BIOL 226 Lab 1: General Senses, Smell, Taste, Cranial Nerves
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering general senses, smell, taste, and the functions and pathways of various cranial nerves including Olfactory, Facial, Glossopharyngeal, Vagus, and Trigeminal nerves, as well as different types of sensory receptors and related conditions.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Olfactory Nerve (I)
Conducts sensory impulses to the brain for the sense of smell.
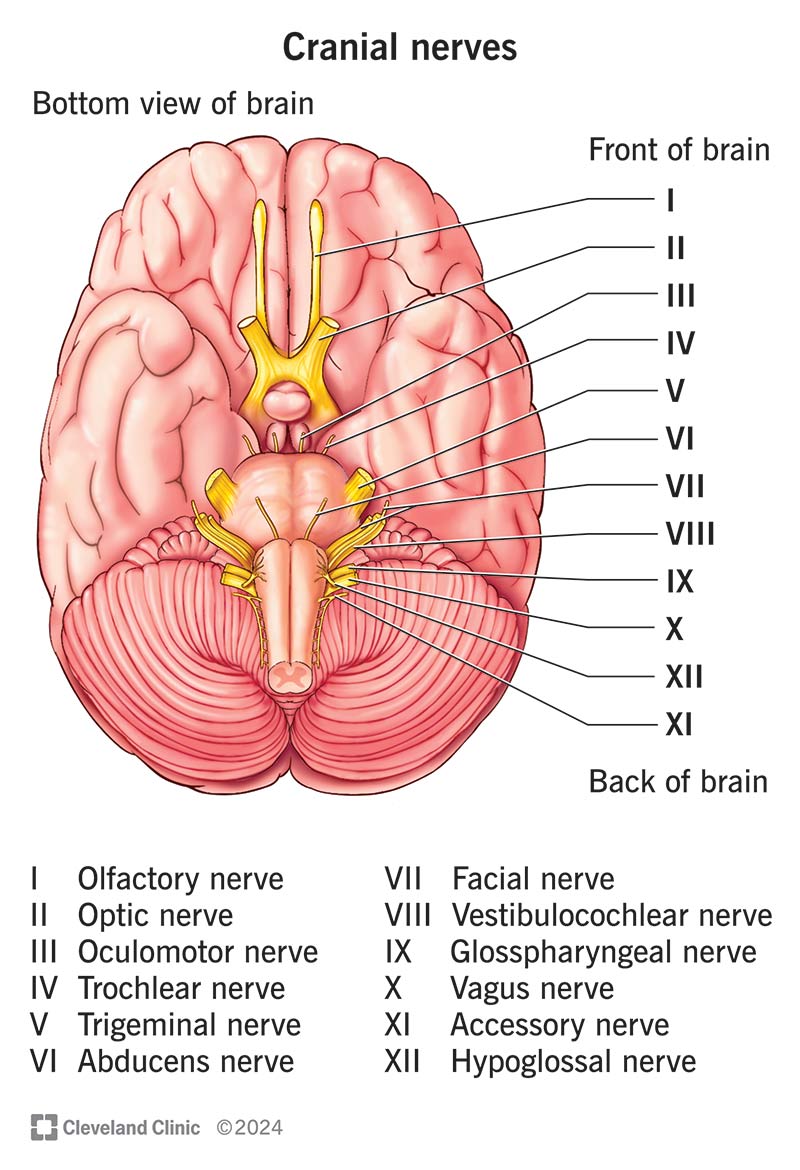
Facial Nerve (VII)
Conducts sensory impulses from the anterior 2/3 of the tongue and motor impulses to facial expression muscles.
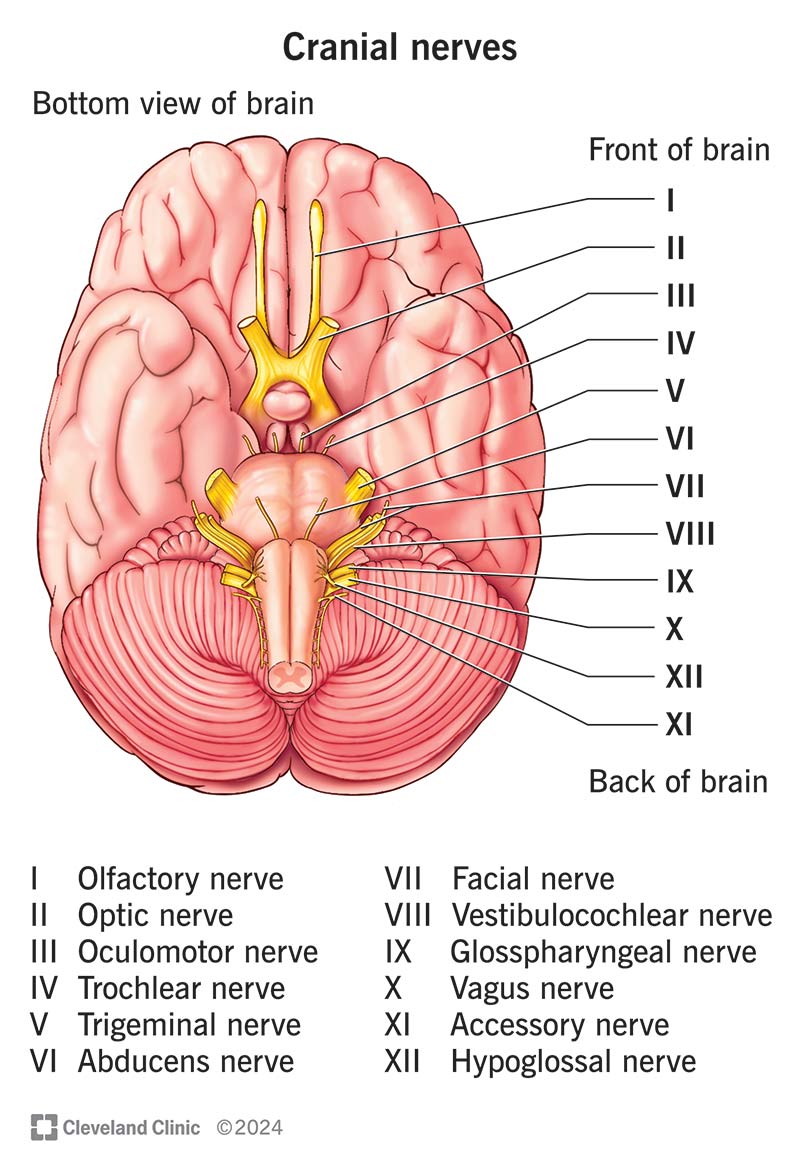
Glossopharyngeal Nerve (IX)
Conducts sensory impulses from the lining of the pharynx, tonsils, and posterior 1/3 of the tongue, and motor impulses to salivary glands and muscles for swallowing.
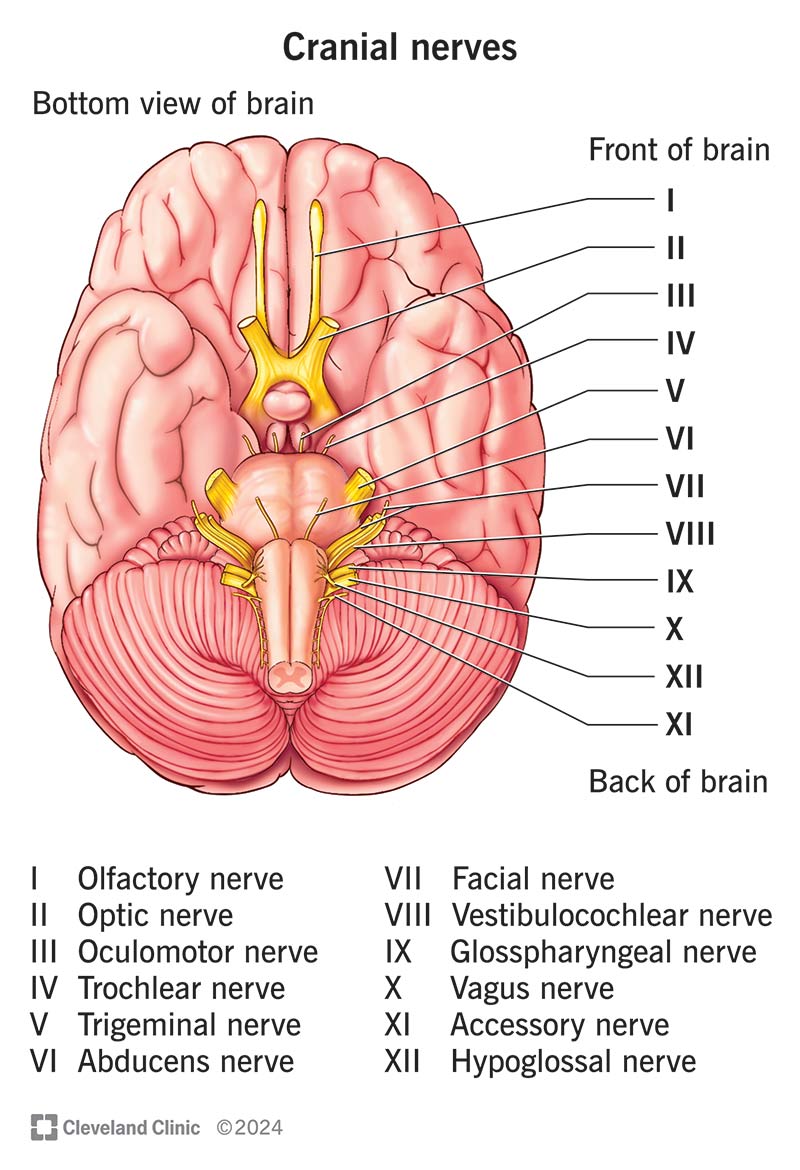
Vagus Nerve (X)
Conducts sensory impulses from the lining of the pharynx, larynx, esophagus, and viscera of thorax and abdomen, and motor impulses to muscles for speech and swallowing.
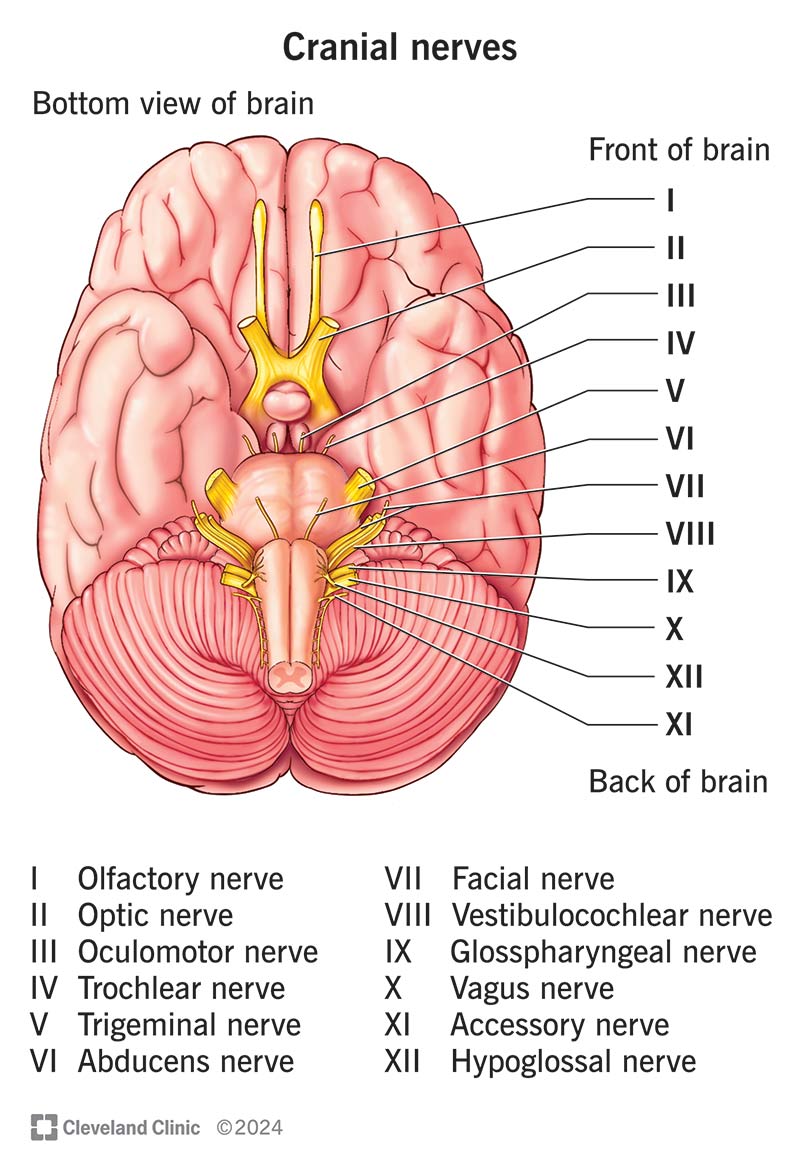
Trigeminal Nerve (V)
A cranial nerve with three branches (Ophthalmic, Maxillary, Mandibular) responsible for sensation in the face and motor function for mastication.
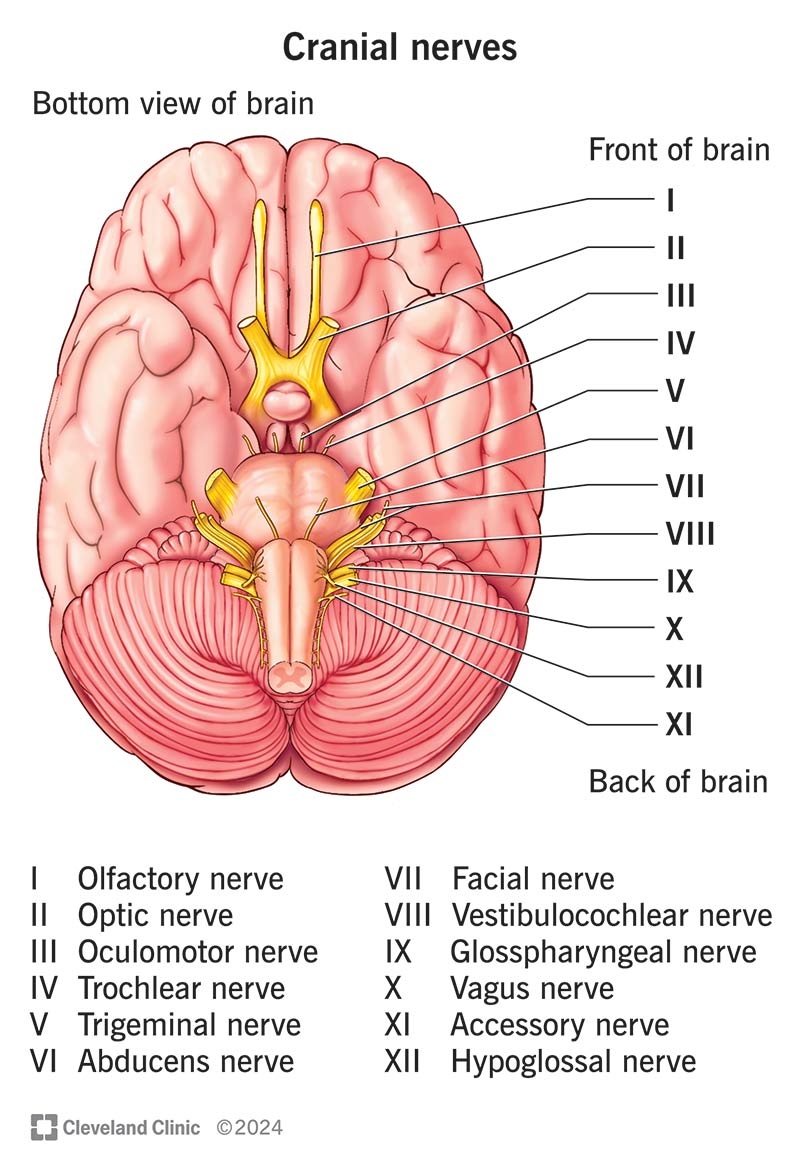
Ophthalmic Branch (Trigeminal V)
Conducts sensory impulses from the eye, tear gland, skin of anterior scalp, forehead, and upper eyelid.
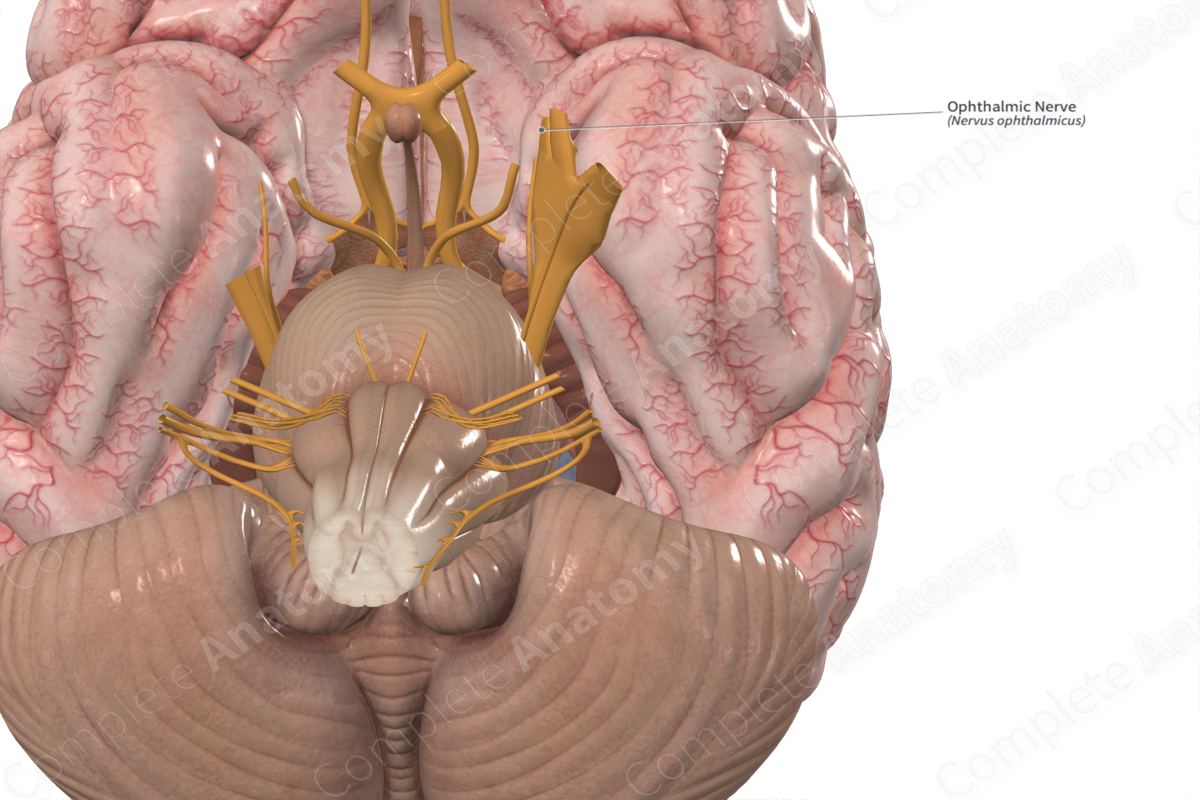
Maxillary Branch (Trigeminal V)
Conducts sensory impulses from the upper teeth, gum and lip, mucous lining of the palate, and facial skin.
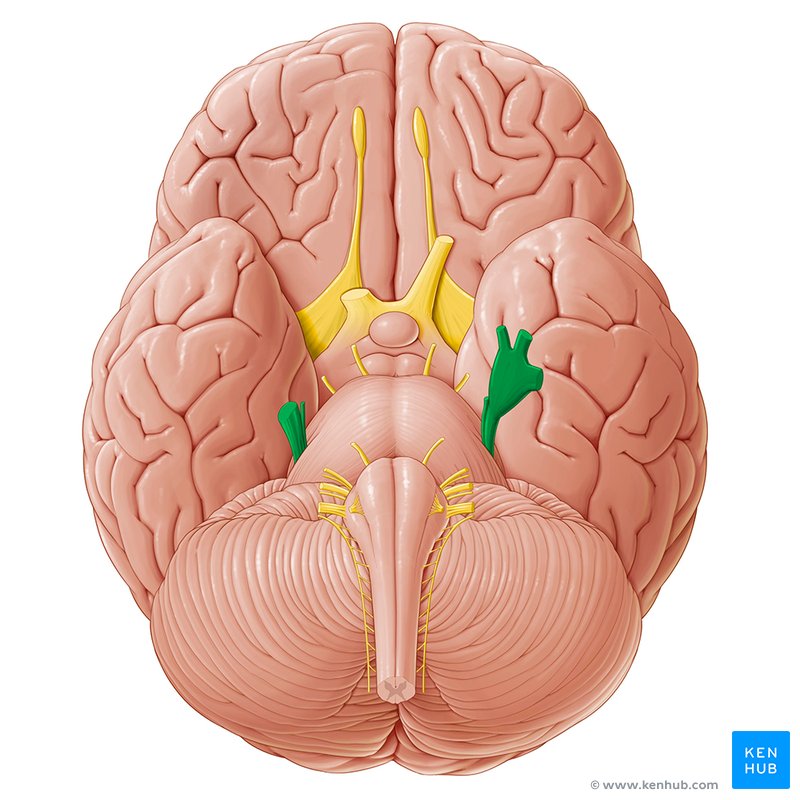
Mandibular Branch (Trigeminal V)
Conducts sensory impulses from the scalp behind the ears, skin of jaw, lower teeth, gum, and lip, and conducts motor impulses to muscles of mastication.
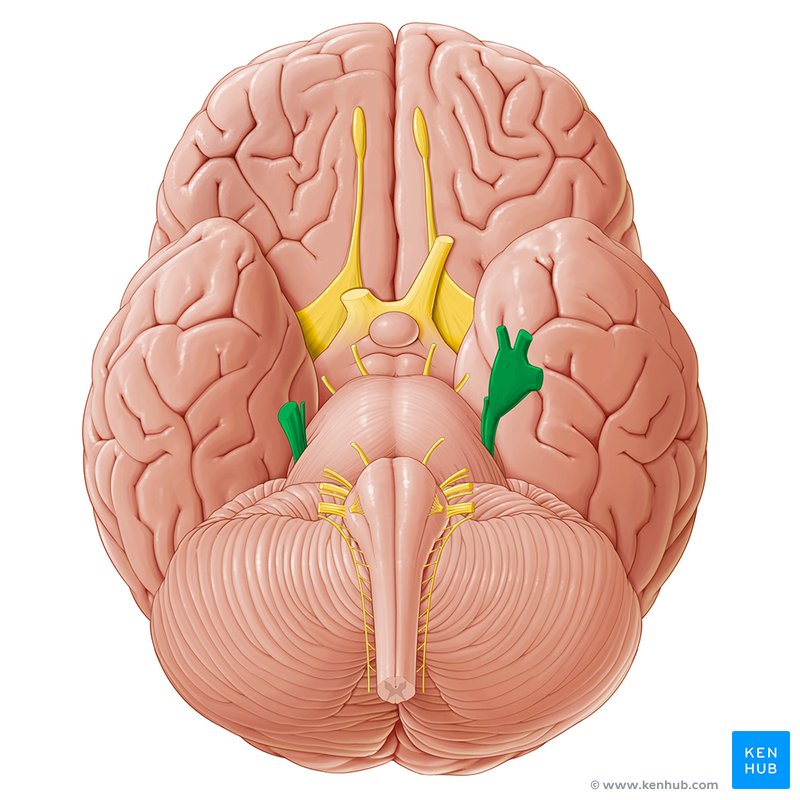
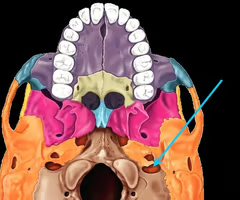
Superior Orbital Fissure
An opening in the skull through which the Ophthalmic Branch of the Trigeminal nerve passes.
Foramen Rotundum
An opening in the skull through which the Maxillary Branch of the Trigeminal nerve passes.
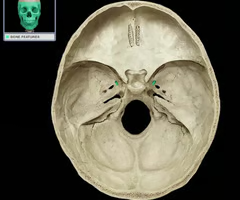
Foramen Ovale
An opening in the skull through which the Mandibular Branch of the Trigeminal nerve passes.
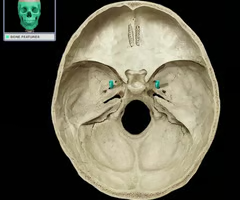
Stylomastoid Foramen
An opening in the skull through which the Facial nerve passes.
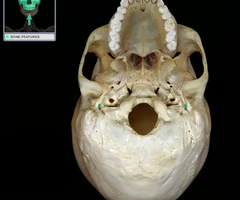
Jugular Foramen
An opening in the skull through which the Vagus and Glossopharyngeal nerves pass.
Chemoreceptor
A type of receptor that senses chemicals, such as flavor molecules and scent molecules.
Mechanoreceptor
A type of receptor that senses touch and movement.
Thermoreceptor
A type of receptor that senses temperature.
Photoreceptor
A type of receptor that senses light.
Nociceptor
A type of receptor that senses pain, primarily through free nerve endings.
Taste bud
A specific type of chemoreceptor that opens to the surface in a taste pore with a taste hair that binds molecules.
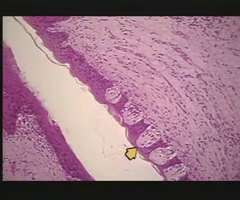
Olfactory epithelium
A specific type of chemoreceptor responsible for the sense of smell.
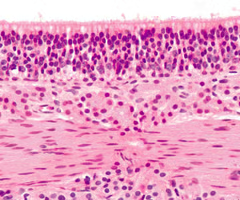
Tactile (Meissner's) corpuscle
A specific type of mechanoreceptor that senses light touch.
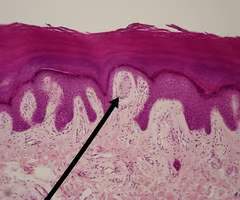
Lamellated (Pacinian) corpuscle
A specific type of mechanoreceptor that senses deeper pressure.
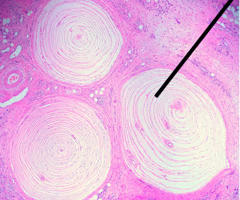
Cribriform plate
Part of the ethmoid bone through which olfactory nerves pass.
Referred pain
Pain perceived at a location different from the site of the painful stimulus, due to shared nerve pathways.
Sensory adaptation
When sensory receptors stop firing action potentials due to repeated stimulation.
Hyposmia
Diminished sense of smell.
Anosmia
Loss of the sense of smell.
Dysgeusia
Distorted sense of taste.
Hypergeusia
Heightened sense of taste.
Synesthesia
A genetic condition in which one sense is perceived as coming from a different sense.
geusia
relates to the sensation of taste.
mia
refers to smell