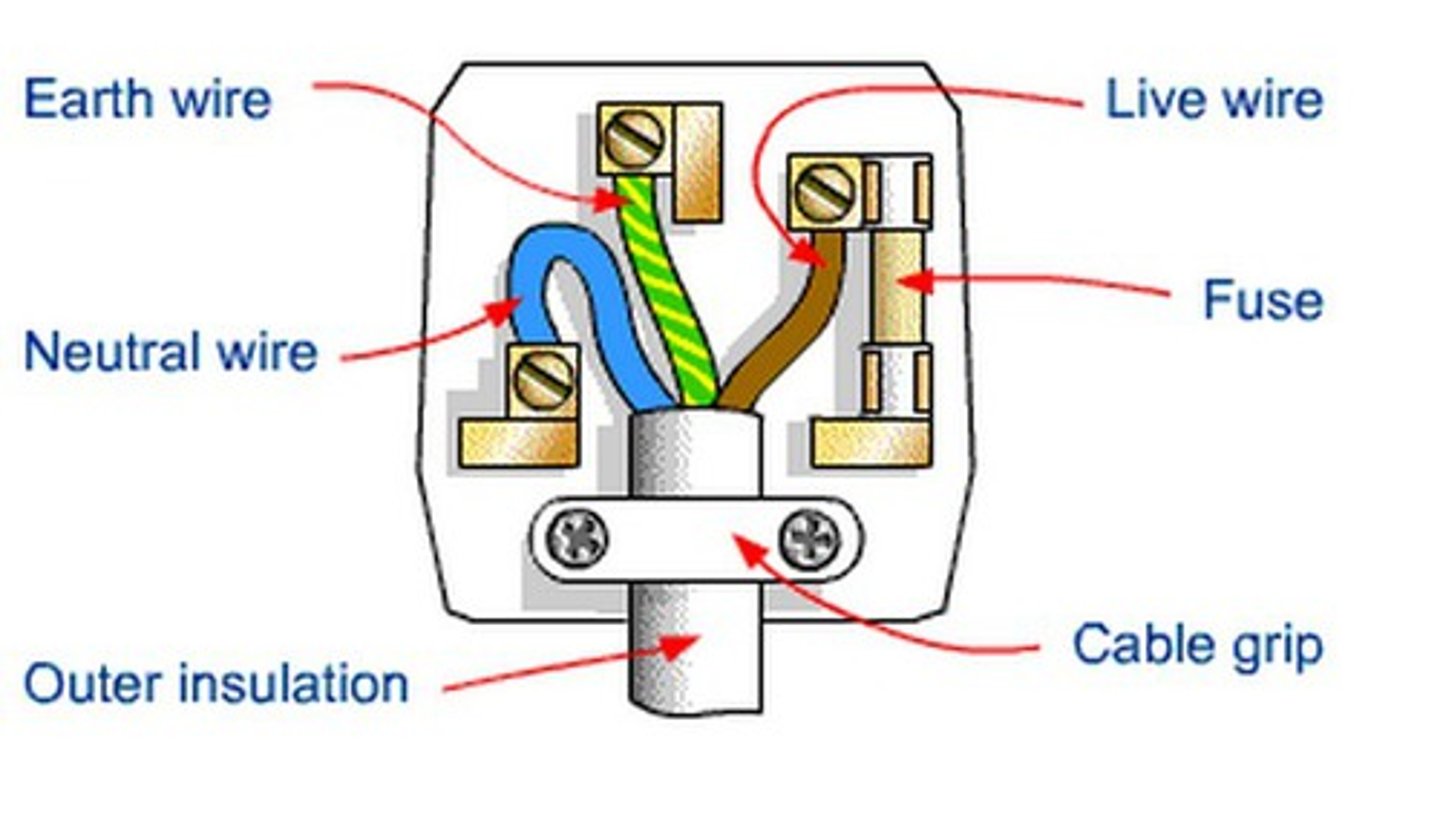
neutral wire
a wire that carries current away from the component; it is coated in blue plastic
conductors have a lot of...
delocalised electrons
insulators have none or hardly any...
delocalised electrons
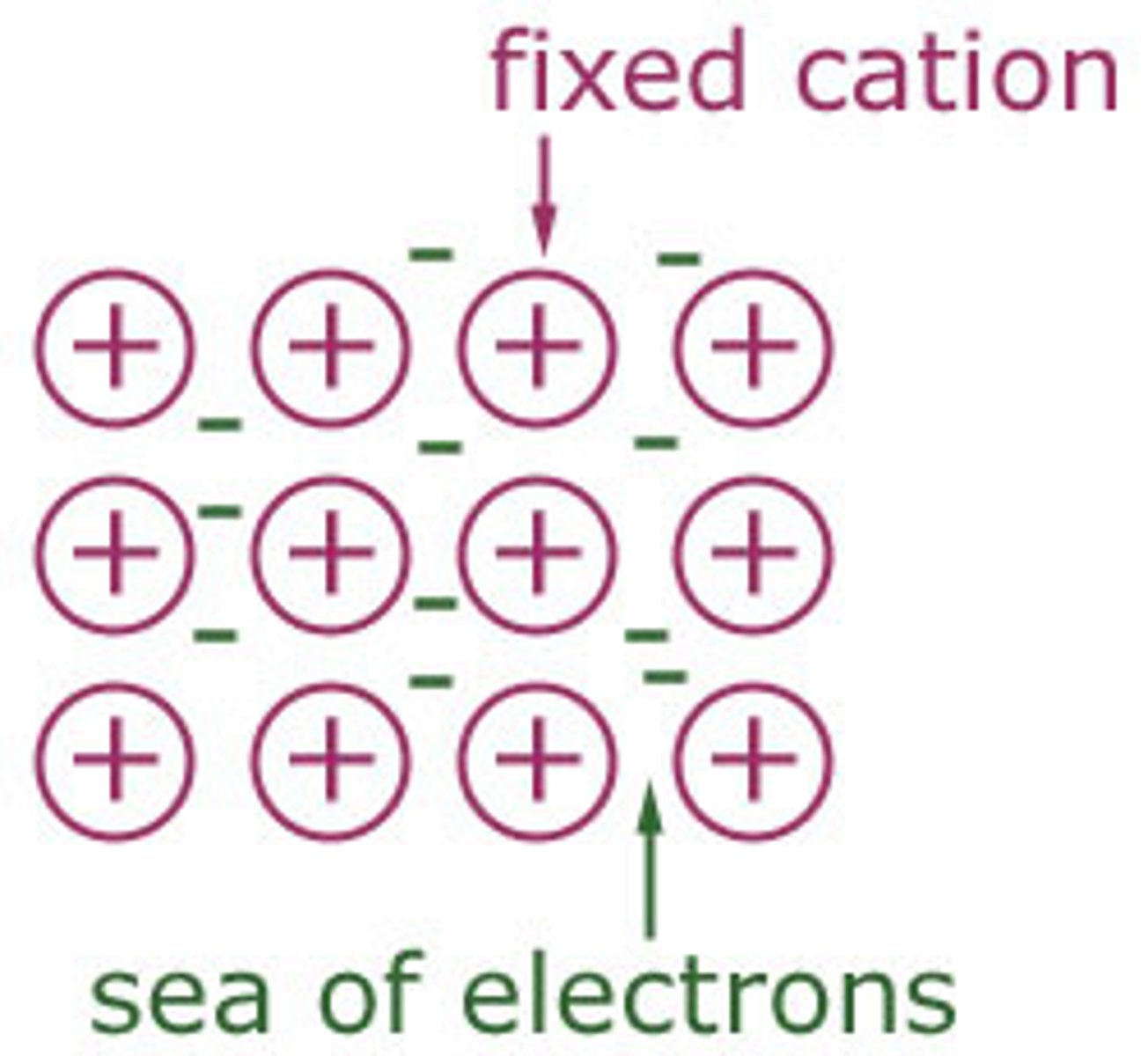
metallic structure
positive metal ions in a sea of negative delocalised electons
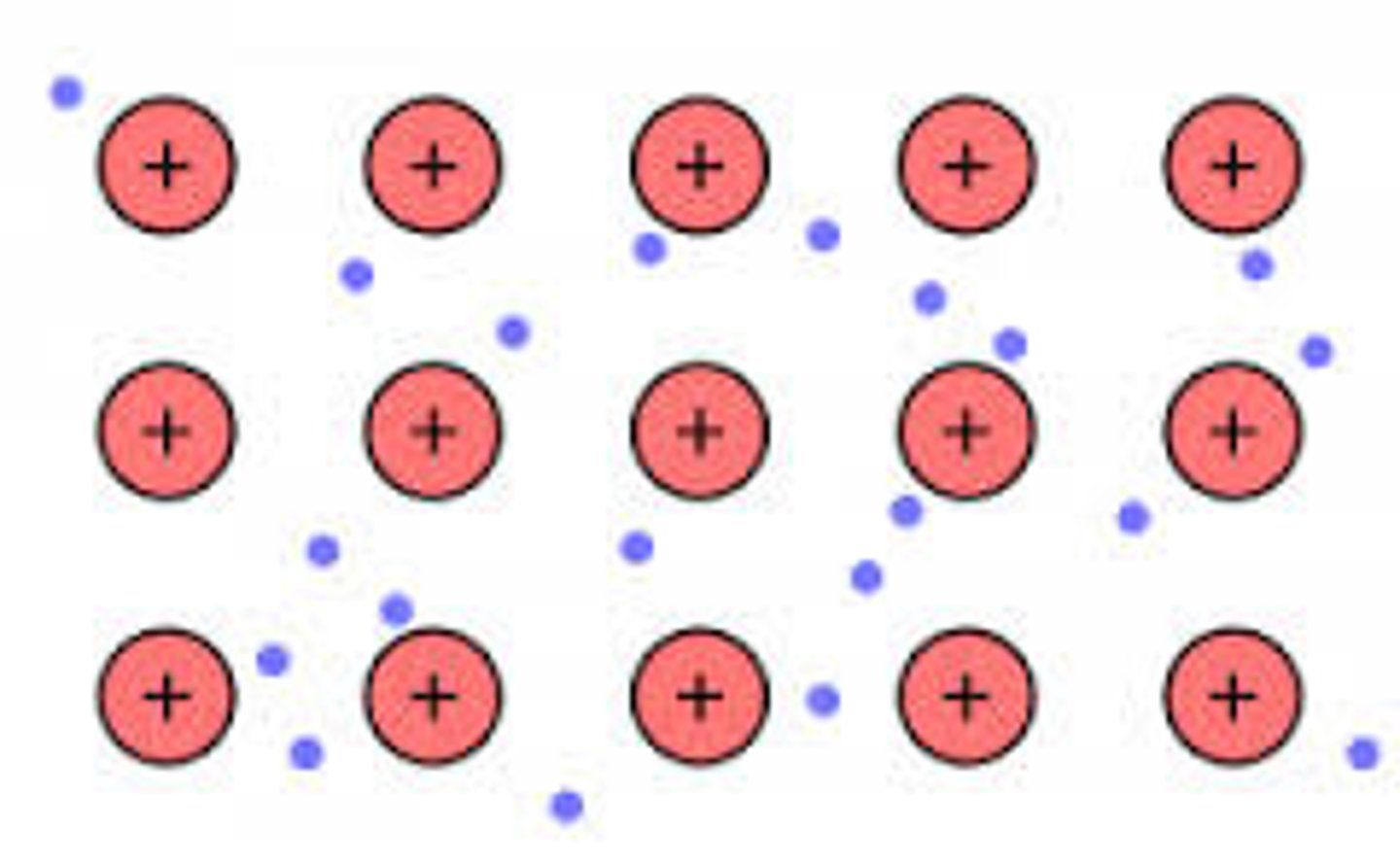
when delocalised electrons drift together there is a...
flow of electric current
randomly moving delocalised electrons means there is...
no flow of electric current
amps
unit for current

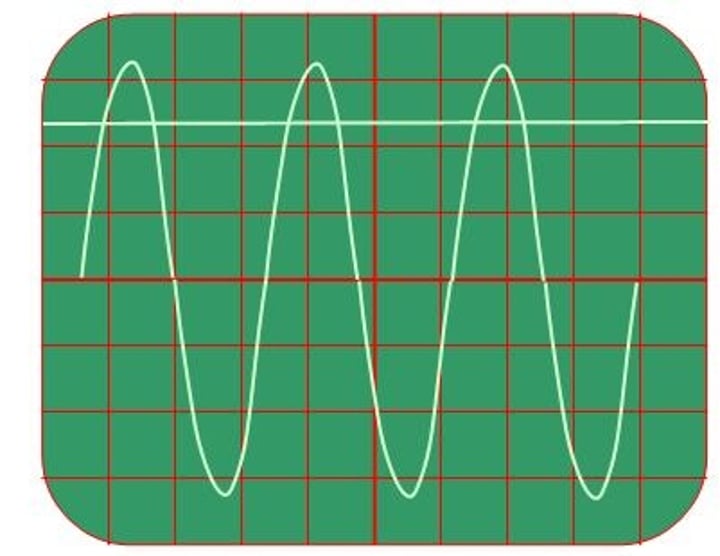
oscilloscope
a laboratory instrument used to measure voltage waves
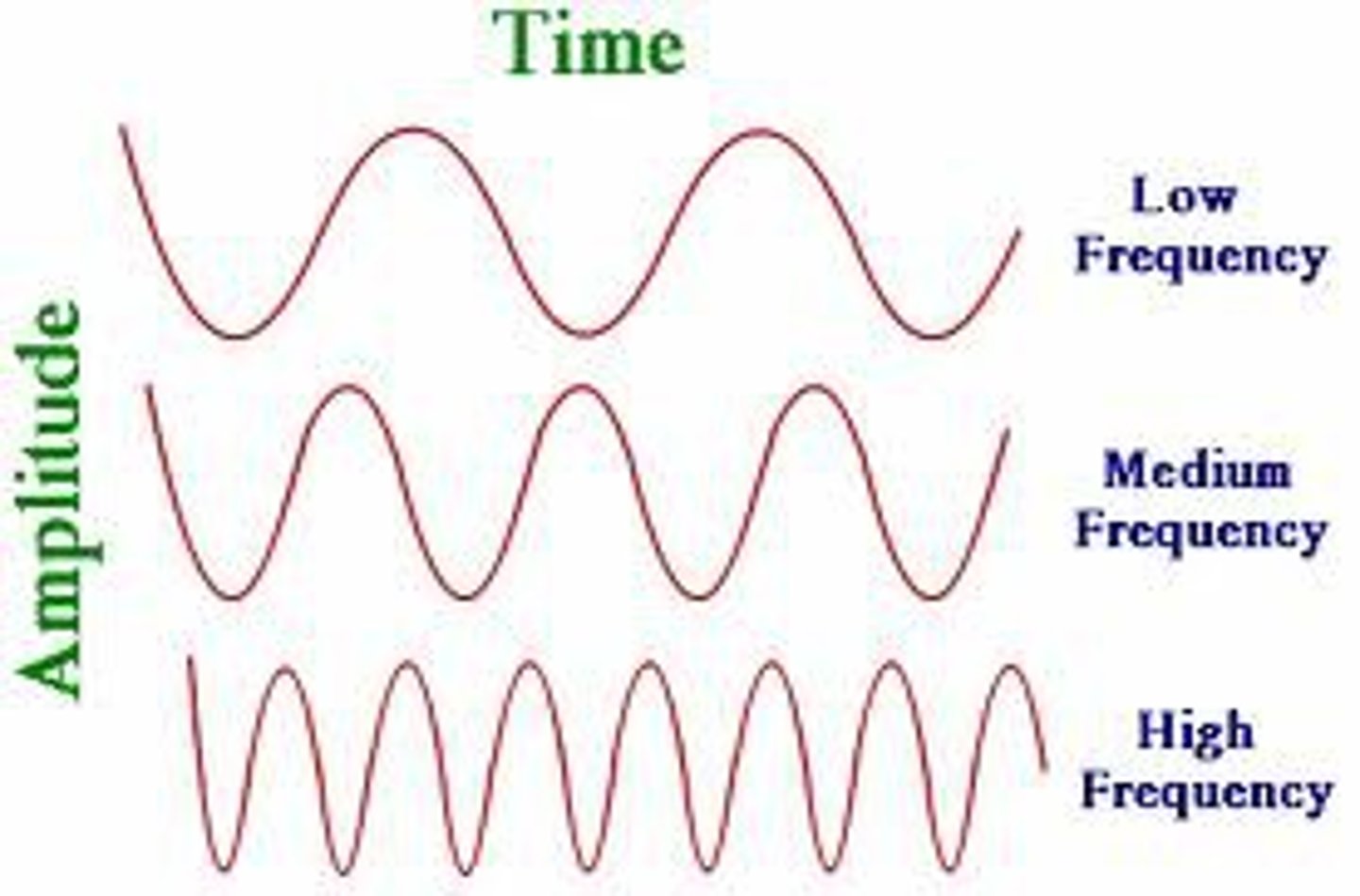
frequency
the number of complete wavelengths that pass a point in a given time
volts
unit for voltage

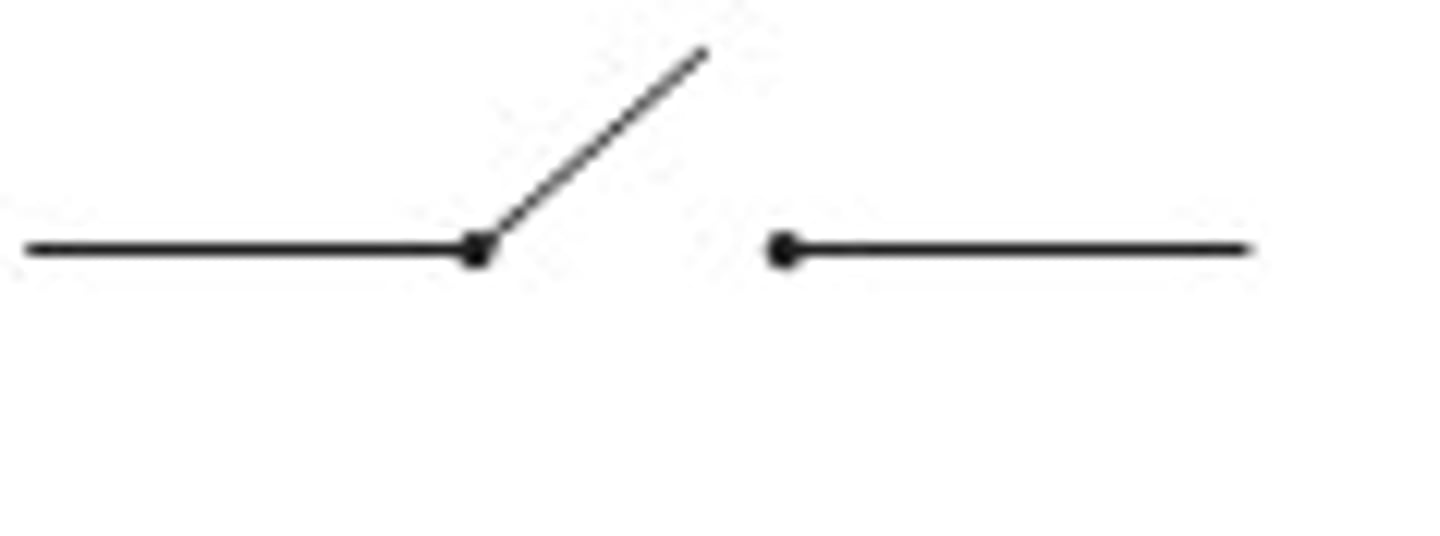
switch
completes or breaks the circuit
cell
provides energy
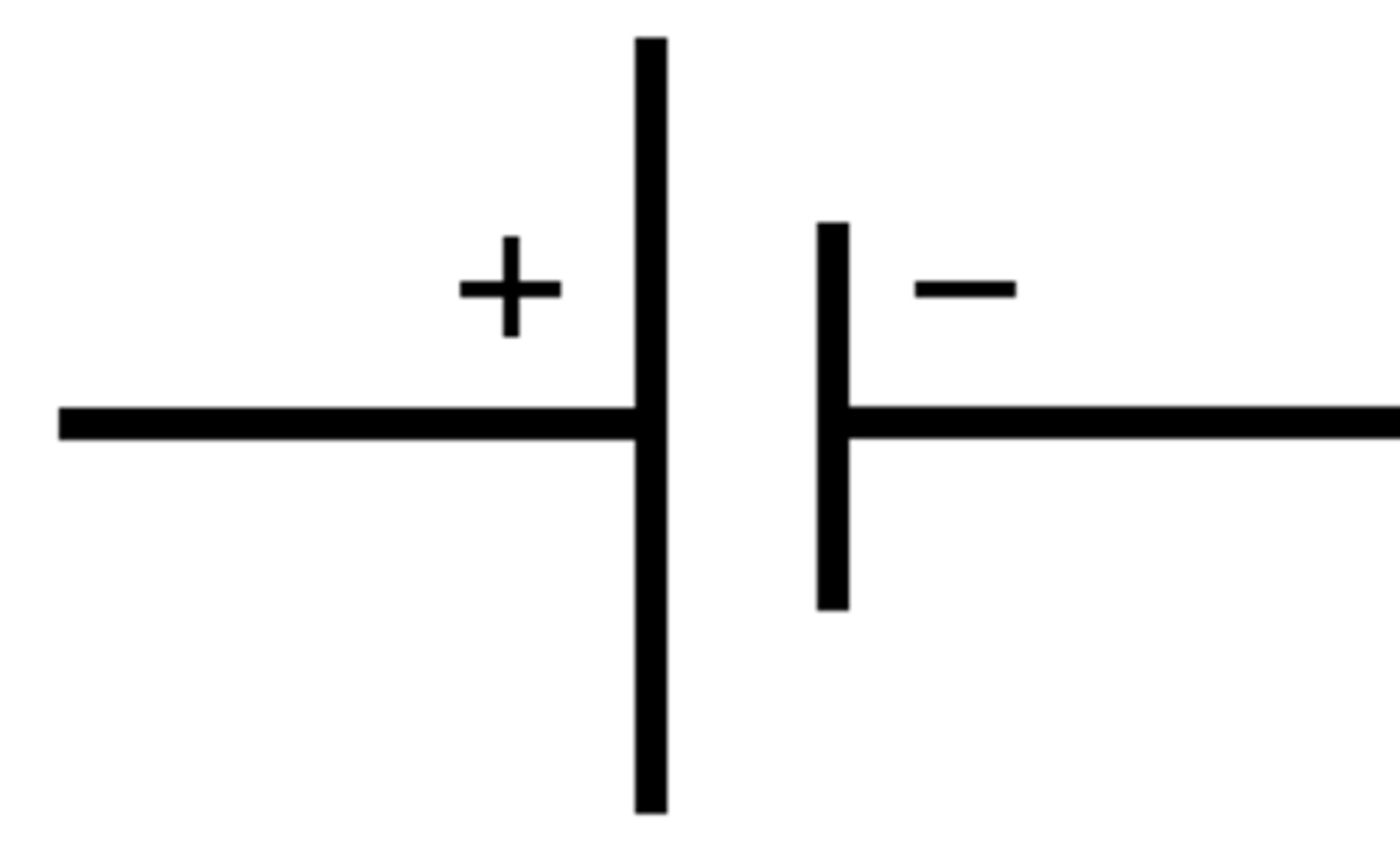
light bulb
converts energy

wires
used to pass current from one part of the component to another

ammeter is connected in
series
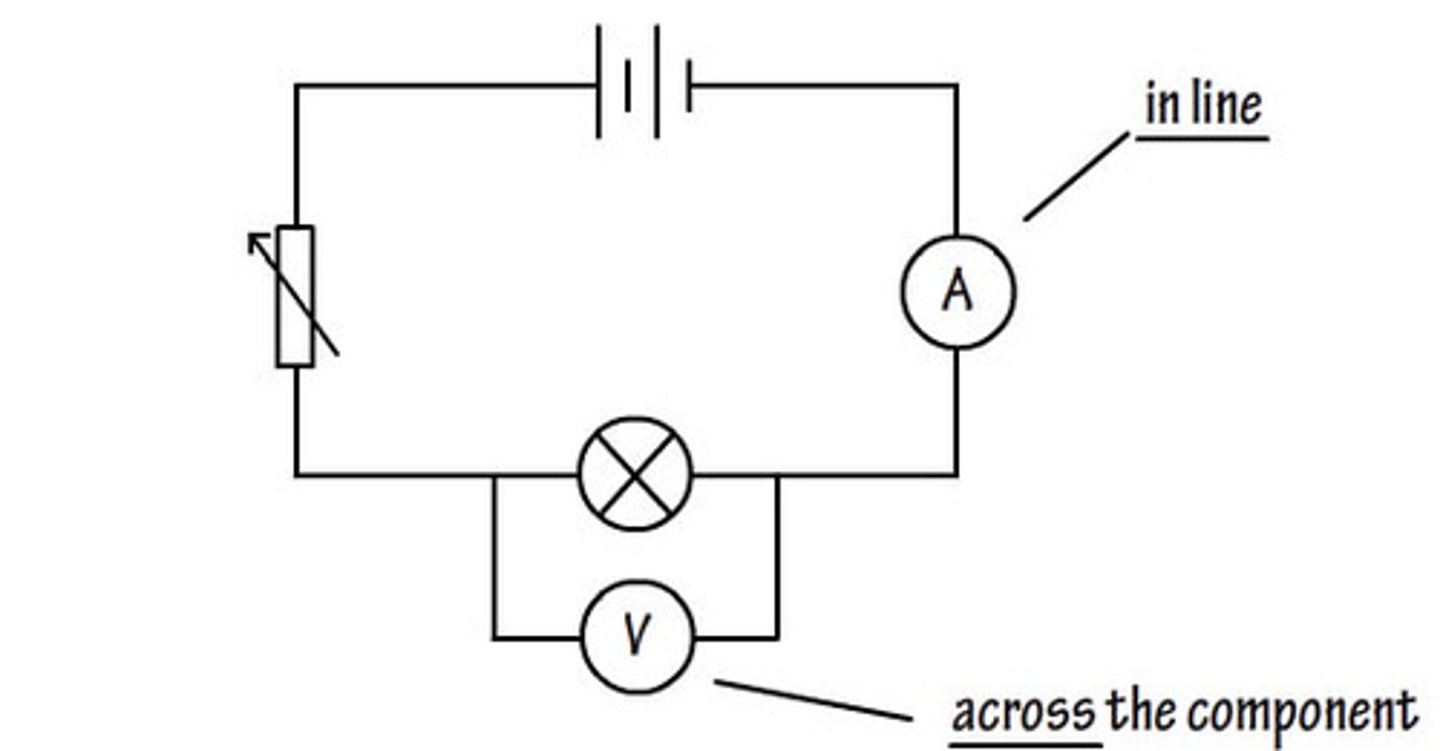
voltmeter is connected in
parallel across a component
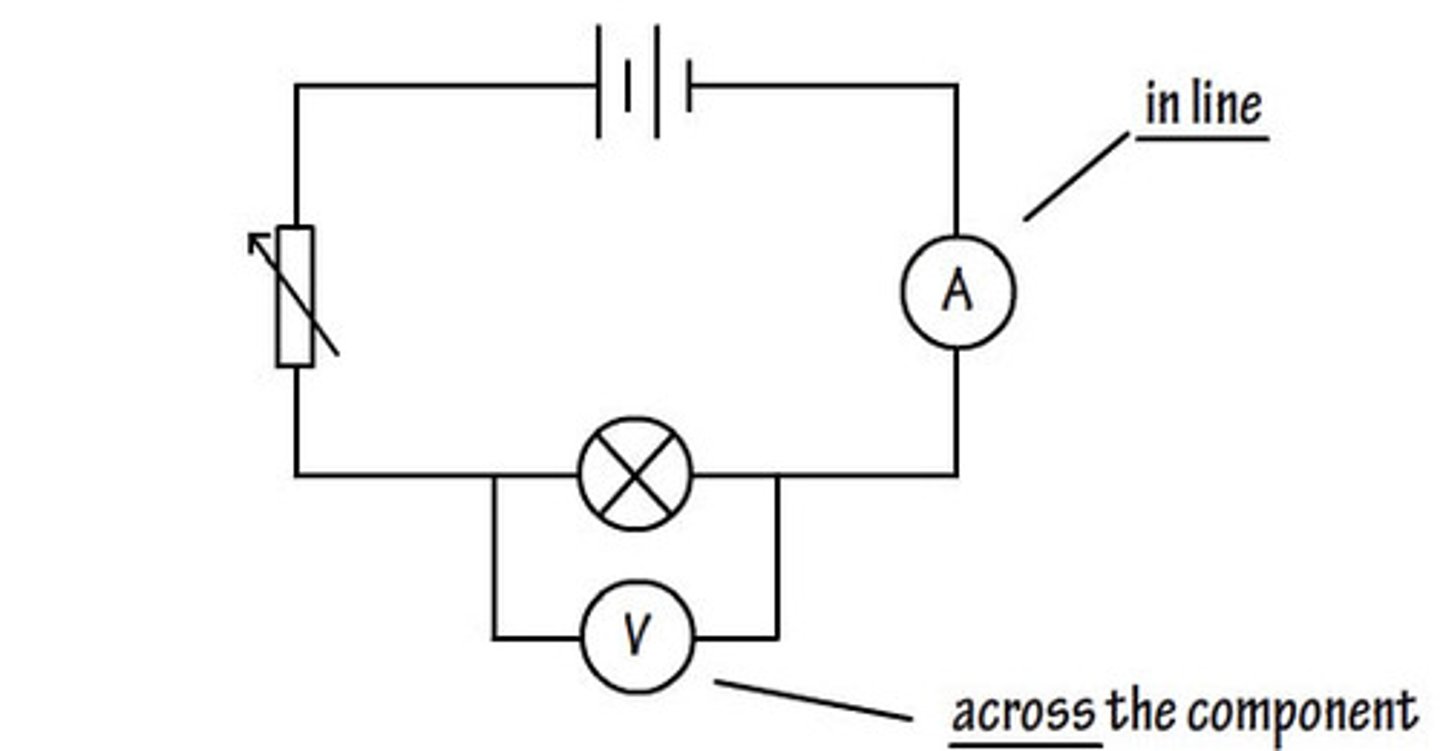
voltmeter
used to measure differences in energy (potential) around an electrical circuit
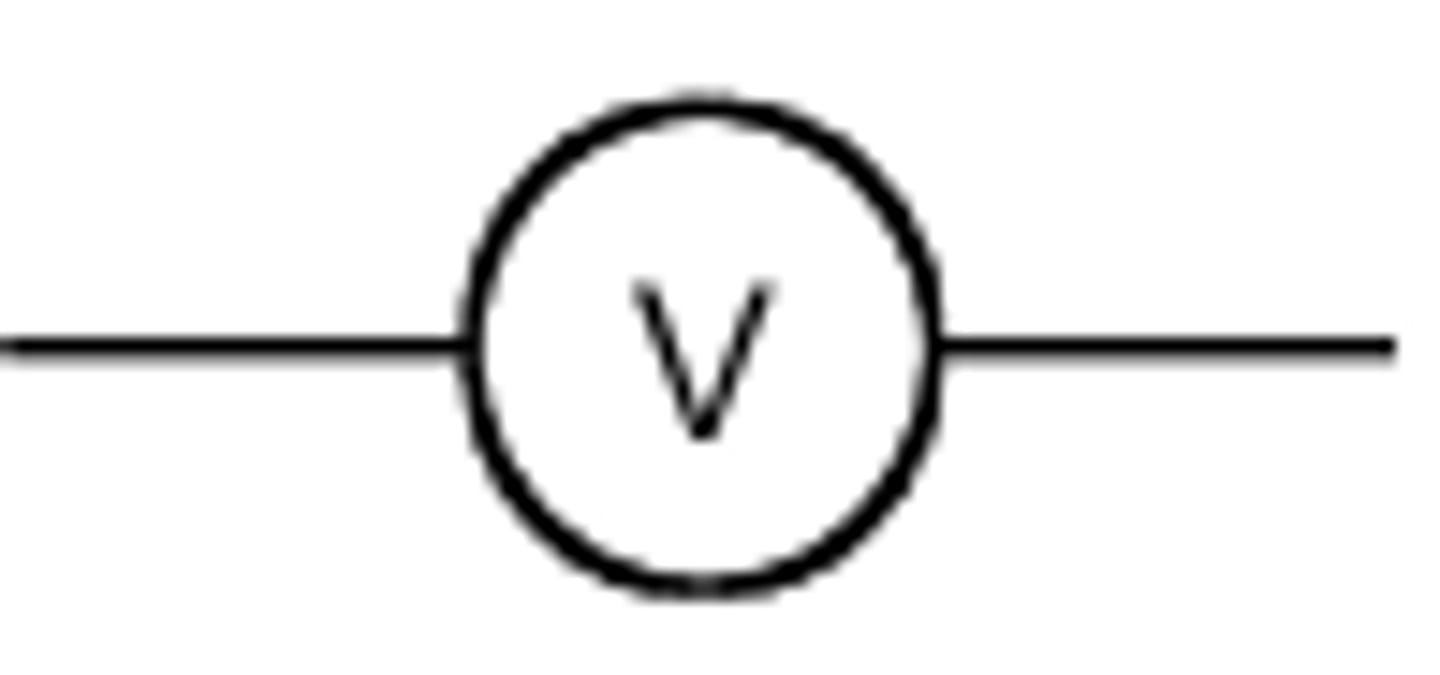
potential difference
the difference in energy by a component
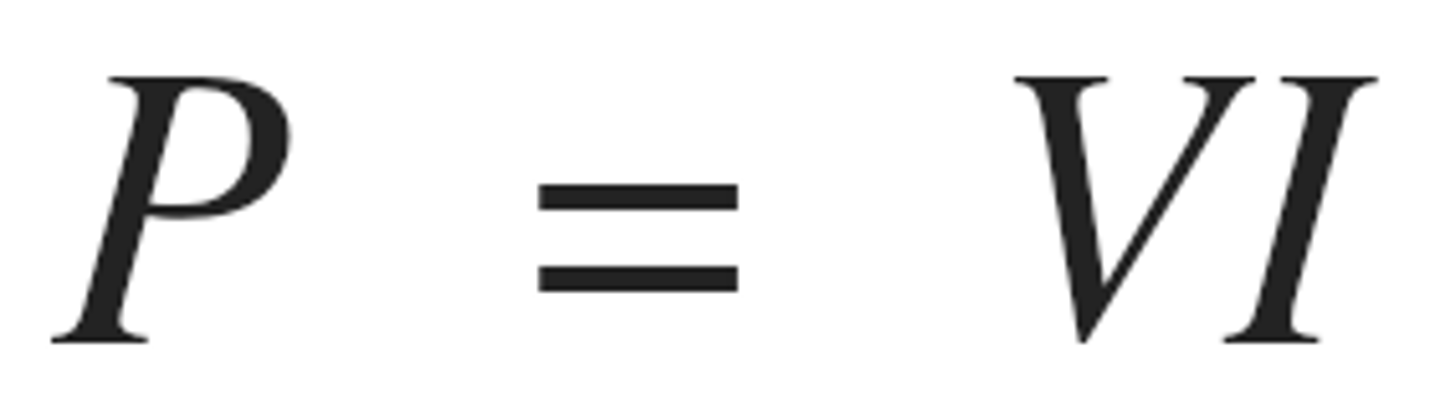
energy transferred
electrical work done
watts
unit for power

joules
unit of energy
ohm
unit of resistance

every circuit component acts as a
resistor
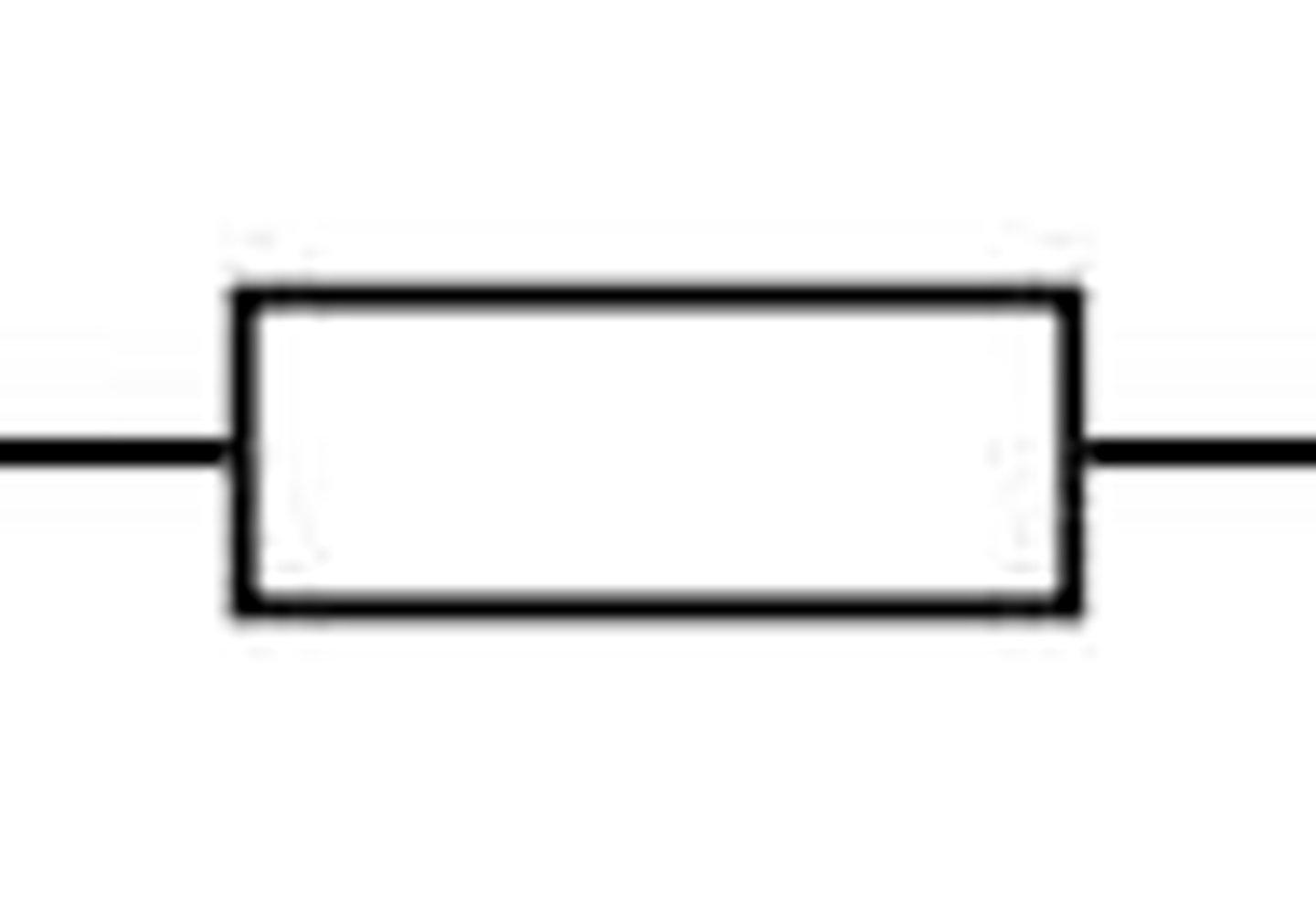
the voltage is trying to push the current round the circuit,
and the resistance is opposing it
if you increase the voltage... as long as the temperature remains constant
then more current will flow
If you increase the resistance... as long as the temperature remains constant
then less current will flow
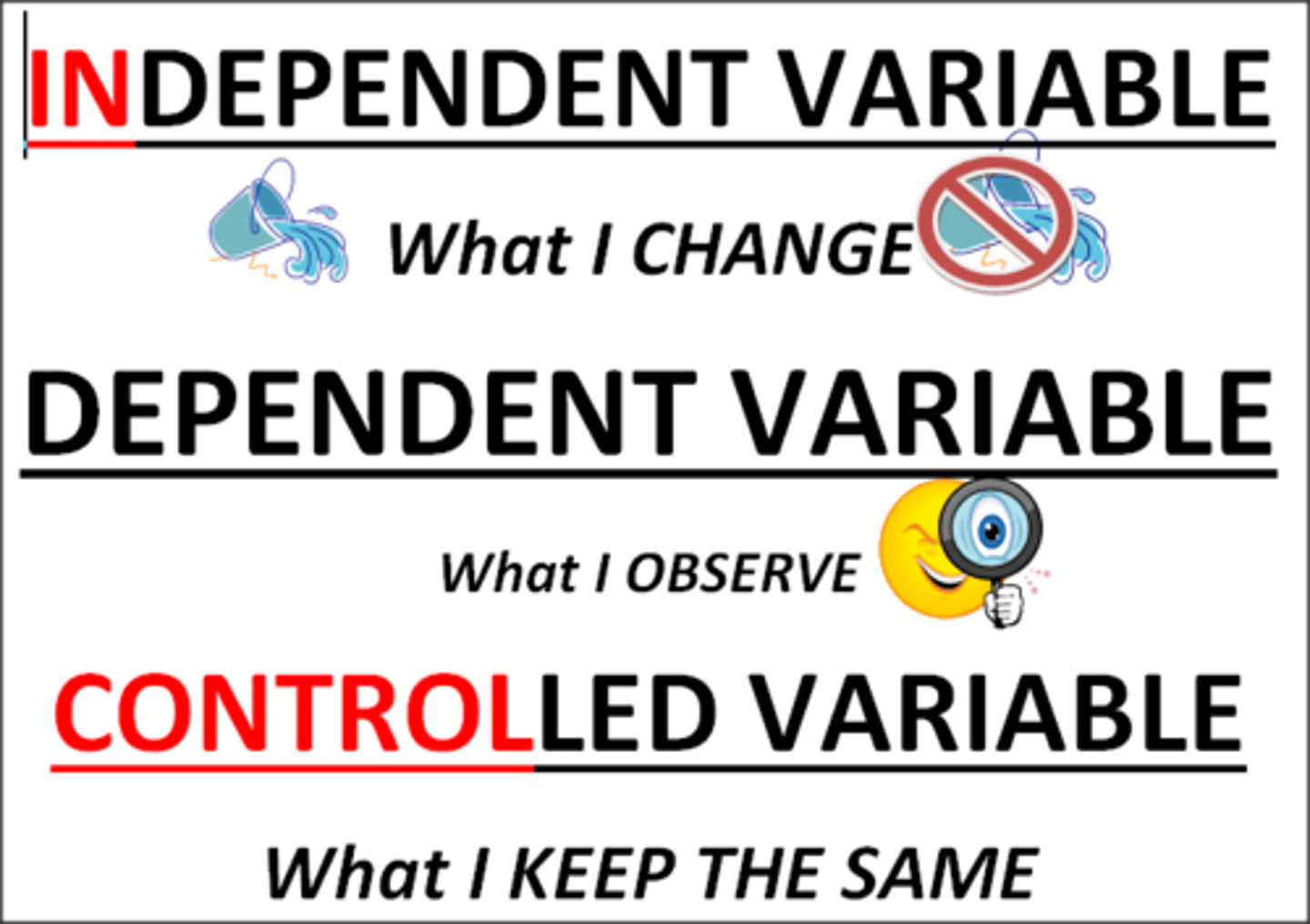
independent variable
variable that is manipulated
dependent variable
the variable that may change in response to manipulations of the independent variable
control variable
a variable that is kept constant during a controlled experiment
resistance is caused by...
electrons colliding with metal ions
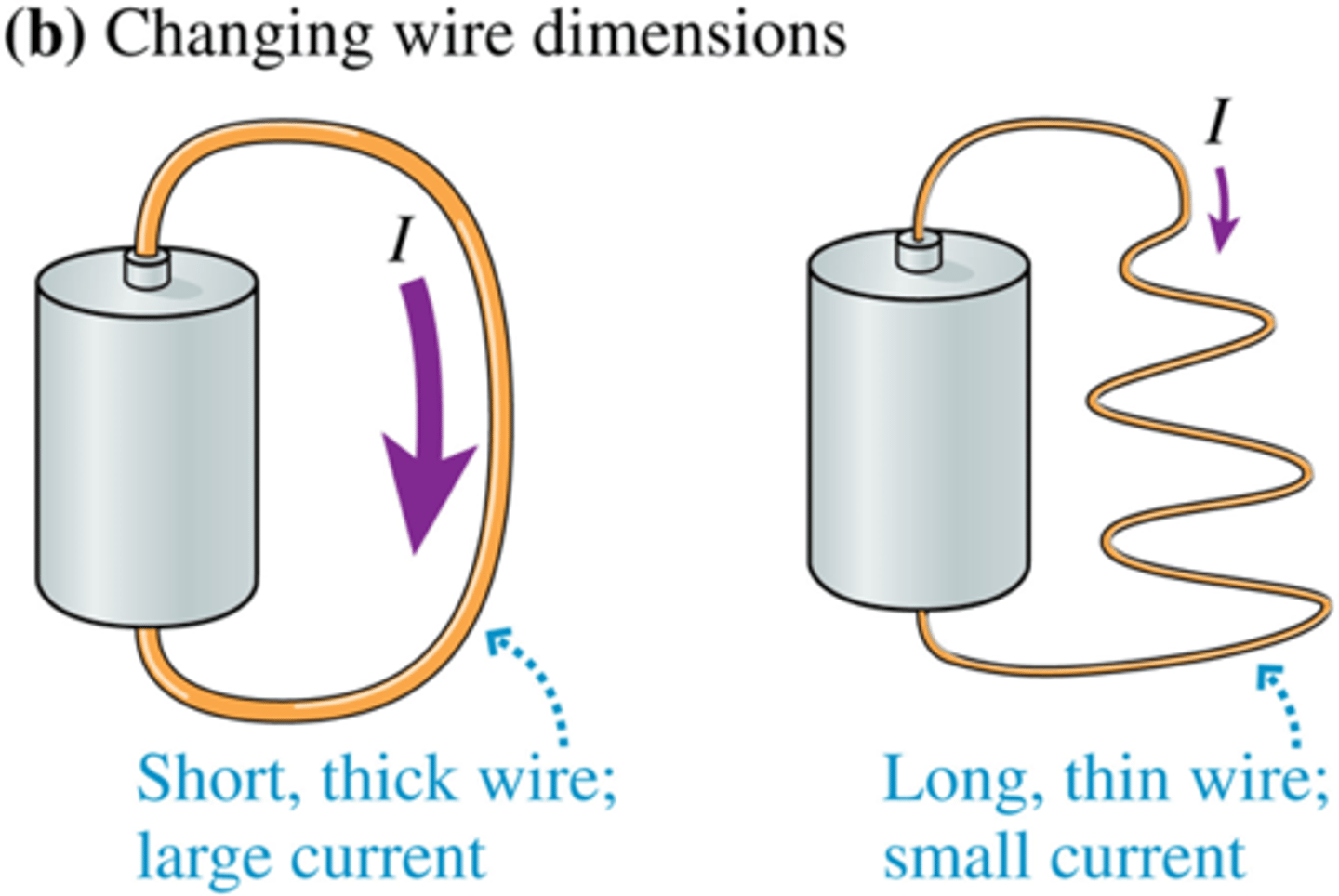
when the length of a wire is increased,
the electrons have to travel further, so the chance of collision will increase, causing the resistance to increase
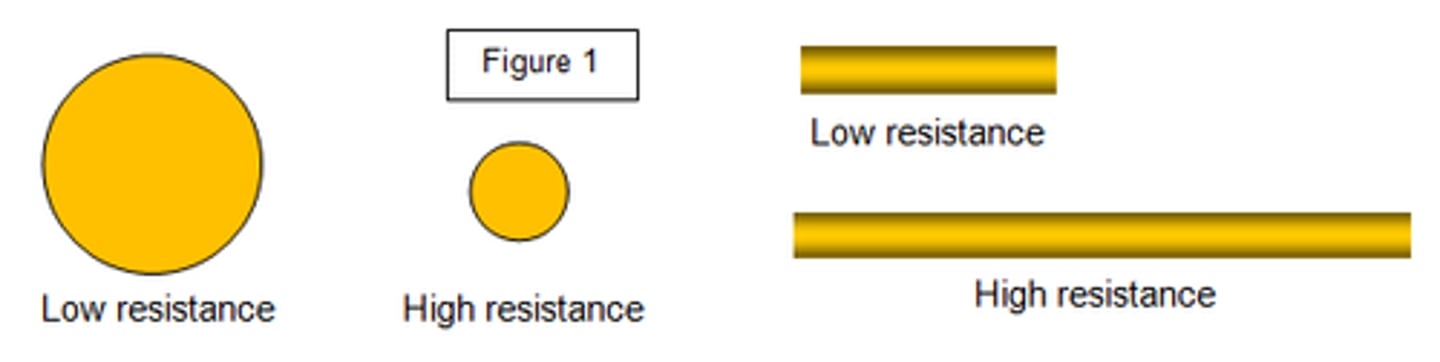
increasing the thickness of a wire,
increases the SA that electrons can flow through, this decreases the chance of collisions with metal ions, reducing resistance
fixed resistor
the resistance of the resistor is constant
semi-conductor
element that does not conduct electricity as well as metal but conducts better that a nonmetal
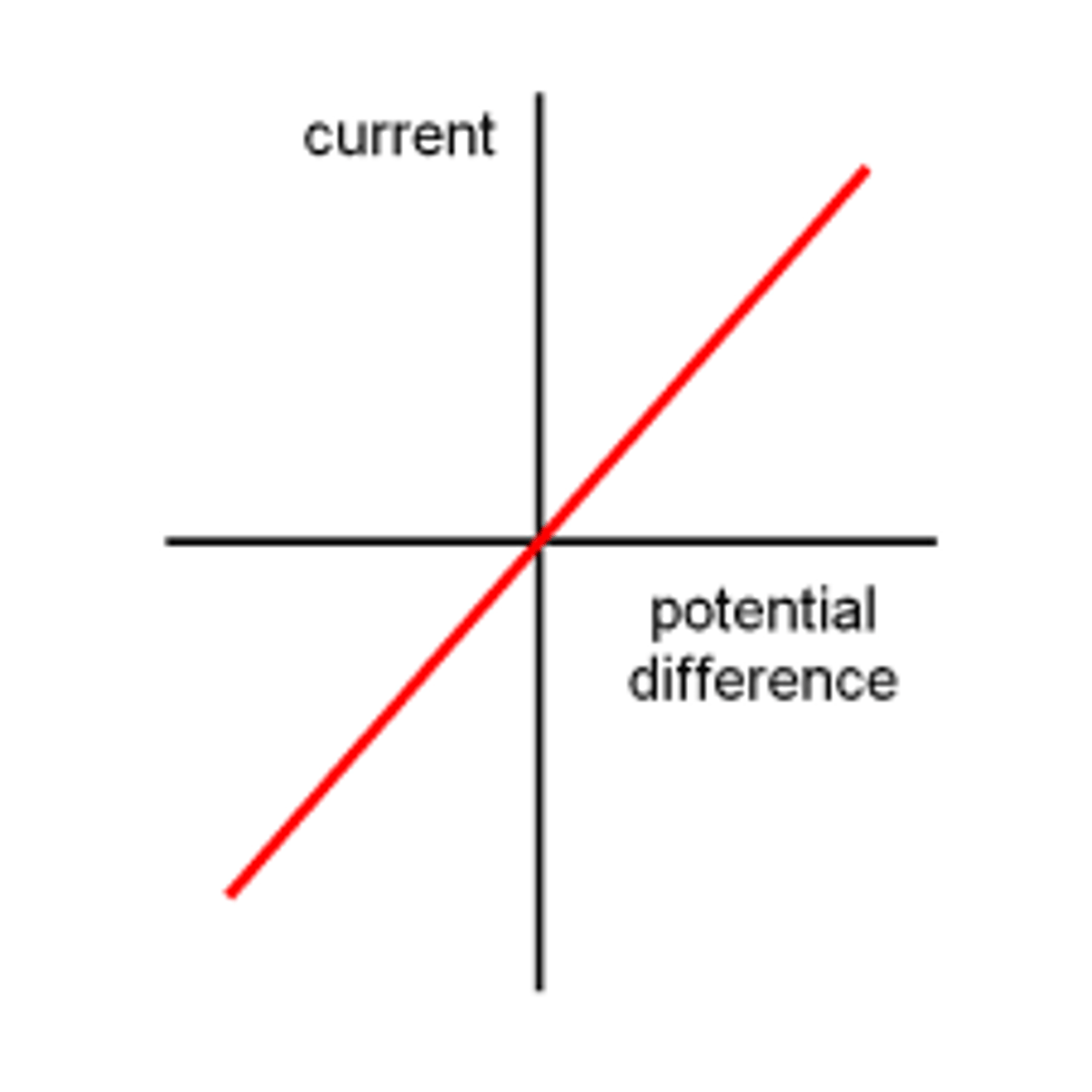
I-V graph for a fixed resistor
at constant temperature has a constant resistance
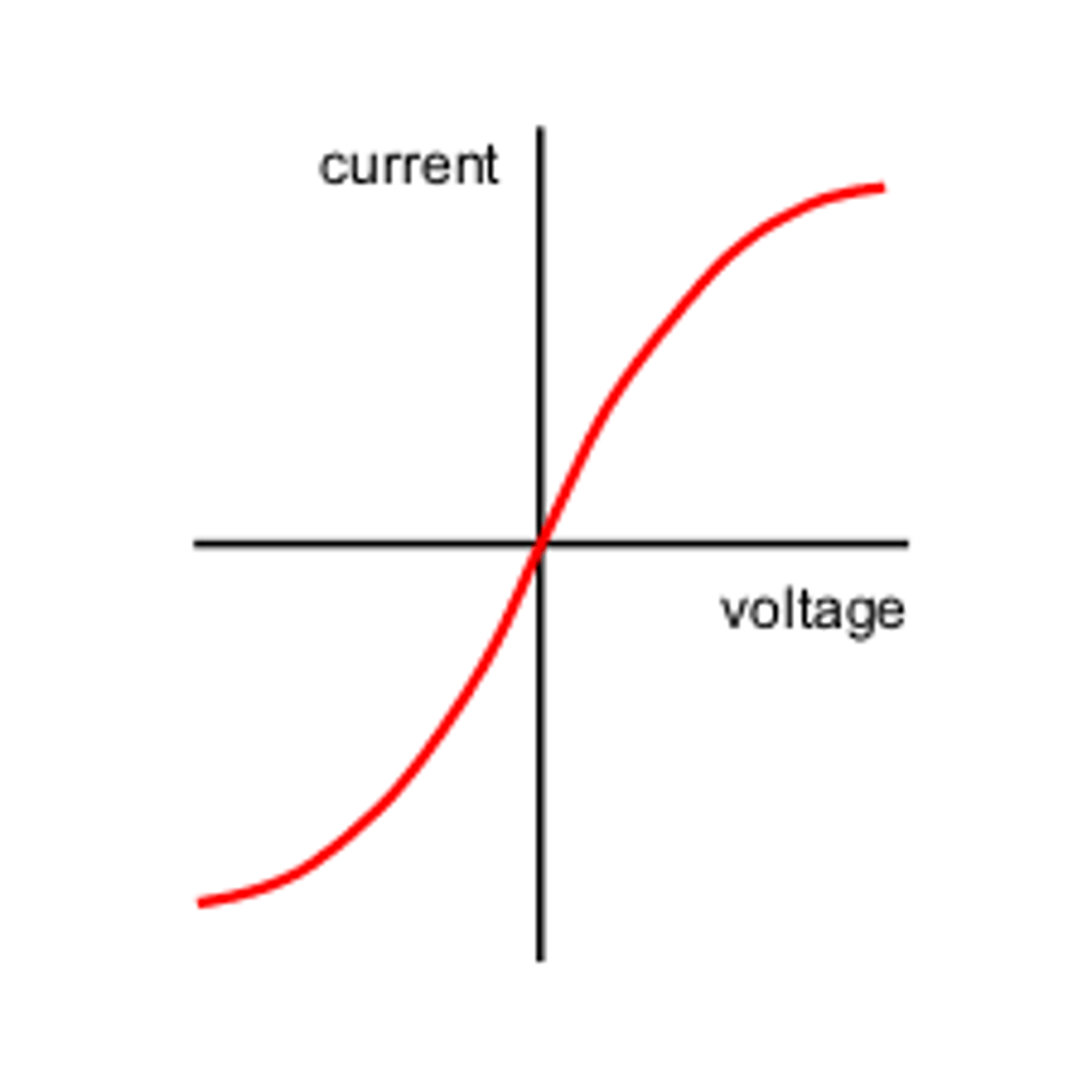
I-V graph for filament lamp
as the current increases, the temperature of the filament in the lamp increases, so resistance increases
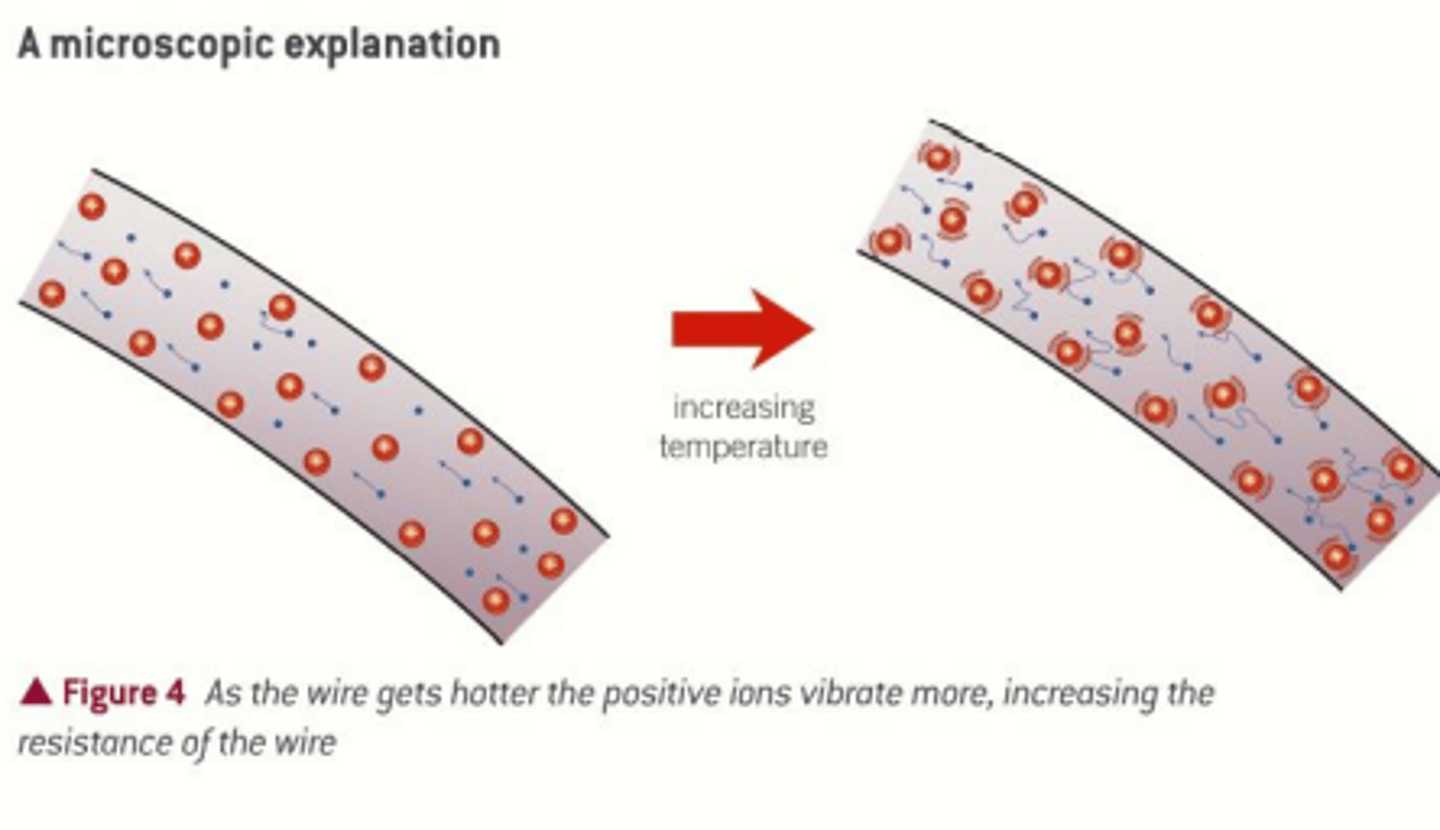
why does increasing the temperature increase resistance?
the delocalised electrons have more kinetic energy, so the rate of collisions increases, therefore resistance increases
changing gradient in an I-V graph means...
changing resistance
the shallower the gradient of an I-V graph, the ... the resistance
greater
variable power supply
an output voltage that can be easily adjusted to significantly different values
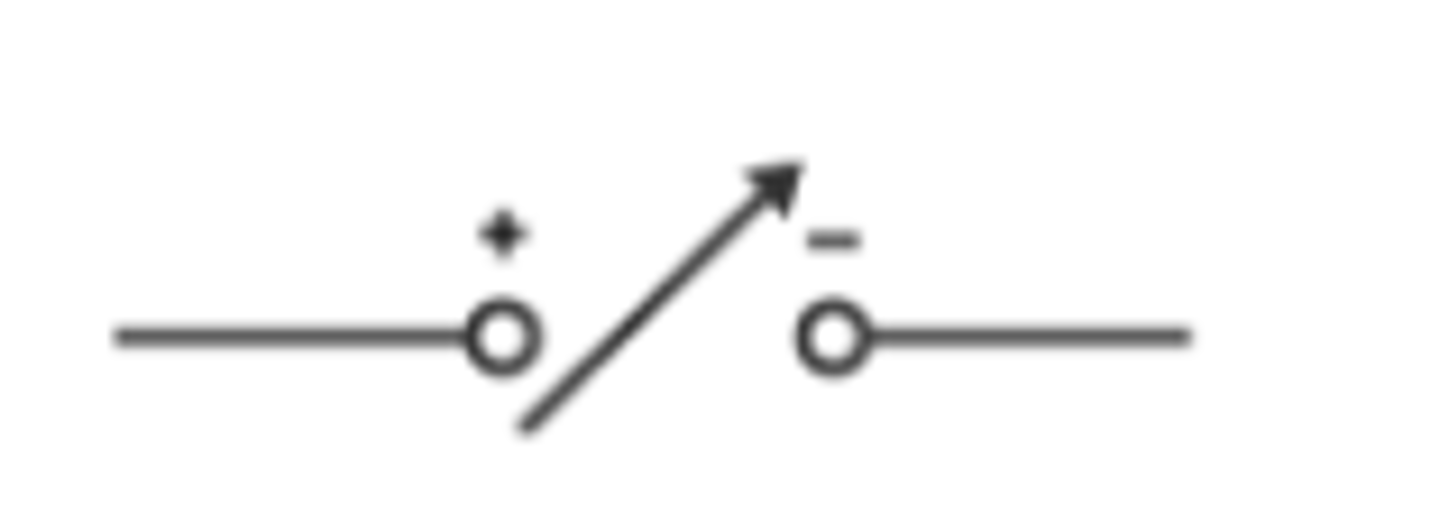
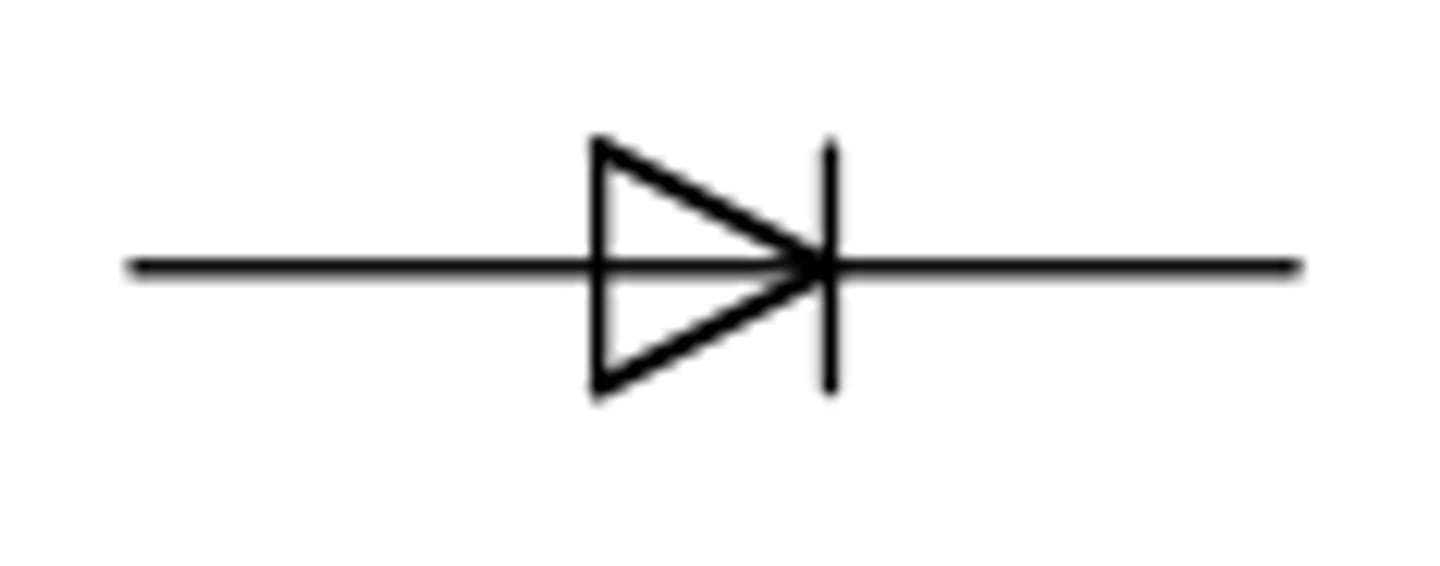
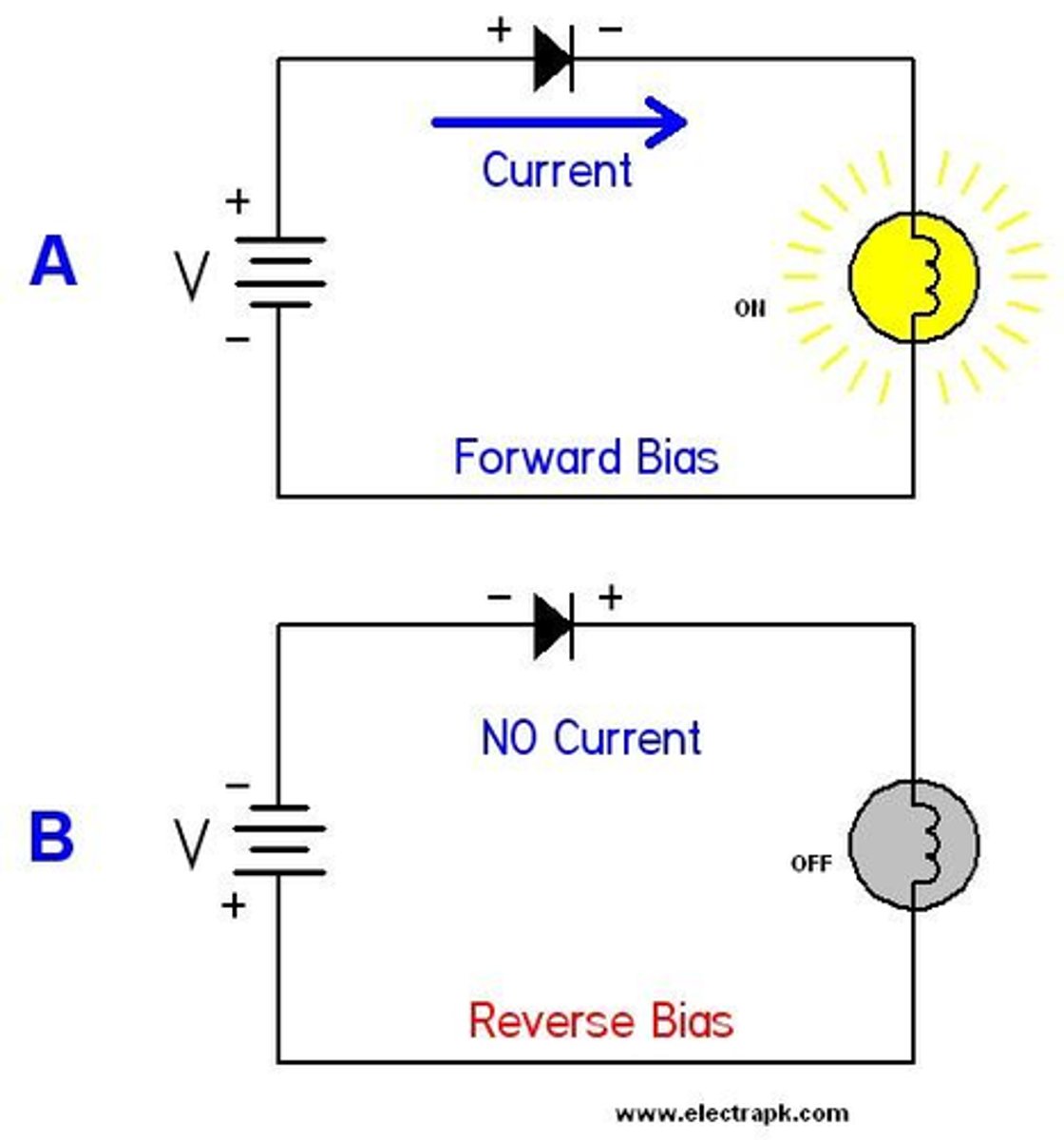
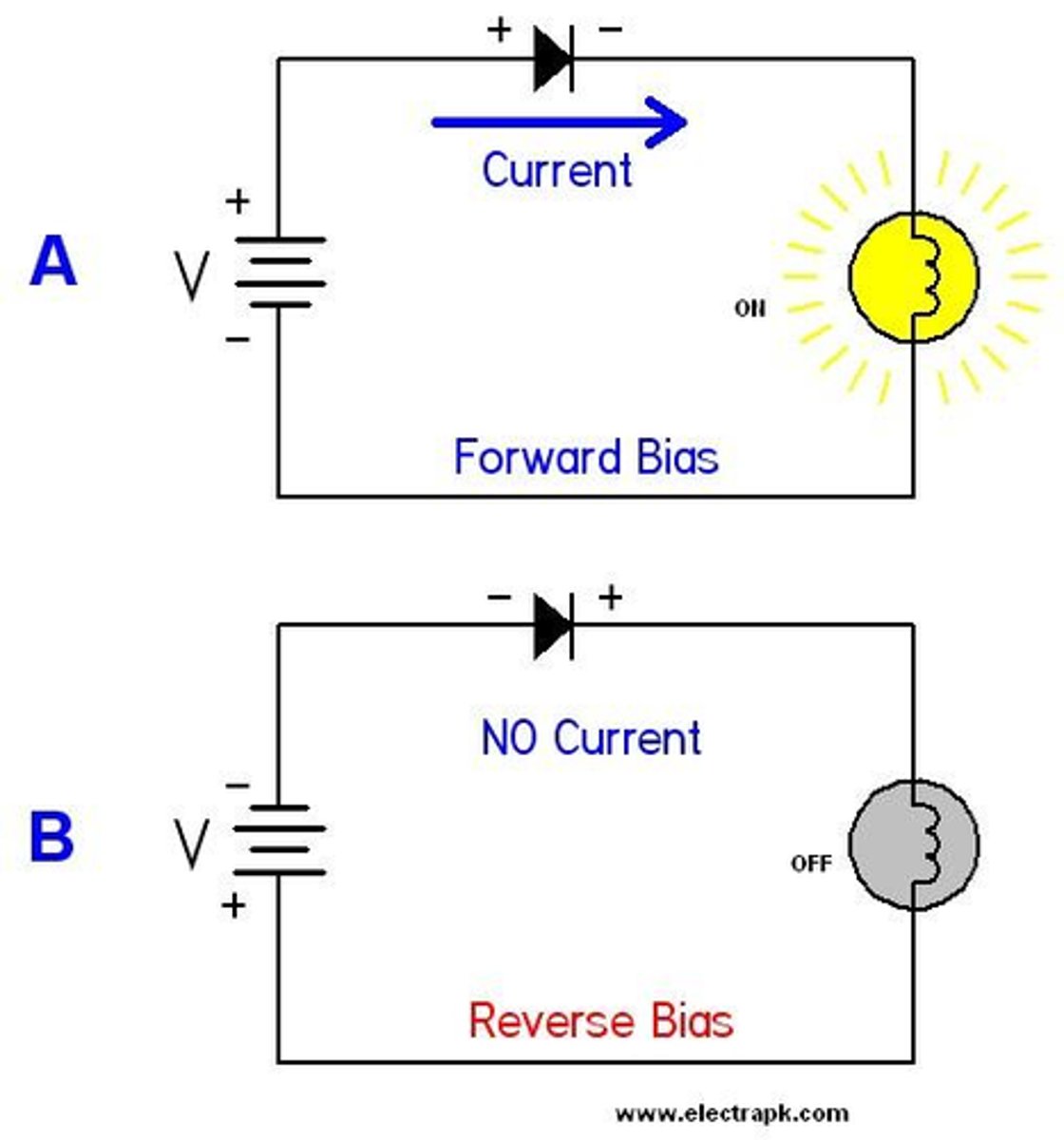
diode
a component that only allows current to flow in one direction
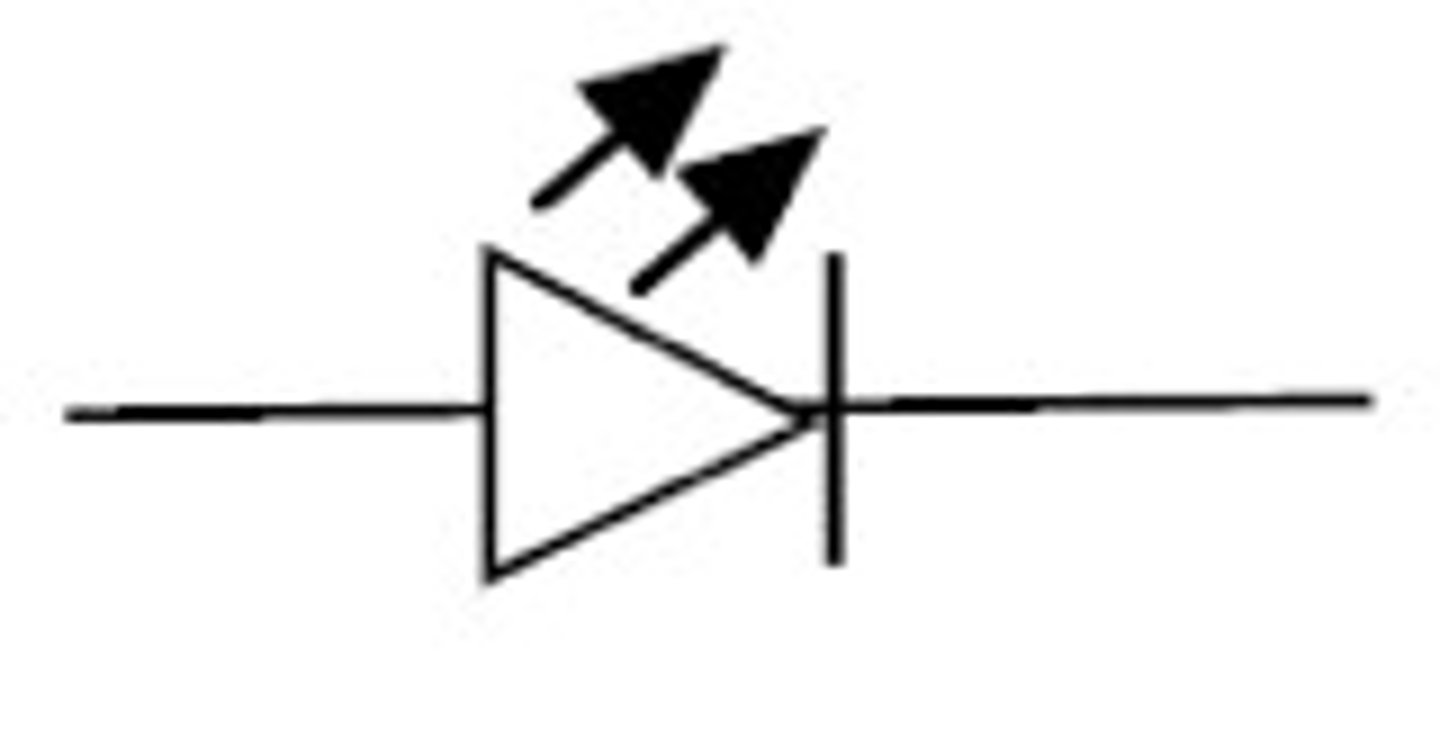
LED
a diode that will produce light when current flows through it
I-V graph for an LED
current will only flow through a diode in one direction so once current flows the resistance decreases, and the LED emits light
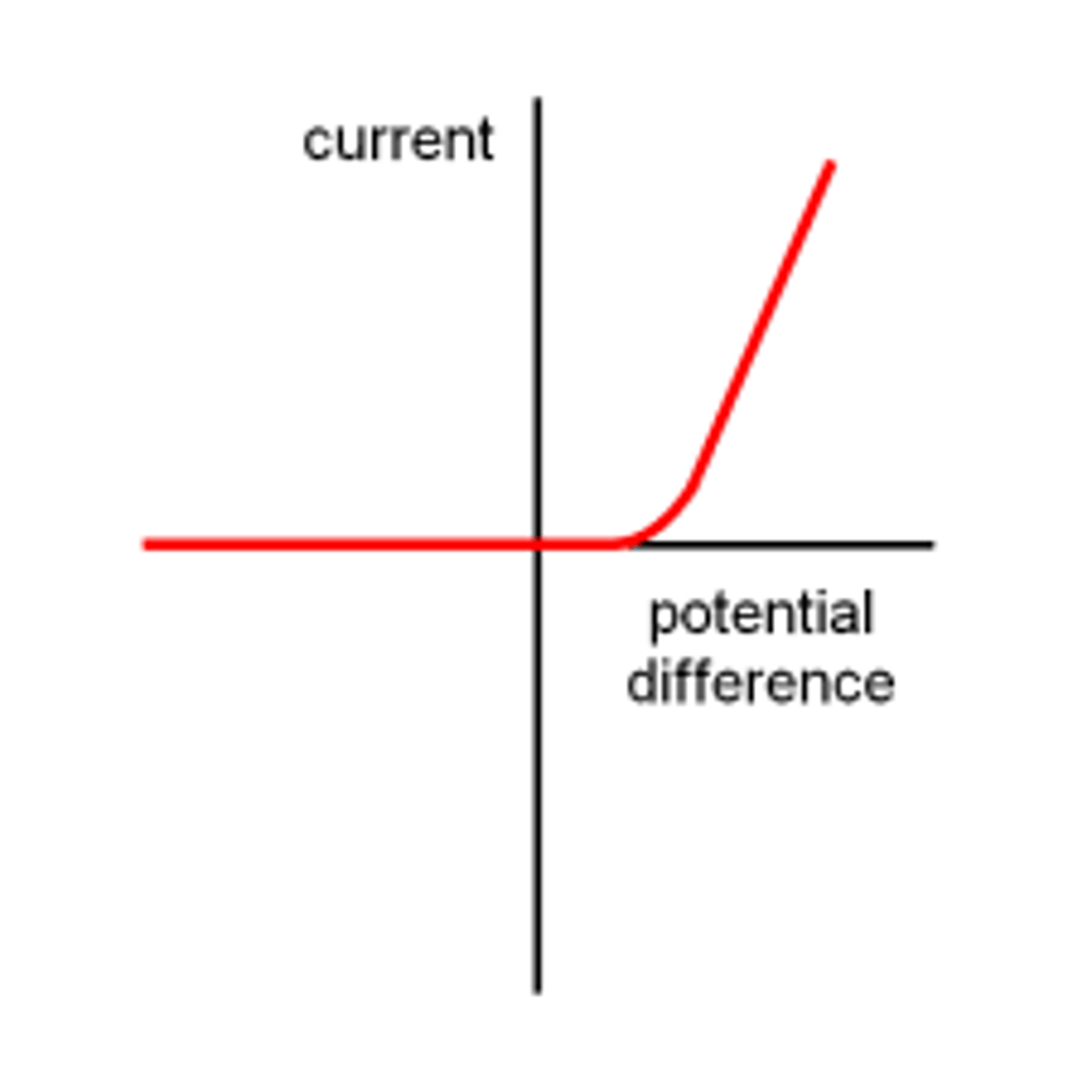
I-V graph for a diode
current will only flow through a diode in one direction so the line is straight then goes up on a shallow curve
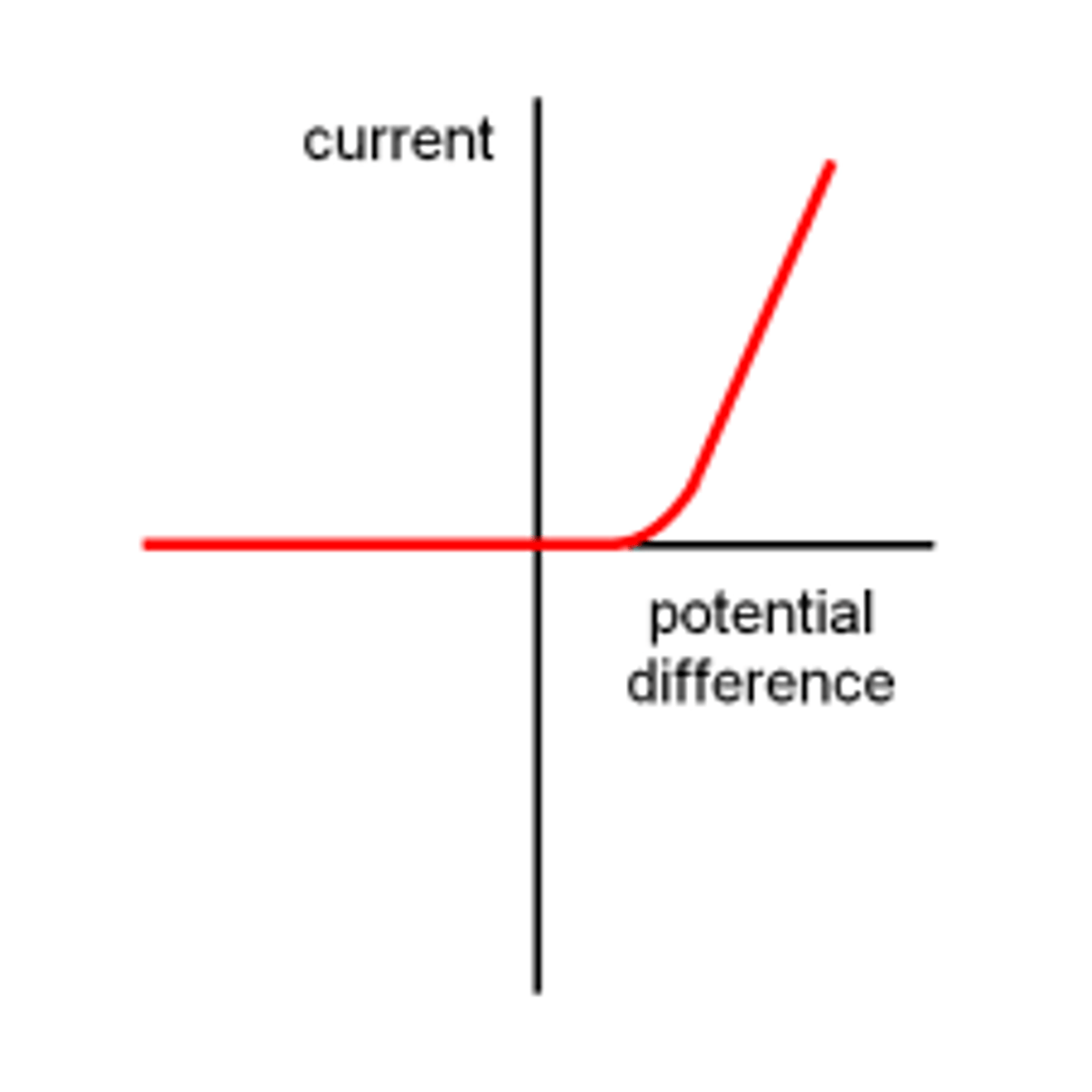
forward bias
a diode only allows current to flow in one direction only
reverse bias
the diode has infinitely high resistance, and therefore no current flows
the independent variable is on the ... axis
x
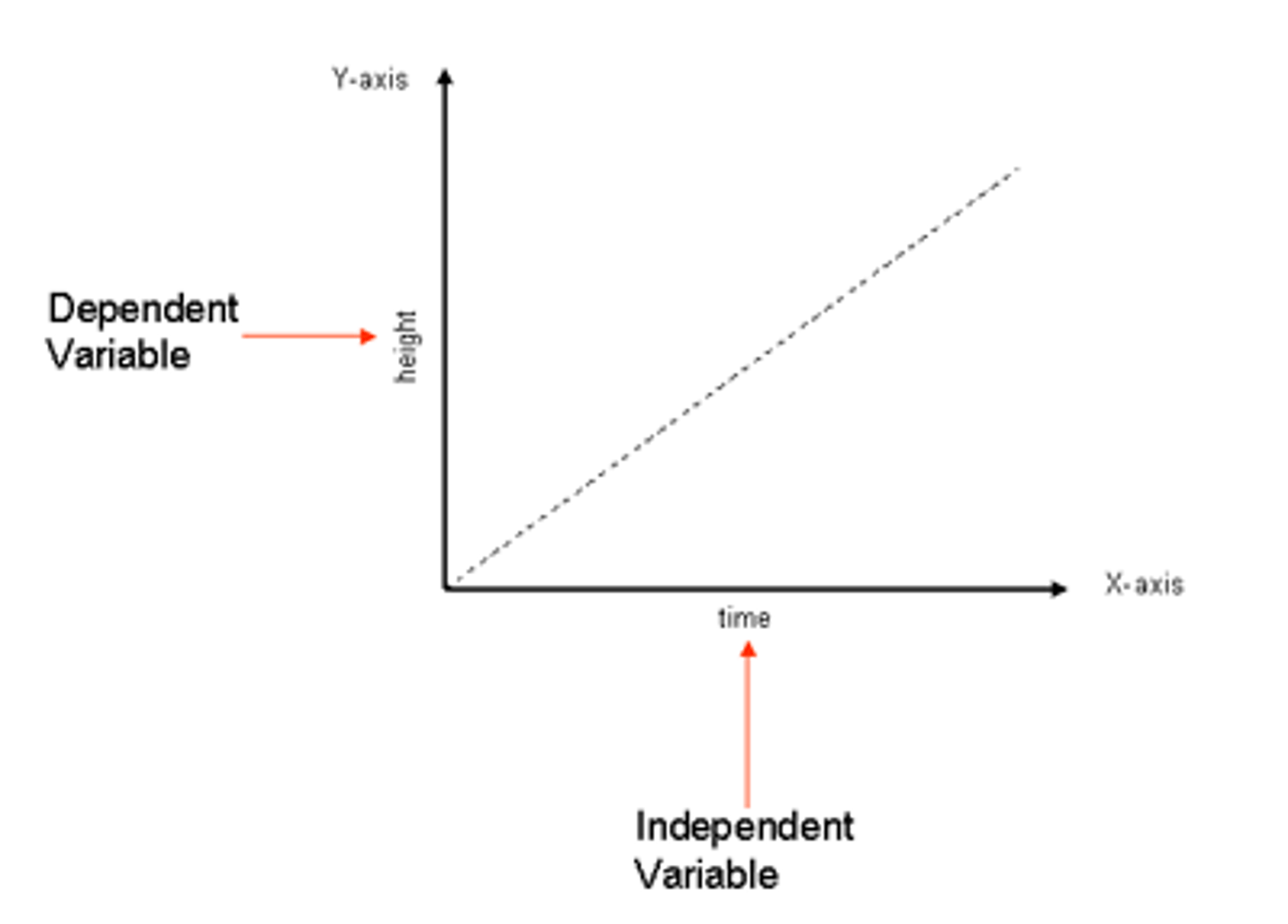
the dependent variable is on the ... axis
Y
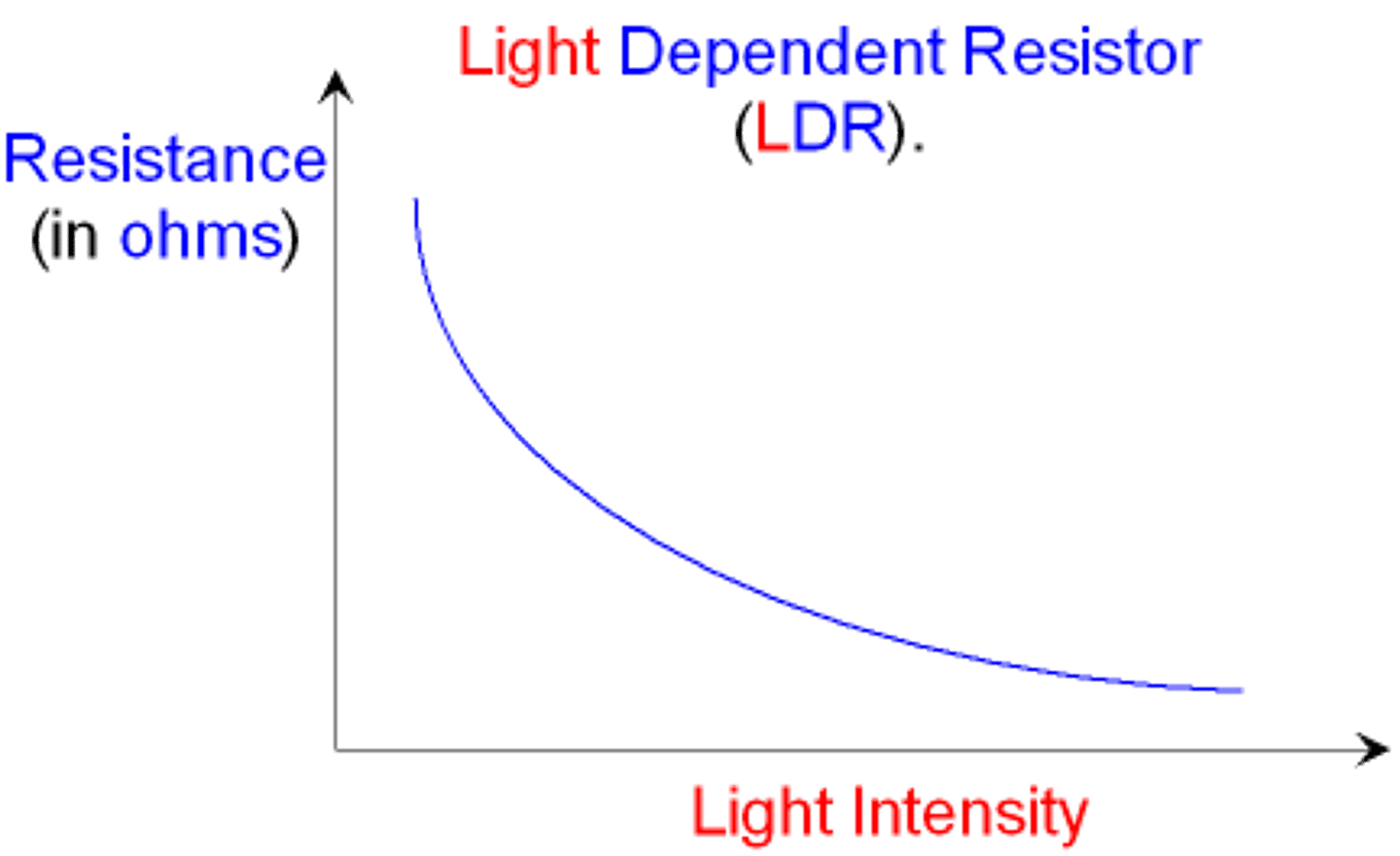
light intensity-resistance graph of the LDR
as light intensity increases, the resistance decreases
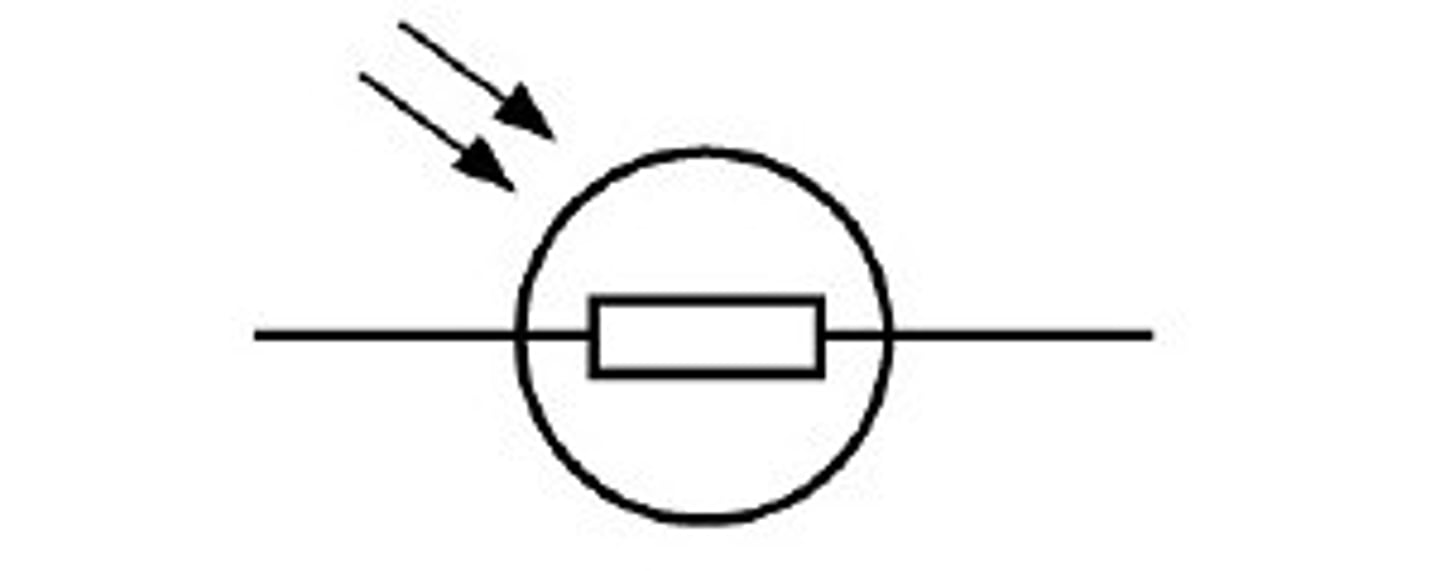
in dark conditions, does the LDR have high or low current?
in dark conditions, the LDR contain few free electrons and so have high resistance, and low current
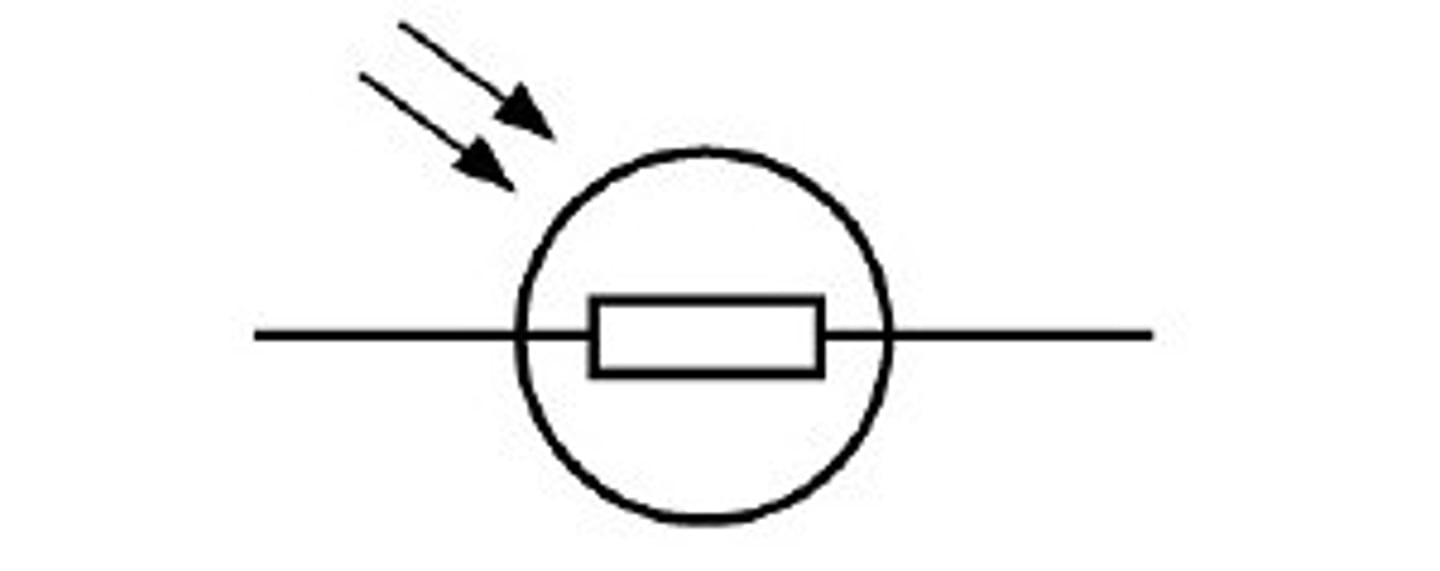
if light is shone, does the LDR have high or low current?
if light is shone onto an LDR more electrons are freed and the resistance decreases, and high current
CRO
cathode ray oscilloscope
temperature-resistance graph of the thermistor
as temperature increases the resistance decreases
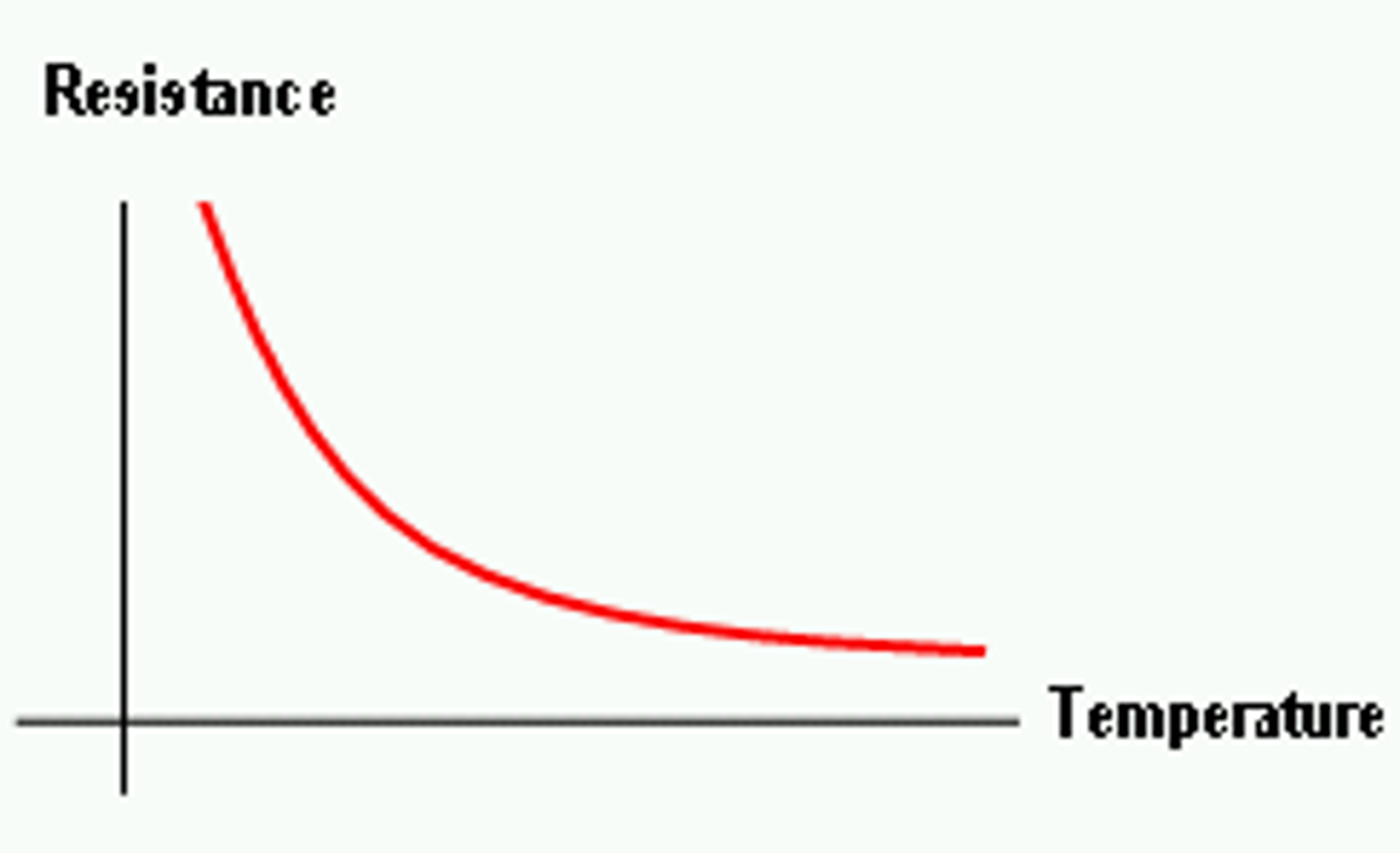
at room/low temperature
at room/low temperature the number of free electrons is small and so the resistance of a thermistor is large, so low current flows

at warmed/high temperature
the number of free electrons increases and its resistance decreases, so high current flows
resistance in series circuits
the more components are added to the circuit the higher the total resistance is, and so the flow of electric current decreases
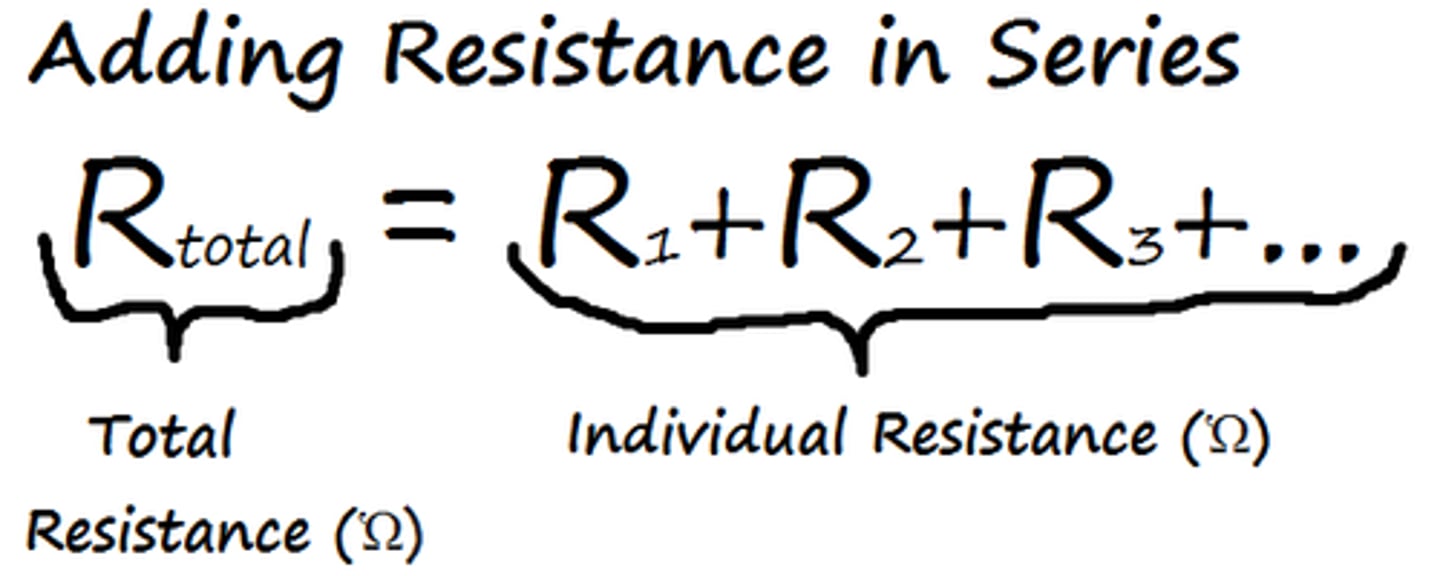
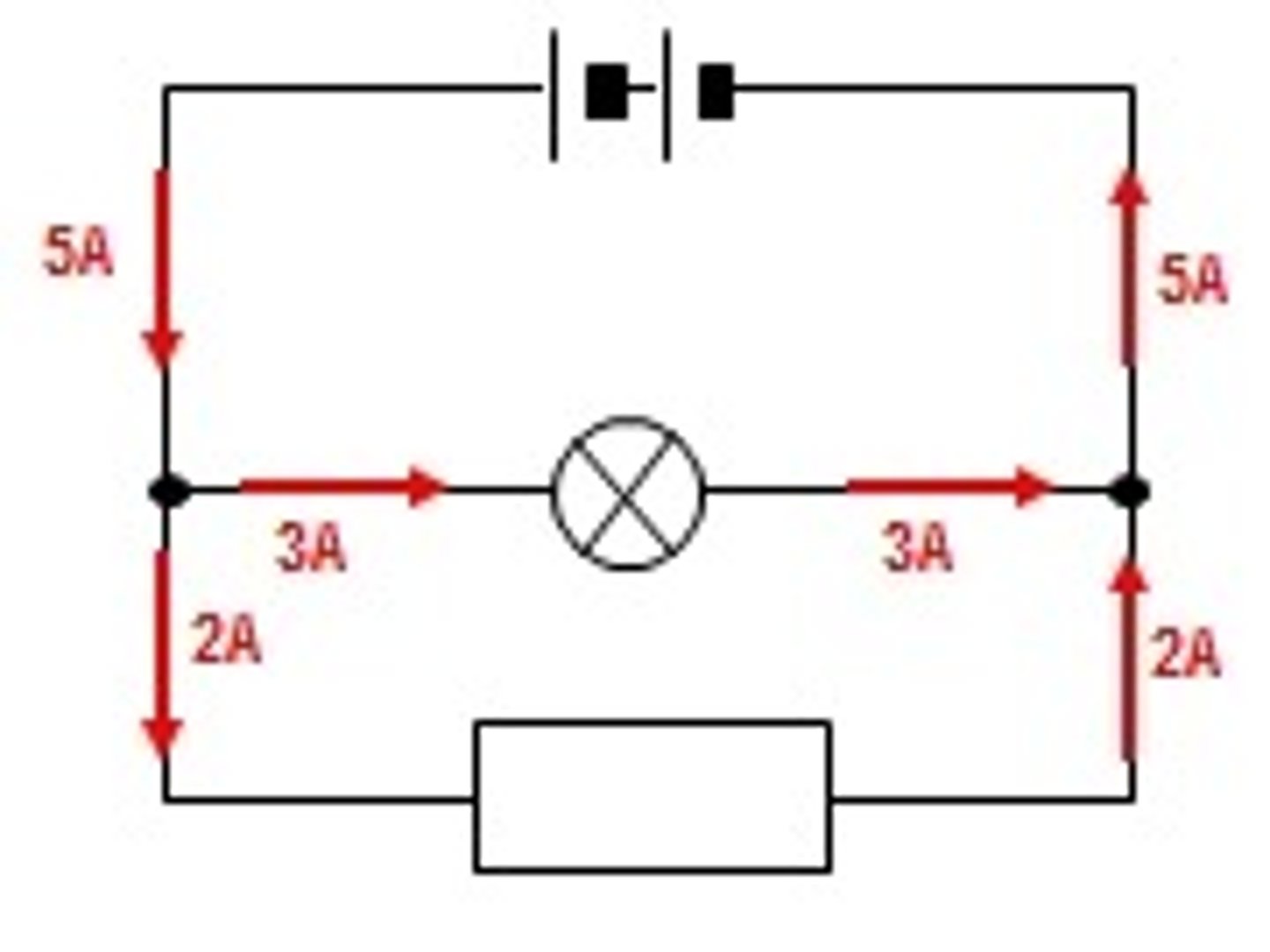
measuring current in a parallel circuit
current splits up in the junctions
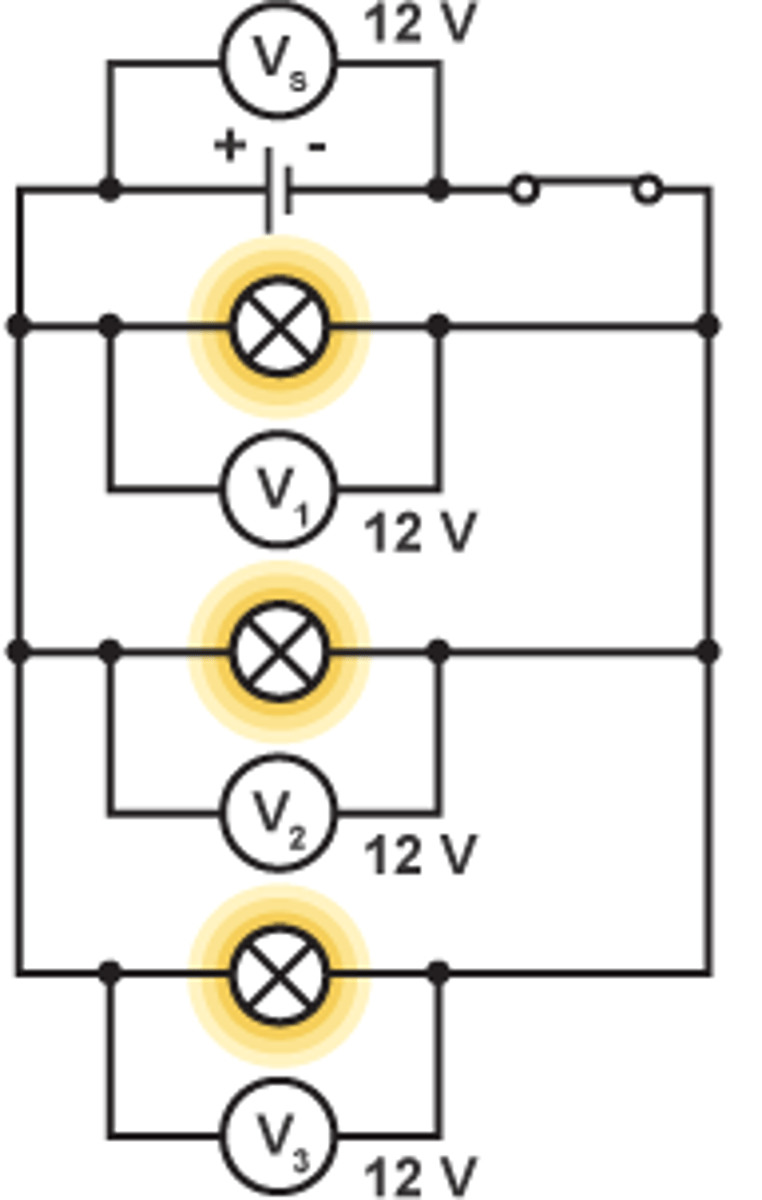
measuring voltage in a parallel circuit
they are all equal
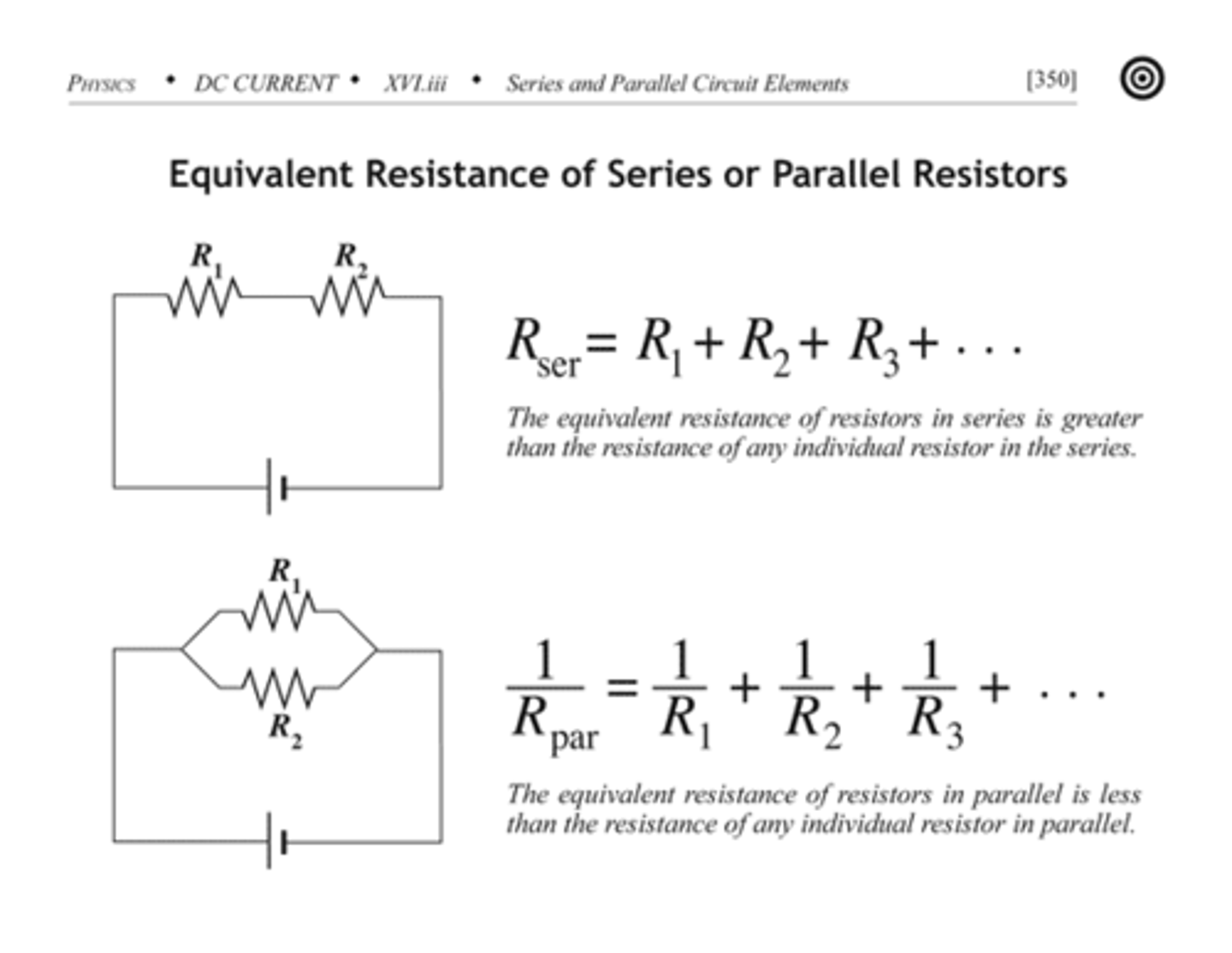
resistance in parallel circuits
the total resistance of the circuit decreases by adding more components so the flow of electric current increases
live wire
allows electric current to flow in (brown/black)
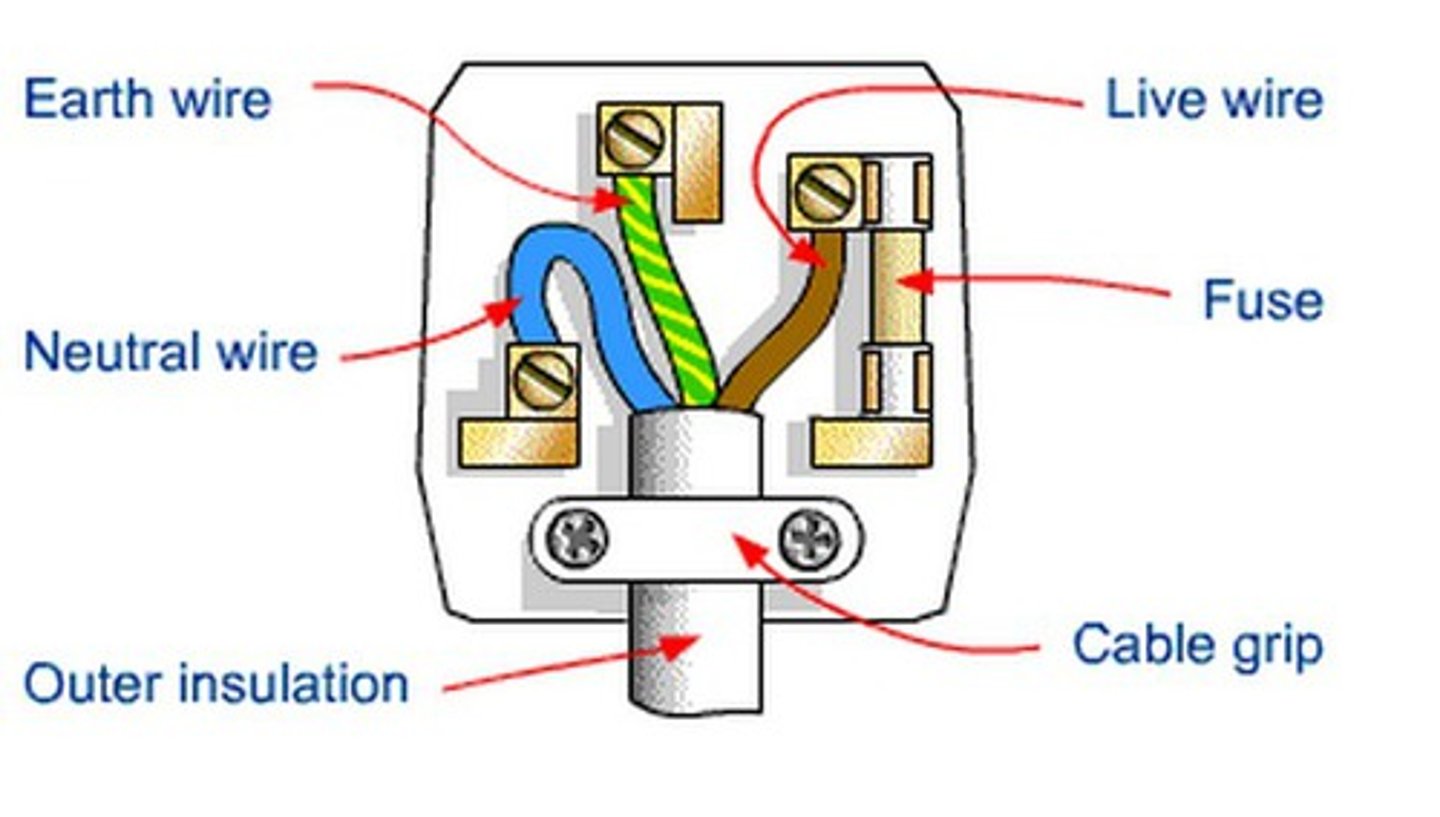
fuse
when current is too high, the fuse wire melts, breaking the circuit so there is no electrocution for the user
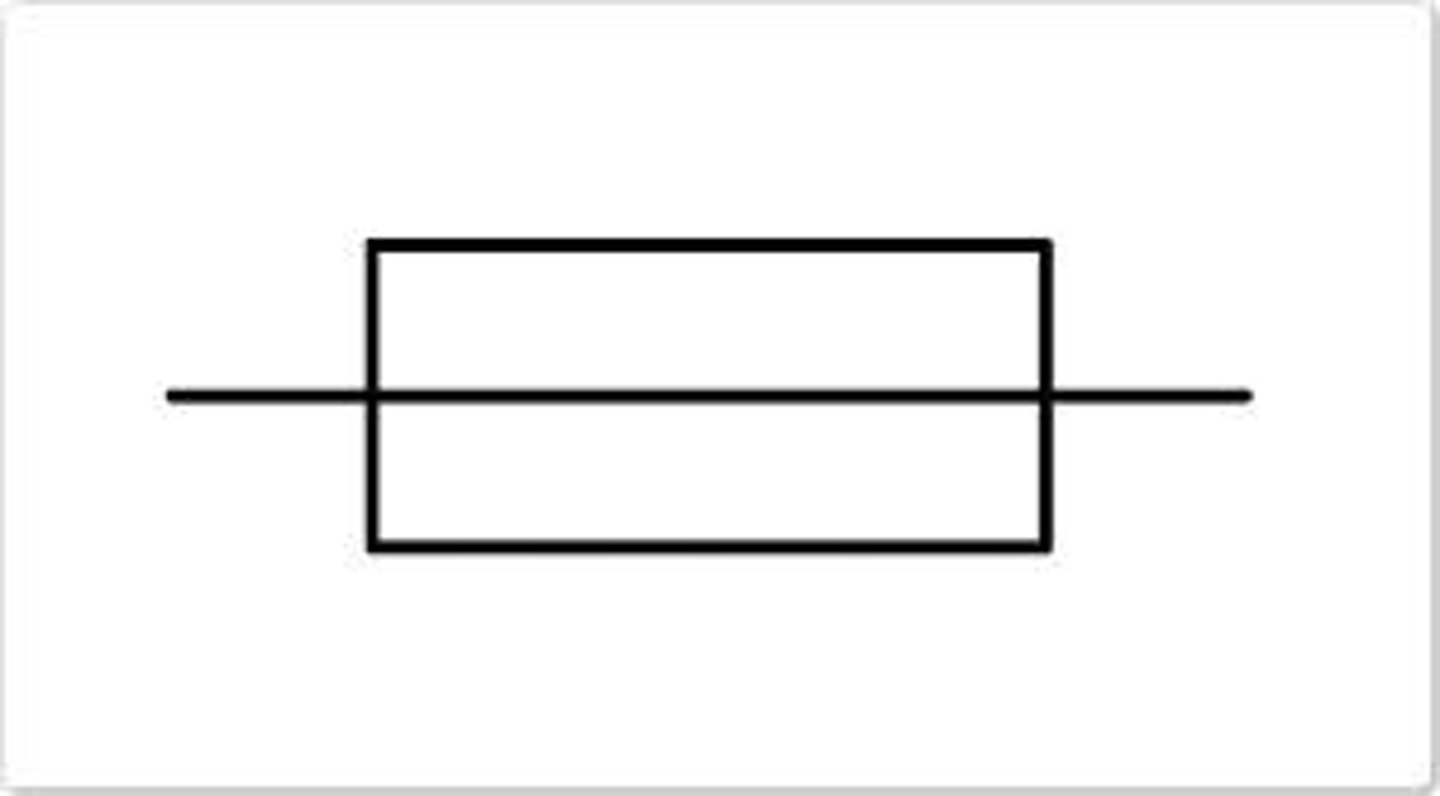
double insulation
an appliance that has a plastic casing for extra safety and does not need an earth wire
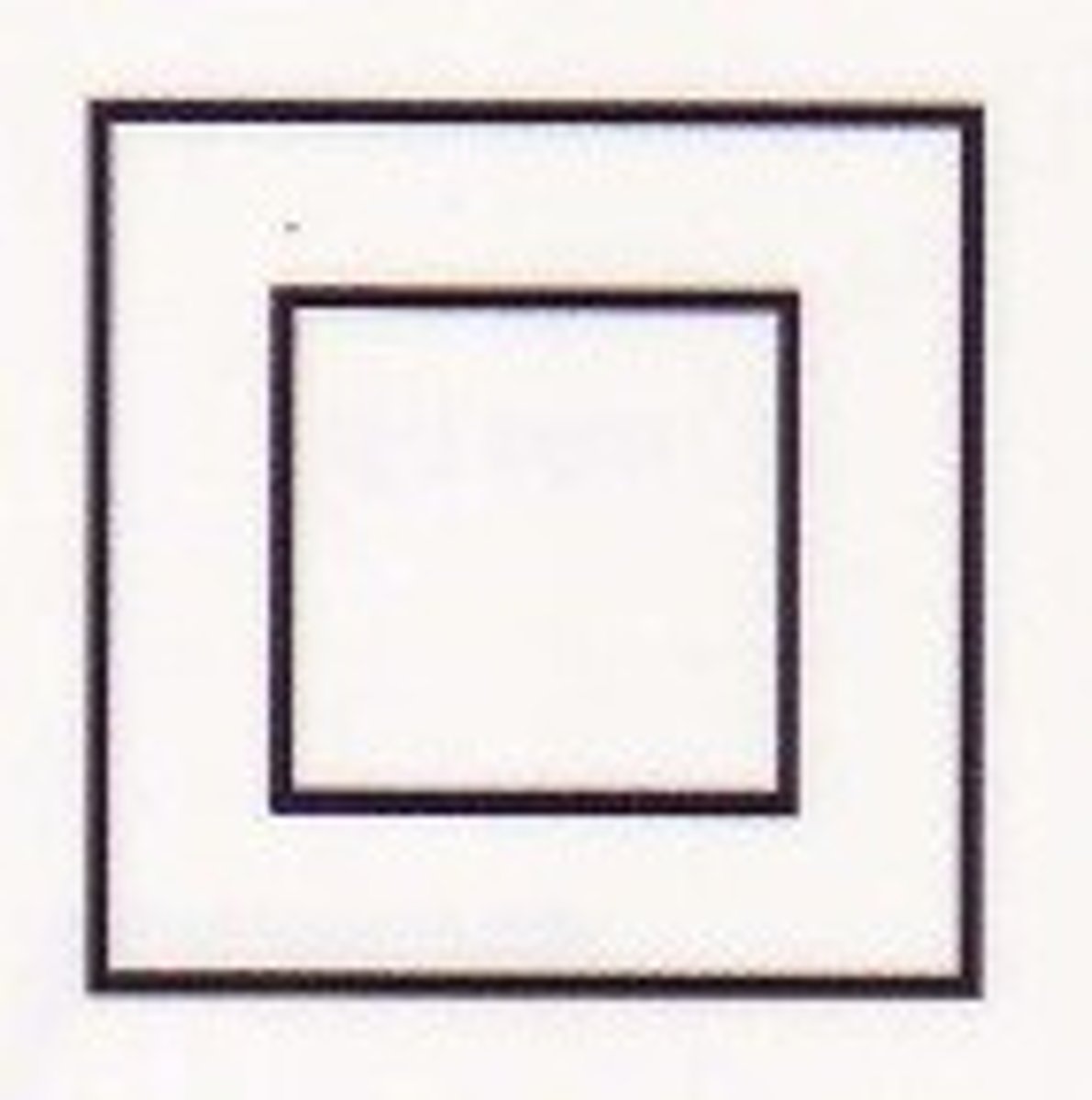
circuit breaker
monitor the current flowing in and out of a circuit and if there is difference they break the circuit

RCCB
Residual Current Circuit Breaker

the heating effect of current
when current flows through a resistor energy is transferred to the resistor and becomes warm
the energy is transported by the electrons
when electrons collide with positive ions in the lattice the energy is transmitted to the ions which is emitted as heat/thermal energy

how do you choose the correct fuse?
a fuse is labelled with the maximum current that it will allow to flow through it
always choose the one with the closes rating that is just greater than the operating current of the device

UK/EU mains
230v AC

static electricity
the build up of charge that does not move
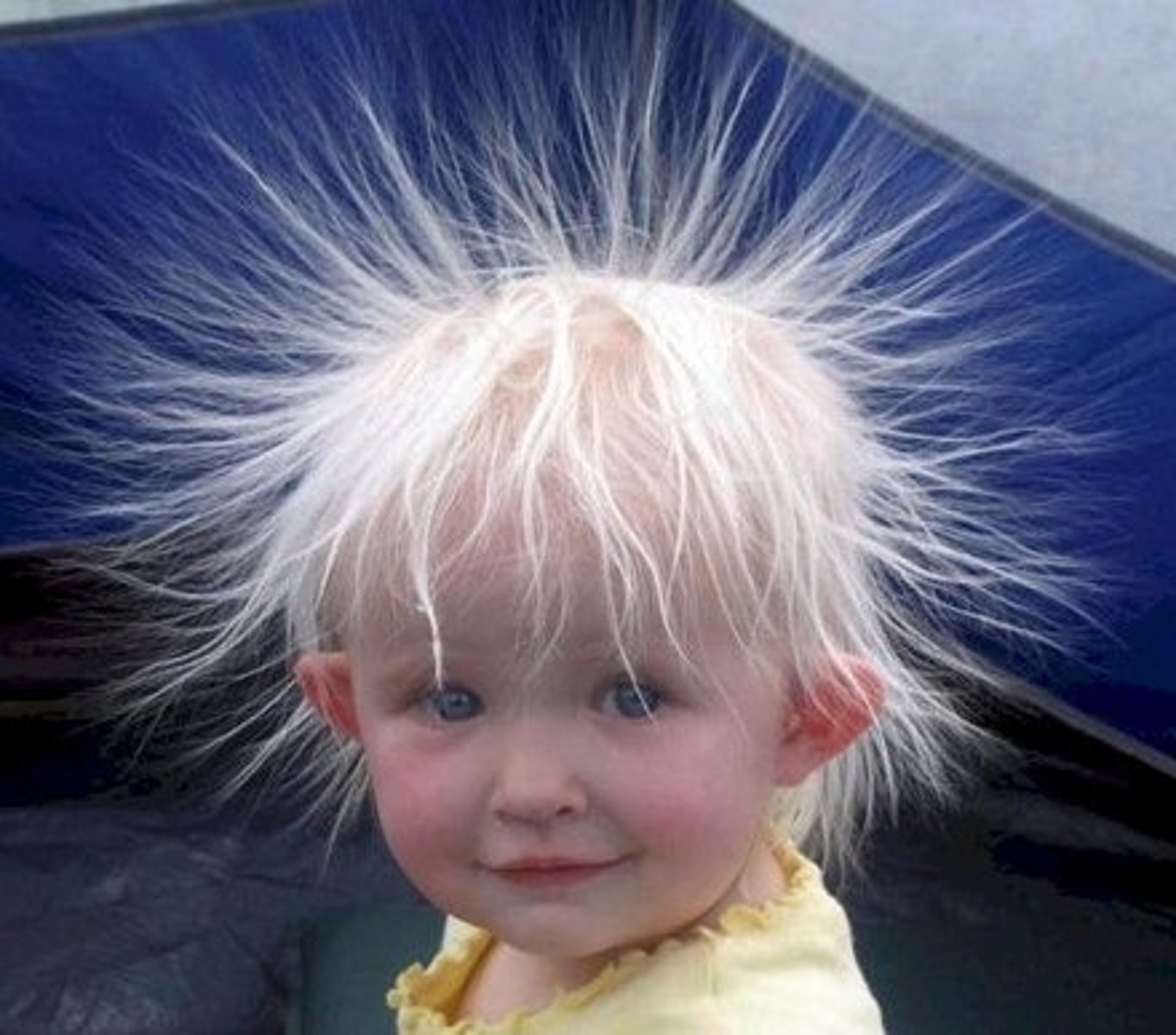

what happens when electrical insulators are rubbed together?
electrons are removed and transferred from one material to the other
