2.2b aviation weather hazards
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 3:21 PM on 4/3/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
1
New cards
Types of Aviation Weather Hazards
* Thunderstorms
* Icing/Frost
* Fog
* Turbulence and Wind Shear
* Icing/Frost
* Fog
* Turbulence and Wind Shear
2
New cards
Thunderstorms
* Turbulence may cause **structural damage**
* Lighting can blind you and cause electrical problems
* Lighting can blind you and cause electrical problems
3
New cards
Necessary Components to create Thunderstorms
1. Unstable Air
2. High Humidity
3. Lifting Agent
4
New cards
Life Cycle of a Thunderstorm
1. **Cumulus Stage (3-5 mile height)**
2. **Mature Stage (5-10 mile height)**
3. **Dissipating Stage (5-7 mile height)**
5
New cards
**Cumulus Stage**
* Cloud is growing vertically
* May exceed 3,000 ft./min
* Droplets are increasing in size
* Towering Cumulus is the **end result** of this stage
* May exceed 3,000 ft./min
* Droplets are increasing in size
* Towering Cumulus is the **end result** of this stage
6
New cards
**Mature Stage**
* Cloud droplets are very large
* Precipitation begins (“Nimbus”)
* Downdrafts begin
* Updrafts still exist!
* Lightning
* Friction of the air moving up and down causes it
* Icing
* Precipitation begins (“Nimbus”)
* Downdrafts begin
* Updrafts still exist!
* Lightning
* Friction of the air moving up and down causes it
* Icing
7
New cards
**Dissipating Stage**
* Storm loses its moisture content and its energy
* Starts to die
* Whole cycle takes 20 to 30 minutes
* Starts to die
* Whole cycle takes 20 to 30 minutes
8
New cards
Types of Thunderstorms
* “Air Mass” thunderstorms
* “Frontal” thunderstorms
* “Frontal” thunderstorms
9
New cards
“Air Mass” thunderstorms
* Form as a result of daytime heating
* Typical in the afternoon
* Easiest to avoid - usually visible and not part of an organized line or formation
\
* Typical in the afternoon
* Easiest to avoid - usually visible and not part of an organized line or formation
\
10
New cards
“Frontal” Thunderstorms
* Associated with squall lines
* Form along the **leading edge** of a front
* **Cold front** → produce the largest, most active storms
* **Warm front** → will be “embedded” → **hard to see**
* Often form in **organized lines**
* Can be hundred of miles long
* Hard to avoid
* Form along the **leading edge** of a front
* **Cold front** → produce the largest, most active storms
* **Warm front** → will be “embedded” → **hard to see**
* Often form in **organized lines**
* Can be hundred of miles long
* Hard to avoid
11
New cards
Thunderstorm Avoidance
* Thunderstorm will exist as a threat for most of the summer (PROB30/40)
* **Visual avoidance** is the best
* 20 miles is the recommended distance
* **Visual avoidance** is the best
* 20 miles is the recommended distance
12
New cards
What if you can’t see the thunderstorm?
**Types**
* Night time
* Embedded storms blanketed by other clouds
**∴ Detection Equipment**
* Night time
* Embedded storms blanketed by other clouds
**∴ Detection Equipment**
13
New cards
Thunderstorm Avoidance Equipment
* **On-board weather RADAR**
* Works well but
* Heavy and not possible on many aircraft
\
* **Satellite Download**
* Can be viewed through many GPS devices
* Subscription required
* Not intended for thunderstorm avoidance
* Time lag
\
* “Stormscope” + “Strikefinder”
* Both detect the presence of severe weather through lightning discharge
* Lightweight; can fit into any aircraft
* Works well but
* Heavy and not possible on many aircraft
\
* **Satellite Download**
* Can be viewed through many GPS devices
* Subscription required
* Not intended for thunderstorm avoidance
* Time lag
\
* “Stormscope” + “Strikefinder”
* Both detect the presence of severe weather through lightning discharge
* Lightweight; can fit into any aircraft
14
New cards
Airframe Frost and Icing
* Not allowed to takeoff with snow, frost, etc. adhering to the critical surfaces of the airplane
* Adversely affects the **aerodynamic efficiency** of the airfoil
* Ice adds **weight**
* Significant but not the biggest factor
* Adversely affects the **aerodynamic efficiency** of the airfoil
* Ice adds **weight**
* Significant but not the biggest factor
15
New cards
**Frost**
* Forms when water vapour sublimates directly onto your airplane
* **Must** be removed prior to flight
* Most common on cold, clear evenings
* **Must** be removed prior to flight
* Most common on cold, clear evenings
16
New cards
**Airframe Ice**
* Must have “super-cooled droplets”
* Found only in cloud or freezing precipitation
* Found only in cloud or freezing precipitation
17
New cards
“Supercooled” Droplets
* Still in liquid form
* But temperature is at or below zero
* Becomes ice when disturbed by airplane
* Faster the airplane → More accumulation
* Tail ices up **faster** than wing
* Large droplets are worse than small
* But temperature is at or below zero
* Becomes ice when disturbed by airplane
* Faster the airplane → More accumulation
* Tail ices up **faster** than wing
* Large droplets are worse than small
18
New cards
Where are large/small droplets found?
**Large droplets:**
* Cumulus Clouds
* Freezing Rain/Drizzle
**Small droplets:**
* Less accumulation
* “Stratus clouds”
* Cumulus Clouds
* Freezing Rain/Drizzle
**Small droplets:**
* Less accumulation
* “Stratus clouds”
19
New cards
Types of Icing
* Rime Ice
* Clear Ice
* Mixed Ice
* Clear Ice
* Mixed Ice
20
New cards
**Rime Ice**
* Generally found in layer type cloud
* Small super-cooled droplets
* Freeze immediately; leaves numerous air spaces
* Ice is “milky” in appearance
* Tends to be more brittle
* Small super-cooled droplets
* Freeze immediately; leaves numerous air spaces
* Ice is “milky” in appearance
* Tends to be more brittle
21
New cards
**Clear Ice**
* Generally found in Cumulus type clouds; FZRN or FZDZ
* Large super-cooled water droplets that spread before freezing; very few air bubbles
* Clear in appearance and is hard
* Tends to build rapidly
* Large super-cooled water droplets that spread before freezing; very few air bubbles
* Clear in appearance and is hard
* Tends to build rapidly
22
New cards
**Mixed Ice**
* Super-cooled water droplets of various sizes
* May appear as a combination of Rime and Clear Ice
* May build rapidly
* May appear as a combination of Rime and Clear Ice
* May build rapidly
23
New cards
Factors Affecting Ice Accumulation
1. Size and number of super-cooled droplets
2. Aircraft Speed
3. Surface Profile
24
New cards
Size and Number of Droplets
Ice will build rapidly when
* Super-cooled droplets are large and numerous
* Cumulus clouds are present
* Temperatures are just below freezing
* Super-cooled droplets are large and numerous
* Cumulus clouds are present
* Temperatures are just below freezing
25
New cards
Aircraft Speed
* The faster you go, the more ice you’ll catch
* Must balance desire to go slow with stall speed increasing
* Must balance desire to go slow with stall speed increasing
26
New cards
Surface Profile
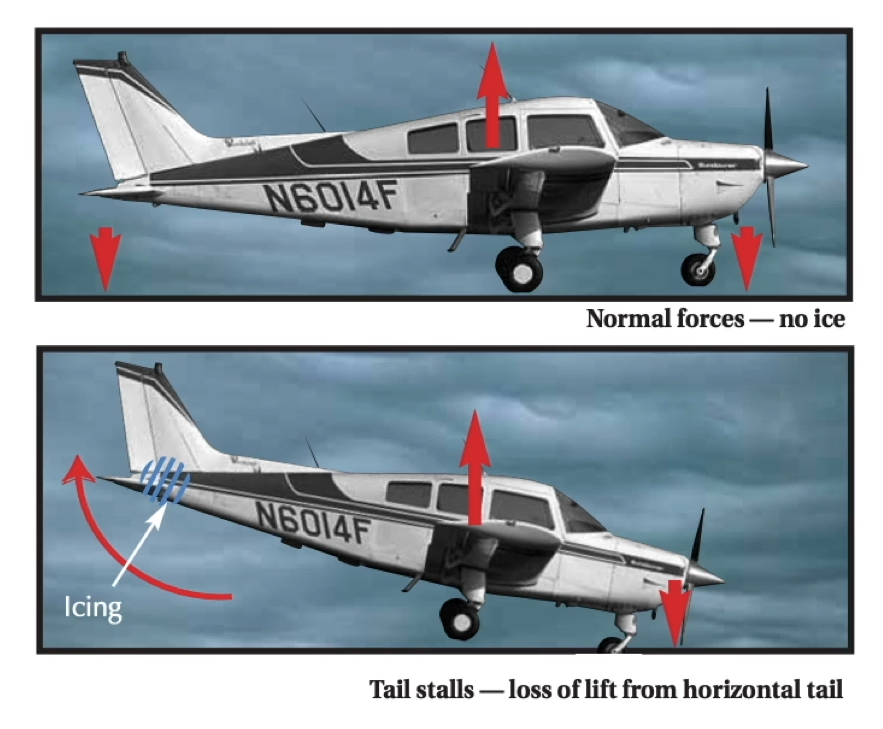
* Ice builds faster on **thin profile surfaces** vs. thick ones
* Typically builds faster on tail than on main wings
* Can cause “**tail plane stall**”
* Tail plane holds nose up by creating **down force** on tail
* If down force removed, nose will pitch down
* Not controllable
* Typically builds faster on tail than on main wings
* Can cause “**tail plane stall**”
* Tail plane holds nose up by creating **down force** on tail
* If down force removed, nose will pitch down
* Not controllable
27
New cards
Recognition and Recovery from Tail Plane Icing
**Occurrence**
* May notice buffeting similar to a normal stall
* May occur after flaps have been deployed
* May occur at normal operating speeds
**Recognition**
* Pushing forward to recover will **increase buffeting**
* Correct recovery requires gentle back pressure to stop buffeting
* Autopilot may mask tail plane icing
* May notice buffeting similar to a normal stall
* May occur after flaps have been deployed
* May occur at normal operating speeds
**Recognition**
* Pushing forward to recover will **increase buffeting**
* Correct recovery requires gentle back pressure to stop buffeting
* Autopilot may mask tail plane icing
28
New cards
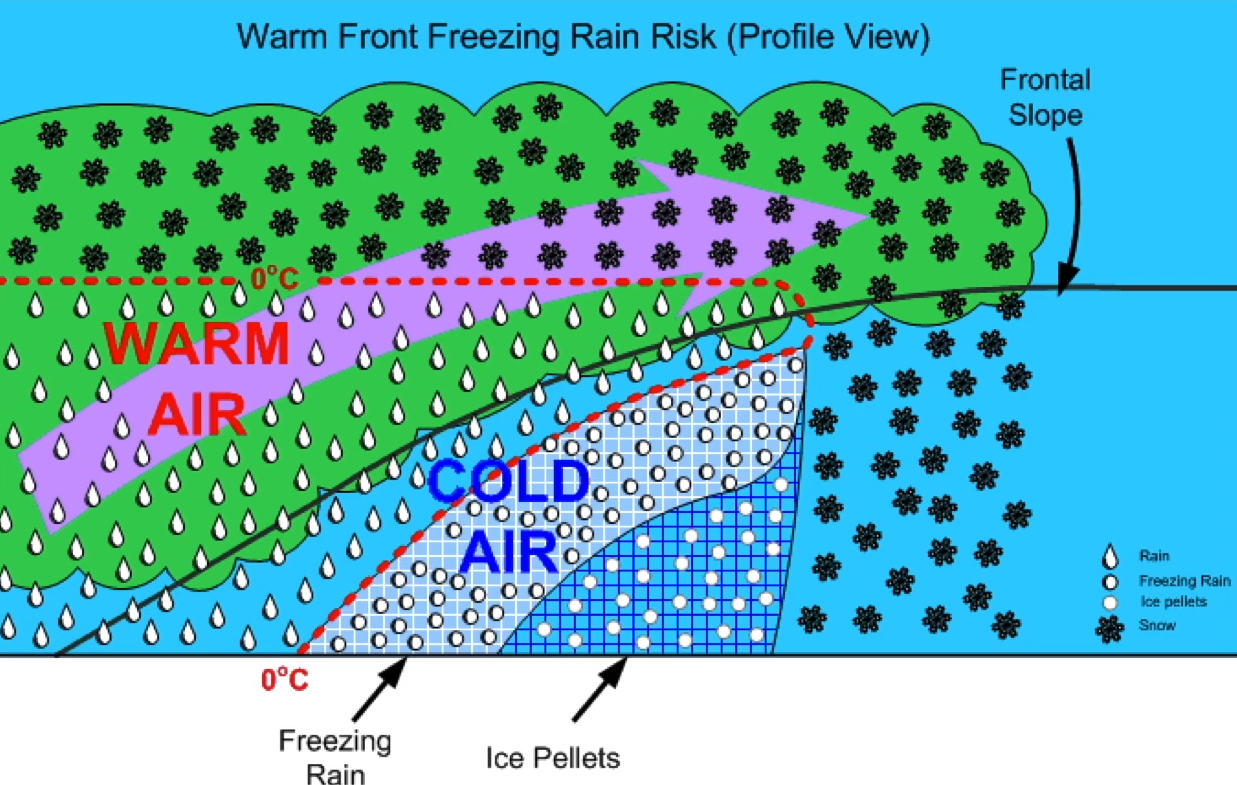
Winter Warm Front
* Common cause of airframe icing
* Allows for droplets to be within a **few degrees of freezing**
* Freezing Rain/Drizzle; problem to VFR pilots
\
* Allows for droplets to be within a **few degrees of freezing**
* Freezing Rain/Drizzle; problem to VFR pilots
\
29
New cards
Warm Front Freezing Rain Risk
Flying from **cold to warm side**
* Snow
* Ice pellets
* Freezing rain
* Rain
Flying from **warm to cold side**
* Rain
* Freezing rain
* Ice pellets
* Snow
* Snow
* Ice pellets
* Freezing rain
* Rain
Flying from **warm to cold side**
* Rain
* Freezing rain
* Ice pellets
* Snow
30
New cards
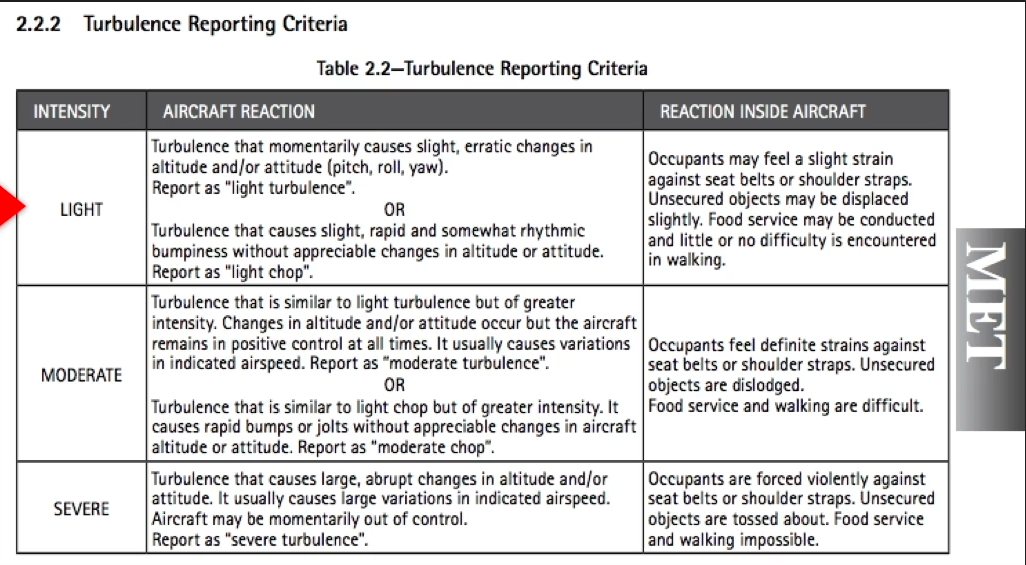
Turbulence/Wind Shear
* Problem: Aircraft is difficult to control and damage may occur
* Turbulence is rated according to table from AIM
* Wind shear is a problem for **take-off and landing**
* Turbulence is rated according to table from AIM
* Wind shear is a problem for **take-off and landing**
31
New cards
What causes wind shear?
* Air moving in different directions and/or speeds
Common near the ground with
* Thunderstorms
* Strong surface inversions
* Strong surface winds
* Common near fronts
Common near the ground with
* Thunderstorms
* Strong surface inversions
* Strong surface winds
* Common near fronts
32
New cards
What happens in wind shear?
* May experience and “uncommanded” change in airspeed and/or aircraft
* Aircraft could stall or overshoot the runway
* Aircraft could stall or overshoot the runway
33
New cards
**Increased Performance Shear**
* Increase in airspeed
* Decrease in rate of descent
* Decrease in rate of descent
34
New cards
**Decreased Performance Shear**
* Decrease in airspeed
* Increase in rate of descent
* Increase in rate of descent
35
New cards
Performance Shear
* Follows the headwind
* **“Headwind up”** → Performance up
* **“Headwind down” →** Performance down
* **“Headwind up”** → Performance up
* **“Headwind down” →** Performance down
36
New cards
Fog/Mist
* Restricts visibility
* Basically a cloud on the ground
* Fog is classified by the **process that contributes to its formation**
* **Fog →** ½ SM visibility or less
* Mist → More than ½ SM visibility
* Many processes which contribute to fog/mist formation
* Basically a cloud on the ground
* Fog is classified by the **process that contributes to its formation**
* **Fog →** ½ SM visibility or less
* Mist → More than ½ SM visibility
* Many processes which contribute to fog/mist formation
37
New cards
Types of Fog/Mist
* Radiation Fog
* Advection Fog
* Orographic (Upslope) Fog
* Arctic Sea Smoke
* Precipitation Induced Fog
* Advection Fog
* Orographic (Upslope) Fog
* Arctic Sea Smoke
* Precipitation Induced Fog
38
New cards
Radiation Fog
* Air is cooled from below by contact with the ground
* Requires **narrow temp/dew point spread** but enough water vapour to be significant
* Wind → 5 kts or less
* Clear skies at night will allow ground to cool quickly and aids in formation
* Requires **narrow temp/dew point spread** but enough water vapour to be significant
* Wind → 5 kts or less
* Clear skies at night will allow ground to cool quickly and aids in formation
39
New cards
Advection Fog
* **Advection:** Horizontal movement of air
* Moist air moving over a cooling surface causes air to cool to dew point
* Cooling surface: Cold water currents or land
* Prevalent in coastal areas
* Moist air moving over a cooling surface causes air to cool to dew point
* Cooling surface: Cold water currents or land
* Prevalent in coastal areas
40
New cards
Orographic (Upslope) Fog
* Requires a slope high enough to cause significant cooling
* Air is cooled adiabatically and is forced to rise until condensation occurs
* Prevalent where there are mountains but even a rise of a **few hundred feet** will work
* Air is cooled adiabatically and is forced to rise until condensation occurs
* Prevalent where there are mountains but even a rise of a **few hundred feet** will work
41
New cards
Arctic Sea Smoke
* Cold air moves over open portions of ice pack
* Air is quickly saturated and condensation occurs rapidly
* Looks like “smoke” coming out of the holes in the ice
* Air is quickly saturated and condensation occurs rapidly
* Looks like “smoke” coming out of the holes in the ice
42
New cards
Precipitation Induced Fog
* Air becomes saturated by rain evaporating as it falls
* Must have constant rain of sufficient duration to increase moisture content of the air
* When dewpoint = temperature you have fog
* Must have constant rain of sufficient duration to increase moisture content of the air
* When dewpoint = temperature you have fog