Capacitance
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
what is the function of a capacitor
to store electrical energy in which charge is separated
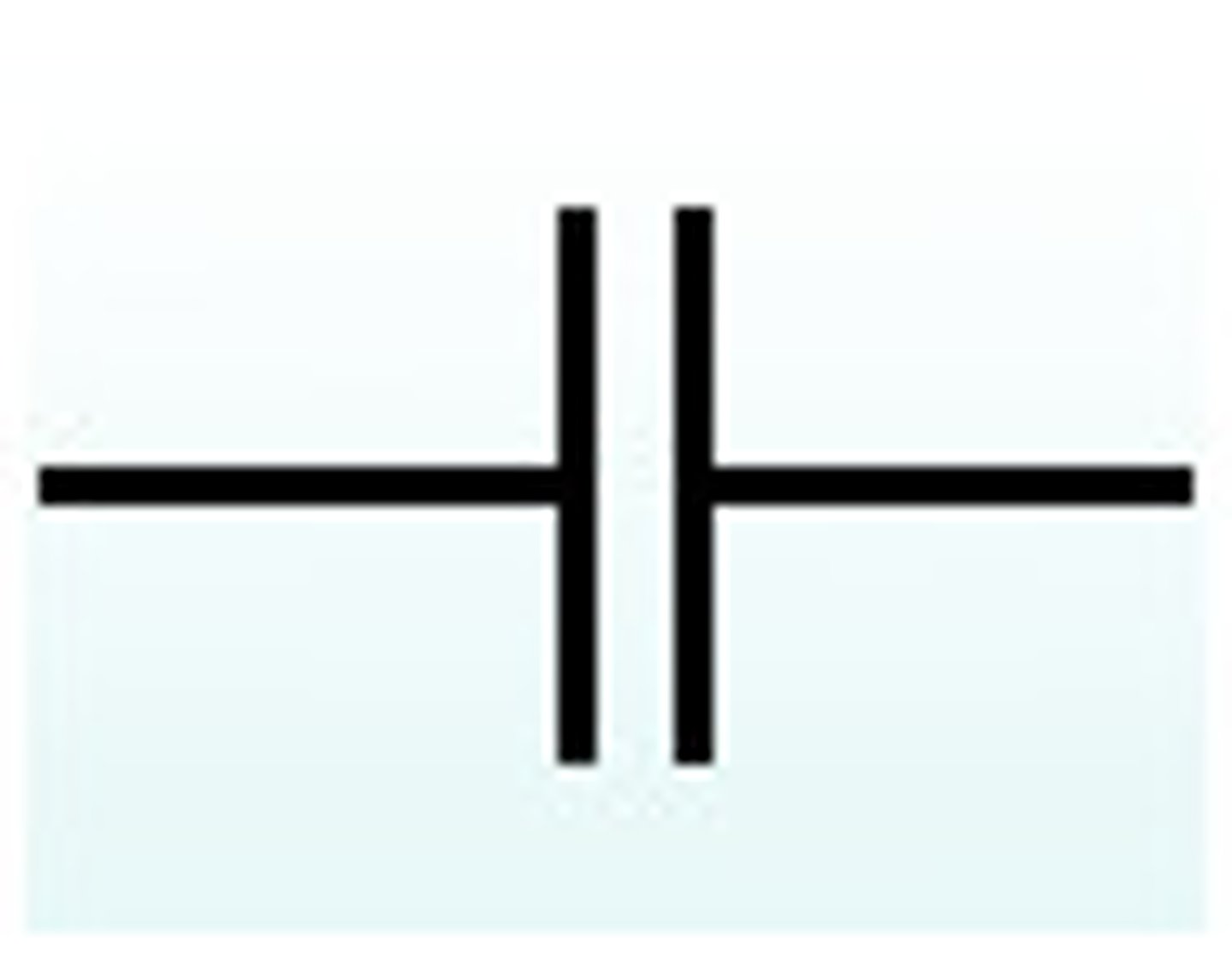
what is the circuit symbol of a capacitor
describe how a capacitor becomes charged when it is connected to a cell
Electrons will flow from the negative terminal of the cell to the negative terminal of the capacitor. They cannot travel between the plates because of insulation
The excess electrons on the negative plate are going to repel electrons off the positive plate of the capacitor, which will move towards the positive terminal of the cell
The current in the circuit must be the same at all points and charge must be conserved. Overall the plates will acquire an equal and opposite charge. Therefore there is a potential difference across the plates. The current in the circuit falls to zero when the pd across the plates is equal to the emf ε of the cell. The capacitor is then fully charged. The net charge on the capacitor is zero
what is the net charge on the capacitor plates when fully charged
zero
describe the basic construction of a capacitor
2 metallic plates separated from each other by an insulator often known as dielectric
how is capacitance defined
the charge stored per unit of potential difference across it
what are the units of capacitance and the SI base units
Farad (F)
A^2 s^4 kg^-1 m^-2
How is total capacitance calculated for capacitors in parallel
Ct = C1 + C2
How is total capacitance calculated for capacitors in series
1/Ct = 1/C1 + 1/C2
what is the voltage stored across a capacitor in a parallel circuit
the voltage is the same across each parallel branch of the circuit
what is the charge stored across a capacitor in a parallel circuit
(and how it related to current)
The charge is shared, as current is shared
what is the voltage stored across a capacitor in a series circuit
the p.d. is shared by kirchoff's 2nd law
what is the charge stored across a capacitor in a series circuit
(and how it related to charge)
Each capacitor will experience the same current. so it will acquire the same charge
how can the energy stored on a capacitor be determined from a graph of p.d. against charge for a capacitor
work done = area underneath the graph
describe in simple terms the charging of a capacitor
initially the pd across the capacitor is 0
the pd across the capacitor decreases
the pd across the resistor decreases
the current decreases as the capacitor is charging
describe what happens when a capacitor discharged through a resistor in terms of electron flow
The charge stored by the capacitor decreases with time and hence the pd across it also decreases. The current in the resistor decreases with time as the pd across it decreases accordingly. Eventually the pd, the charge stored by the capacitor and the current in the resistor are all zero
what can be inserted into this equation : X = Xo e^-t/CR
current, I
charge, Q
Potential difference, V
what is the time constant
the product of capacitance and resistance (CR)
what happens if time is equal to time constant
the potential difference, the charge and the current drop to 37% of their initial value
LEARN ITERATIVE MODELLING
LEARN PRACTICAL
describe how the time constant of a circuit can be determined experimentally in the labratory
Connect a voltmeter or data-logger or oscilloscope across the resistor (or capacitor) or an ammeter in series with the resistor.
A stopwatch is started when the switch is opened and stopped when the p.d. or the current to decreases to 37% of its initial value.
The time constant is the time taken for the p.d. or the current to decreases to 37% of its initial value.
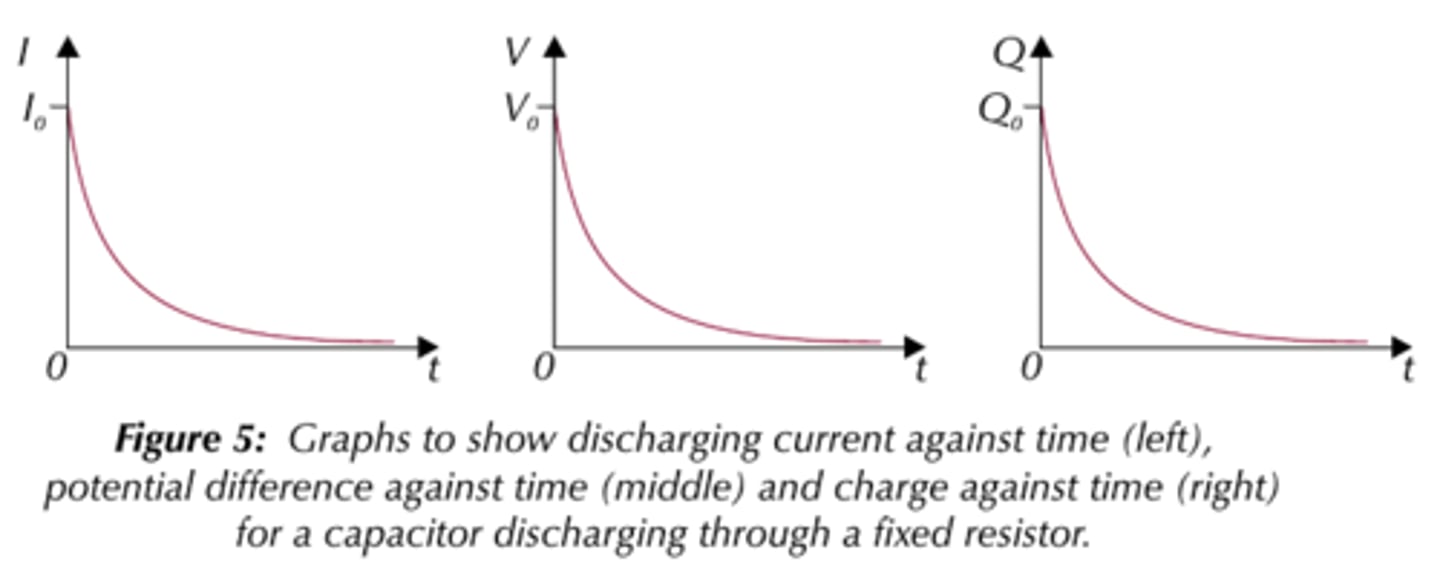
what is the I,Q,V against t graph as a capacitor discharges through a resistor
and state the equation used
X=X0 e^ -t/cr
what is the current against time graph as a capacitor is charged
and state the equation used
I=I0 e^ -t/cr

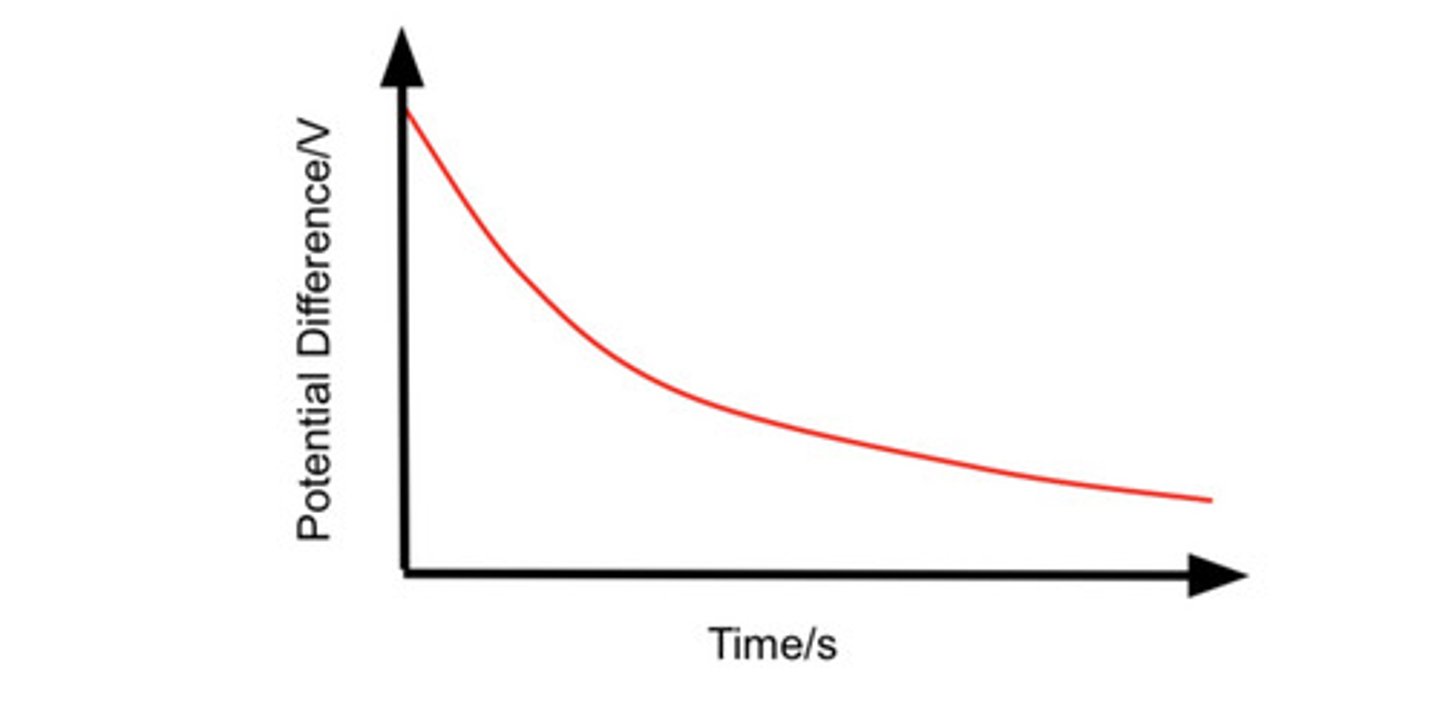
describe how the pd across the resistor changes with time as the capacitor is charged and state the equation used
V=Vo e^ -t/cr
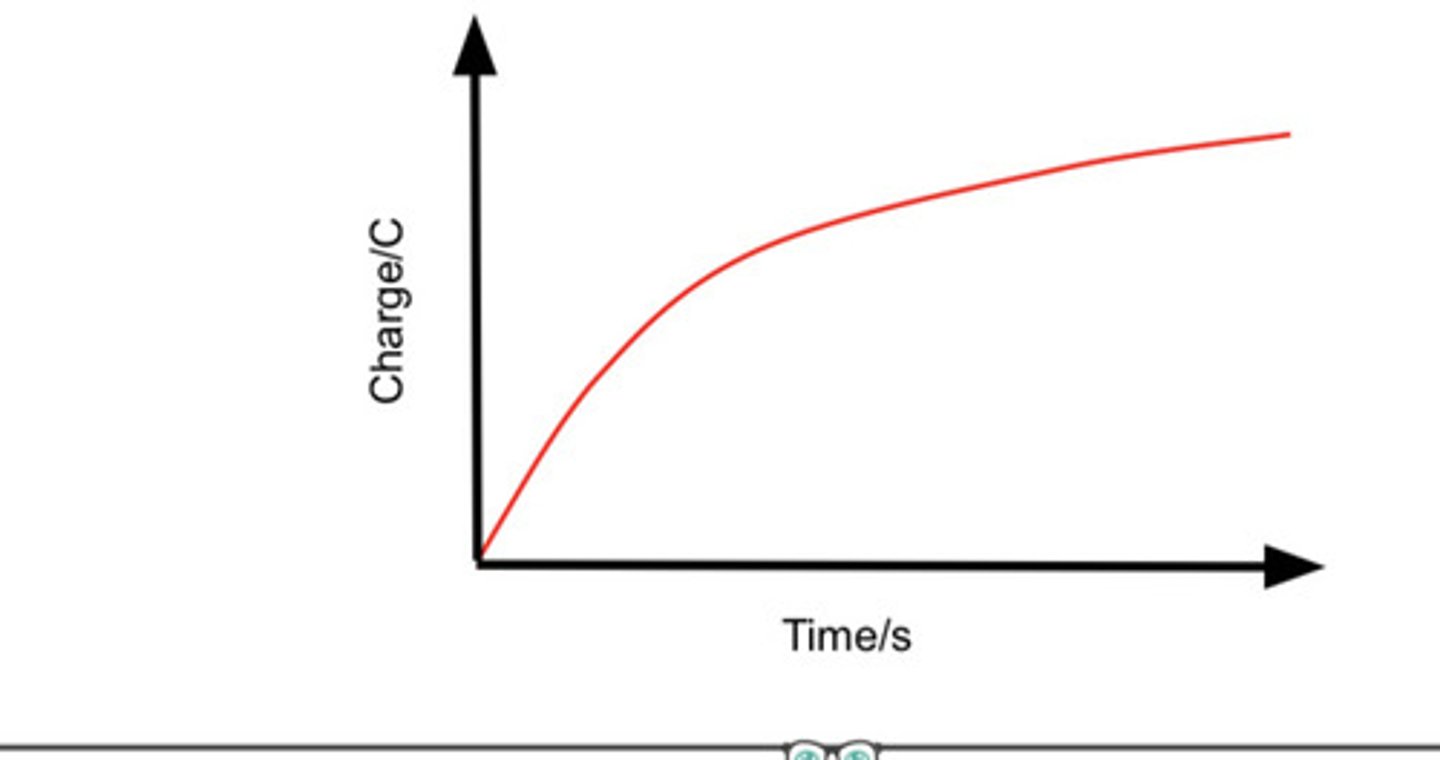
describe how the pd across the capacitor changes with time as the capacitor is charged and state the equation
V=Vo (1-e^ -t/cr)
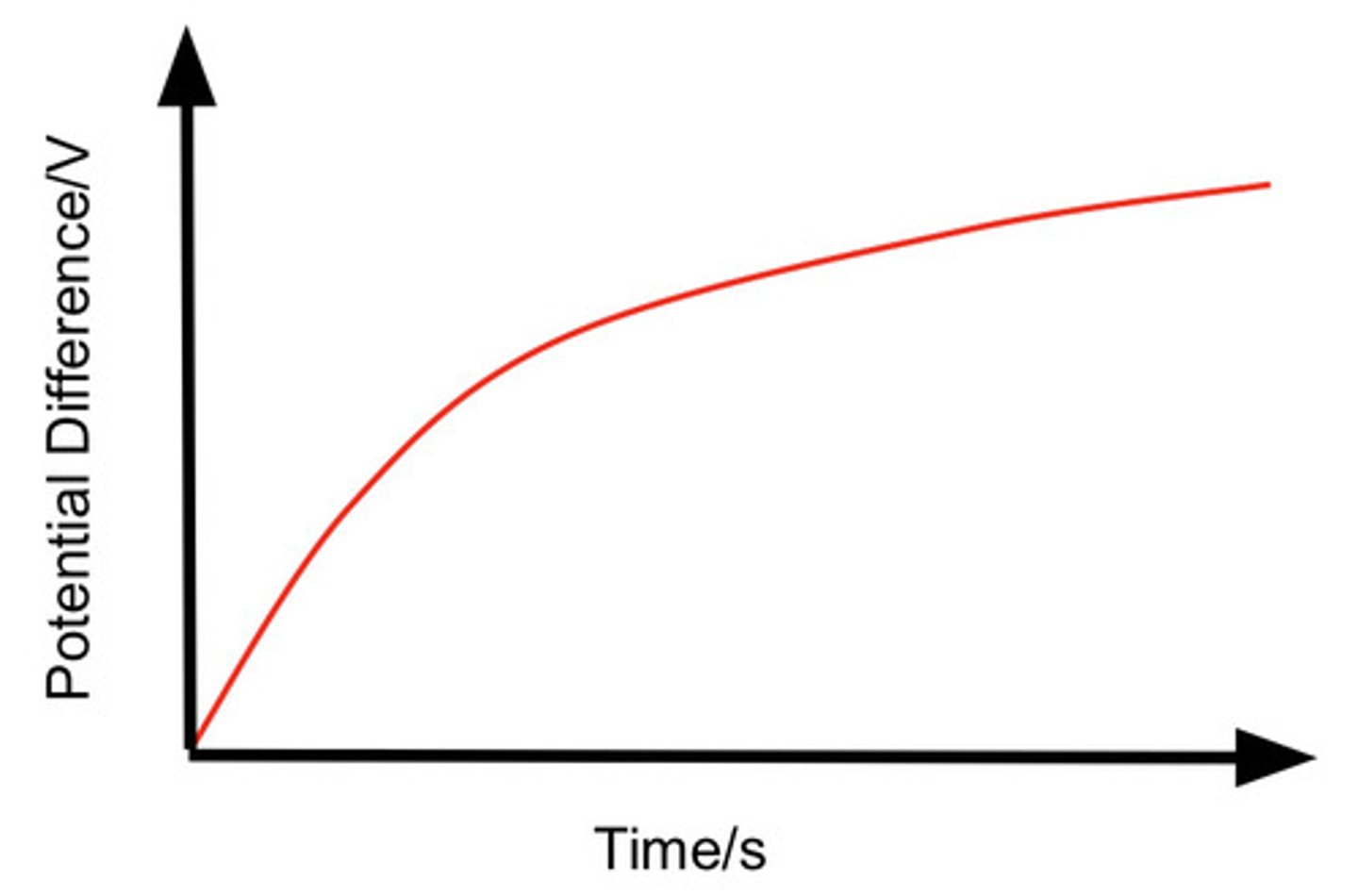
describe how the charge stored by the capacitor changes with time as the capacitor is charged and state the equation
Q=Qo (1=e^ -t/cr)