VCE BIO UNIT 1 AOS1
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/80
Last updated 6:54 AM on 3/28/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
1
New cards
Extracellular fluid
Fluid present outside of the cells of a multicellular organism.
2
New cards
Intracellular fluid
Fluid present inside of the cell.
3
New cards
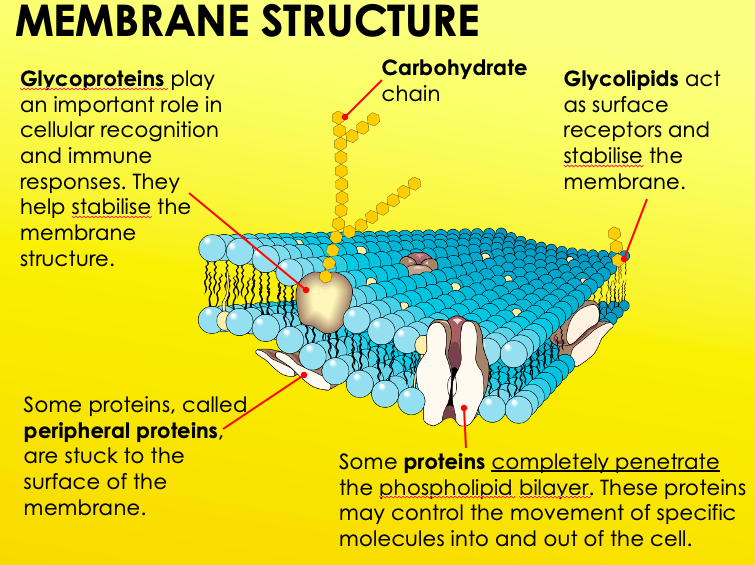
Phospholipid Bilayer
Quite fluid, with proteins flowing within it. Glycoproteins, glycolipids, and cholesterol are also apart of membrane structure.
4
New cards
Functions of the plasma membrane
* Maintains internal cell environment.
* Allows movement of substances in and out of the cell.
* Recognition and communication through cells.
* Allows movement of substances in and out of the cell.
* Recognition and communication through cells.
5
New cards
Glycoproteins
Have an important role in cellular recognition and immune responses. They help stabilise the membrane structure.
6
New cards
Glycolipids
Act as surface receptors and stabilise the membrane.
7
New cards
Cholesterol
Makes the membrane more stable.
8
New cards
What **can** pass through the plasma membrane? (Hydrophobic or hydrophilic)
Hydrophobic molecules, eg:
* water
* alcohol
* oxygen
* water
* alcohol
* oxygen
9
New cards
What **cannot** pass through the plasma membrane? (Hydrophobic or hydrophilic)
Hydrophilic molecules, eg:
* ions
* large molecules
* ions
* large molecules
10
New cards
4 Types of Diffusion
* Simple diffusion
* Facilitated diffusion
* Osmosis
* Active transport
* Facilitated diffusion
* Osmosis
* Active transport
11
New cards
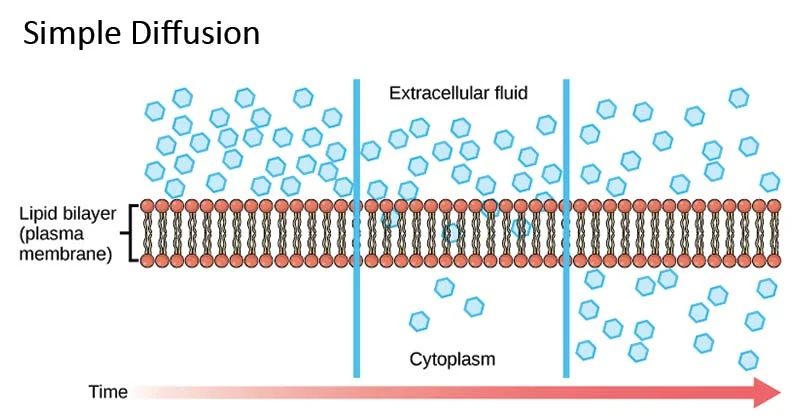
Simple diffusion
The net movement of a substance from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration.
Movement occurs **down** a concentration gradient, passive process.
Movement occurs **down** a concentration gradient, passive process.
12
New cards
Factors affecting rate of diffusion
* Distance
* Concentration gradient
* Physical barriers
* Surface area
* Concentration gradient
* Physical barriers
* Surface area
13
New cards
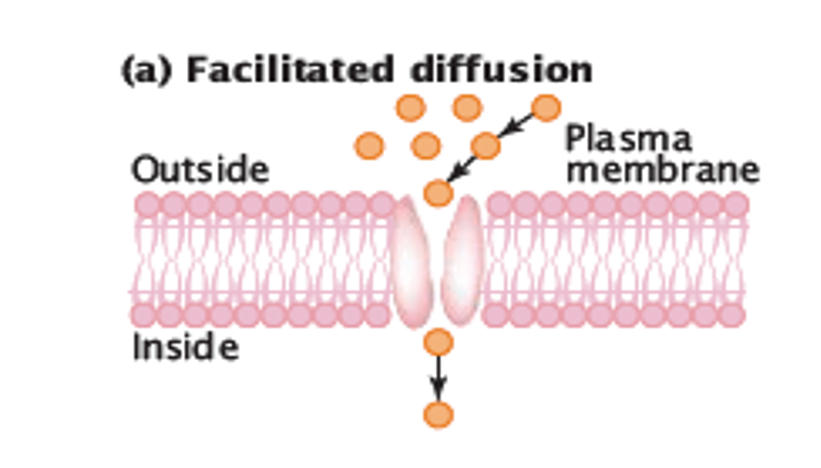
Facilitated Diffusion
When a protein channel and/or carrier is used to help pass proteins through the membrane.
14
New cards
Protein Channel
A channel in membrane that some substances need to move through protein instead of passing straight through.
15
New cards
Protein Carrier
A carrier that is supplied in addition to a protein channel, in order to pass through the membrane.
16
New cards
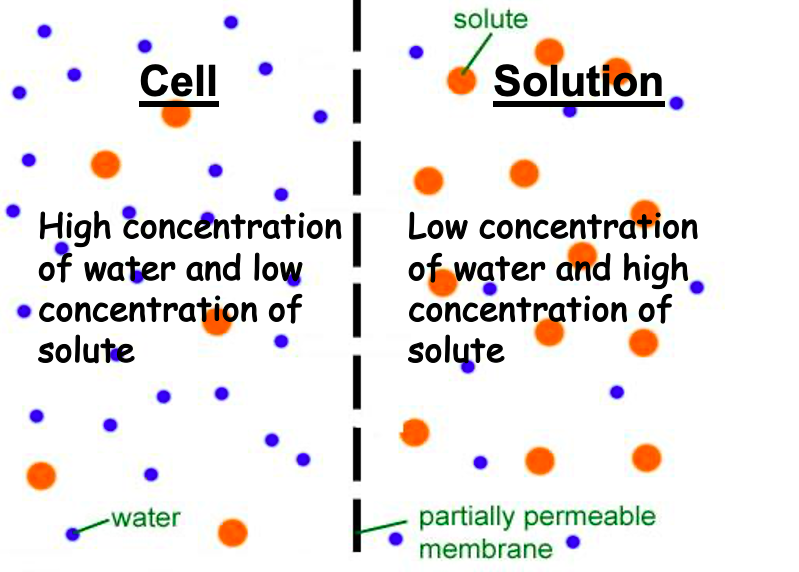
Hypertonic Solution
The solution has a **higher** concentration of solute than the cell or solution that it is being compared to.
17
New cards
Hypotonic Solution
The solution has the **lower** concentration of solute as the cell or solution it is being compared to.
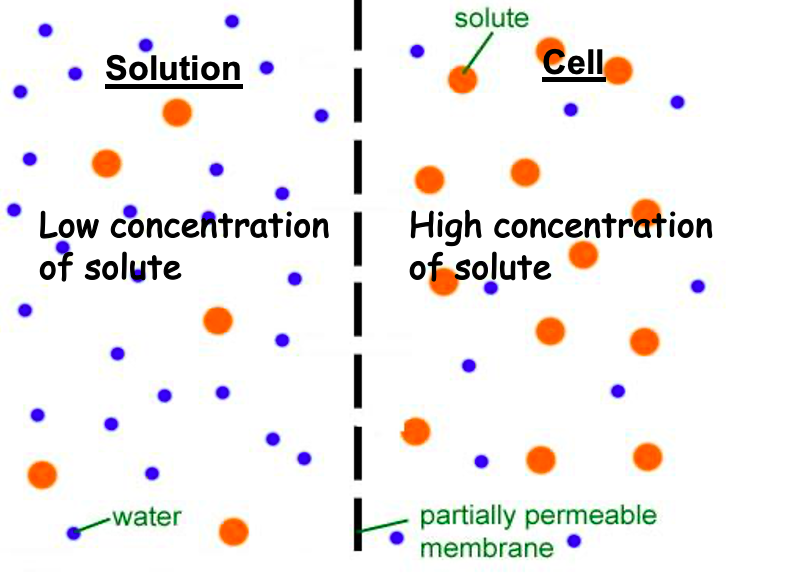
18
New cards
Isotonic Solution
The solution has the **same** concentration of solute as the cell or solution it is being compared to.
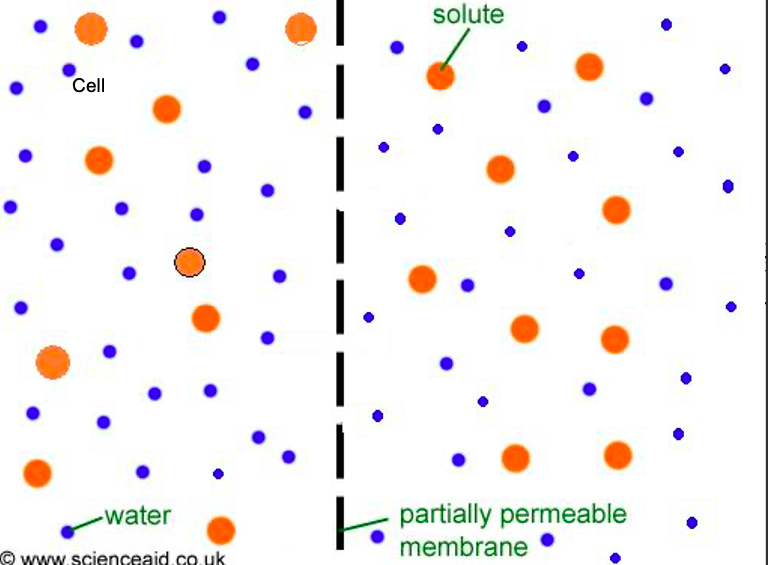
19
New cards
Osmosis
The movement of water from a dilute solution to a more concentrated one.
20
New cards
Dilute
A solution with a low concentration of solute, more water molecules than the solute.
21
New cards
Why do cells need osmosis?
It is how they gain water, making them turgid. (swollen, full)
22
New cards
Active Transport
Substances are moved across a membrane __against__ a concentration gradient. It is an active process as it requires energy (ATP). Used to **pump** substances in or out of the cell with specific protein carrier molecules.
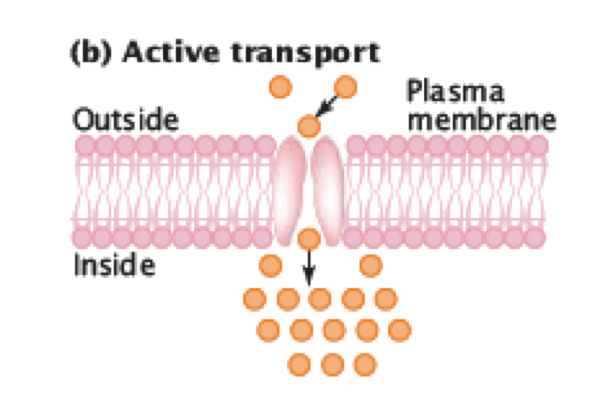
23
New cards
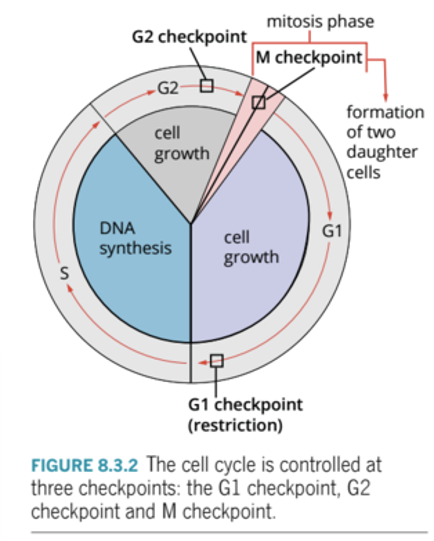
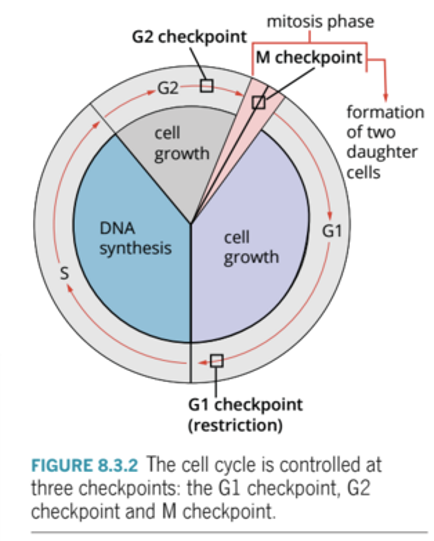
What is the cell control system?
A group of proteins that regulate the cell cycle.
24
New cards
How does the cell internally regulate itself?
By using three checkpoints, G1, G2, M.
25
New cards
What happens if the conditions of the checkpoints are not met?
The cell will not enter the next phase of the cell cycle.
26
New cards
G1 Checkpoint (restriction)
End of G1
* Are there adequate resources (nucleotides) for division? Is the cell large enough? Has the DNA been damaged?
* Are there adequate resources (nucleotides) for division? Is the cell large enough? Has the DNA been damaged?
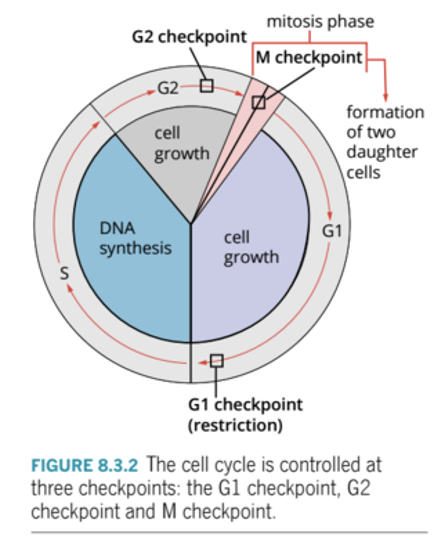
27
New cards
G2 Checkpoint
End of G2
* Are there adequate resources (mitotic proteins) for division? Is the cell large enough? Has the DNA been damaged?
* Are there adequate resources (mitotic proteins) for division? Is the cell large enough? Has the DNA been damaged?
28
New cards
M Checkpoint
End of Metaphase
* Have the spindle fibres attached correctly to the chromatids? Are the chromosomes aligned correctly?
* Have the spindle fibres attached correctly to the chromatids? Are the chromosomes aligned correctly?
29
New cards
External Cell Cycle Controls
* Molecular signals: contact with other cells, tumours release signalling molecules, hormones promote cell division in tissue.
* Environmental conditions: pH levels, temperature, nutrients.
* Environmental conditions: pH levels, temperature, nutrients.
30
New cards
What happens if uncontrolled cell division occurs in a mature organism?
A neoplasm may form.
31
New cards
What is a neoplasm?
An abnormal growth of tissue that can form a mass, for example a tumour. They can eventually become cancer.
32
New cards
What exactly is cancer?
Unregulated and abnormal cell division. It is commonly caused by the increased rate of cell division or the suppression of apoptosis.
33
New cards
Benign Neoplasm
Form localised masses but do not transform into cancer.
34
New cards
Potentially Malignant Neoplasm
Form localised masses that **will eventually** invade other tissues and transform into cancer.
35
New cards
Malignant Neoplasms
Form masses that invade other tissues and transform into cancer.
36
New cards
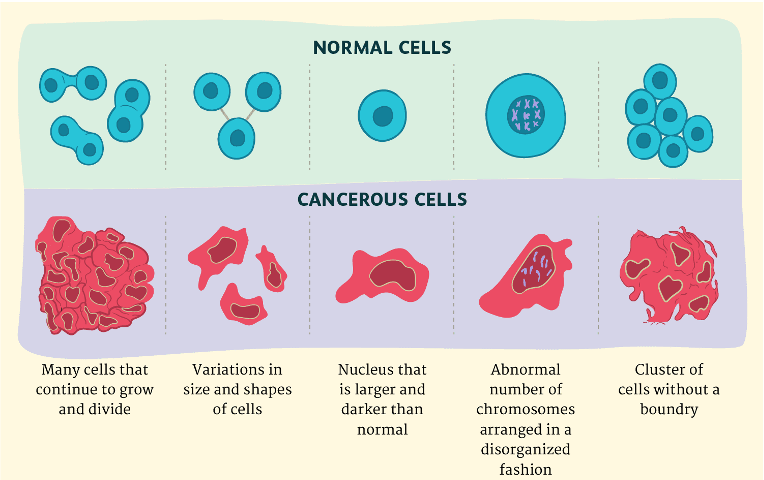
How are cancer cells different from normal cells?
* Faster division
* Less specialised
* Develop their own blood supply
* DNA mutations occur
* No limited number of divisions
* Can spread to other parts of the body.
* Less specialised
* Develop their own blood supply
* DNA mutations occur
* No limited number of divisions
* Can spread to other parts of the body.
37
New cards
What are proto-oncogenes?
They control the stimulation of cell growth and are required for normal growth and development.
38
New cards
Causes of Cancer: Genetic Factors
* Mutations to proto-oncogenes: mutation turns them to oncogenes that promote uncontrolled cell division
* Mutations to tumour suppressor genes
* Hereditary cancers: when someone inherits mutated genes.
* Mutations to tumour suppressor genes
* Hereditary cancers: when someone inherits mutated genes.
39
New cards
Mutagens
Environmental factors that can damage DNA.
40
New cards
Carcinogens
Cancer causing agents.
41
New cards
Causes of Cancer: Environmental Factors
* Chemical: tobacco, air pollution
* Physical: X-Rays, UV light
* Biological: Viruses
* Physical: X-Rays, UV light
* Biological: Viruses
42
New cards
Apoptosis
Programmed cell death, highly coordinated process that does not spill cell contents or trigger an immune response.
43
New cards
Why does Apoptosis occur?
* Cells which are damaged or defective must be eliminated.
* During fetal development, the removal of excess cells.
* During fetal development, the removal of excess cells.
44
New cards
What are Caspases?
Apoptotic Enzymes
45
New cards
What is Phagocytosis?
The breakdown of apoptotic bodies by the phagocytes.
46
New cards
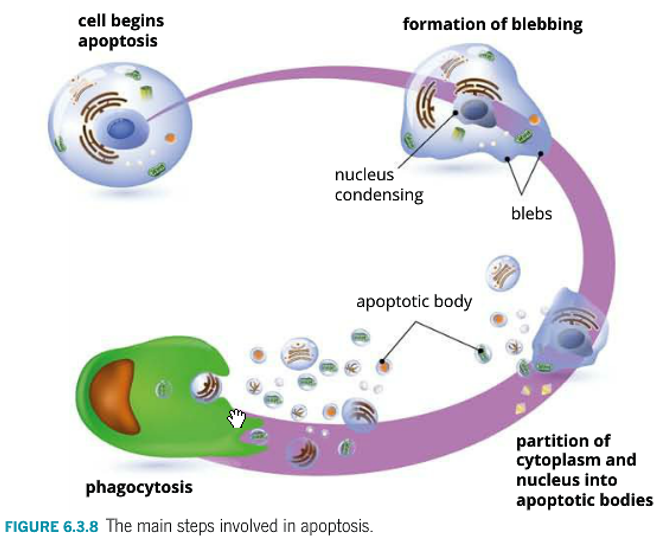
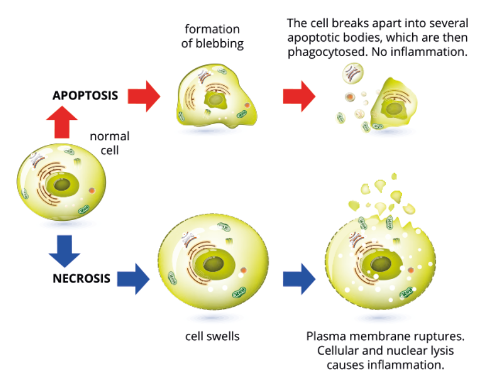
Major Steps of Apoptosis
1. Activation of caspases and begin breakdown of cell contents.
2. Cell shrinks and blebs begin to form.
3. Cells continue to shrink and package themselves into apoptotic bodies.
4. Phagocytosis.
47
New cards
Necrosis
Accidental and uncontrolled cell death, can cause inflammation and damage to surrounding cells.
48
New cards
Why does the cell explode during Necrosis?
The plasma membrane is damaged and ruptures, therefore the cell explodes and contents are released.
49
New cards
What causes Necrosis?
Caused by physical damage, toxins, pathogens, lack of oxygen.
50
New cards
Apoptosis vs Necrosis
* In necrosis, external factors cause internal tissue damage and cell disfunction.
* Apoptosis is pre-planned, and required for smooth bodily functioning..
* Necrosis is cellular death when exposed to extreme conditions.
* Apoptosis is pre-planned, and required for smooth bodily functioning..
* Necrosis is cellular death when exposed to extreme conditions.
51
New cards
Apoptotic Pathways
* Mitochondrial Pathway (Intracellular): Triggered when cell components, DNA, is damaged. Proteins signal for beginning of cascade reactions.
* Death Receptor Pathway (Extracellular): Triggered by immune cells outside the target cell. Cells under stress can all trigger this pathway.
* Death Receptor Pathway (Extracellular): Triggered by immune cells outside the target cell. Cells under stress can all trigger this pathway.
52
New cards
Malfunctions in Apoptosis
* Too much apoptosis can lead to degenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s.
* Too little apoptosis is seen in Syndactyly, where the skin between digits is not removed during embryonic development.
* Too little apoptosis is seen in Syndactyly, where the skin between digits is not removed during embryonic development.
53
New cards
How can Apoptosis cause Cancer?
Due to apoptosis not occurring when it should:
* Genetic mutations that increase cell division rate.
* Caspases mutations that prevent function.
* Defects in proteins leading to caspases activation
* Defects in signal reception of apoptosis triggers.
* Genetic mutations that increase cell division rate.
* Caspases mutations that prevent function.
* Defects in proteins leading to caspases activation
* Defects in signal reception of apoptosis triggers.
54
New cards
Cascade
Series of caspases reactions.
55
New cards
Why do cells divide? (3 Reasons)
Replace damaged or worn out cells.Allow multicellular animals to grow.Repair damage cells after injury.
56
New cards
How do prokaryotes multiply?
Binary fission
57
New cards
How do eukaryotes multiply?
Mitosis or Meiosis
58
New cards
Binary Fission
Division of prokaryotic cells, asexual production. There are no distinct phases.
59
New cards
Define ‘The Cell Cycle’
The period between the formation of a cell and when it divides.
60
New cards
What are the two phases of the cell cycle?
Interphase and Mitosis
61
New cards
What does IPMATC stand for?
Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, and Cytokinesis.
62
New cards
What is Interphase (G1-S-G2) ?
Cell is undergoing all of its normal activities and doubles in size from the growth of cytoplasm. The chromosomes are not visible as distinct bodies.
63
New cards
Interphase: G1 Stage
G1: growth, organelles are being made and cell specialisation
64
New cards
Interphase: G0
Only occurs if there is a lack of resources or wrong conditions, resting phase.
65
New cards
Interphase: S Phase
The synthesis of DNA, chromosomes are now made of 2 sisters chromatids.
66
New cards
Interphase: G2 Phase
Growth and preparations for division, the synthesis of materials needed for division.
67
New cards
What phase do cells spend most of their time in?
Interphase
68
New cards
What is Mitosis?
The division of eukaryotic cells, one cell divides to form two daughter cells. They all have the same genetic material.
69
New cards
Mitosis: Prophase
Chromosomes condense and become visible, centrioles move to opposite sides and spindle fibres begin to form. Nuclear membrane disappears.
70
New cards
Mitosis: Metaphase
Centromeres of chromosomes attach to spindle and are aligned in the centre of the cell.
71
New cards
Mitosis: Anaphase
Spindle fibres contract, splitting centromere and pull the now separated chromosomes to opposite poles.
72
New cards
Mitosis: Telophase
Nuclear membrane reforms around the two sets of chromosomes as the spindle disappears and chromosomes become longer and thinner.
73
New cards
Mitosis: Cytokinesis
The cells separate and the cell cycle starts again, back to interphase.
74
New cards
Chromosome vs Chromatid
A chromatid is one of the identical halves of a chromosome. It is then replicated and joined with another sister chromatid by the centromere in order to form a chromosome.
75
New cards
What are stem cells?
Cells that have not become specialised yet with the potential to become different types of cells.
76
New cards
The three types of stem cells
* Embryonic stem cells
* Adult (somatic) stem cells
* Induced pluripotent stem cells
* Adult (somatic) stem cells
* Induced pluripotent stem cells
77
New cards
The 4 Potencies of Stem Cells
* Totipotent
* Pluripotent
* Multipotent
* Unipotent
* Pluripotent
* Multipotent
* Unipotent
78
New cards
Embryonic Stem Cells
Undifferentiated cells from zygote to blastocyst stage.
Totipotent or pluripotent.
Totipotent or pluripotent.
79
New cards
Adult Stem Cells
Found in small numbers in adult tissues. Multipotent or unipotent.
80
New cards
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (IPSC)
Adult somatic cells that have been genetically reprogrammed to an embryonic cell-like state.
81
New cards
Ethical Dilemmas of Stem Cell Therapies
* Does harvesting embryotic stem cells kill embryos? Taking lives?
* Why use embryos when IPSCs exist?
* Why use embryos when IPSCs exist?