Lecture 14 - Nitrogen Sulfur Phosphorus and Other Nutrients
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
Nitrogen
N2 gas is most common form of N (78% of atmosphere) • Not easily used by organisms
• In aquatic ecosystems N can be in inorganic and organic forms
• Most important inorganic forms of N in aquatic ecosystems are:
• Nitrate (NO3 −) & Ammonium (NH4 +)
• Nitrite (NO2 −) and Nitrous Oxide (N2O) can also be present in significant quantities
• Many organic forms • Amino acids, Nucleic Acids, Proteins and Urea • Organic forms can be dissolved or particulate
Nitrogen Fluxes
• Nitrogen is required for life • Component of many essential biological molecules • Amino acids, DNA, etc •
Many consumers can only assimilate organic nitrogen • Fish, insects, mammals • Use enzymes to break down complex organic molecules • Important source of organic and inorganic nitrogen to system → excretion
• Primary producers and bacteria can take dissolved inorganic nitrogen from the water
• Nitrate, Nitrite and Ammonium • Ammonium is preferred (mostly) because requires less energy to use
Nitrogen Fixation
Many bacteria and some archaea can assimilate (“Fix”) N2 gas
• Includes some cyanobacteria (often associated with algal blooms)
• Enzyme nitrogenase → Energetically costly
• Inactivated by oxygen →use specialized cells (heterocysts) to protect enzyme from oxygen
• Fixation also occurs from lightning
Nitrification/Denitrification
Denitrification is process of reducing nitrate to nitrogen gas
• Process is used to convert organic carbon to energy
• Only occurs in anoxic waters
• Results in removal of inorganic N from aquatic systems
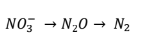
Presence of N in the Environment
Inorganic N is most abundant as ammonium or nitrate • Balance depends on presence of oxygen
Phosphorus
• Limiting nutrient in many aquatic ecosystems
• One dominant inorganic form → Phosphate (𝑃𝑂4 3−)
• Concentrations often below detection in pristine waters (< 1 ug P/l)
• Many organic phosphorus forms • Lipids, nucleic acids, etc.
• P is often bound to particles such as sediments • Not bioavailable
Phosphorus Transformations
• Availability of phosphate determined by interactions with iron
• In oxic conditions, phosphate precipitates with 𝐹𝑒3+ and other metals • Leads to deposition of particulate phosphorus in the sediments
• In anoxic conditions (e.g., hypolimnion), phosphates dissociates from metals and is released to water column
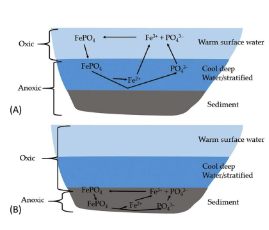
Sulfur
Complex cycle driven by numerous redox states in which sulfur can occur
• Many bacteria and archaea involved in cycle
• Important as is tightly linked to inorganic metal cycles (e.g., iron) and thus indirectly to phosphorus cycle
Silicon
Highly abundant element on Earth, but…
• Limited solubility so not a major dissolved ion in water
• Abundance in water dependent on geology/weathering
• Most in volcanic areas, least in limestone areas
•Critically important to diatoms
• Make frustules (specialized cell wall) from silicon
• Can deplete silicon in lakes in summer → replenished by weather and erosion
Iron
• Key element in many biological elements
• But generally low demand compared to C, N, and P
• Present in several dissolved forms – often dependent on O2
• For example, 𝐹𝑒3+ (oxic conditions), 𝐹𝑒2+ (anoxic conditions)
• Recall: Important to P availability
Other important nutrients
• Manganese, Copper, Selenium, Zinc, Molybdenum
• Sodium, Potassium, chloride and boron
• Needed in trace amounts and most are not naturally abundant
• Many are toxic when abundan