PSYCH 105 FLASHCARDS: Ch 2, 9, 10
1/135
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
136 Terms
Empiricism
belief that accurate knowledge of the world can be acquired through observation
Dogmatism
tendency to adhere to one’s beliefs without consideration for evidence or others opinions
Scientific Method
procedure using empirical evidence to establish facts by developing a theory, deriving a hypothesis from the theory, and to test the hypothesis through observation
Theories
explanations of natural phenomena
Hypothesis
falsifiable prediction made by a theory
Empirical Method
a set of rules and techniques for observation
Operational Definition
a description of a property in measurable terms
Construct Validity
how well an operational definition represents or reflects a concept that is not directly measurable
Power
ability of a measure to detect the conditions specified in the operational definition
Reliability
ability for a certain property to consistently and accurately measured
Demand Characteristics
aspects of observational setting that cause people to behave as they think someone else wants or expects
Naturalistic Observation
technique for gathering information by unobtrusively observing people in their natural environments
Observer Bias
tendency for observer’s expectations to influence what is believed to be observed and what is actually observed
Double-Blind Study
study in which neither researcher nor participant knows how the participants are expected to behave
Population
complete collection of people
Sample
a partial collection of people drawn from a population
Frequency Distribution
a graphic representation displaying the how often a property appears in a dataset
Negatively Skewed Distribution
more values are concentrated on the right side of a distribution
Positively Skewed Distribution
more values are concentrated on the left side of a distribution
Normal Distribution
distribution in which the frequency of measurements is highest in the middle and decreses symmetrically in both directions
Descriptive Statistics
summary statements capturing the essential information from a frequency distribution
Central Tendency
descriptive statistic that attempts to describe a whole set of data with a single value that represents the middle of a distribution
Mode
central tendency measuring the most frequently observed value
Mean
central tendency measuring the average value of all the measurements
Median
central tendency measuring value in the middle of the frequency distribution
Range
value of the largest measurement minus the value of the smallest measurement in a frequency distribution
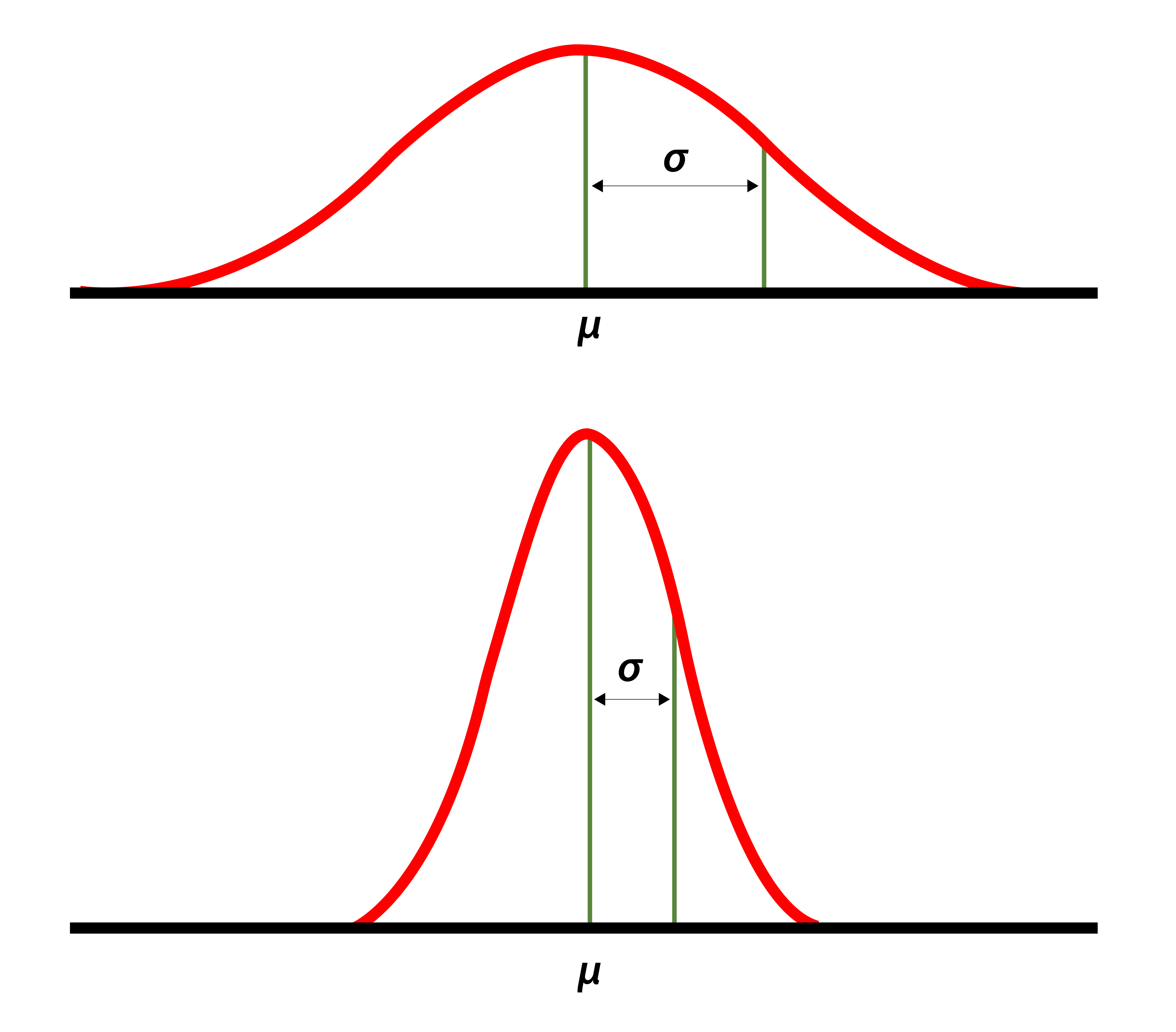
Standard Deviation
statistic describing how each measurement differs from the mean; high SD=values in frequency distribution are further apart, low SD=values in frequency distribution are closer together
Variables
properties that can change/be assigned to different values
Correlation
statistical relationship between variables measuring the degree to which the variables are linearly related
Correlation Coefficient
mathematical measure of the direction and strength of a correlation symbolized by the letter r
Perfect Positive Correlation
y increases by the same value as x, r=1
Perfect Negative Correlation
y decreases by the same value x increases, r=-1
No Correlation
there is no relationship between x and y values, r=0
Natural Correlation
correlation observed in the natural world
Third-Variable Problem
natural correlation between two variables cannot be taken as evidence of a causal relationship because a third variable may be causing them both
Experimentation
technique for establishing the causal relationship between variables
Manipulation
technique for determining the causal power of a variable by actively changing its value
Independent Variable
the variable manipulated in an experiment
Dependent Variable
variable that is measured in an experiment
Self-Selection
problem occurring when anything about a participant determines the value of the independent variable to which the participant was exposed
Random Assignment
procedure assigns participants to conditions by chance
Statistical Significance
measures the likelihood that the results of data generated by testing or experimentation can be attributed to a clear and identifiable source rather than by chance; p<0.5
Internal Validity
extent to which a piece of evidence supports a claim about cause and effect, within the context of a particular study
External Validity
extent to which variables have been operationally defined in a representative way that can be applied outside the context of a particular study
Case Method
procedure for gathering scientific information by studying a single individual
Random Sampling
technique for selecting participants that ensures that every member of a population has an equal chance of being included in the sample
Replication
experiment using the same procedures as a previous experiment with a new sample from the same population
Type I Error (False Positive)
conclusion of a causal relationship between two variables when there is not
Type II Error (False Negative)
conclusion that there is no casual relationship between two variables when there is
Sir Francis Bacon
described a new method for discovering facts about the natural world (scientific method)
Informed Consent
verbal agreement made by an adult informed of all possible risks to participate in a study
Debriefing
verbal description of the true nature and purpose of a study
Replacement
researchers must prove there is no alternative to using animals in research and that animal use is justified by the scientific/clinical value of the study
Reduction
researchers must use the smallest number of animals possible to achieve their research
Refinement
procedures must be modified to minimize discomfort, infection, illness, and pain for animals
Language
system for communicating with others using signals that are combined according to rules of grammar and used to communicate
Grammar
set of rules that specify how the units of language can be combined to produce meaningful messages
Phonemes
smallest units of speech distinguishing one word from another
Phonological Rules
indicate how phonemes can be combined to form words
Morphemes
smallest meaningful units of language
Morphological Rules
indicate how morphemes can be combined to form words
Function Morphemes
serve grammatical functions
Content Morphemes
refer to things and events
Syntactic Rules
indicate how words can be combined to form phrases and sentences
Overregularizing
part of the language-learning process in which children extend regular grammatical patterns to irregular words
0-4 Months
language milestone where infants can tell the difference between all possible phonemes, cooing especially in response to speech
4-6 Months
language milestone where infants babble consonants
6-10 Months
language milestone where babies understand some words and simple requests
10-12 Months
language milestone where toddlers begin to use single words and cannot distinguish phonemes outside of their native language
12-18 Months
language milestone where toddlers have a vocabulary of 30-50 words including simple nouns, adjectives, and action words
18-24 Months
language milestone where two-word phrases are ordered according to syntactic rules, vocabulary consists of 50-200 words, and rules are understood
24-36 Months
language milestone where children have a vocabulary of about 1000 words and produce phrases and incomplete sentences
36-60 Months
language milestone in children where vocabulary grows to more than 10000 words, full sentences are produced, mastery of grammatical morphemes and function words, can form questions and negations
Telegraphic Speech
speech devoid of function morphemes, consisting of mostly content words
Nativist Theory
language development is best explained as an innate biological capacity
Universal Grammar
collection of processes that facilitate language learning, postulating that there are innate constraints on the grammar of a possible human language
Wernicke’s Area
area in the left temporal cortex involved in language comprehension (spoken or signed)
Wernicke’s Aphasia
inability to comprehend speech, producing grammatically correct speech that conveys no mearning
Broca’s Area
area in the left frontal cortex involved in the production of sequential patterns in vocal and sign languages
Broca’s Aphasia
inability to produce speech & proper grammatical structure
Aphasia
difficulty in producing or comprehending language
Linguistic Relativity Hypothesis
idea developed by Whorf that language shapes the nature of thought
Concept
mental representation that groups or categorized shared features of related objects, events, or other stimuli
Necessary Condition
condition that must be true of the object in order for it to belong to the category
Sufficient Condition
condition that guarantees, by its presence alone, the desired outcome. It is sufficient to belong to the category, regardless of any other factors
Prototype Theory
concept that new objects are classified by comparing them to the “best” or “most typical” member of a category
Exemplar Theory
category judgements are made by comparing a new instance with stored memories of other instances of the category
Category-Specific Deficit
neurological syndrome characterized by an inability to recognize objects belonging to a particular category, even when object recognition for other categories is undisturbed
Rational Choice Theory
classical view that decisions are made by determining how likely something is to happen, judging the value of the outcome and multiplying the two
Availability Heuristic
items more readily available in memory are judged as having occurred more frequently
Heuristic
process by which humans use mental shortcuts to arrive at decisions, not necessarily always right or accurate
Algorithm
well defined sequence of procedures or rules that guarantee a solution to a problem
Representativeness Heuristic
mental shortcut involving making a probability judgement by comparing an object/event with a prototype of the object/event
Conjunction Fallacy
belief that two events are more likely to occur together rather than separately
Framing Effects
cognitive bias where people's decisions change depending on how options or statements are framed, even when they are logically identical
Sunk-Cost Fallacy
framing effect in which people make decisions about a current situation on the basis of what they have previously invested in the situation
Optimism Bias
individual belief that they are more likely to experience positive events and less likely to experience negative events in the future
Prospect Theory
individuals choose to take on risks when evaluating potential losses and avoid risks when evaluating potential gains
Ill-Defined Problem
problem with no clear goal or defined path to a solution
Well-Defined Problem
problem with clearly specified goals and clearly defined solution paths