MIS 180 Barra In Person Exam Study Guide 2024
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
117 Terms
What is data? Provide and example
Data: Points of information
Ex: text, numbers, photos
What is information? Provide an example
Data converted into meaningful and useful context
What is business intelligence? Provide an example
information collected from multiple sources such as suppliers, customers, and competitors that analyzes patters, trends and relationships for strategic decision making
What is a fact? What qualities does it have?
a statement that can be proven
What is the difference between a useful fact and misleading fact?
Useful: Verifiable, relevant, credible
Misleading: Partial, redundant, requires extensive verifying
What is triangulation?
Gathering information
What is corroboration?
evidence that confirms or supports a statement
What does "information literacy" mean?
The ability to find, evaluate, and use information effectively to achieve goals
What is a relative address/reference in excel?
A cell reference that adjusts when copied or used with AutoFill
- "Drag down"
What is an absolute address/reference in excel?
A cell reference that DOES NOT adjust when used with autofill
- "$"
What is the proper format for a calculation if you want to add, subtract, divide, or multiply 2 numbers by referencing their cell reference?
= Cell A +,-,/,* Cell B
What is the proper format/syntax for the IF function?
=IF(logical test, value if true, value if false)
Which function would you use to sum a columns or row of 50 numbers? Given a range, what is the proper format? Be able to apply this to avg, max, and min
=SUM(G1:G50)
What is the difference between a system and a process?
They effectively mean the same thing.
A structured collection of processes that work together to produce an outcome
What are the 6 parts of any system?
1. Inputs
2. processes (that transform inputs)
3. Outputs
4. Controls
5. Feedback
6. Adjustment
How do supersystems, systems, subsystems, and processes relate to each other?
Supersystem --> The greater system
System --> the general system
Subsystem --> systems within the system
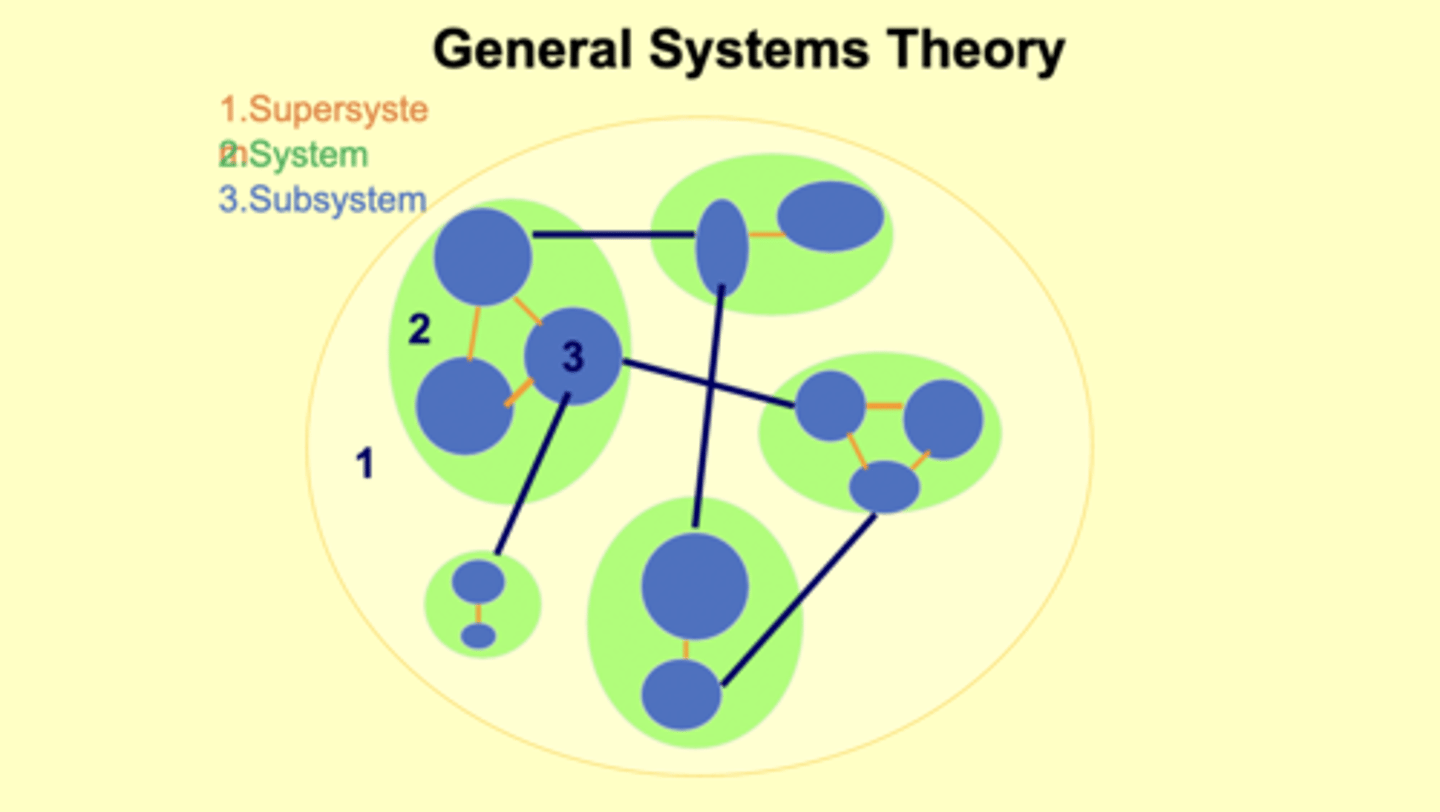
What is interdependence? Provide an example
Parts that depend on each other
Ex: The food web
What is synergy? Provide an example
how different parts of an information system or business functions work together to create greater efficiency
What is entropy/obsolesce? Provide an example
All systems fall apart over time if they don't adapt
Ex: Campfire, solid wood turns into ash, smoke, gasses
What is optimization/sup-optimization? Provide an example
Subsystems often must optimize to enable the system to operate at maximum efficentcy
What is an open system?
The transformation process set but inputs and outputs can vary
- designed to adapt and evolve
Ex: Algorithms
What is a closed system?
A system where neither matter nor energy can enter or leave
Ex: TV Remote
What are the functional parts of an enterprise and what do they do?
Hint: know "Internal View of an Enterprise" Slide
Sales - selling goods or services
Accounting - Records monetary transactions
Finance - tracks strategic financial issues
HR - Maintains policies for effective management
Marketing - supports sales by planning, pricing, and promoting goods and services
Operations Mgmt. - Manage the process of converting resources into goods and services
What are stakeholders? Who are they for most enterprises?
Hint: Know "External View of Enterprises"
Those who benefit in someway from the operation of the company, which may not include owning stock
Ex: customers and suppliers
Stakeholder vs shareholder
- a stakeholder is customer of a business
- a shareholder owns part of a company through stock ownership
What are parts of a business information system and how do they work together? Provide examples
Data - audio, video, text, numbers
Hardware - clients, servers, robots
Software - operating systems, applications
Media - WiFi, cell networks, satellites
Procedures - Hiring, manufacturing, evaluating
People - Executives, HR, customers
What are the 3 main problems when evaluating information? Provide an example
1. Information overload - we can access so much information
2. More variability in info quality - quality of information has become questionable
3. Information evaluation is hard - we tend to jump to conclusions
What is Pro Concentration?
Information used to be of higher quality, with the abundance of information, the quality has diminsihed
What is Pro Distribution?
Professional committees ensured their information was accurate, now anyone can post anything
What does it mean when we are described as "cognitive misers"? What does it mean as a way of describing how humans make decisions about information?
We tend to solve problems in the easiest or simplest way possible. Can lead to negligence or skipping of crucial information
Bias vs Perspective? How does this affect your judgement
Bias: Prejudice in favor of one thing; unfair
Perspective: A particular attitude to one thing; not fair or unfair
How do humans deal with information overload?
Filtering (using heuristics) and withdrawal (disconnection)
How would you evaluate information in terms of its "usefulness" and "believability"?
Accurate, complete, consistent, timely, relevant, meaningful, accessable
What is disinformation? Provide examples
The intentional creation and transmission of known false information
Ex: NYT and "12 Russian Agents Indicted in Mueller Investigation"
Who are the biggest players in the Search Engine Market?
Google - Web browsing
Amazon - Products
Etsy - Arts and crafts
Indeed - Jobs
Yelp - Businesses/Restaurants
YouTube - video
Zillow - Real Estate
What is the state of the internet?
The internet is evolving with AI, 5G, cloud, IoT, and cybersecurity challenges.
How does a search engine work with:
Spider/bot
Database
User
Spider - computer application whose purpose is to find and index content on the web - pull relevant results to what you are looking for
Database - contains links and some summary content
User - people and programs who are trying to find a page/information
How does a search engine populate its database?
A spider/bot gathers information and gathers it for the user
When a user conducts a search, what are they actually doing?
Users are using a database, not the web directly
Why is the job of a search engine difficult?
We rely on natural language while the computer relies on indexed language. It must bridge the gap
What is a general search engine?
Contains a broad range of information
What is a vertical search engine?
A focused search engine
Ex: Amazon is a search engine for products
What does "vertical" mean in business?
Focused
What is a URL?
A link to a web page
Stands for Uniform Resource Locator
What is the surface web?
Sites and pages that the search engines know about and index for users to find
What is the deep web?
Sites and pages behind firewalls that cannot be indexed by engines
Casual user often does not even know these sites exist
What is the dark web?
Pages that are encrypted and aren't visible to anyone without special access
Know the functions and defintions of computer hardware
CPU/Processor, clock speed/GHz, RAM (Primary storage), Hard Drive (Secondary Storage), ROM (read only memory) (stores BIOS and basic information), Input/Output devices
When should you spend the money on more expensive computer equipment?
When the task you are doing is worth this investment!
Bit
Short for binary digit
smallest element of data
0 = off, 1 = on
Byte
Group of 8 bits
represents 1 character or number
What is an Operating System?
Works between hardware and apps
What is an application?
An "app", a program that does something the user wants to do
Why do humans create applications?
Does something the user wantes
What are the most common types of programming languages?
Java, Pyth, C#, and Visual Basic
What is source code?
Code written by the programmer
What is object code?
Code that the computer can understand
What does open source refer to?
Original source code that is free to the public
Why would a company use open source over proprietary applications?
Customizable, purchase what you want, specific tailoring
Why would a company use proprietary applications over open source?
Prebuilt, less skill required, less time to research, simpler installation
What is a General Purpose Application?
An application that can be used for a range of purposes
What is a Functional Application for a business?
A software program designed to support a specific business function
Ex: Accounting software
What are the 3 ways businesses aquire software?
Build, Buy, Rent
Why would a business choose a certain way to acquire a software?
Build - custom to needs
Buy - convenient
Rent - Pay as you go, non permanent
What is a business strategy?
The overall vision and goals for the enterprise's future
- planning, large scale, "what" and "why"
What is a business tactic?
A set of specific actions that execute the enterprise's strategy
- doing, smaller scale, "how", shorter time frame
What are the performance metrics?
Critical Success Factors (CSF), Key Performance Indicators (KPI), Benchmarking, Return on Invsetment (ROI)
What does CSF measure?
The steps companies take to acheive their goals and objectives to implement their strategies
What does KPI measure?
(Key Performance Indicator) Quantifiable metrics that are used to evaluate progress towards a CSF goal
What does Benchmarking measure?
Quantifiable metrics a company uses to evaluate how well their doing in comparison to a baseline
What does ROI measure?
A specific financial KPI

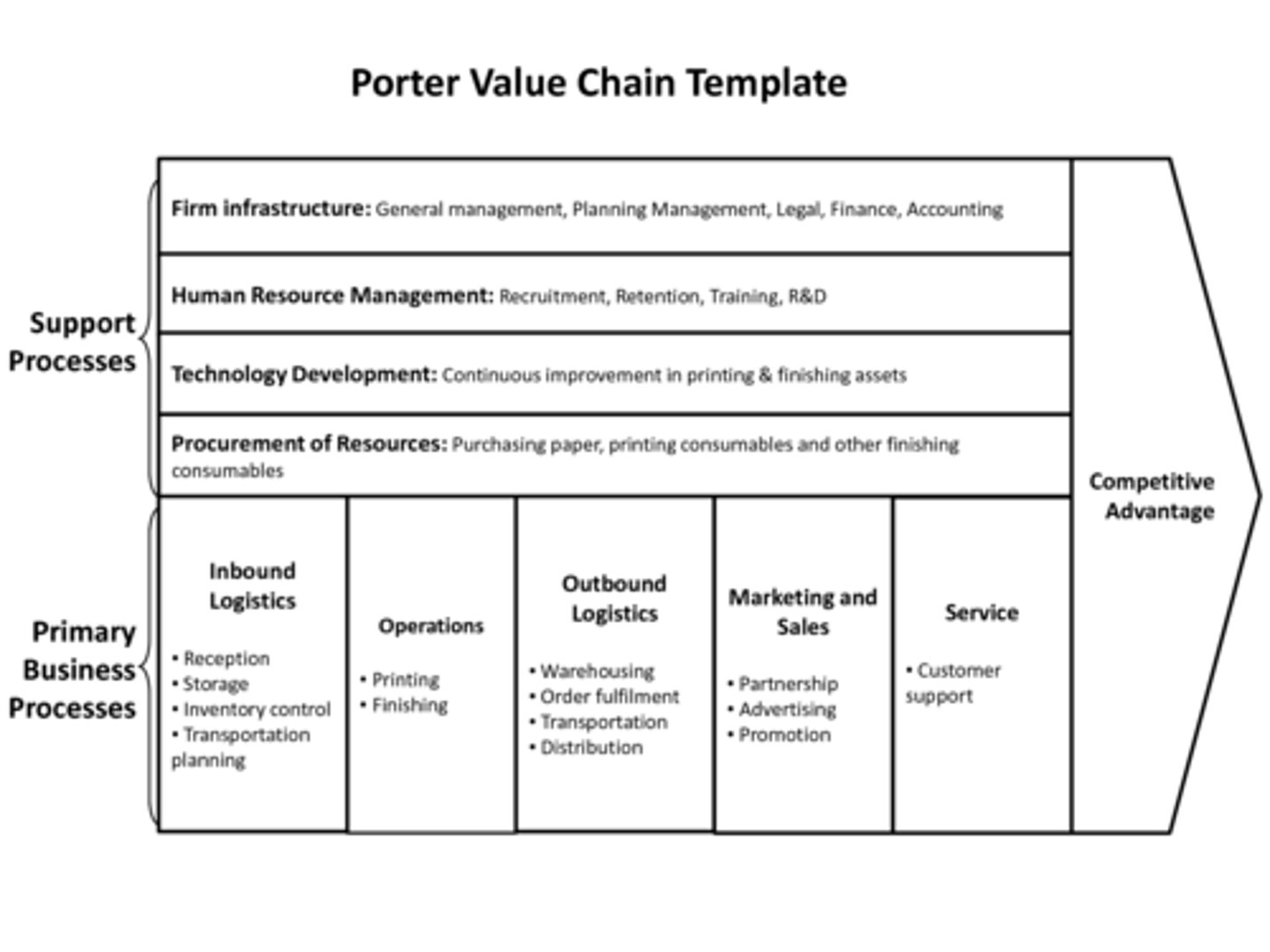
What is the value chain and why is it useful?
Looks at all of the inputs and what the enterprise does to add value to the output and how to produce cheaper helps grow
What does SWOT stand for and how is it used?
Strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, threats
Used to identify features of the overall business that need management attention
What is a customer facing process?
A process that results in a product or service that is received by an external customer
What is a business facing process?
Invisible to the external customer but essential to the effective management of the business
What are the Functional Business Areas?
Marketing – Promotes products/services and attracts customers.
Finance – Manages money, budgets, and financial planning.
Operations – Oversees production and ensures efficiency.
Human Resources (HR) – Handles hiring, training, and employee management.
IT (Information Technology) – Manages technology, data, and security.
Sales – Sells products/services and builds customer relationships.
Customer Service – Supports customers before and after purchases.
What is structured data?
Facts, questionnaire/survey, data points
Easier for businesses to process because it requires less filtering
What is unstructured data?
Emails, voice messages, texts, video/photo, "stuff"
Harder for businesses to process due to ambiguity
What do people mean by "Big Data"?
The name given to the incredibly huge collection of data captured from the world
"the internet of things"
What are th5 "V"'s?
Velocity - the speed at which data is gathered and stored
Variety - the kinds of new data
Volume - the quantity of data being gathered and stored
Veracity - the quality of the data
Value - what you can do with the data
Why should businesses use database management systems to store data instead of 1 big Excel sheet? List 3 reasons
Database systems are DESIGNED to store data and make it accessible, a big spreadsheet can lead to redundancies
1. Data is centrally accessible
2. Data quality and access is managed by professionals
3. Everyone can access the data they need
What are the qualities of high quality data?
Accurate
Complete
Consistent
Timely
Accessible
What do the qualities of poor data management mean? What do they mean?
Data Redundancy 📂📂 – You have multiple copies of the same worksheet in different folders.
Data Inconsistency ❌ – One notebook says the test is on Friday, another says it’s on Monday.
Data Isolation 🔒 – Your homework is locked in different lockers, making it hard to find.
Data Insecurity 🚪 – lots of access points which makes entry and corruption easier
What is the name of the activity or technique that clients and IT do together to create an understanding of the data requirements for the database?
Data modeling
What is the difference between a database and a database management system?
Database: refers to a set of files of stored data; static
Database management system: includes the database AND the applications that let people use the database
What are the parts of a database management system?
Media - wired and wireless connections among devices
Procedures - policies developed by the people who use data that is embedded in software, human policies and practice
Networks - connect databases with applications and devices
Why are these advantages of having a database management system: data are located centrally, data quality is controlled, data is accessible, data are easier to maintain
Centrally: 1 point of access
Quality Controlled: reliable information
Accessible: easy to access
Maintenance: no convolutions and easier to manage
In a relational data base, what do these terms mean: Data value, field, record, file/table, database, SQL
Data value: an actual piece of information
Field: the smallest meaningful type of data
File/Table: collection of related records
Rocord: A row in a table containing related data
Database: Collection of files/tables
SQL: the standard language for accessing and manipulating databases
What does it mean to populate a database?
Adding data to a database with values
What is a primary key in a relational database? How is it used?
A key identifier used to access a specific piece of data.
Specifies fields you want to report on
Ex: "Alex Biebel, 888-888-8888"
What is a foreign key? How is it used?
A primary key of 1 table that appears as a field in another table
Connects 2 or more tables
What does a basic, correctly formed SQL query look like?
Select
From
Where
Order by
How do primary and foreign keys work together to link data from different tables?
links columns and rows to reference other tables in order to extract informaiton
What is a structured decision?
A decision that is routine and repetitive
Ex: A --> B --> C
What is a semi structured decision?
A decision for which some parts are known and unknown
Ex: What price should we give our new product?
What is an unstructured decision?
A decision that is novel and lacks an agreed upon, well understood procedure
- we don't know what we don't know
What is a decision?
a choice made from available alternatives
What is a problem?
a matter regarded as unwelcome or harmful and needing to be dealt with
outcome: a process that leads to a different situation
- urgent
What is an opportunity?
a set of circumstances that makes it possible to do something different
outcome: a realization of a possible action
- not very urgent
What is a paradox?
A self-contradictory statement that when explained MAY PROVE to be true
Outcome: a change in how you see reality which leads to a different or opposite action
Ex: "If you use fewer words, you sound more intelligent"