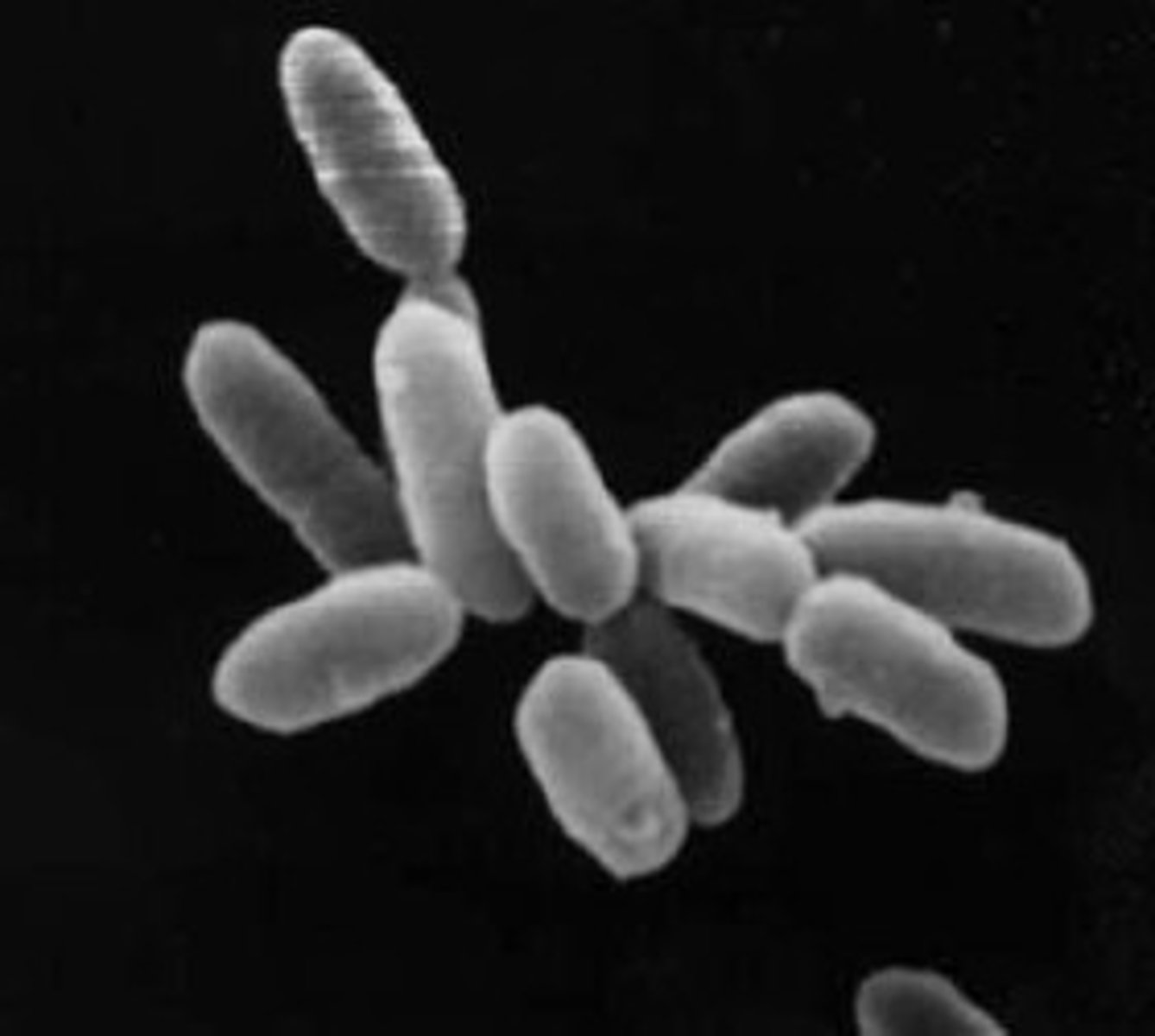
Microbial Biology: Prokaryotes, Archaea, and Bacterial Structures
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Can microbes live in lava?
No, it's too hot (1000°F). They can live in volcanic deposits, not lava.
What does "prokaryote" mean?
"Pro" = before, "kary" = nucleus → No true nucleus, no membrane-bound organelles.
Biodiversity fact
Bacteria = 78% of known global biodiversity.
Size of bacteria
0.5-1 μm wide, 1-2 μm long. Red blood cell = 5 μm.
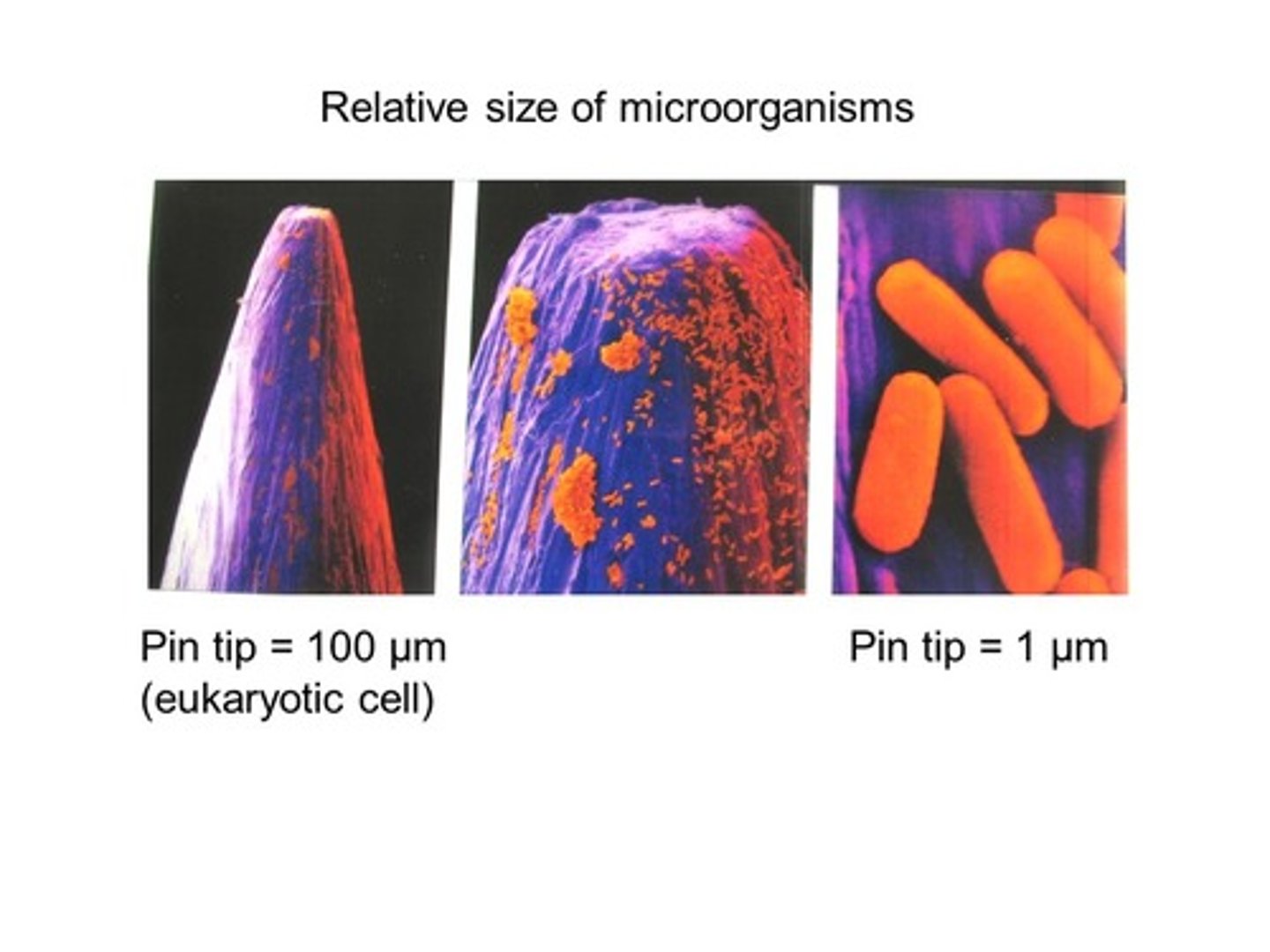
Why do bacteria replicate so fast?
High surface-area-to-volume ratio.
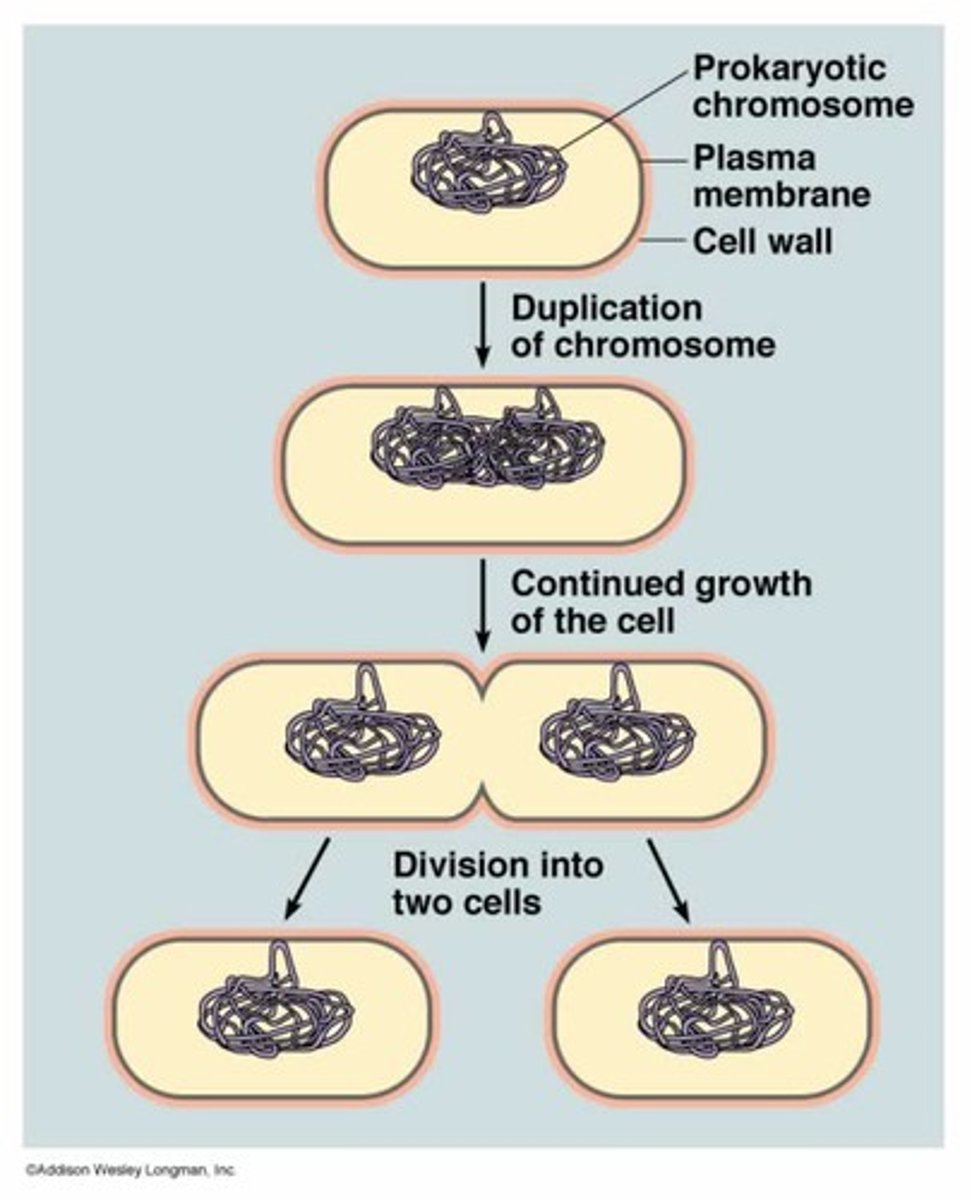
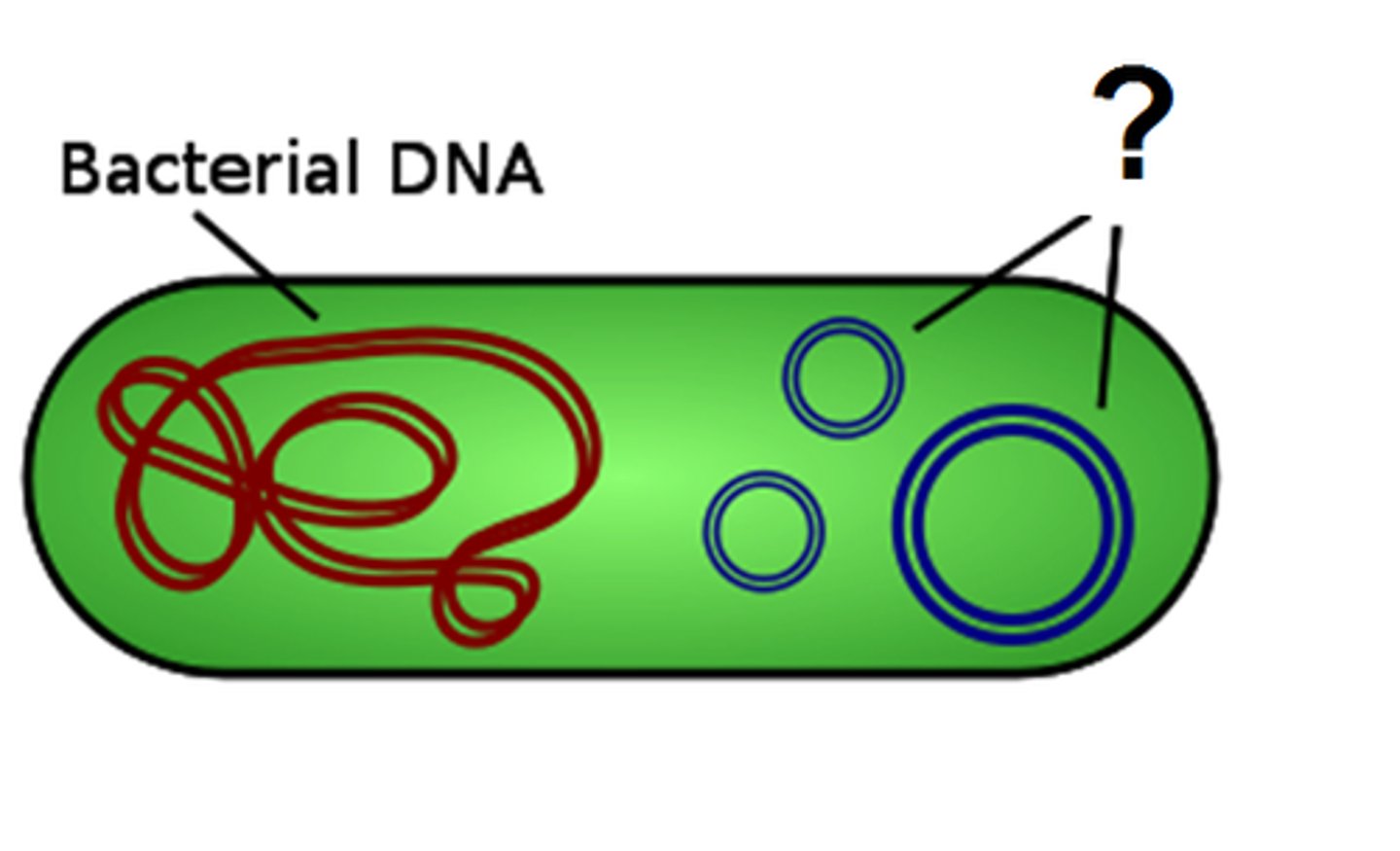
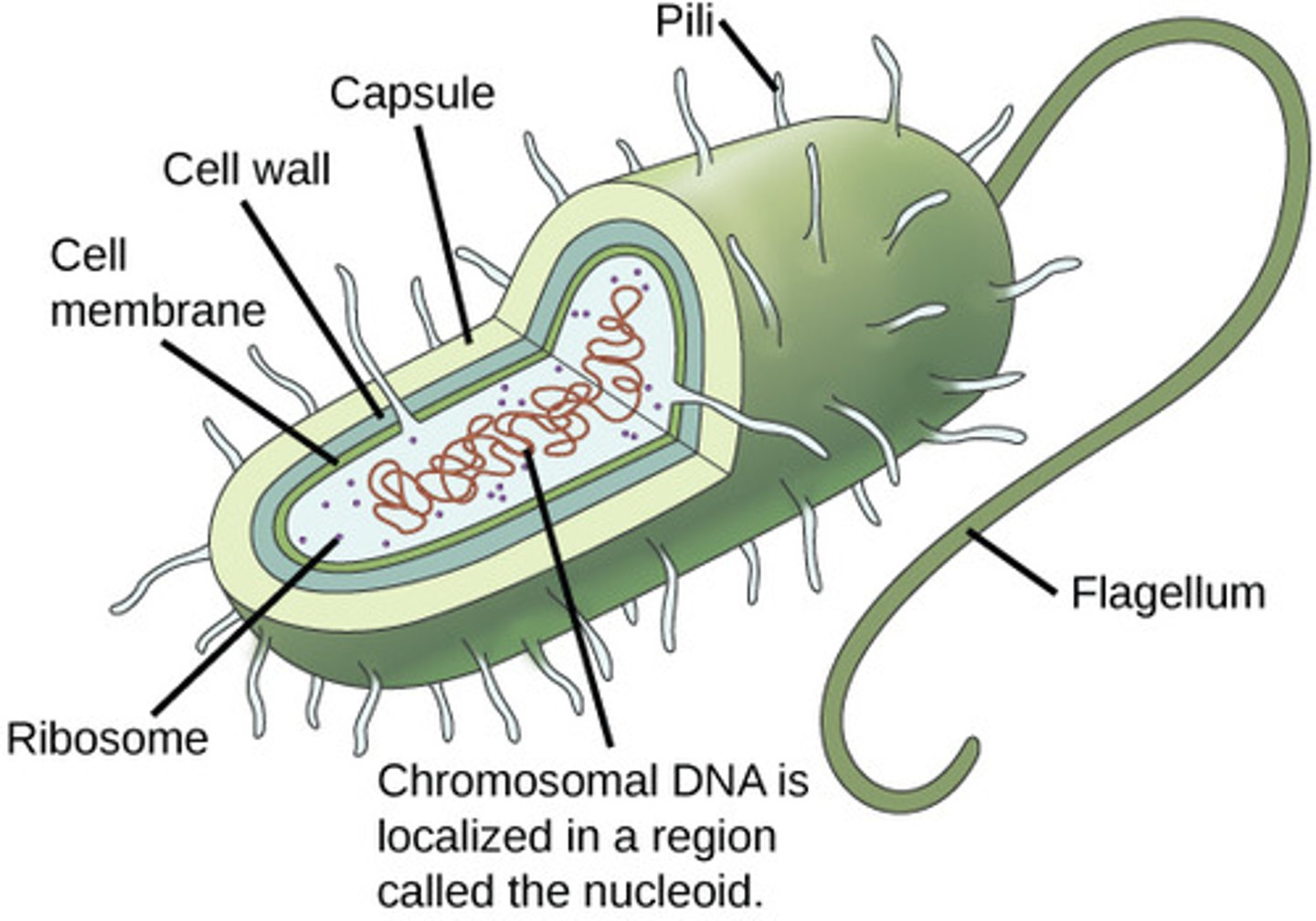
Nucleoid
circular chromosome (DNA)
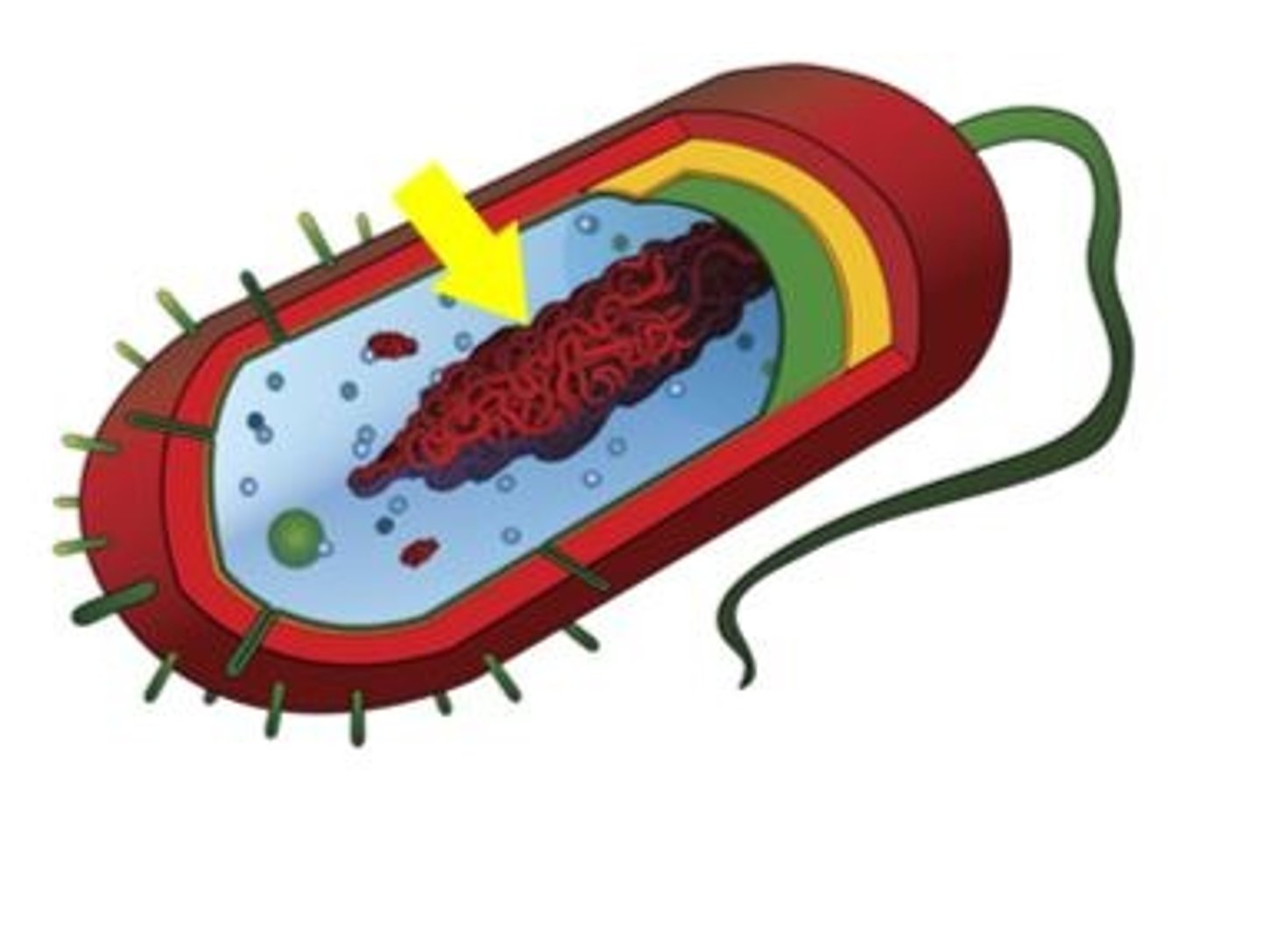
Plasmids
Small, extra DNA, not required for survival but beneficial
Ribosomes
Protein synthesis
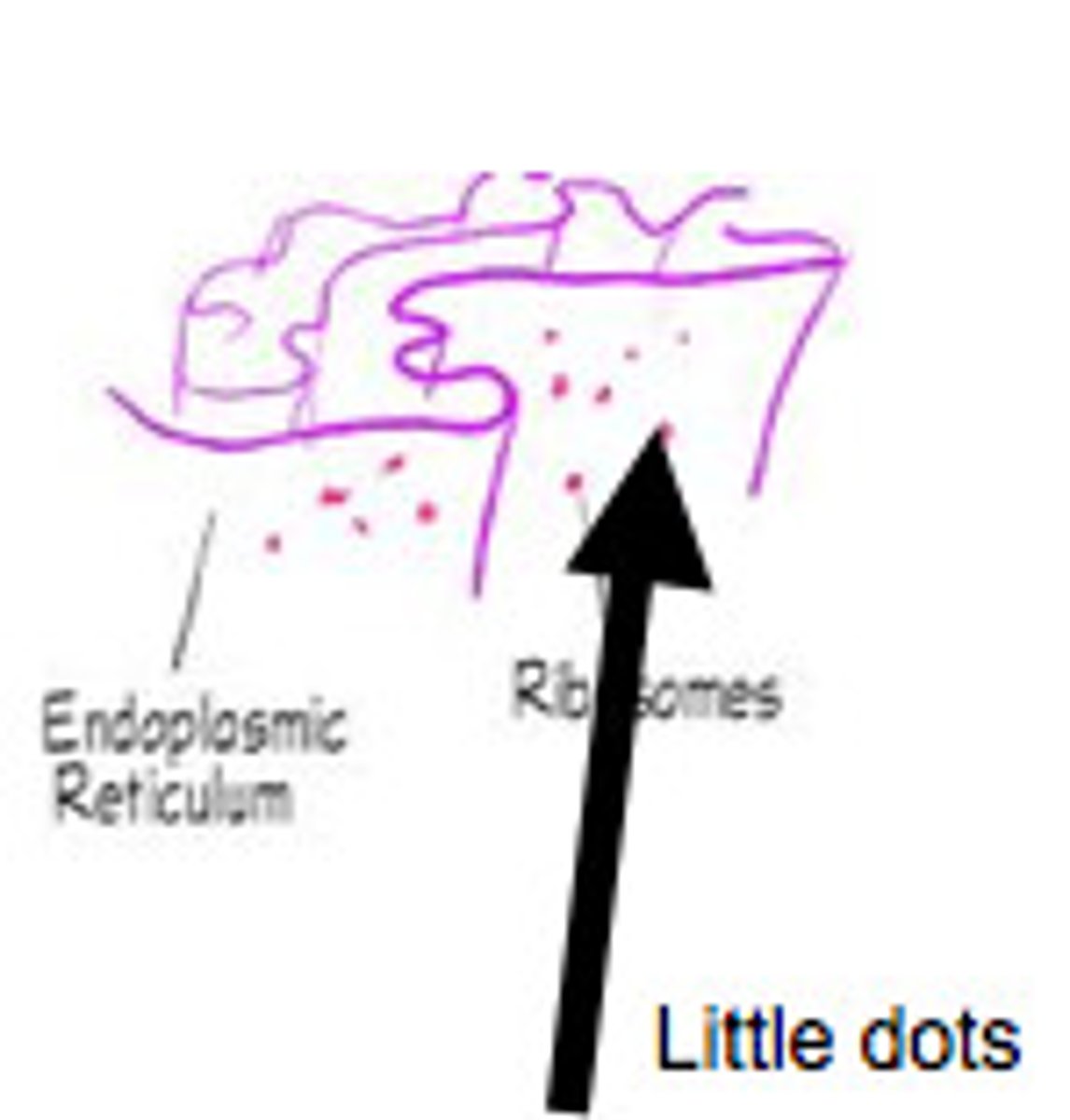
Cytoplasm
Gel matrix holding ribosomes and molecules
RNA types
mRNA (codes), rRNA (ribosome core), tRNA (brings amino acids)
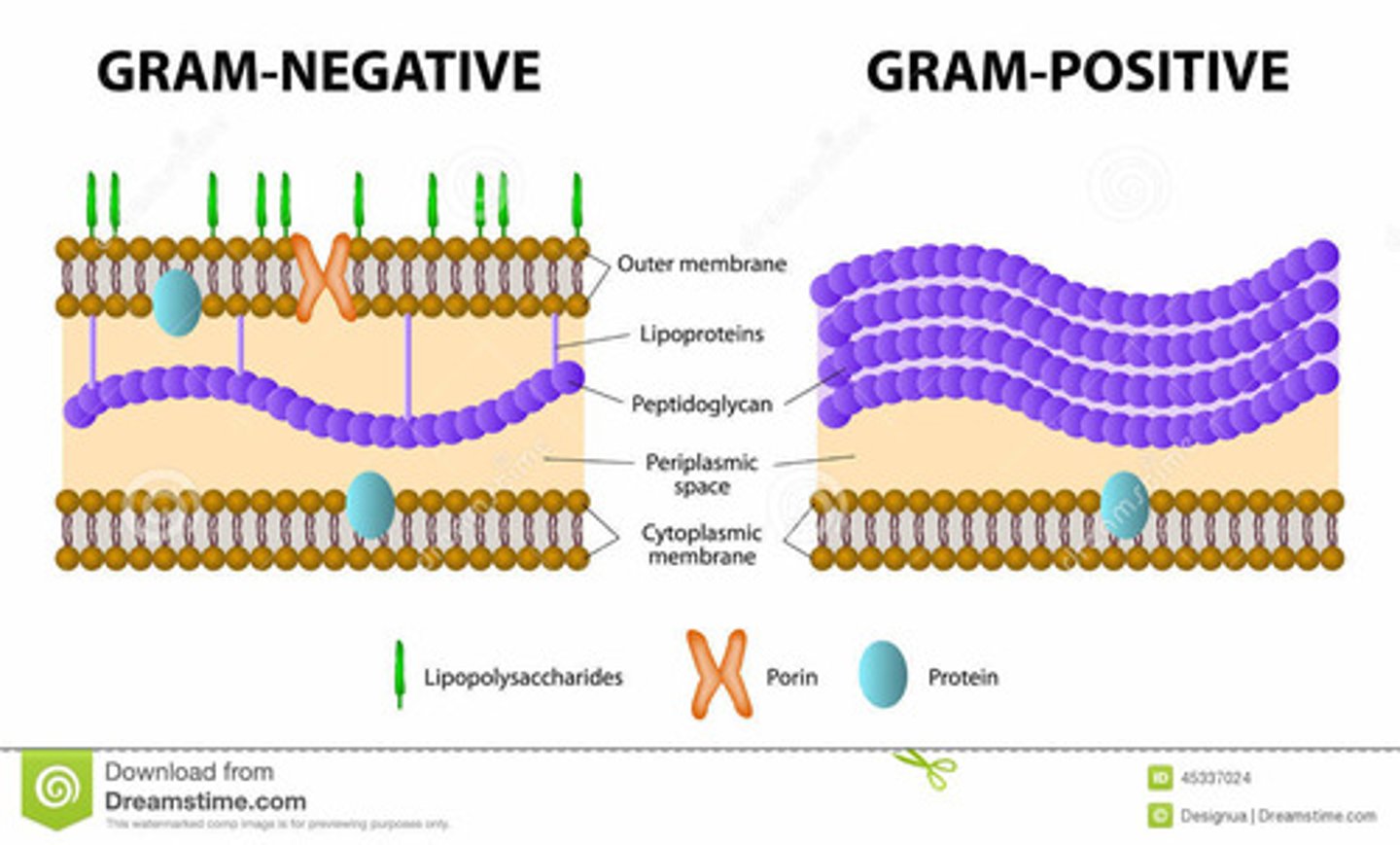
Gram Positive
- Thick peptidoglycan → stains purple.
- "Monoderm."
- Has teichoic acids (immune response, adhesion).
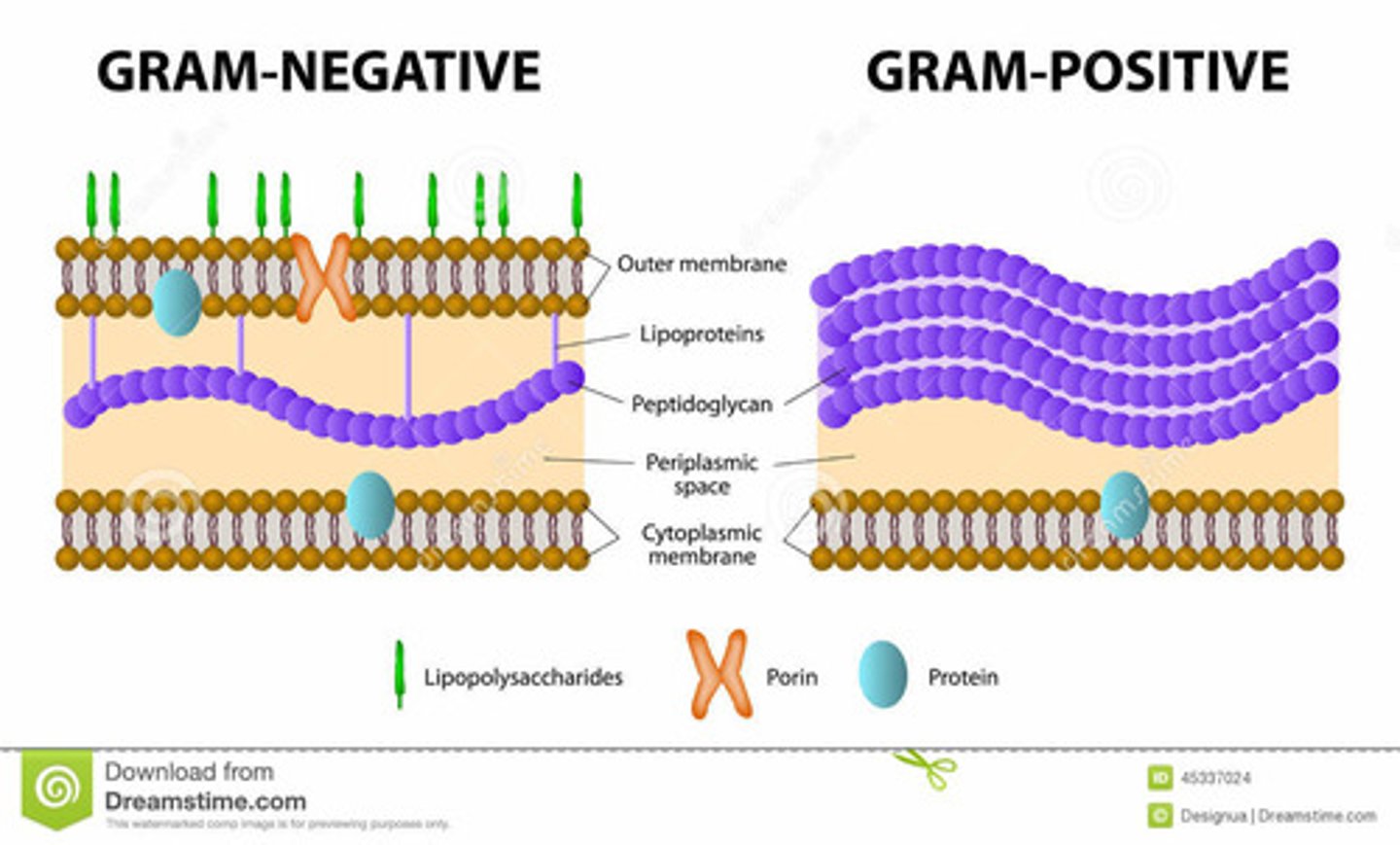
Gram Negative
- Thin peptidoglycan → stains pink.
- "Diderm."
- Outer membrane with LPS (lipopolysaccharides → toxic response).
- Periplasmic space with enzymes & transport proteins.
Glycocalyx (capsule/slime layer)
- Extra polysaccharide coating.
- Protects against drying, predation, antimicrobials.
- Helps with surface attachment & biofilm formation.
Flagellum
motility
Fimbriae
attachment, not motility
Pilus
- only in Gram -
- used in conjugation (DNA transfer)
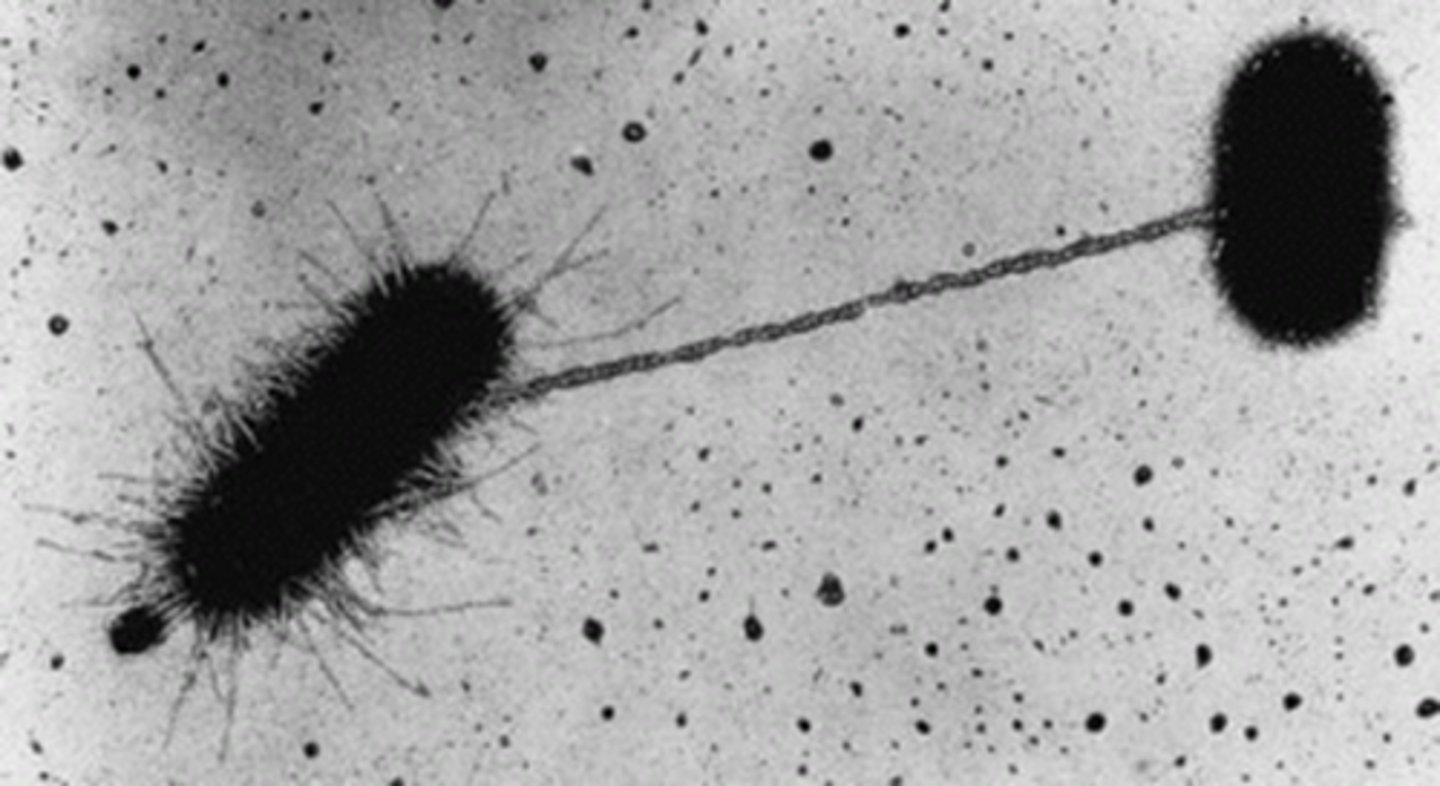
Conjugation
Pilus forms, plasmid strand transferred
Transformation
Uptake of free DNA from environment
Transduction
Bacteriophages transfer bacterial DNA between hosts
Archaea's similarities to Bacteria
- Size
- Shape
- Lack Nucleus
Archaea's differences to Bacteria
- Cell membranes have ether linkages
- Use phytanyl sidechains (more stable in extreme environments)
- Genes & Enzymes more similar to eukaryotes
Where Archaea Lives
High Salt, hot springs, hydrothermal vents, wetlands, acid mine drainage
what is archaea
prokaryotes that often live in Earth's extreme environments