GENBIO: Classification of Tissues
1/113
Earn XP
Description and Tags
pptx
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
114 Terms
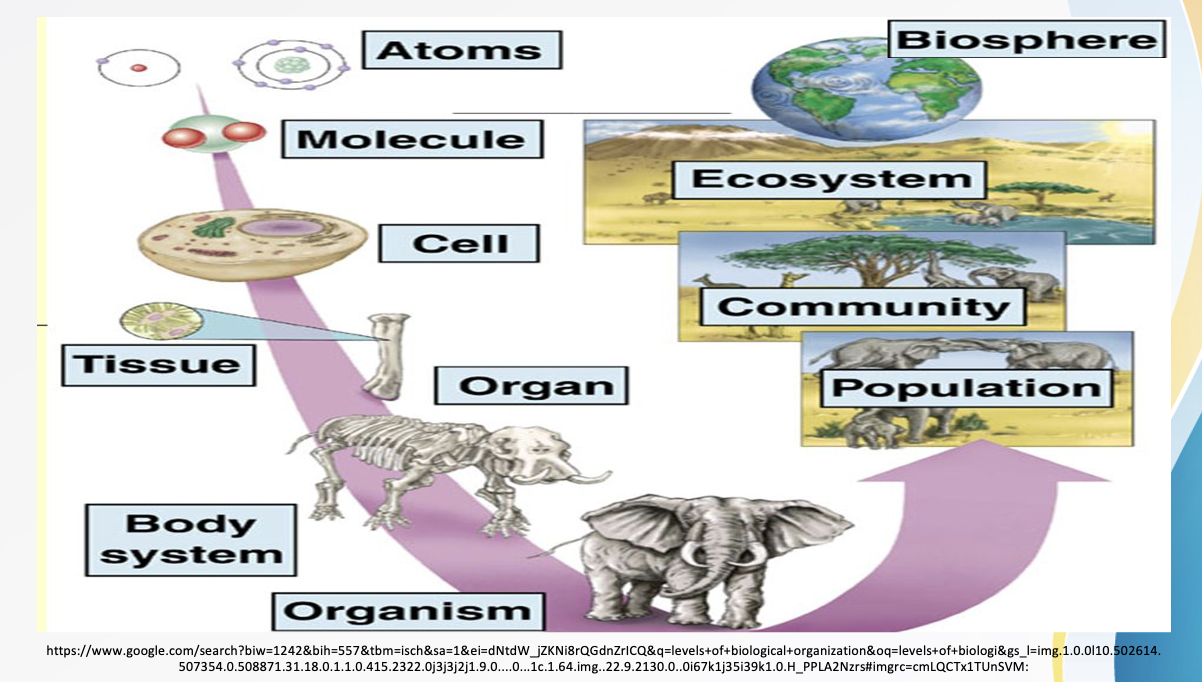
Cell → Tissue → Organ → Organ System → Organism → Population → Community → Ecosystem → Biosphere
Levels of Biological Organization
Structure
determines the function
the body plan, or the way the parts are arranged and made of
Function
the job for that part of the organism
Tissue
groups of cells with a common structure and function
different types of ___ have different structures that are especially suited to their functions
Animal Tissues
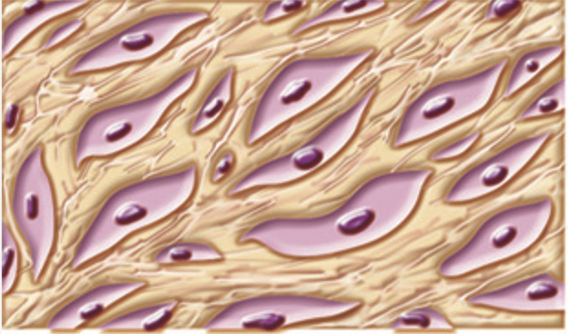
Connective tissue
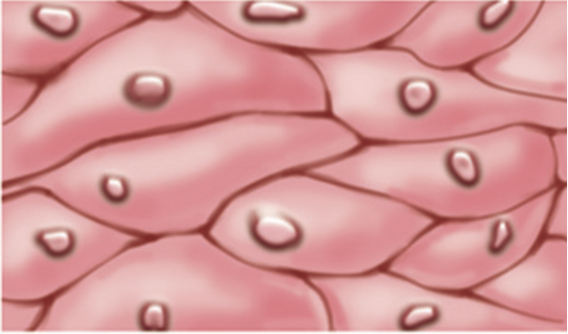
Epithelial tissue
Muscle tissue
Nervous tissue
Connective tissue
Epithelial tissue
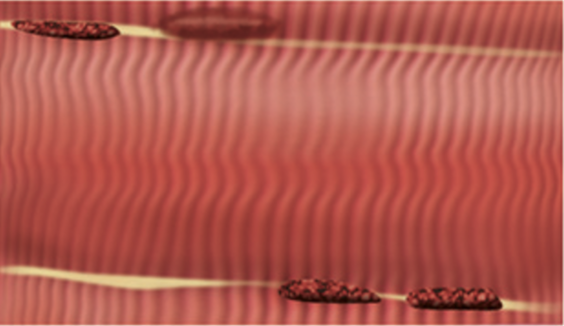
Muscle Tissue
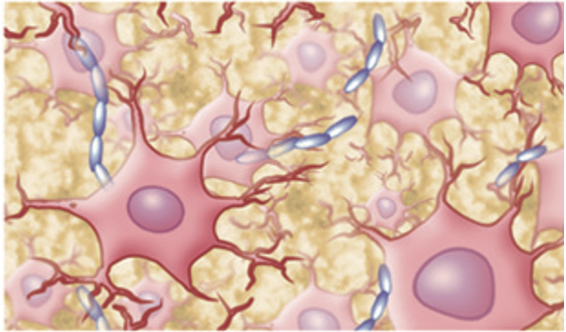
Nervous tissue
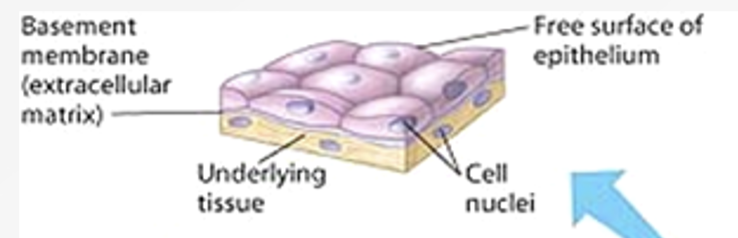
Epithelium
a sheet of cells that covers a body surface or lines a body cavity
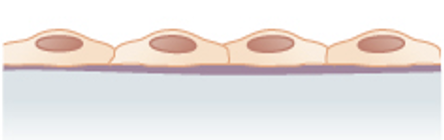
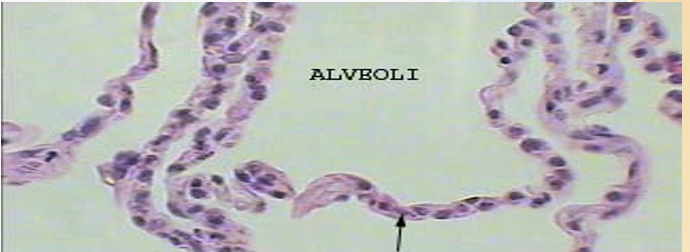
Simple squamous epithelium
(lining the air sacs of the lung)
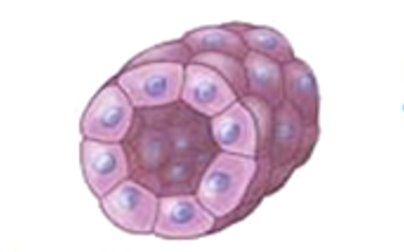
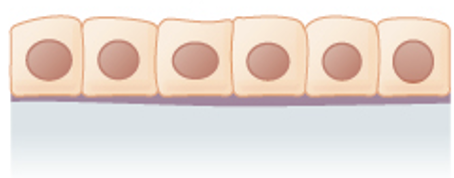
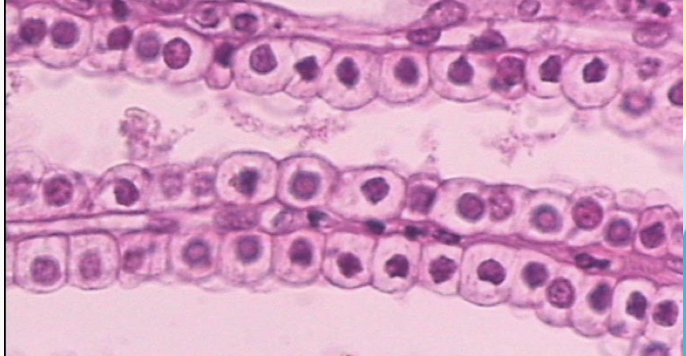
Simple Cuboidal epithelium
(forming a tube in the kidney)
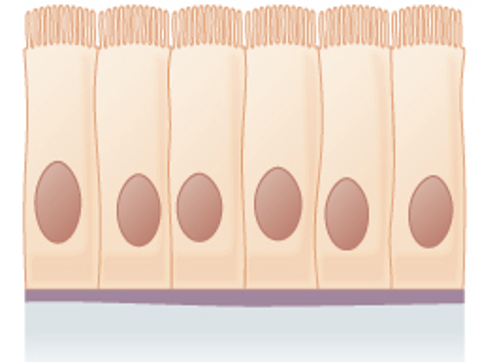
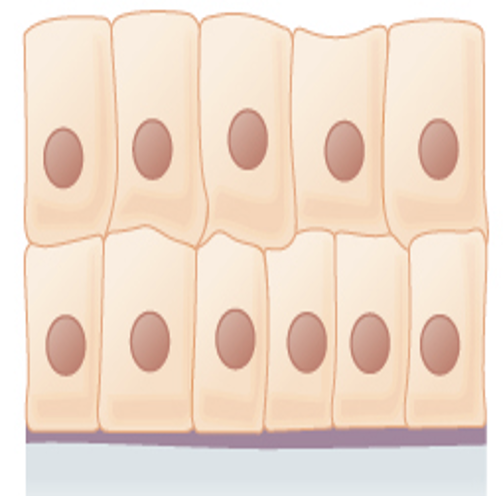
Simple Columnar Epithelium
(Lining the intestine)
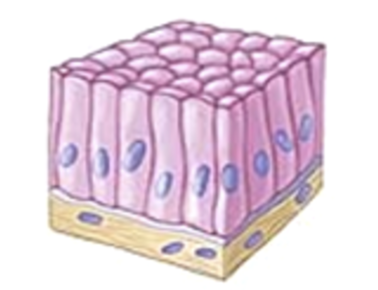
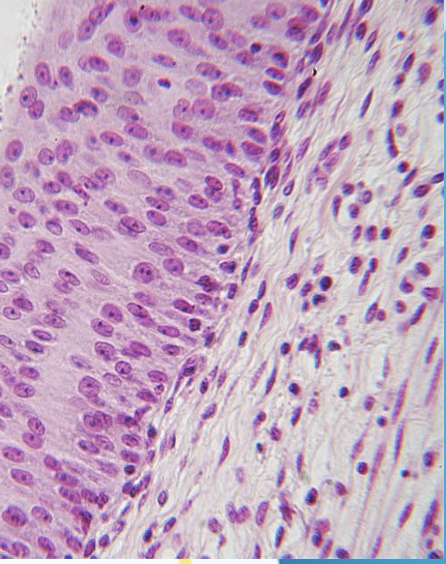
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
(Lining the esophagus)
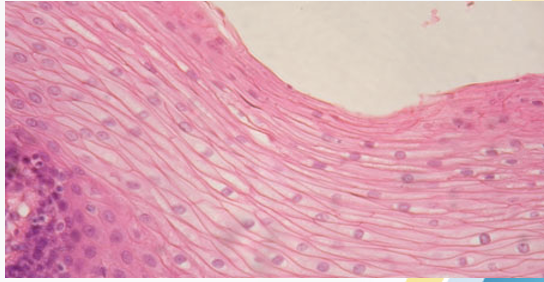
Stratified squamous epithelium
(human skin)
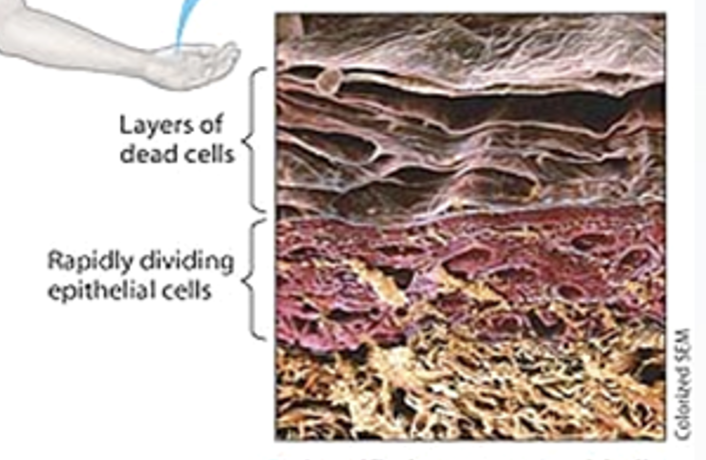
Functions of a Epithelium Tissue
Protection — skin
Absorption — stomach and intestinal lining (gut)
Filtration — Kidney
Secretion — forms glands
(exocrine glands, such as: salivary glands, sweat glands, and gastric glands)
Characteristics of Epithelium tissue
Polarity — have an apical surface and attached basal surface
Specialized contacts — fit closely together and form continuous sheets
Supported by connective tissue — basal surface is attached to underlying connective tissue
Avascular and innervated — has no blood vessels and supplied by nerve fibers
Regeneration — can regenerate itself
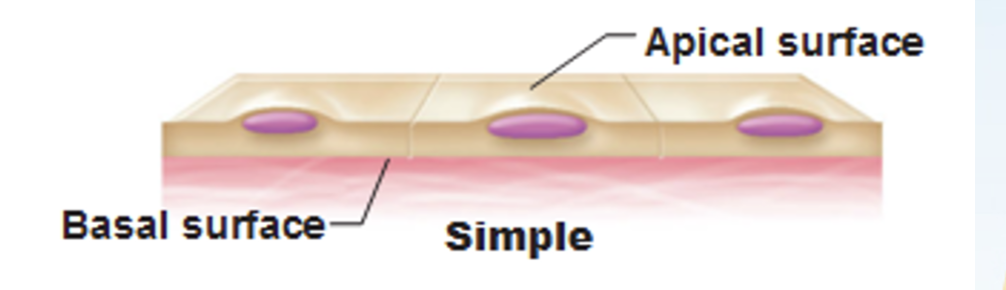
Apical Surface
the "top" or "free" surface of an epithelial cell that faces the external environment, a body cavity, or the lumen of an organ or duct.
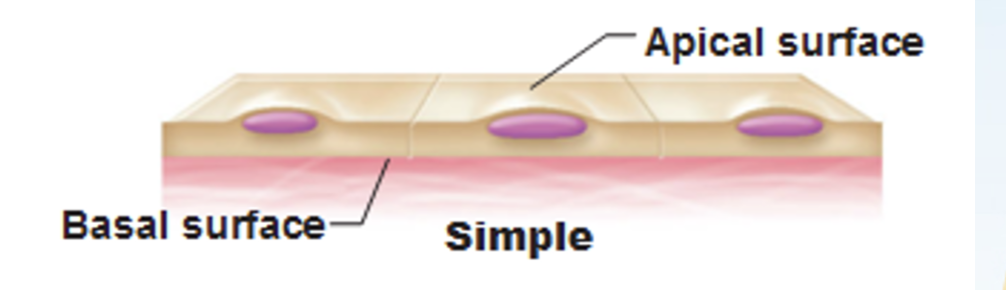
Basal Surface
the bottom-facing surface of a cell or tissue, specifically the edge that rests on a basement membrane and anchors it to underlying connective tissue.
Number of Cell layers
Simple
Stratified
Pseudostratified
Transitional
Simple
consist of single cell layer that attached to the basement membrane
Stratified
composed of 2 or more layers stacked atop each other
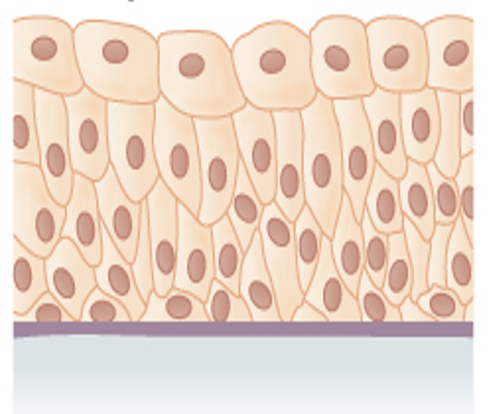
Pseudostratified
a single layer of cells that appears to be multiple layers due to variance in heaight and location of the nuclei in the cells
Transitional
Cells are rounded and can slide across one another to allow stratching
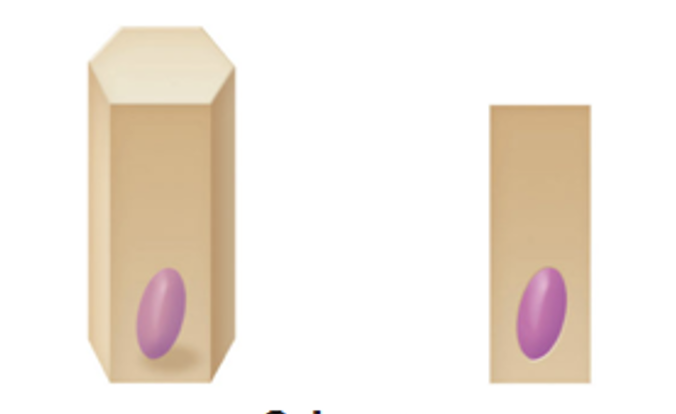
Shape of Cells
Squamous
Cuboidal
Columnar
Squamous
flat, thin, scale-like cells

Cuboidal
Cells that have a basic cube shape. Typically the cell’s height and width are about equal.

Columnar
tall, rectangular, or column shaped cells. Typically taller than they are wide
Simple squamous epithelium
location: air sacs of lungs and the lining of the heart, blood vessels, and lymphatic vessels
Simple cuboidal epithelium
Location: in ducts and secretory portions of small glands and in kidney tubules
Simple columnar epithelium
Location:
Ciliated tissues are in bronchi, uterine tubes, and uterus,
smooth (nonciliated tissues), are in the digestive tract, bladder
Simple squamous epithelium
Simple cuboidal epithelium
Simple columnar epithelium
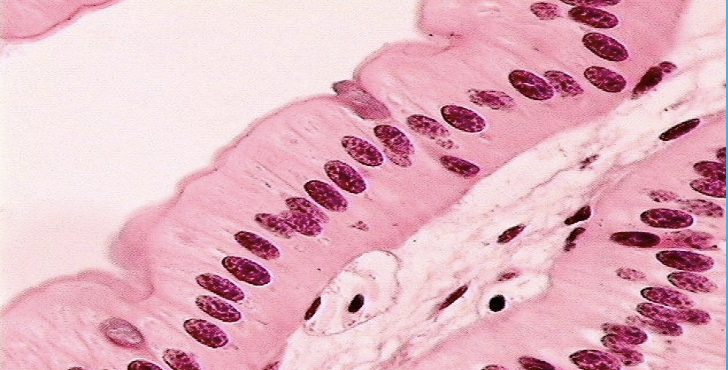
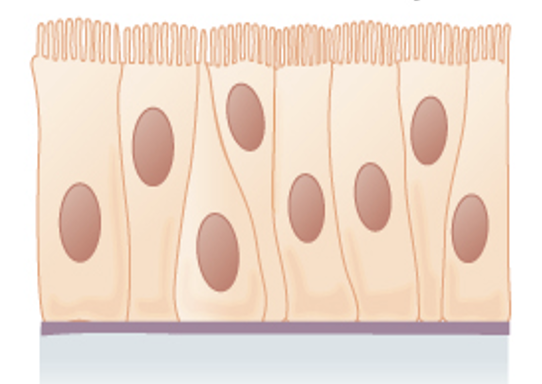
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
Ciliated tissue lines the trachea and much of the upper respiratory tract
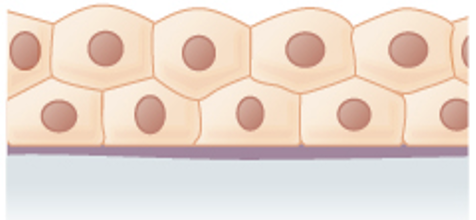
Stratified squamous epithelium
Line the esophagus, mouth, and vagina
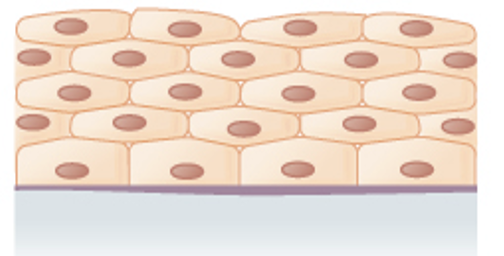
Stratified cuboidal epithelium
Sweat gland, salivary glands, and the mammary glands
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
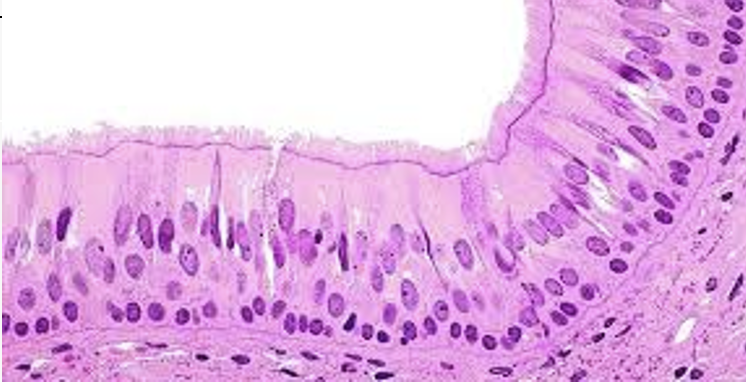
Stratified squamous epithelium
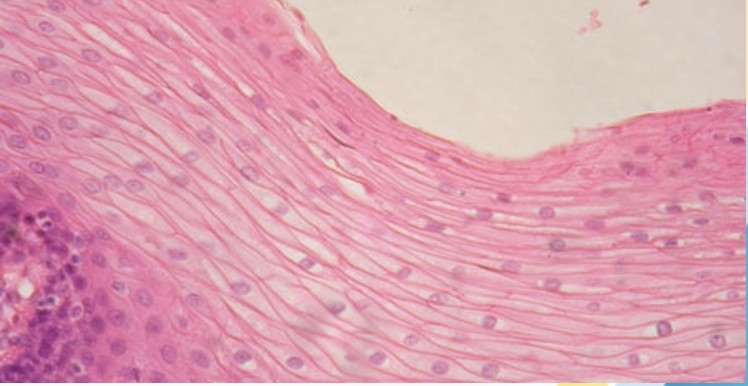
Stratified cuboidal epithelium
Stratified Columnar epithelium
The male urethra and the ducts of some glands
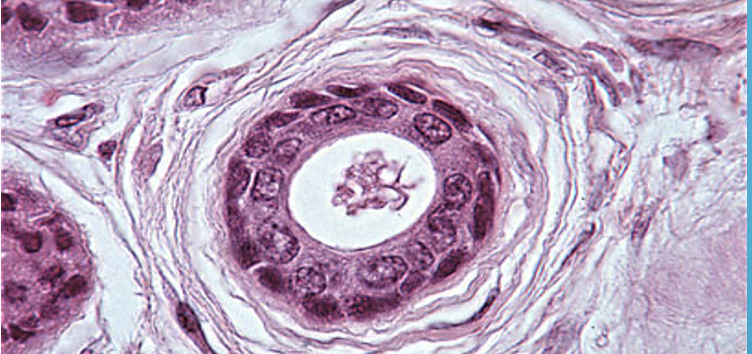
Transitional epithelium
Line the bladder, urethra, and the ureters
Stratified Columnar epithelium
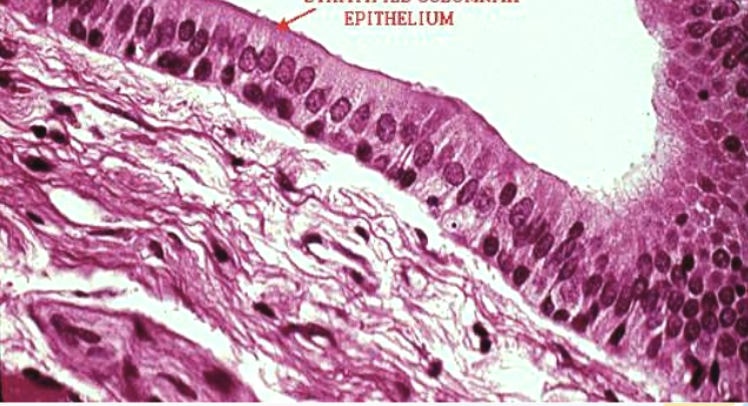
Transitional epithelium
Connective Tissue
Supporting tissue that surrounds other tissues and organs
Functions: Protect, support, and bind together parts of the body. Also, it store nutrients and runs through organ capsules and in deep layers of skin giving strength
Characteristics: They occur throughout the body. Tend to be very vascular (have rich blood supply) but not all.
Types of Connective Tissues
Collagenous connective tissue
Reticular connective tissue
Elastic connective tissue
Collagenous Connective Tissue
predominantly made up of type I collagen
Classification of Collagenous Connective Tissue
A. Loose Connective Tissue
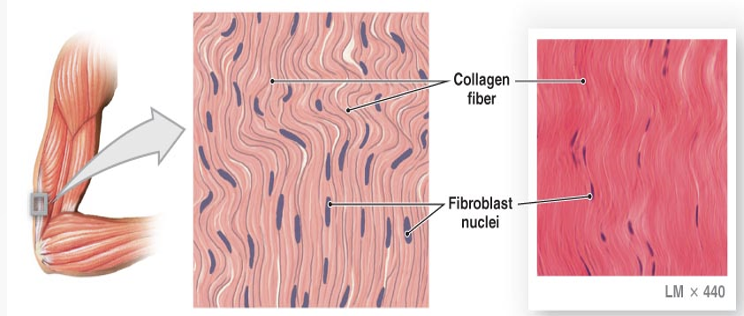
B. Dense Regular Connective
C. Dense Irregular Connective
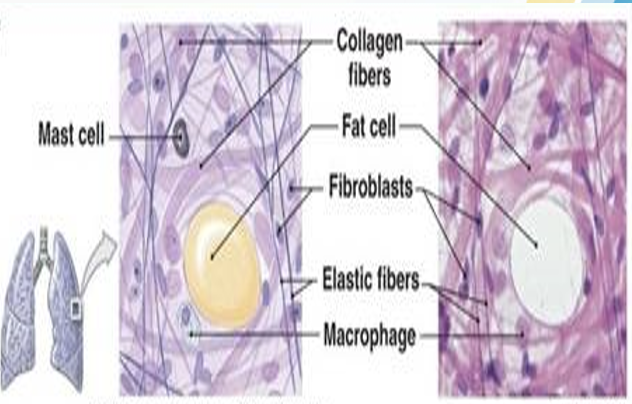
Loose Connective Tissue
Areolar Connective Tissue — cushion around organs, loose arrangement of cells and fibers.
Dense Regular Connective Tissue
tendons and ligaments, regularly arranged bundles packed with fibers running same way for strength in one direction
Dense Irregular Connective tissue
skin, organ capsules, irregular arranged bundles packed with fibers for strength in all
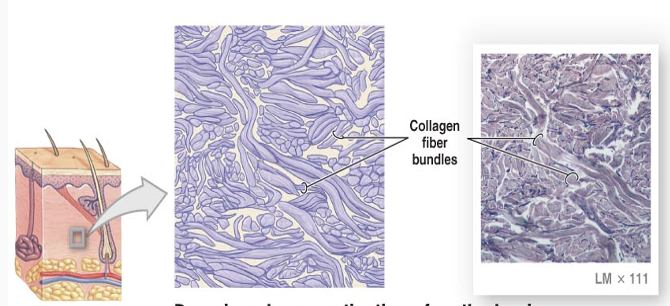
Reticular Connective Tissue
formed type III collagen (protein found in bondes and cartilage)
internal supporting framework of some organs, delicate network of fibers, and cells directions
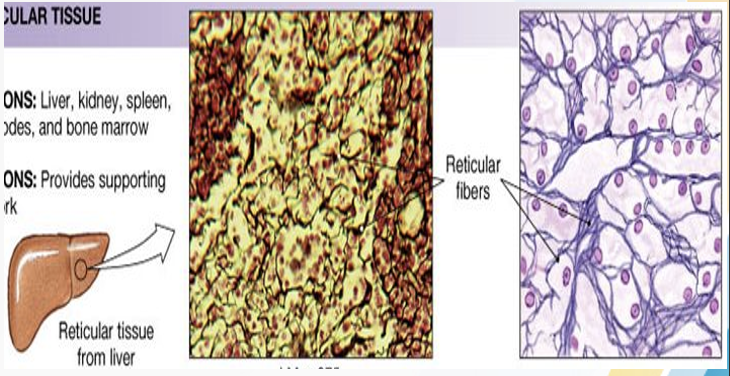
Classification of Reticular Connective Tissue
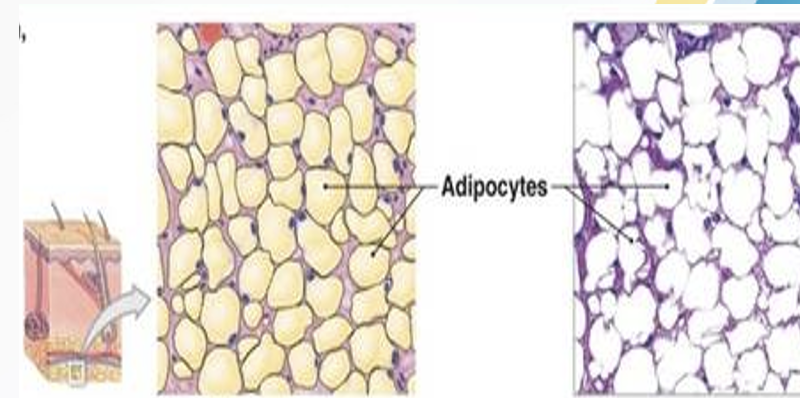
A. Adipose Tissue
adipose Tissue
storehouse for nutrients, packed with cells and blood vessels
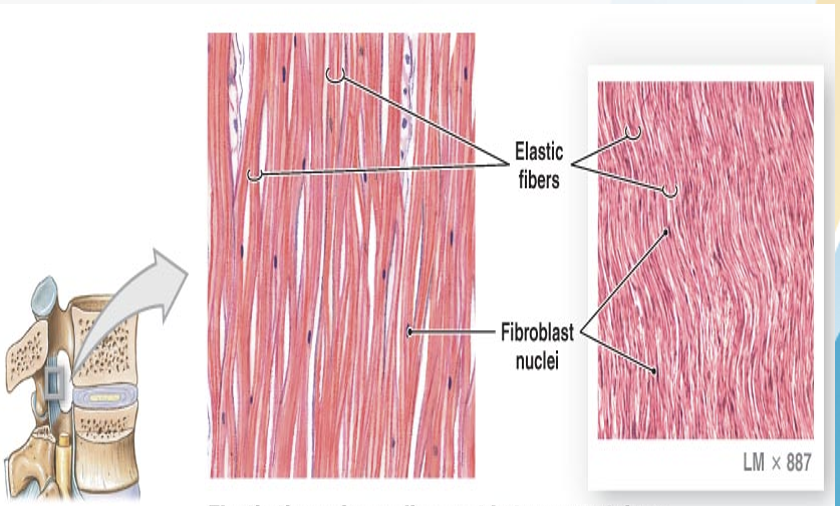
Elastic Connective Tissue
formed by type II collagen, component of joint cartilage
often found in bronchi, trachea, blood vessels, and hollow organs
Specialized Connective Tissue
Cartilage:
a) Hyaline
b.) Elastic
c.) Fibrocartilage
Bone (osseous tissue)
Blood
Cartilage
provides strength with flexibility while resisting wear, i.e. epiglottic, external ear, larynx
cushions and shock absorbs where bones meet, i.e. intervertebral discs, joint capsules
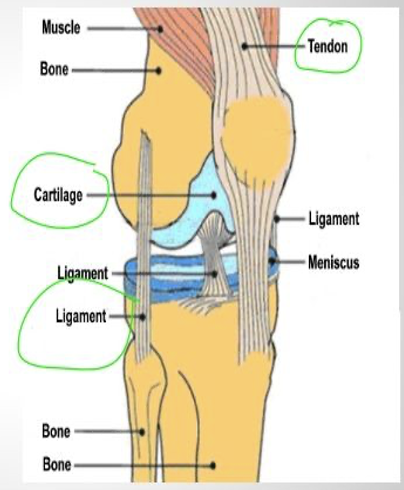
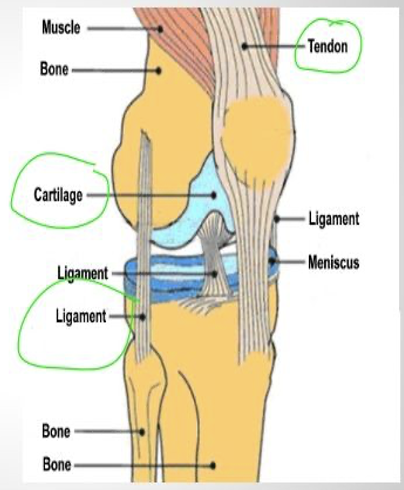
Cartilage
cushion between joints, not as rigid as bone, not as flexible as muscle
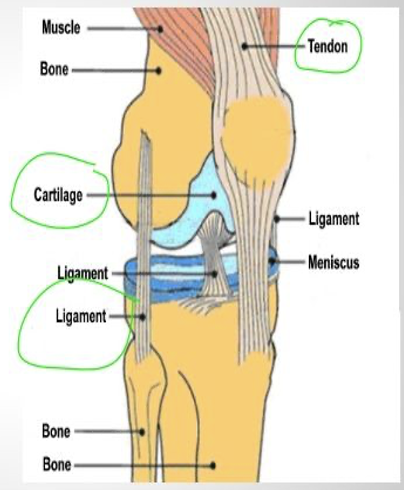
Ligaments
connect bones to bones
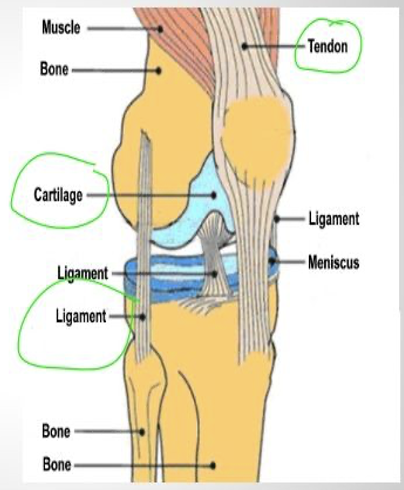
Tendons
Connects muscle to bone
Hyaline Cartilage
exists on the ventral ends of ribs, in the larynx, trachea, and bronchi, and on the articulating surface of bones. It gives the structures a definite but pliable form.
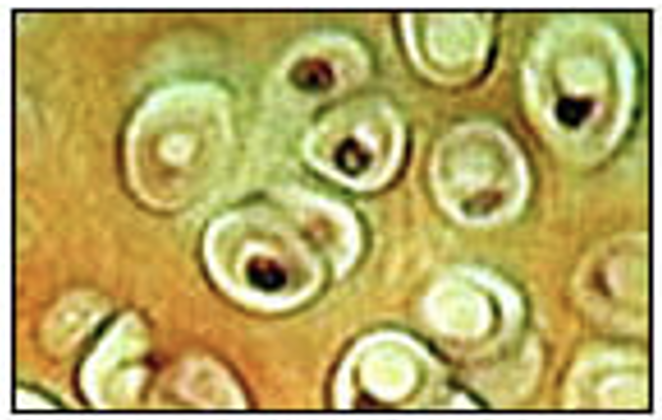
Elastic Cartilage
great flexibility so that it is able to withstand repeated bending. The chondrocytes lie between the ribers. It is found in the epiglottis (part of larynx), the pinnae (external ear flaps of many mammals)
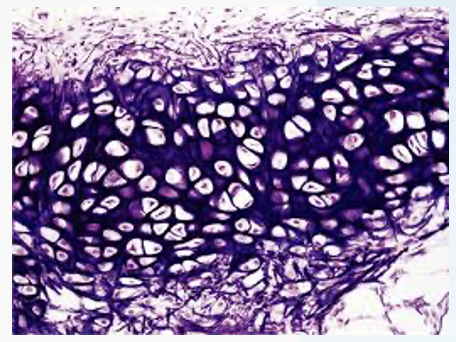
chondrocytes
specialized cells found only in cartilage, responsible for producing and maintaining the cartilage's extracellular matrix (ECM), which gives it its strength and flexibility
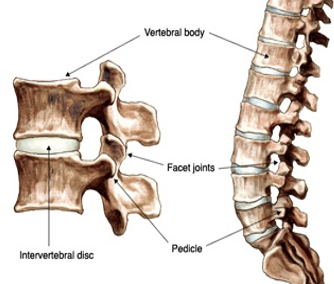
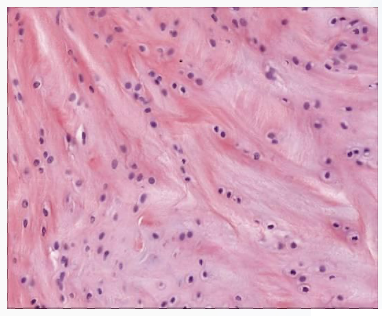
Fibrocartilage
tough, very strong tissue found predominantly in the intervertebral discs and at the insertions of ligaments and tendons; it is similar to other fibrous tissues but contains cartilage ground substance and chondrocytes
Bone
“osseous tissue“ — provides framework and strength for body; allows movements; stores calcium; contains blood forming cells
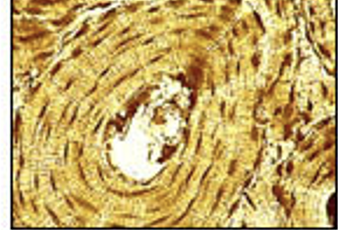
Bone marrow
acts as a factory for producing red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets from stem cells.
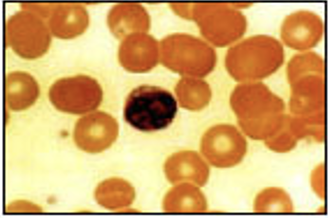
Blood
transports oxygen, carbon dioxide, and nutrients around the body’ immune response
Muscle Tissue
responsible for body movement
moves blood, food, waste through body’s organs
responsible for mechanical digestion (mouth)
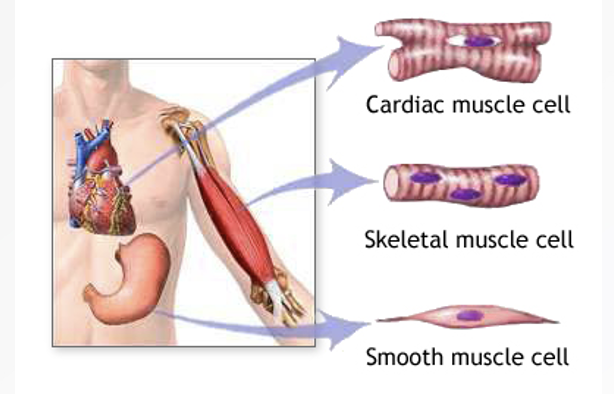
Types of Muscle
Smooth
Skeletal
Cardiac
Smooth Muscle
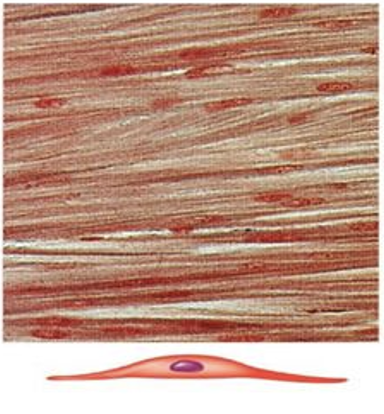
organ walls and blood vessel walls, involuntary, spindle-shaped cells for pushing things through organs
Skeletal Muscle
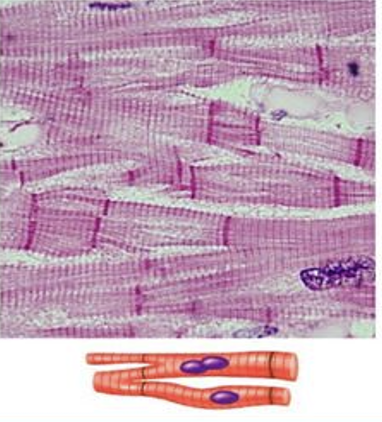
large body muscles, voluntary, striated muscle packed in bundles and attached to bones for movement
Cardiac Muscle
heartwall, involuntary, striated muscle with intercalated discs connecting cells for synchronized contractions during heart beat
Skeletal muscle
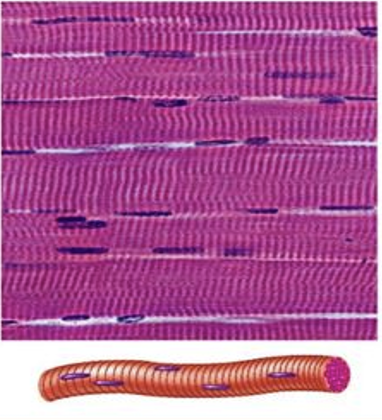
Cardiac Muscle
Smooth muscle
Nervous Tissue
conducts impulses to and from body organs via neurons
controls all activities of the body
3 Elements of Nervous Tissue
Brain
Spinal cord
Nerves
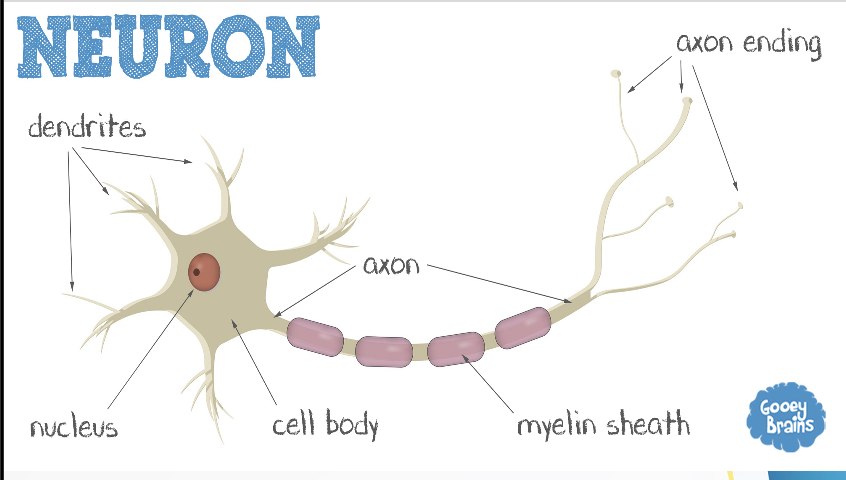
Neuron
electrically excitable cells un the nervous system that function to process and transmit information
Parts of the neuron
Cyton
Axon
Dendrites
Cyton
A star shaped body called ____ (cell body) which has nucleus and cytoplasm
Axon
A single long part called ____ that carries messages away from the Cyton
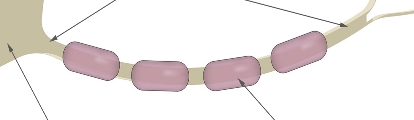
Dendrites
short, branched part called _____ that carries messages towards cyton
Types of Neurons
Sensory neurons
Motor neurons
Sensory neurons
carry information obtained from the interior of the body and the environment to the CNS (central nervous system)
Motor neurons
carry impulses away from the CNS to the effector organs
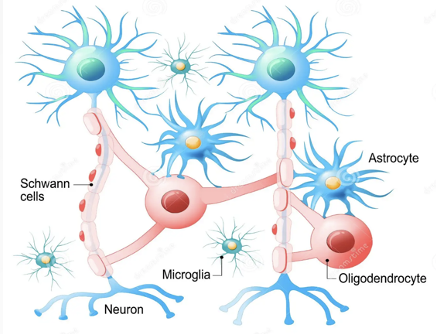
Nueroglia
support and protect neurons; found in the nervous system
VF fill at L6/S1
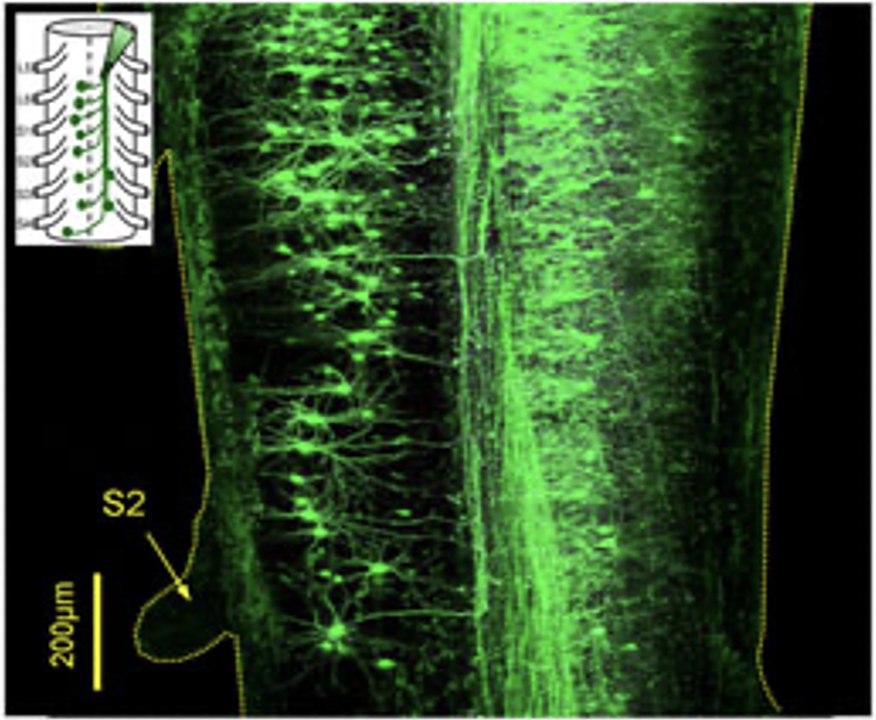
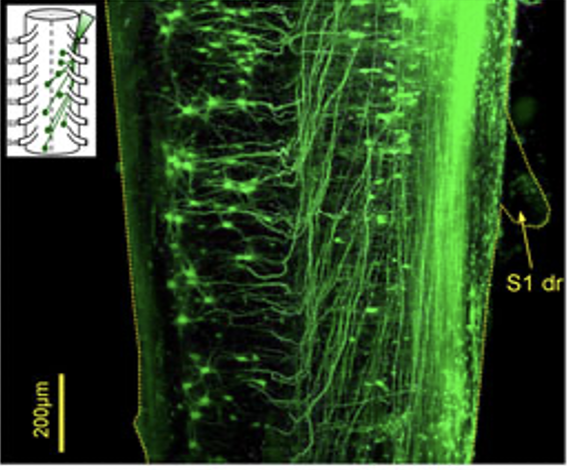
VLF fill at L6/S1
Plant tissues
Meristematic or embryonic tissue
Non-meristematic or permanent tissue
Meristematic or embryonic tissue
tissues comprise of cells which have the dividing capacity
immature and help plants to divide continuously
Types: Apical, lateral, and intercalary meristems (enlarge the cell and increase the length and width of the stem, roots, and leaves)
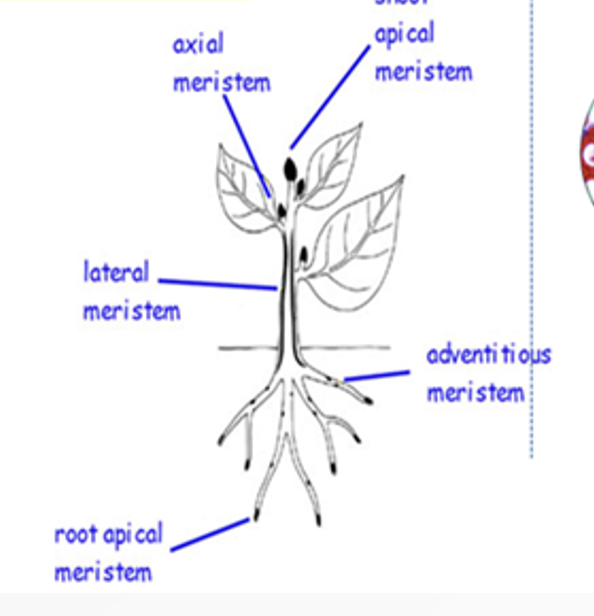
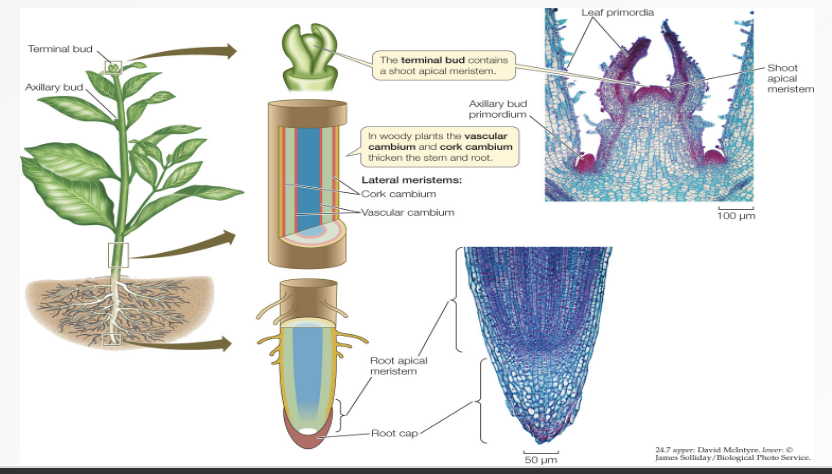
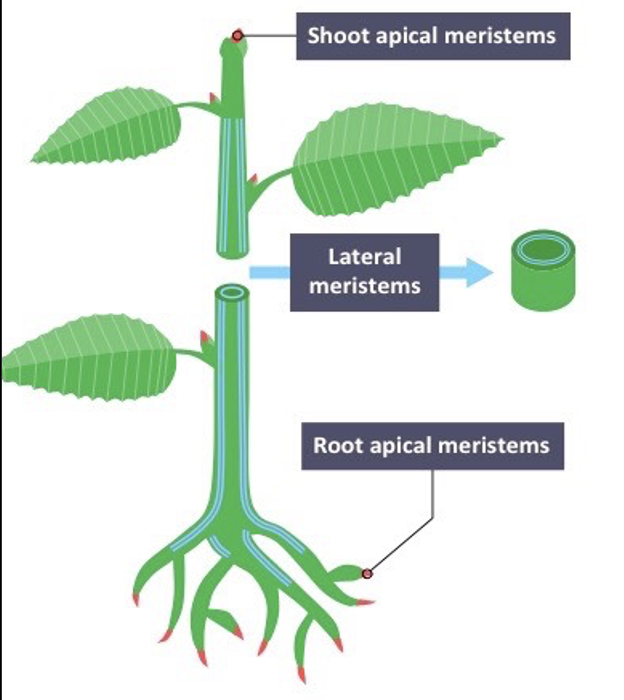
Apical Meristems
found at the tips of the shoots and roots which increase in length as the apical meristems produce new cells.
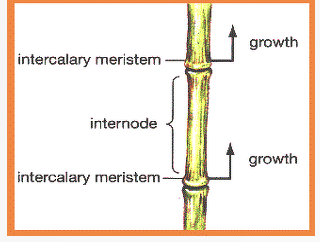
Intercalary meristems
found at the vicinity of nodes which occurs at intervals along stems. Just like the apical meristems, they also increase the length of stems.
responsible for growth of plant from leaf and nodes
Lateral Meristems
increase the girth or diameter of plants. They are found along the sides of some roots and stems.
Apical Meristems
Causes primary growth (lengthening of plant)
Occurs at tips of shoot and roots, Produces new leaves and flowers
Lateral Meristems
Causes secondary growth (widening of plant) occurs at the cambium, produces bark on trees
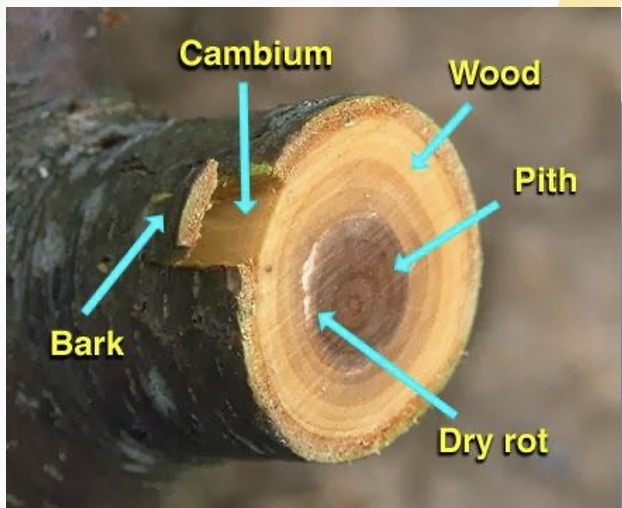

Non-meristematic or Permanent tissue
derivative of meristematic tissue
don’t have the dividing capability
aid in other functions like conductions of subsstances, storage of food etc.
Types: simple and complex permanent tissue
Simple permanent tissues
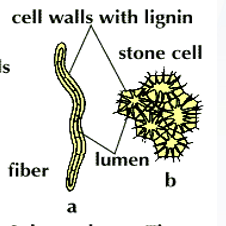
parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma
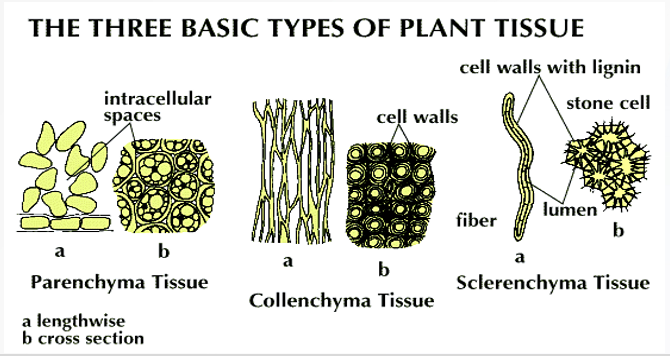
Parenchyma tissue
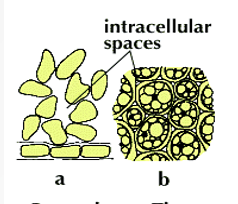
Collenchyma Tissue
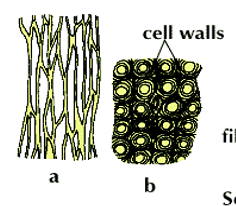
Sclerenchyma Tissue