BACTE_Finals_Lec: Vibrio, Aeromonas, Camplylobacter (copy)
1/88
Earn XP
Description and Tags
CM = Colony Morphology
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

89 Terms
Vibrio species
Commonly found in wide variety of aquatic environments, they are responsible for marine and freshwater diseases, including gastroenteritis.
V. cholerae
most common Vibrio species that causes diarrhea
consumption of raw seafood
recent immigration of foreign travel
Gastroenteritis with cholera like or rice water stools
Accidental trauma with marine water products (shellfish,oyster or clam shells, fishhooks
Factors in identifying vibrio infection
V. cholerae O1
V. cholerae O139
V. parehaemolyticus
V vulnificus
most common vibrio spp.
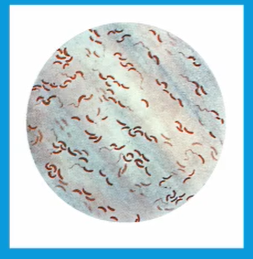
Asporogenous, curved (comma) or pleomorphic gram (-) rods
Micro Morpho of Vibrio
V. metschnikovii
All vibrio spp. are CPOP and Nitrate reduction except what sp.
susceptible @ 150 ug
Vibrio are 0/129 (Susceptible/resistant), at what concencetration
MAC
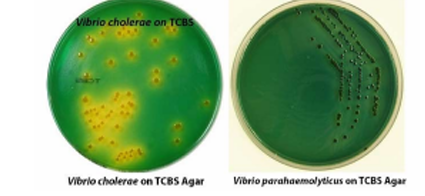
> TCBS (Thiosulfate Citrate Bile Sucrose) Agar
Culture media where vibrio spp. can grow?
> what routine media?
> Vibrio
> 0.5% Sodium desoxycholate
these ____ spp. are (+) in string test after emulsification of colonies in _% _____
V. cholerae, V. mimicus
The only Vibrio spp. that are not halophilic (salt-loving)
sodium
What is added on the culture media in order for Vibrio spp. to grow?
V. cholerae O1
V. cholerae O139
V. cholerae non-O1
3 major subgroups of Vibrio
Flagellar (H) antigen
Somatic (O) Antigen
V.F of 3 major subgrps. of V. cholerae
Ogawa (India)
Inaba (Philippines)
Hikojima (Japan)
3 serotypes of V. Cholerae O1 organims
V. cholerae
Causative agent of cholera aka Asiatic cholera or epidemic cholera
Cholera toxin (Choleragen)
a protein enterotoxin that is responsible for rice watery stool
azithromycin (AZM)
ciprofloxacin (CPFX)
Antibiotics for Cholera
2 types of cholera
Classical type
El tor Type - more serious type
Voges-Proskauer Test
Polymyxin B
Serological test using Chicken RBC as Antigen
Tests used to differentiate Classical Type and El Tor Type of Cholera
<insert image for Classic vs El Tor Type>
Determine the test result
VIBRIO PARAHAEMOLYTICUS
causes summer diarrhea
raw, improperly cooked seafood (i.e. oysters)
Kanagawa-toxin positive
Kanagawa-toxin
This is a toxin that Produces a heat-stable hemolysin that is able to lyse human erythrocytes in a special, high salt mannitol medium Wagatsuma Agar
Wagatsuma Agar
a special high salt mannitol medium used for the detection of Kanagawa Toxin
V. alginolyticus
(V. alginolyticus/V. vulnificus) is Least pathogenic; most frequently isolated
V. vulnificus
(V. alginolyticus/V. vulnificus)
has Two categories of infection:
primary septicemia
wound infections
Vibrio
This genus:
in SBA and CAP colonies: medium to large colonies that appear smooth, opaque, and iridescent with a greenish hue
a and B- hemolysis
hemolytic pattern of Vibrio on SBA
V. vulnificus
T/F
ALL Vibrio spp. in MAC are Lactose fermenter except what Vibrio sp.
No, V. vulnificus is NLF
Are all Vibrio spp. Lactose fermenters?
Vibrio spp.
Determine what genus:
MAC and CIN agar can give false-positive oxidase reactions
Cary-Blair Media
Transport media for Vibrio
not recommended
For Vibrio spp:
Buffered Glycerol Saline - (not recommended/recommended) for transport
TCBS (thiosulfate citrate bile salt sucrose agar)
Recommended selective medium for Vibrio spp.
Vibrio spp. - NON-SUCROSE FERMENTER
V. mimicus
V. parahaemolyticus
V. damsela
V. vulnificus strains
(My Pair of Dancing Vulgar)
Vibrio spp. - SUCROSE FERMENTER
Tip: FFACC Me
V. cholerae
V. alginolyticus
V. fluvialis
V. furnissii
V. cincinnatiensis
V. metschnikovii
alkaline peptone water with 1% NaCl can be inoculated (at least 20 mL) and incubated for 5 to 8 hours at 35° C before subculturing in TCBS
Enrichment procedure for Vibrio spp. before subculture in TCBS
V. cincinnatiensis
some strains of V. metschnikovii
All Vibrio spp. are inositol nonfermenter except
(+) in String test
(+) in Vibriostatic agent O/129
what tests separates Vibrio from Aeromonas
V. cholerae - B-hemolysis
V. parahaemolyticus - a-hemolysis
Based on the picture describe the hemolytic pattern of the ff Vibrio spp.
(-) in inositol fermentation
what test separates Vibrio from Plesiomonas
(+) Oxidation rxn
what test separates Vibrio from Enterobacteriaceae excluding Plesiomonas
(+) Carbohydrate metabolism
what test separates Vibrio from Pseudomonas
Aeromonas
these species live in similar environment like Vibrio but prefer fresh water
A. hydrophila
A. sobria
A. caviae
Major clinical specimens of Aeromonas
A. caviae
most commonly isolated Aeromonas sp.
Motile with single tuft of flagella
Aeromonas Motility:
A. caviae
Aeromonas sp. mostly associated with gastrointestinal (GI) infection
Cellulitis
most common presentation of wound infection by Aeromonas sp.
Aeromonas
Genus:
COLONY APPEARANCE: large, round, raised, opaque colonies with an entire edge and a smooth, often mucoid surface
strong B-hemolysis
hemolytic pattern of Aeromonas
Mannitol
Aeromonas spp:
CIN colony appearance – pink-centered colonies (____ fermentation)
Oxidase test
this test separates the Oxidase (+) Aeromonas from Oxidase (-) Yersinia
positive (+)
ALL AEROMONAS are Indole (+/ -)
Aeromonas: (-)
Plesiomonas: (+)
Aeromonas vs. Plesiomonas in term of Inositol test
String test where Aero. are (-) and Vibrio is (+)
What test separates Aeromonas from Vibrio
A. caviae
Aeromonas sp. that is Lactose Fermenter
True
T/F:
Aeromonas are overlooked as normal biota E. coli in MAC
resistant
Aeromonas spp:
Vibriostatic O/129 (resistant/susceptible)
Camp. are asaccharolytic (non-fermenters)
what makes Campylobacter diff from Vibrio in terms of carb. fermentation
C. jejuni subsp. jejuni
C. coli
C. fetus subsp. fetus
3 spp. of Camp.
C. jejuni
among the Campylobacter spp.:
most common cause of bacterial gastroenteritis worldwide
C. fetus
Camp. sp.: causative agent of bacteremia
C. jejuni
Camp. sp.: causative agent of Guillain-Barre Syndrome
GUILLAIN- BARRE SYNDROME
an autoimmune disorder with acute paralysis due to PNS destruction caused by Campylobacter jejuni
Helicobacter pylori
Helicobacter s.: important species
H. pylori
bacteria that is a major cause of type B gastritis or peptic ulcer
Helicobacter pylori
_______ (bacteria) is a carcinogenic agent that causes gastric carcinoma during long term infection
True
T/F: Camp. and Hel. are considered fastidious
Cary-Blair medium
transport medium for Campy. spp.
Buffered-glycerol saline
transport medium that should be avoided in transporting Campy. spp.
blood with incubation at 35◦C to 37◦C
specimen choice for C. fetus
gastric biopsy material
Spx. for Helicobacter pylori
Stuart medium
Cysteine-brucella Broth with 20% glycerol and frozen at −70° C
Transport medium fro H. pylori specimens; and
their Storage condition
CampyBAP (blood agar plate)
selective media for C. jejuni
Butzler medium and Skirrow’s medium
other medium for C. jejuni aside from Campy Blood Agar Plate (CampyBAP)
CAP
Brucella agar with 5% Horse red blood cells
Commonly used media for H. pylori
Skirrow’s agar
Selective media for H. pylori
Vancomycin
Trimethoprim
Polymyxin B
Amphotericin B
Cephalothin
Antimicrobial agents of Campy Blood agar plate
(Tip: VTPAC)
Incubation temp for
C. jejuni - 42 C
H. pylori - 37 C
Incubation temp for
C. jejuni
H. pylori
Both
(Both/Neither) Campylobacter spp. and Helicobacter spp. require a microaerophilic and capnophilic environment
aerobic (O2) and anaerobic (CO2) conditions for
Campy. - – 5% O2, 10% CO2
Heli. - 5% to 10% O2 and 5% to 12% CO2
aerobic (O2) and anaerobic (CO2) conditions for
Campy.
Heli.
Campylobacter spp.
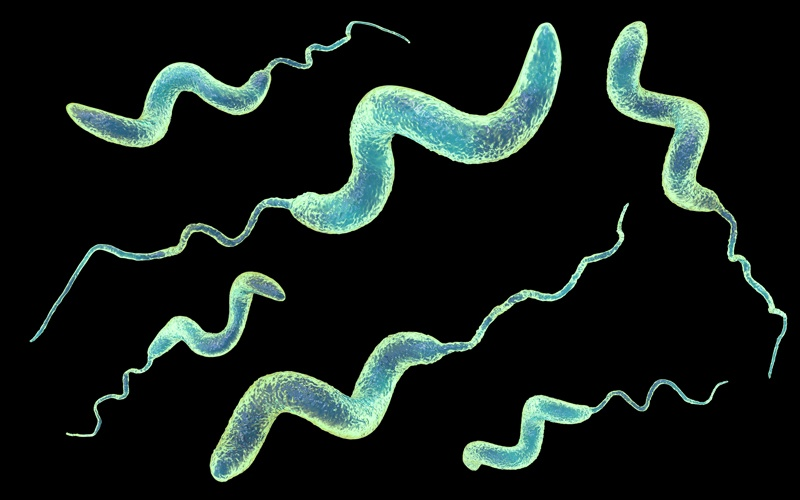
curved non–spore-forming, gram-negative rods
May appear as long spirals or ‘S’ or seagull-wing shapes
Carbol fuchsin
recommended as a counterstain fro Campy.
Campylobacter
“Darting” motility (corkscrew movement) on hanging drop preparations
Brucella or Tryptic Soy Broth
(motility can be inhibited by Distilled water or saline)
medium used for motility testing of Campy. spp.
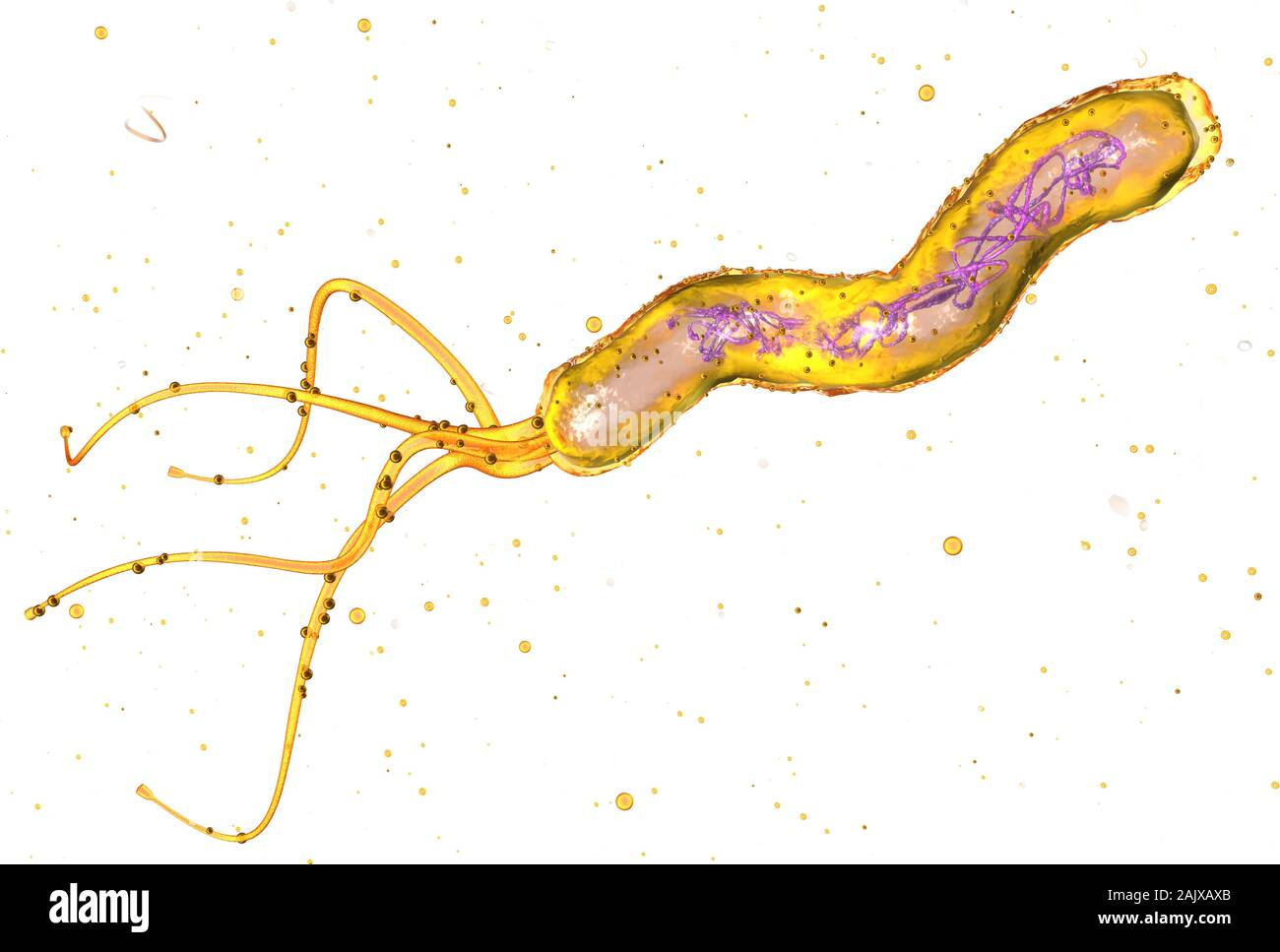
Helicobacter spp.
➢ Curved or U-shaped
➢ Motile with multiple flagella at one pole
smooth, convex, translucent colonies
CM of C. fetus subsp. fetus
moist, runny looking, and spreading
nonhemolytic
some are round and raised and others may be flat
CM of C. jejuni and other enteric Campylobacters
Campy | Heli. | |
Oxidase | + | + |
Urease | (-) (C. jejuni) | + (H. pylori) |
Hippurate Hydrolysis Test | (+) (C. jejuni) | - |
Campy | Heli. | |
Oxidase | ||
Urease | ||
Hippurate Hydrolysis Test |