bio test- RNA and protein synthesis
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
transcription- what is it, what step and where?
STEP ONE
when DNA turns into RNA
NUCLEUS
translation- what is it, what step and where?
STEP TWO
when RNA turns into PROTEINS(amino acids, ribosomes)
CYTOPLASM
RNA- DEFINE the 3 differences from DNA
1. SINGLE stranded not double
2. sugar is RIBOSE not deoxyRIBOSE
3. base is URACIL
in complimentary base pairing in RNA why is T now U?
because the base of RNA is URACIL not Thymine
amino acids- how many? what controls them?
TWENTY different amino acids
DNA chooses order/sequence(PRIMARY STRUCTURE)
what specifies amino acids and how many?
CODONS
SIXTY ONE
what is a codon and what do they code for?
THREE-letter code for AMINO ACIDS
each code stands for a different amino acid
how many start codons are there and what are they?
ONE
A-U-G
how many stop codons are there?
THREE (UGA, UAA, UAG).
what is code and why?
REDUNDANT
SIXTY ONE codons for TWENTY amino acids
amino acids REPEAT
what is the wobble effect and what base is it?
the THIRD base
less important than the other bases and does not code for specific amino acids
what is mRNA, and where does it go?
leaves the NUCLEUS to FIND RIBOSOMES
a COPY of the SEQUENCE of DNA
leaves through NUCLEAR PORES
what is rRNA, what is it made of, and where is it?
SMALLER rRNA subunit plus LARGER helper PROTEIN subunit
rRNA functions to be a dock point for mRNA from the NUCLEUS
RIBOSOMAL, the two parts of a ribosome
what is tRNA, what does it do, and what does it form?
picks up AMINO ACIDS (consumed in our diet)
takes the AMINO ACIDS to the RIBOSOME so they can link to FORM A POLYPEPTIDE
CYTOPLASM
what is RNA Polymerase?
Uracil goes with Adenine-complimentary base pairing
the gene is UNZIPPED so the mRNA can be constructed by complimentary BASES
what is a ribosome?
PROTEIN factories
assembles POLYPEPTIDES(chains of AM.AC)
consists of TWO parts-
PROTEINS and rRNA
what is the anticodon?
what is a mutation, where is it fixed?
any CHANGE in DNA
usually fixed in proofreading
what are the types of a mutation?
silent/ neutral/ harmful/ or beneficial
what are mutagens?
causes for mutations- unless not spontaneous
chemicals/ UV light, X-rays, GAMMA rays
what is the point mutation?
a mutation where a SINGLE BASE is inserted
what is substitution and what does it coincide with?
POINT MUTATION
when the BASE is CHANGED

what is insertion and what does it coincide with?
POINT MUTATION and FRAMESHIFT MUTATION
when the BASE is ADDED
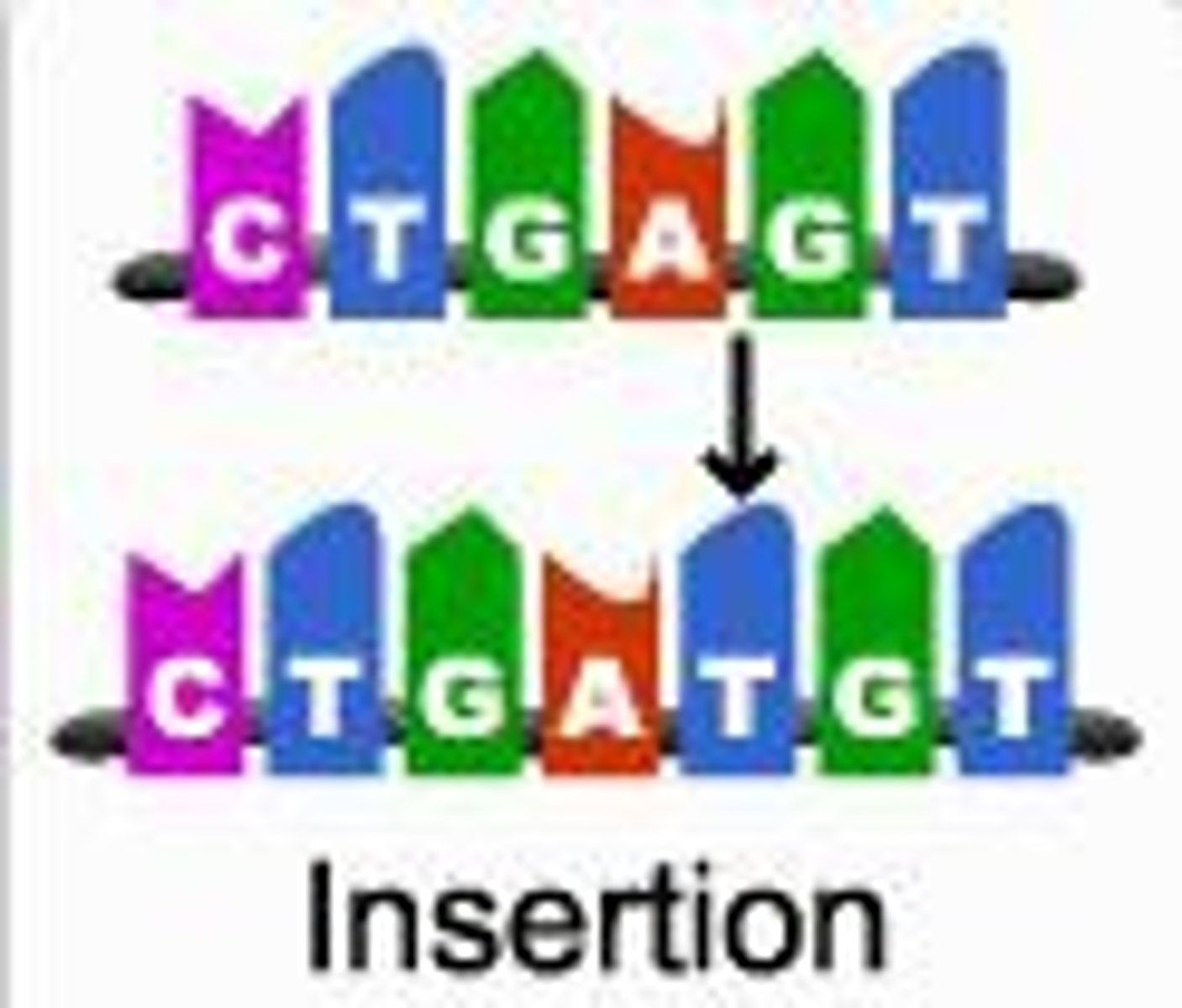
what is deletion and what does it coincide with?
POINT MUTATION and FRAMESHIFT MUTATION
when the BASE is REMOVED

what is FRAMESHIFT mutation and how bad is it?
WORST, MOST harmful, large scale=MANY A.A
LEADS to LARGE SCALE changes in the POLYPEPTIDE chains
RESULTS in a non-functional protein