CompTIA Network+ (N10-009) (Concise) (Personal) (Continuously Editing)
1/125
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Personal flash cards based on what I got wrong and need to study more. I frequently edit and update them to try to get only Net+ Necessary info while being concise (15-20 words max). Terms and definitions largely based on DionTraining's Udemy exams
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
126 Terms
Network Baseline
Documented measurement of normal network performance & traffic
Used to detect abnormalities, misconfigurations, or security incidents
CIDR
Jumbo frames
Ethernet frames with MTU greater than 1500 bytes
Commonly used on SANs to improve performance
Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
Logically isolated virtual network in a public cloud
Where resources run with defined IP ranges and routing
NAT Gateway
Allows private VPC resources outbound internet access
While preventing direct inbound internet connections
Optimizing routing paths
Selecting more efficient network routes
To reduce latency and improve application response times
Wi-Fi PSK (Pre-Shared Key)
Single shared wireless password used by all clients for network access
Enterprise Wi-Fi
Uses 802.1X with RADIUS for per-user authentication
No shared PSK
Designed for managed corporate networks
MDF (Main Distribution Frame)
Central location where external provider cabling enters & terminates
Before distributing to internal network
Backdoor
Hidden access method
Allows unauthorized remote access
Actions aren’t logged
Doesn’t require normal authentication
Wiring Diagram
Shows exact cable-to-port connections (which cable plugs into which switchport)
Physical Network Diagram
Shows physical layout of devices and cabling
Not detailed port-to-cable labels
Logical Network Diagram
Shows
Traffic flow
Subnets
VLANs
Routing
logical relationships
Doesn’t show physical cabling
Site Survey Report
Wireless-focused document
Shows
Coverage
Signal strength
Interference
Access point placement
Voice VLAN
Separate VLAN on switch ports to prioritize VoIP traffic
Uses QoS markings (802.1p)
improves call quality
Data VLAN (Access VLAN)
VLAN assigned to workstation traffic on a switch port
Carries non-voice user data
VLAN Numbers (100, 200, etc.)
Numeric identifiers (1–4094)
Used to logically separate traffic
Numbers themselves have no inherent priority
Triple-homed firewall
Firewall with three interfaces
Connects internal network, external internet, & DMZ
tcpdump command
Command-line packet capture tool
Used to:
Analyze network traffic
Inspect packets in real time
dig command
DNS query tool
Used to verify
DNS records
Nameservers
Domain-to-IP mappings
802.11a
5 GHz band
Up to 54 Mbps
802.11b
2.4 GHz
Up to 11 Mbps
802.11g
2.4 GHz
Up to 54 Mbps
802.11n
2.4 GHz & 5 GHz
Up to 600 Mbps
802.11ac
5GHz
Up to 6.9 Gbps
802.11ax
2.4GHz &5GHz
Up to 9.6 Gbps
VXLAN
Encapsulation technology
Extends Layer 2 networks over Layer 3
Uses UDP tunneling
VXLAN Network Identifier (VNI)
24-bit identifier
Used to distinguish/separate different VXLAN overlay networks
VXLAN overlay network
Virtual Layer 2 network
Built over Layer 3 underlay
Uses VXLAN encapsulation
VXLAN Overlay vs Underlay
Overlay = logical network you design
Underlay = physical IP network carrying the traffic
Native VLAN
VLAN assigned to untagged frames on an 802.1Q trunk
Used for compatibility, not traffic prioritization
Packet-switched Network
Transmits data by breaking it into packets
Routed independently across network
Reassembled at destination
Firewall rules / ACLs
Ordered permit/deny rules evaluated top-down
First rule match stops further rule evaluation
Ends with an implicit deny
ACL rule order
Place specific rules before general rules so they are evaluated first
Implicit deny
All traffic not explicitly permitted is denied by default.
DENY ANY ANY
Blocks all traffic from any source to any destination
Teredo Tunneling
IPv6 transition technology
Encapsulates IPv6 traffic inside IPv4
Enables connectivity over IPv4-only networks
Twinaxial
Short-range high-speed copper cable
Used for:
Switch-to-switch links
SATA 3.0 connections
Link aggregation vs LACP
Link Aggregation is the general concept
LACP (802.3ad) is specific, automated protocol that manages this process dynamically
Routing Protocol Types (Contrast Card)
Distance Vector: Hop count
Link-State: Topology map
Path-Vector: AS paths between networks
Distance Vector
Routers share routes with neighbors
Selects paths using hop count
Example: RIP
Routing Convergence
Time required for routers to agree on best paths after a topology change
Link-State Routing (e.g., OSPF)
Routers share full topology
Calculate shortest path
Fast convergence
Higher overhead
Path-Vector Routing (BGP)
Uses AS-path info & policy to route between autonomous systems
Prioritizes policy, not speed
802.11h
Adds Dynamic Frequency Selection (DFS) and Transmit Power Control (TPC)
To comply with radar-avoidance regulations
Subnet Mask
Defines network & host portions of an IP address
Determines local subnet membership & whether traffic is routed
SIEM (Security Information and Event Management)
Centralizes & correlates logs
Provides real-time
Security alerting
Monitoring
Incident detection
Compliance reporting
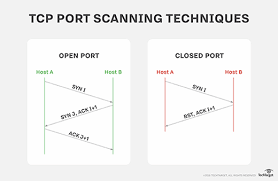
TCP SYN Scan Nmap flag
-sS
Performs a half-open (SYN) scan to identify open TCP ports
UDP Scan Nmap flag
-sU
Scans UDP ports to identify open services (DNS, SNMP, DHCP)
Service Version Detection Nmap flag
-sV
Identifies service types & version numbers running on open ports
Operating System Detection Nmap flag
-O
Attempts to determine the operating system of the target
Virtual IP (VIP)
Shared IP address
Provides a single access point to services hosted by multiple servers
Virtual IP (VIP) high availability
Enables load balancing & failover
Directs client traffic to available servers behind the VIP
LACP
Link Aggregation Control Protocol
Bonds multiple physical switch ports into one logical link for speed & redundancy
LACP Purpose
Increases bandwidth & fault tolerance between network devices by aggregating links
LLDP
Layer 2 discovery protocol
Used by devices to advertise identity, capabilities, and neighbors
L2TP (Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol)
Tunneling protocol used for VPNs
Not for increasing link speed or redundancy
Doesn’t provide encryption
LDAP
Application-layer protocol
Used to access and manage directory services, such as user authentication
Northbound Traffic
Network traffic exiting the datacenter to external networks through a firewall or router
Southbound Traffic
Network traffic entering the datacenter from external networks through a firewall or router.
East-West Traffic
Traffic flowing internally between systems within the datacenter, such as server-to-server communication.
Single-mode Fiber
Fiber with a small core
Carries one light path,
Supporting long distances & higher bandwidth
Multimode Fiber
Fiber with a larger core
Carries multiple light paths
Used for shorter distances
10GBase-FX
10 Gigabit Ethernet
Over single-mode fiber
Not compatible with copper cabling
10GBase-T
10-Gigabit Ethernet
Over twisted-pair copper
Uses Cat 6a cabling up to 100 meters
10GBase-SR
10-Gigabit Ethernet
Over multimode fiber
Uses short-range optical wavelengths
10GBase-SW
10-Gigabit Ethernet
Over fiber
Designed for SONET environments, not standard Ethernet LANs
Border Gateway Protocol Function
Exchange routing information between autonomous systems (AS)
Enables inter-domain routing across Internet
Autonomous System
Collection of IP networks
Under one administrative control
Share common routing policy
Interior vs exterior routing protocols
Interior gateway protocols route within an autonomous system
Exterior gateway protocols route between autonomous systems
RIP (routing protocol)
Distance-vector routing protocol using hop count
Maximum 15 hops
Slow convergence
Legacy networks
Interior gateway protocol
OSPF (routing protocol)
Link-state routing protocol using cost metric
Fast convergence
Commonly used in enterprise networks
Interior Gateway Protocols
EIGRP (routing protocol)
Cisco-proprietary hybrid routing protocol
Uses bandwidth & delay metrics
With fast convergence
BGP (routing protocol)
Path-vector exterior gateway protocol
Used to exchange routing information between autonomous systems
show vlan command
Displays
VLAN IDs
Names
Associated switch ports
Showing network segmentation
show interfaces command
Displays
Interface status
Speed
Duplex
Error counters
Not VLAN segmentation details
show mac address-table command
Displays
MAC addresses learned by switch
Corresponding switch ports for Layer 2 forwarding
Primary DNS server
Main DNS server that holds the writable master copy of the zone file
Secondary DNS server
Holds read-only copy of zone data
Used for load reduction, redundancy, and availability
Authoritative DNS server
Directly answers queries for zones it hosts, either primary or secondary
Recursive DNS server
Resolves names by querying other servers
Doesn’t store authoritative zone files
Network Metrics
Represent quantitative value
Used to determine the best route in routing protocols
VLAN tagging
802.1Q process
Marks Ethernet frames to identify which VLAN they belong to
Layer 2 of the OSI model
Tunneling
Encapsulating packets within another protocol
Done so they can traverse an incompatible/untrusted network
VPN Tunneling Protocols
IPsec & TLS
Commonly used tunneling protocols for VPNs
Tunneling uses
To securely transport VPN traffic across public or untrusted networks
Encapsulation
Process of adding headers and trailers as data moves from OSI Layer 7 down to Layer 1

De-encapsulation
Process of removing headers and trailers as data moves from OSI Layer 1 up to Layer 7
Encapsulation vs de-encapsulation direction
Encapsulation moves Layer 7 to 1 at sender
De-encapsulation moves Layer 1 to 7 at receiver
Signal Degradation
Signal quality loss
Due to
Distance
Interference
Congestion
in Wi-Fi, often worsens during peak usage hours
NTP
Network Time Protocol
Synchronizes clocks over networks
Millisecond-level accuracy for most systems
PTP
Precision Time Protocol
Provides sub-microsecond clock synchronization
Typically used in industrial, telecom, or financial networks
PTP vs NTP
NTP offers general-purpose time sync
PTP provides higher precision using hardware timestamping on supported networks
MAC Spoofing
An attack where a device falsifies its MAC address to impersonate another device on a local network
IP Spoofing
An attack where a packet’s source IP address is forged to impersonate another host
ARP Spoofing
An attack where false ARP messages map an attacker’s MAC address to a legitimate IP address
MAC vs IP vs ARP spoofing difference
MAC spoofs hardware address
IP spoofs source IP
ARP spoofs IP-to-MAC mappings on local networks
IPv4 address Class A range
First octet 1–126
Default subnet mask 255.0.0.0 (/8)
Very large networks
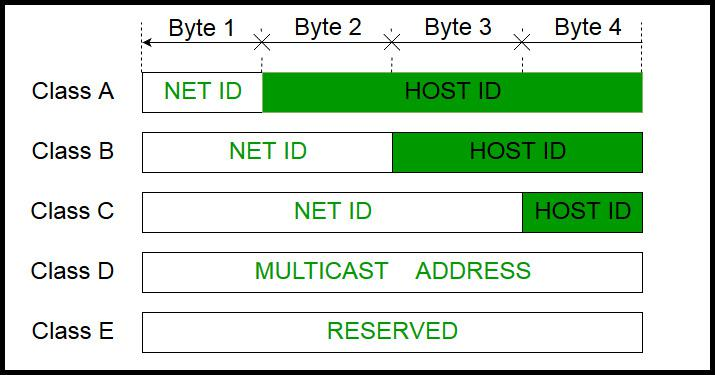
IPv4 address Class B range
First octet 128–191
Default subnet mask 255.255.0.0 (/16)
Medium-sized networks
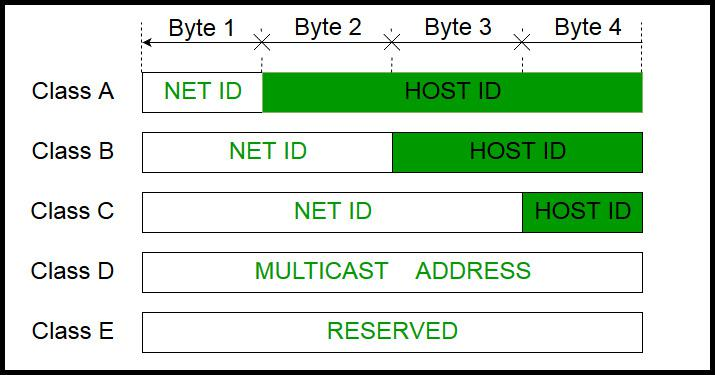
IPv4 address Class C range
First octet 192–223
Default subnet mask 255.255.255.0 (/24)
Small networks.