Cellular Respiration
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Year 12 Biology U3 AOS 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Cellular Respiration
the process by which all living things — plants, animals, fungi, protists, bacteria — create energy in the form of ATP
Involves breaking down of glucose → CO2 and H2O, releasing energy
The complete breakdown of glucose requires oxygen (aerobic)
ATP is a coenzyme
Chemical Equation for Cellular Respiration
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP (energy)
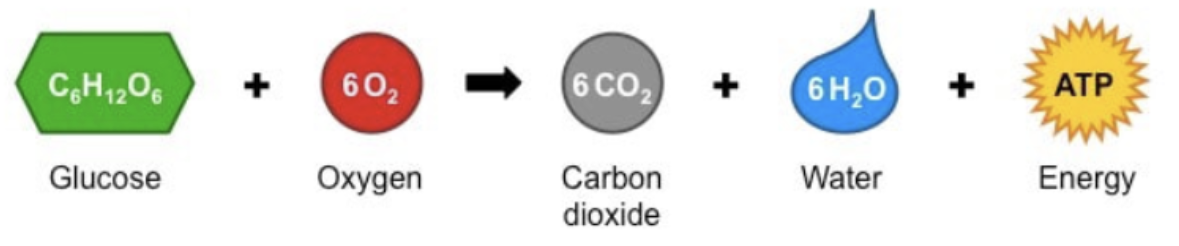
Worded Equation for Cellular Repiration
glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water + energy
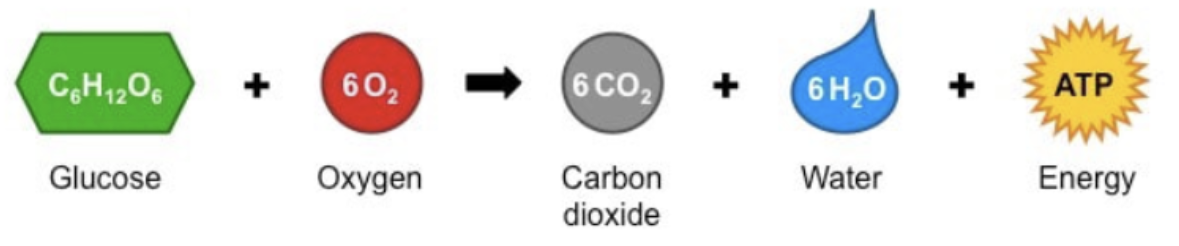
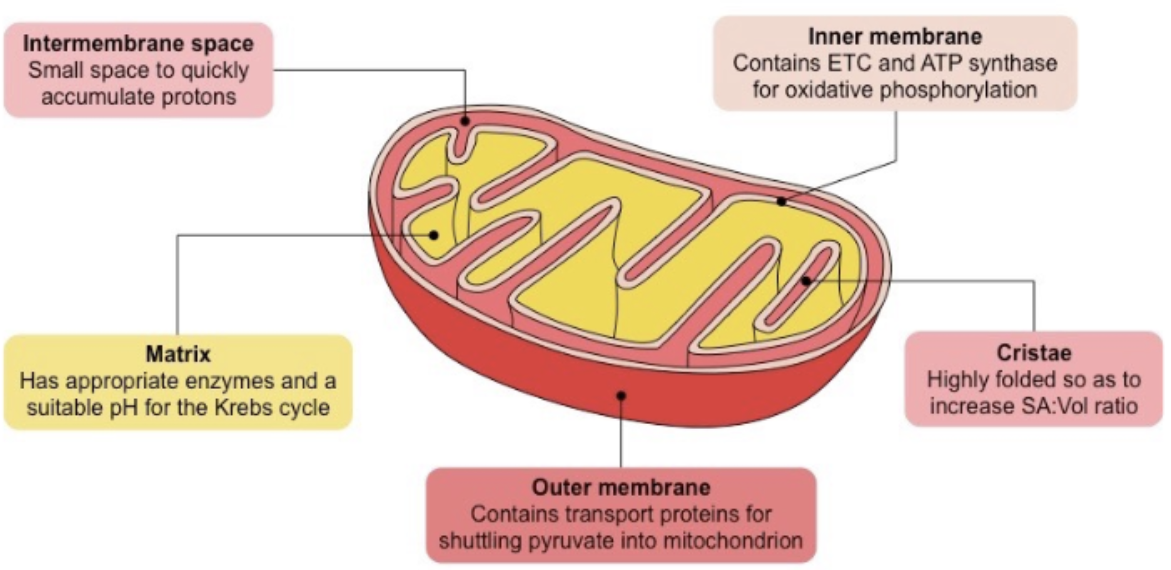
Mitochondrial Structure — Why is it well suited to its function?
the inner membrane (cristae) is highly folded
Providing a large surface area for important chemical reactions (e.g: ETC)
Glycolysis
sugar-breaking/splitting, occurring in the cytoplasm
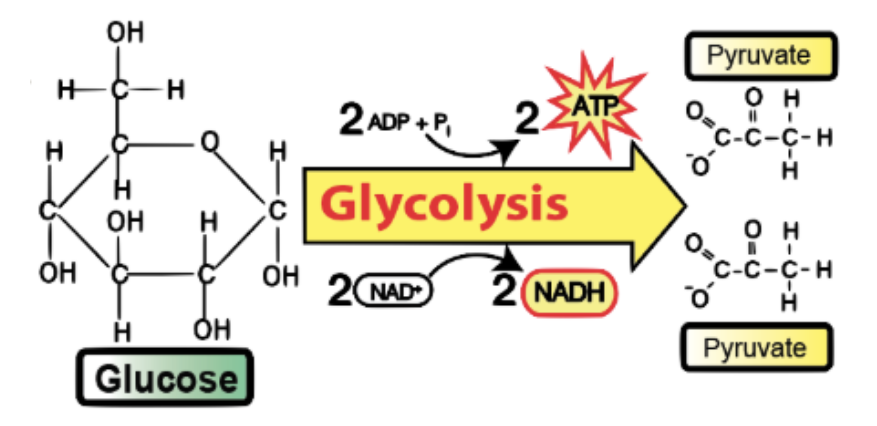
INPUTS of Glycolysis
Glucose
NAD+
ADP + P
OUTPUTS of Glycolysis
Pyruvate (used in Krebs Cycle)
NADH (used in ETC)
2 NET ATP (used for cellular processes) → makes 4 ATP though
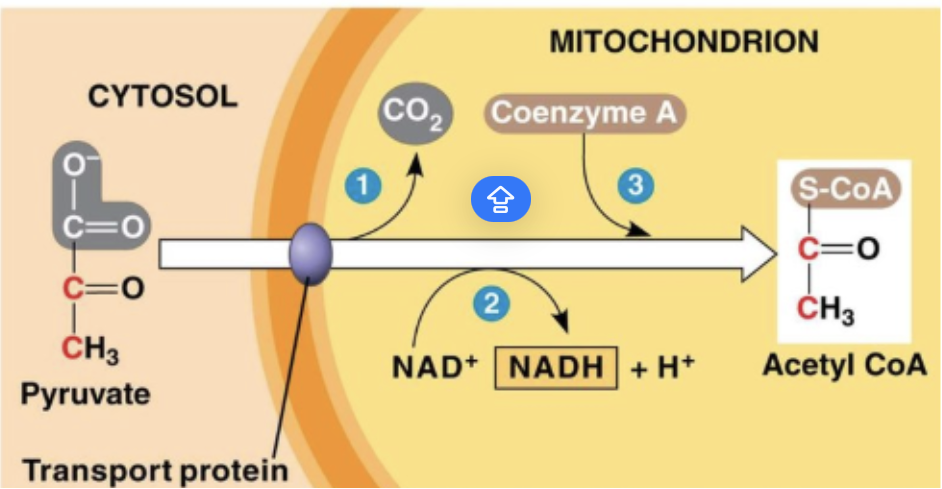
Link Reaction (Modified Pyruvate)
a chemical reaction where pyruvate is transported into the mitochondria, attaching to an enzyme + becomes Acetyl CoA
Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle)
a central series of biochemical reactions, occurring in the mitochondrial matrix
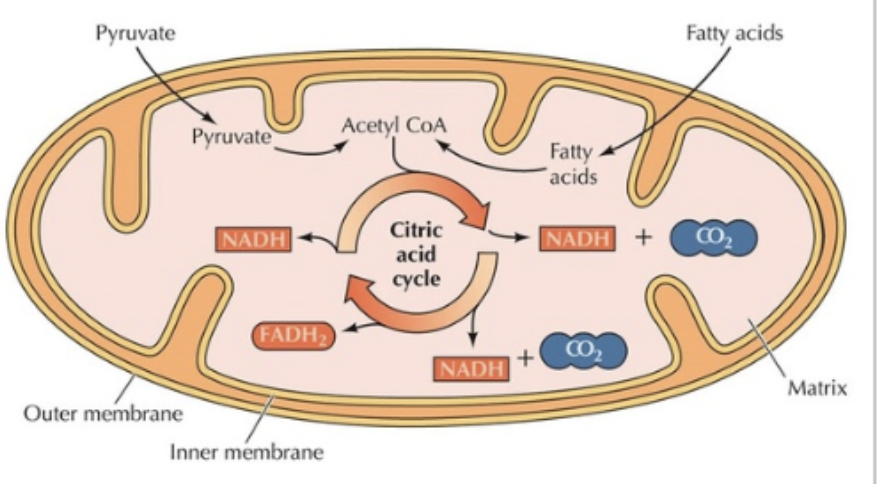
INPUTS of the Krebs Cycle
Pyruvate/Acetyl CoA
NAD+
FAD
ADP + P
OUTPUTS of the Krebs Cycle
NADH + FADH2 (used in ETC)
CO2 (waste)
2 ATP (used for cellular processes)
Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
a series of protein complexes and molecules embedded in the inner mitochondrial/plasma membrane
Major yield of energy comes from the transfer of electrons via ETC
Oxygen is the final receptor
Oxygen binds to hydrogen ions + electrons, ensuring the process continues without electrons building up
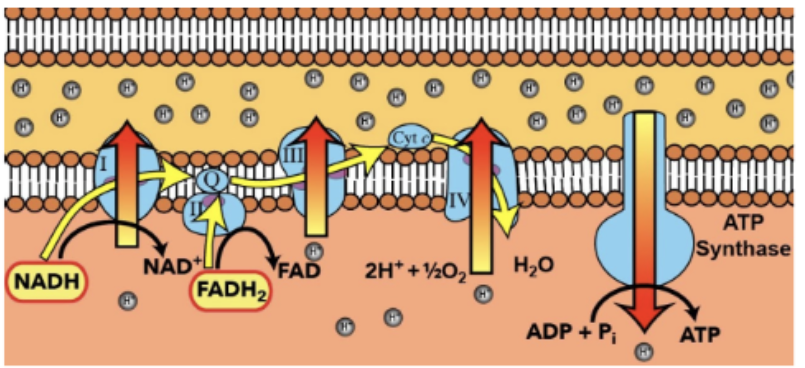
INPUTS of the ETC
NADH + FADH2 (from glycolysis and krebs)
ADP + P
O2
OUTPUTS of the ETC
26 OR 28 ATP
H2O
NAD+
FAD
Anaerobic Respiration
a.k.a: fermentation → allows cells to produce small amounts of ATP (via glycolysis) from glucose when there is no oxygen available
Occurs entirely in the cytoplasm
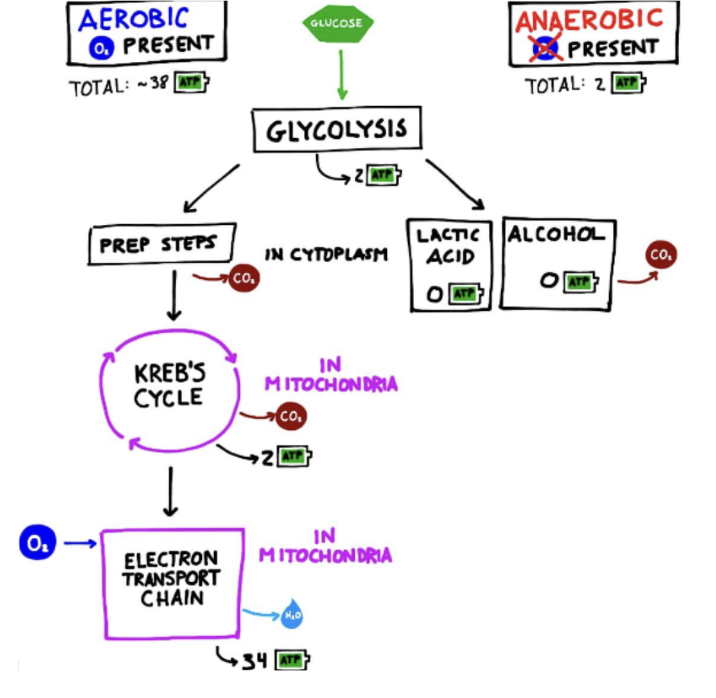
Two types of Fermentation
lactic acid and alcoholic
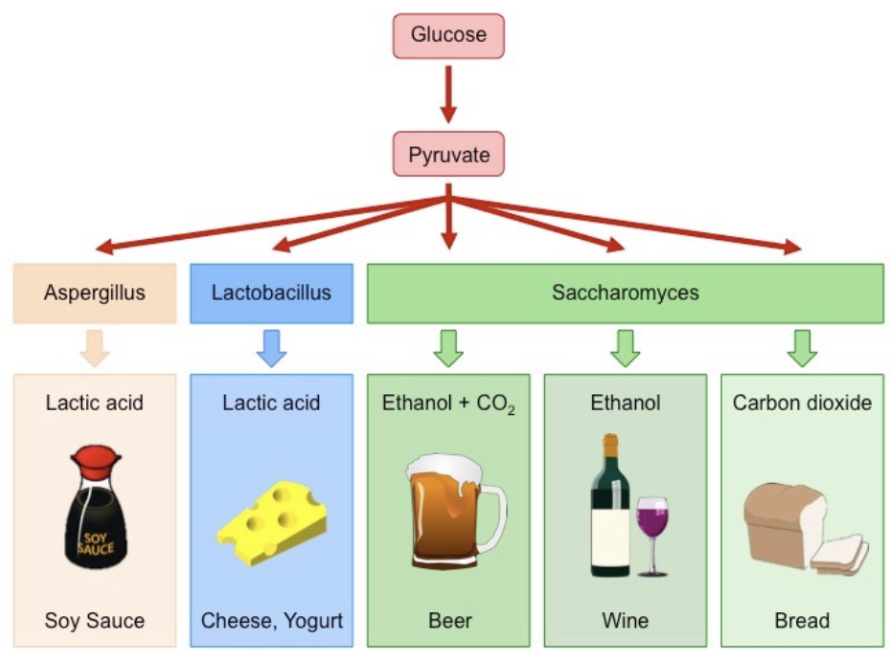
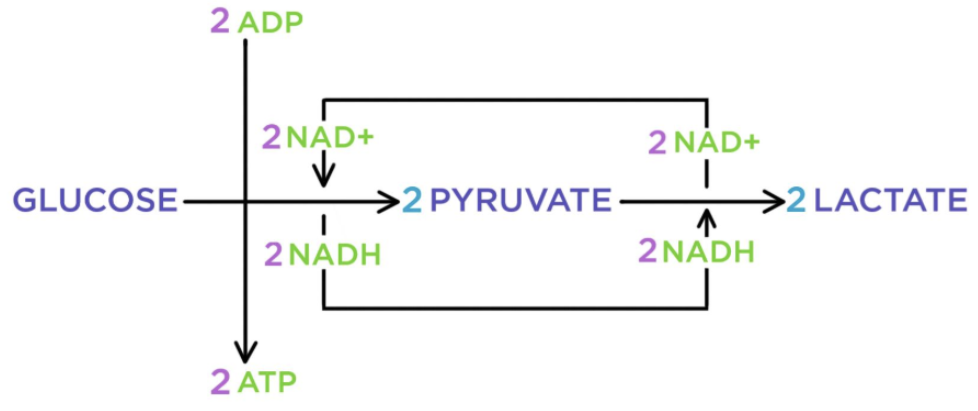
Lactic Acid Fermentation
occurs in animal cells, some bacteria and molds
Produces 2 ATP and lactate (lactic acid)
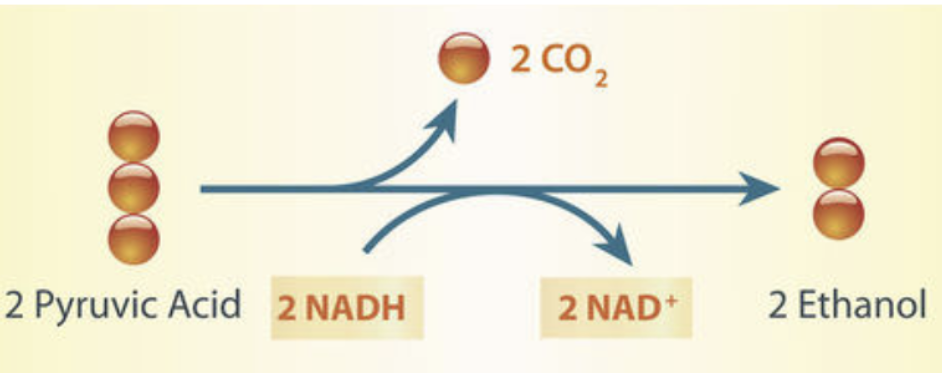
Alcoholic Fermentation
occurs in many yeasts + plants
Produces 2 ATP, ethanol and CO2
Factors affecting the Rate of Cellular Respiration
Glucose availability
Oxygen concentration
Temperature
Biomass
organic material of animal/plant origin, often sourced from a variety of industries
Fossil fuel
a fuel formed from dead organic material over millions of years
Carbon-neutral
a process that has no net release of CO2 into the atmosphere
Non-renewable
resources that are being used up at a faster rate than they are being used
Renewable
resources that are re-formed at the same or faster rate than they are being used
Fossil fuels
Non-renewable as it takes millions of years to complete
Rate of production is much lower than rate of consumption
EXAMPLES: coal and oil
Biofuels
Renewable as they continue supplying plant material/animal by-products indefinitely
Better for the environment → carbon-neutral
CO2 released during combustion is originally captured by plant during photosynthesis
CO2 is cycled back into atmosphere as O2 and can be used again as an input
No net increase in the amount of CO2 released in atmosphere
FIRST step of making Biofuel
Deconstruction
Biomass is broken down so surface area increases (more efficient)
Break cell wall + cellulose via biological, chemical and physical approaches
SECOND step of making Biofuel
Digestion by Enzymes
Broken-down Biomass is exposed to enzymes (amylase)
Breaks down starch and cellulose
Converts into glucose + other sugars
Hydrolysis → breakdown of polysaccharides aided by water
THIRD step of making Biofuel
Ethanol Fermentation
Yeast used to facilitate anaerobic fermentation
Large amount of ethanol produced
Ethanol diffuses out of the yeast cells + harnessed for biofuel
FOURTH step of making Biofuel
Purification/dehydration
Ethanol is distilled via removal of water
Converting into biofuel
Biofuel is purified + ready to be used as liquid fuel
Applications of Biofuel
Transportation need → alt for traditional fuels (petrol/diesel)
Energy generation → used as back-up power systems where emissions must be kept low (school/hospitals)
Implications of Biofuel
Renewability of biomass as a fuel source
Carbon neutrality of biomass consumption