Bacterial diseases
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever
Agent: Rikketsia ricketsii
- transmitted through tick bites.
Symptoms; fever, headache, and a spotted rash.
Brucellosis
Agent: Brucella melitensis
Zoonosis- transmitted from animals to humans
-Transmitted through handling of infected animals or unpasteurized milk
Symptoms: Undulant fever, sweating, chills, headache

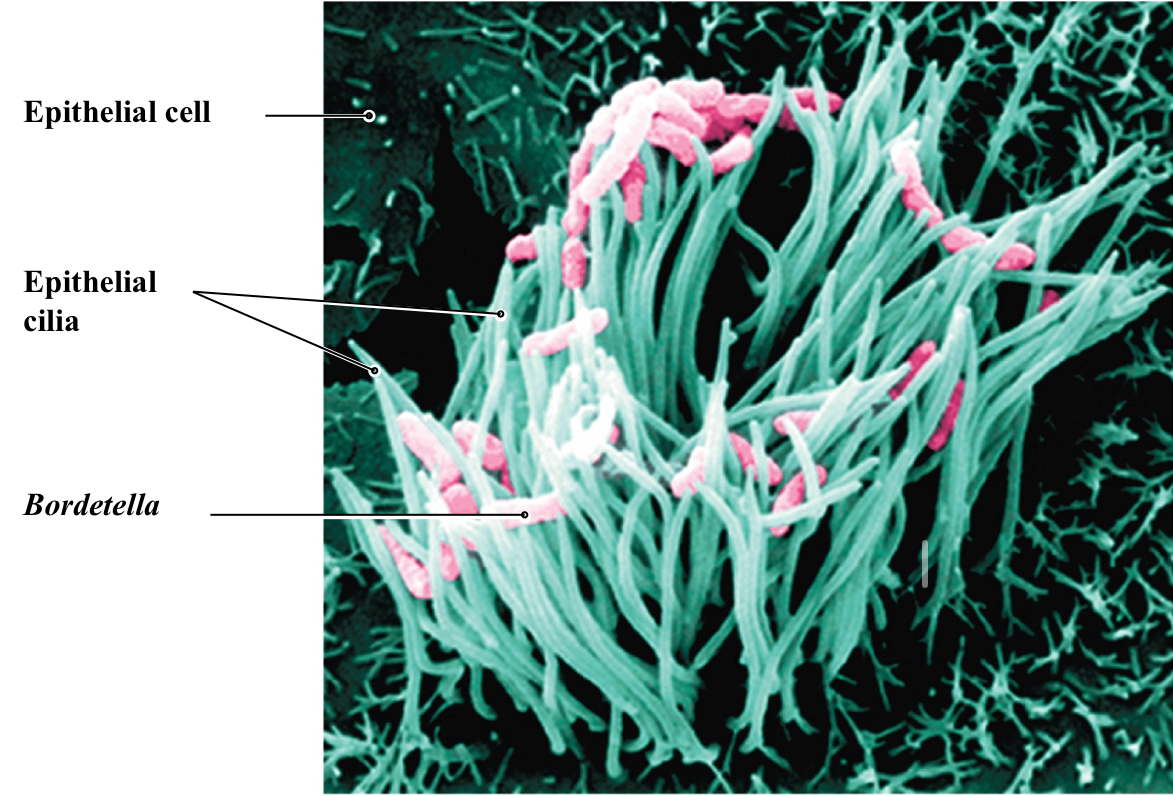
Whooping Cough
Also known as Pertussis
Agent: Bordatella pertussis
Route of Transmission: Inhalation
Symptoms: Catarrhal stage: common cold
Paroxysmal stage: persistent, violent cough without a breath; wheezing inhalation (whoop)
Convalescent stage: several weeks as coughing subsides
- Cyanosis (blue appearance) due to poor oxygen exchange
-Dangerous to children
— kills cilia in throat causing build up of mucus
Identify the different vaccines used for pertussis
– DTP vaccine had more intense side effects (low patient compliance) (endotoxin)
– DTaP vaccine is now used which causes less intense side effects
•Six doses; doesn’t use the endotoxin
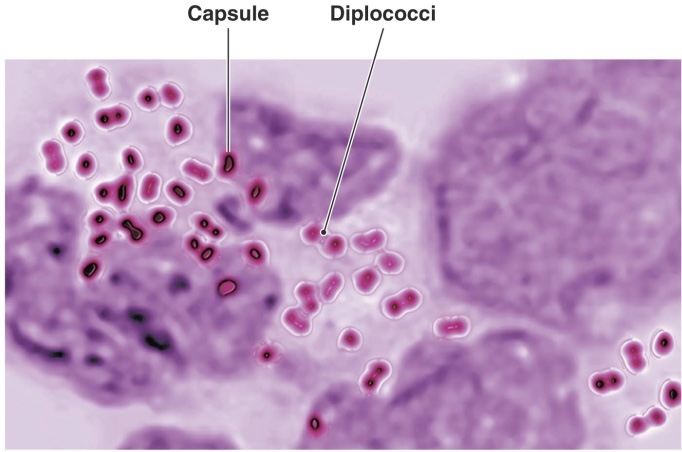
Gonorrhea and (PID)
Agent: Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Transmitted through: Sexual contact or via birth canal to newborns ( through newborns eyes)
Identify parts of bacteria: capsule and diplococci
Consequence of PID: damage to uterine tubes cause infertility
Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection
Blue-green pus due to pigment produced by bacteria; under nails
Opportunistic pathogen; burns or open skin
Route of Transmission: water borne, direct contact, nosocomial infections
— self limiting (cleared by body)
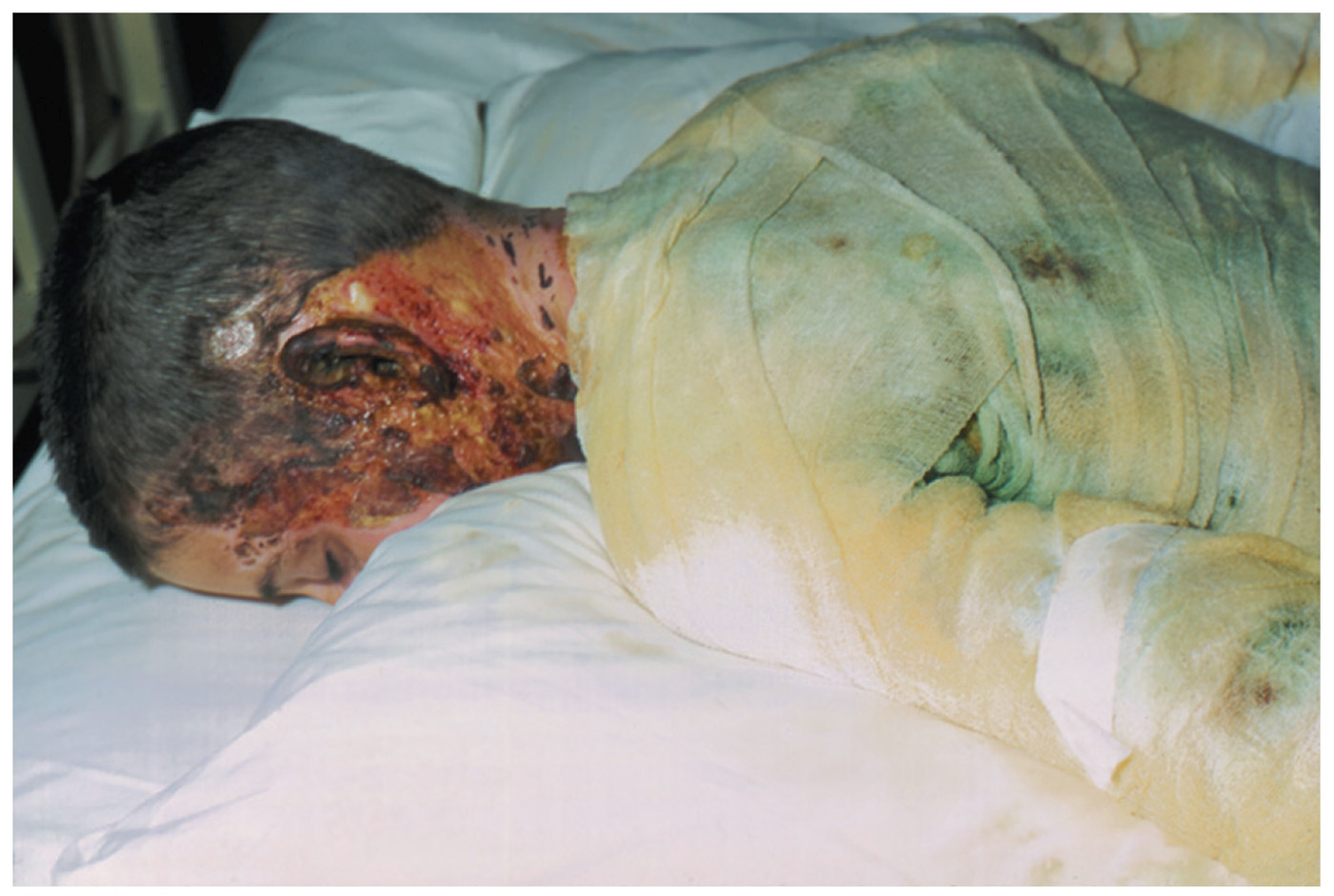
Legionnaire’s disease or legionellosis
Agent: Legionella pneumophila
Route of Transmission: Respiratory
HVAC, Spas, showers, Humidifiers, Warm water lines in hospitals
Symptoms: cough, general symptoms of pneumonia
— “Modern” disease due to their preferred environments; Central heating, water lines, etc. (we didn’t always have these)
Cholera
Agent: Vibrio cholera
Transmitted: through contaminated water or foods
Symptoms: No fever
•Rice-water stool
•Dehydration and hypovolemic shock
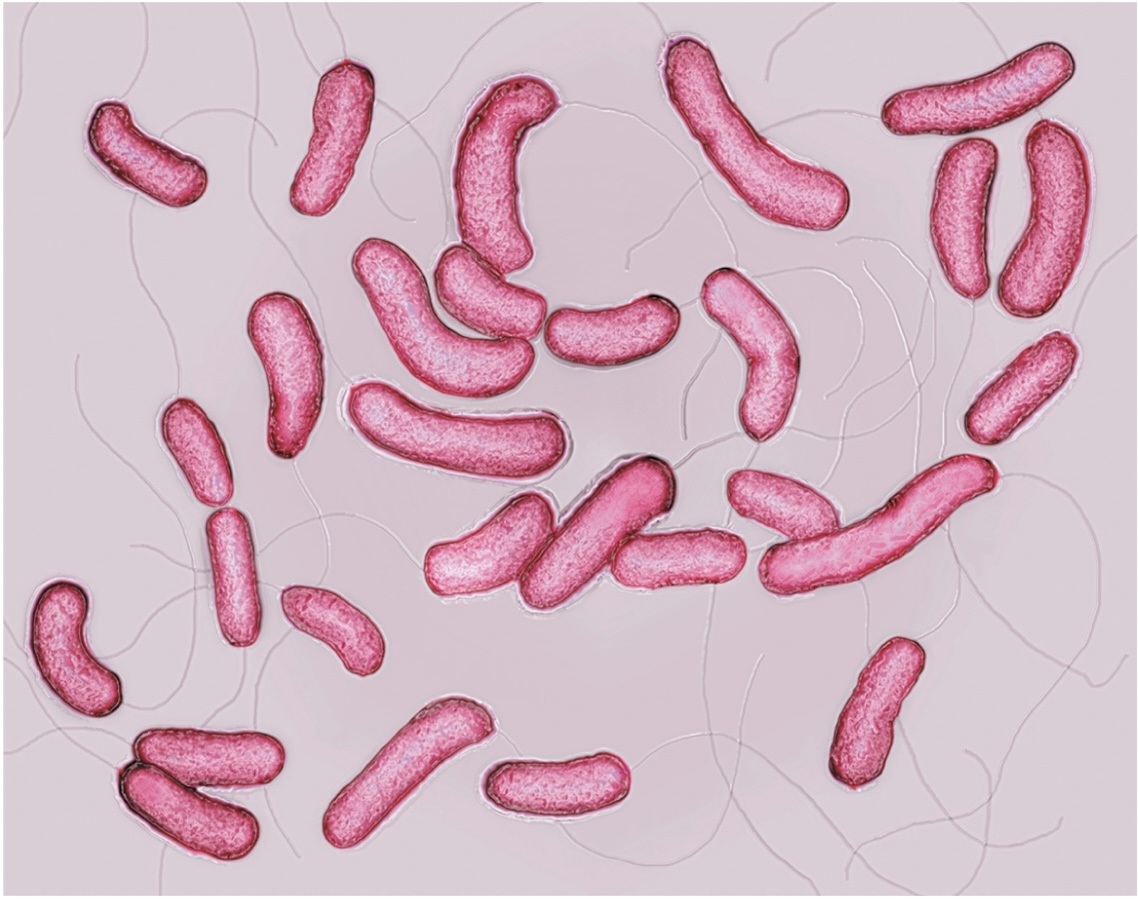
Vibrio cholera
Vibrio shape; Flagella is monotrichous
What does cholera toxin do and how does it relate to osmosis?
-Cholera toxin is important for virulence (causes diarrhea) (shedding of the bacteria into the environment in large amounts)
– The Toxin results in electrolytes leaving the cell and going to the Intestinal lumen.
— results in lots of water inside the intestine(due to osmosis) that gets passed as diarrhea
Osmosis: if high concentration of solutes on one side, water rushes across the membrane to balance out that concentration
UTI & Traveler’s diarrhea
Agent: E. Coli
Most common cause for UTIs
Fecal/ Fecal oral for Travelers diarrhea
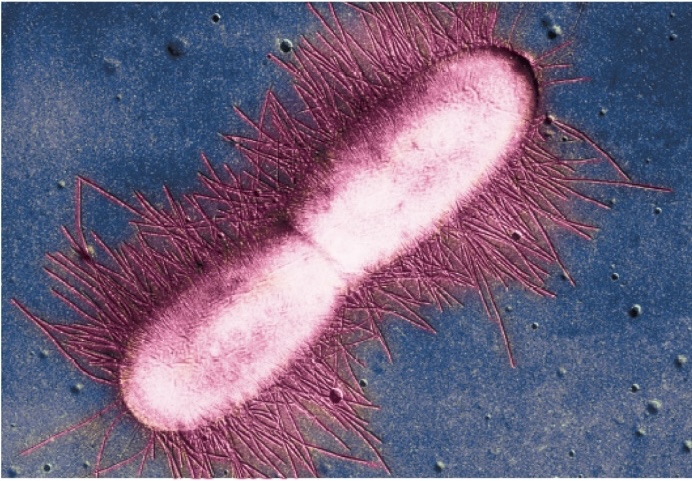
Describe the flagella on E. coli
Peritrichous flagella; multiple flagella that are distributed randomly over the entire surface of a bacterial cell
Bacillary dysentery
Agent: Shigella dysenteriae
Transmitted through: fecal/oral
Symptoms: diarrhea and bloody stool
shiga toxin: can secrete, results in the host cells stopping protein synthesis
— more severe case, usually self limiting

Salmonellosis
Agent: Salmonella species
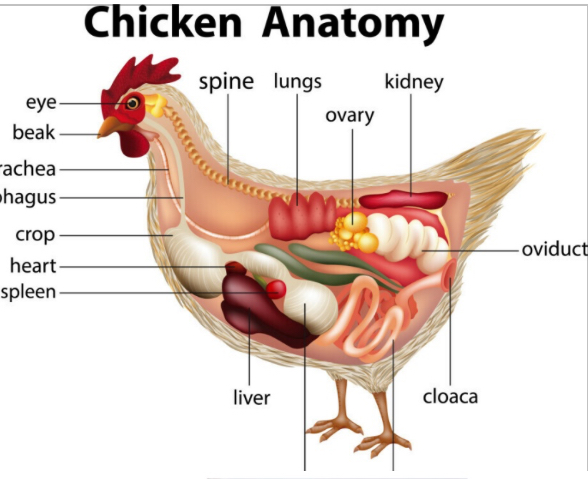
Transmitted through: fecal/oral route from chicken eggs
-Their anatomy, poop comes out same hole
Prevention methods: Boil the egg, cook it, peel it, or forget it
Pneumonia
Agent: Klebsiella pneumoniae
Transmitted: inhalation
Symptoms: Coughing and chest pain; Thick bloody sputum- destruction of alveoli (lung tissue), recurrent chills
-Opportunistic pathogen; clearing oral secretions from the respiratory tract helps with preventing lung disease.
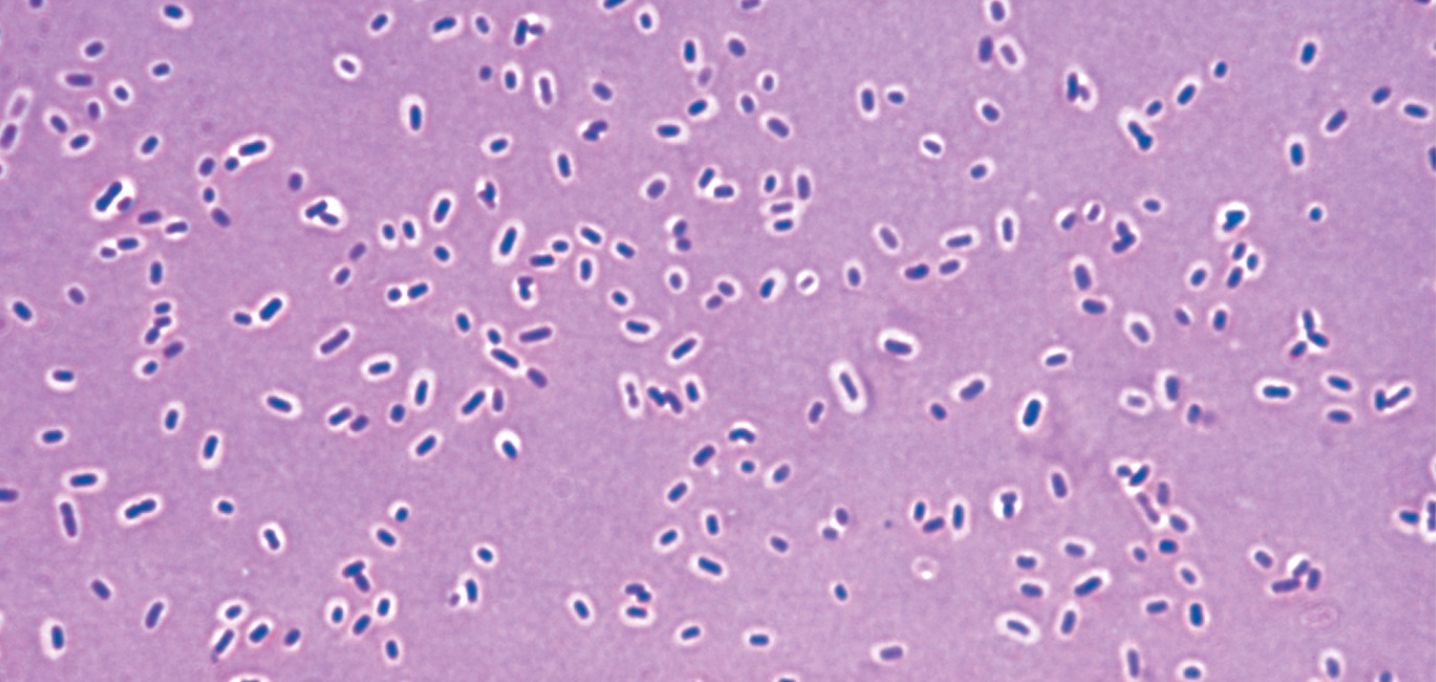
Klebsiella pneumoniae
Capsule surrounding the bacilla helps them avoid phagocytosis by the immune system.
Gram -
Identify the at-risk populations for poor respiratory tract clearance:
Cleaning secretions from respiratory tract helps prevent pulminary disease; some have problems with this
Alcoholics; Compromised immunity like AIDS; Very young or very old
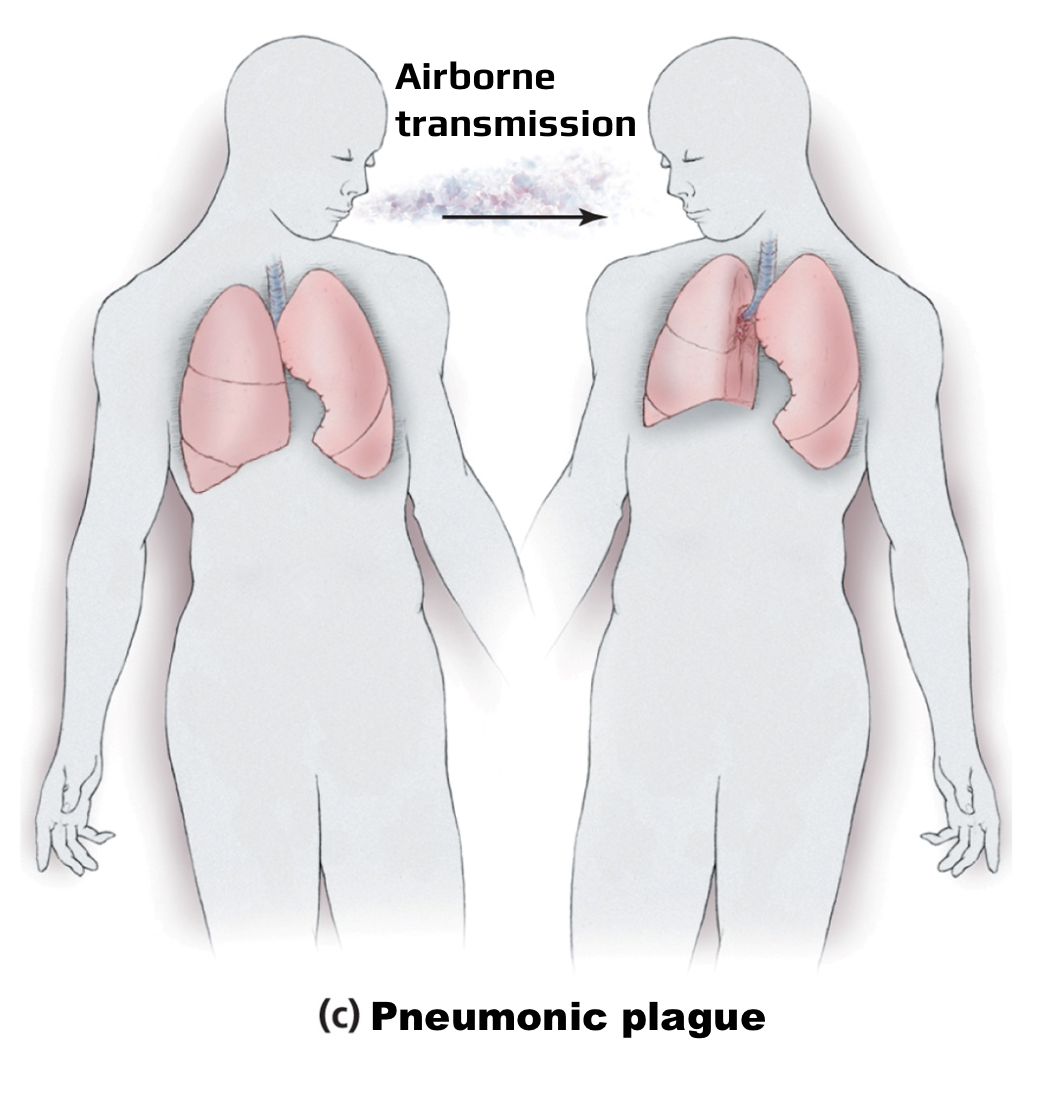
Pneumonic plague
Agent: Yersinia pestis
Transmitted through: inhalation human to human
Symptoms: cough, difficulty breathing, and frothy bloody sputum
Causes pneumonia
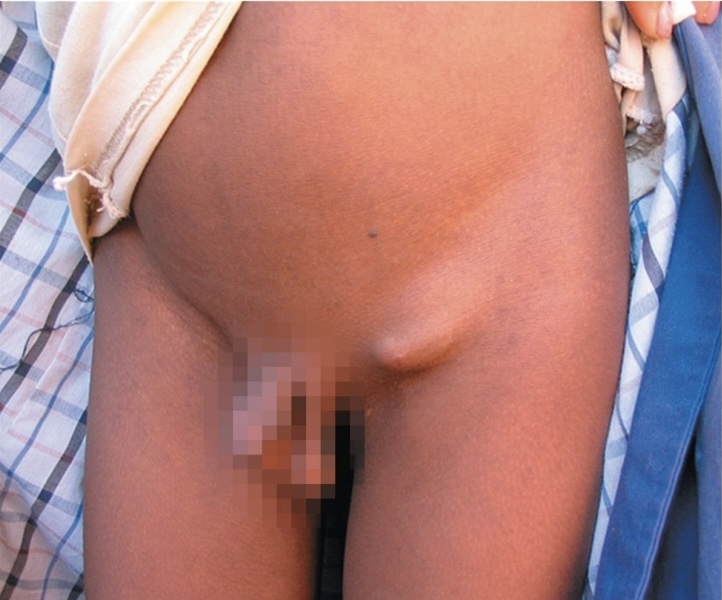
Bubonic Plague (Black plague)
Agent:Yersinia pestis
Transmitted through: flea bite
Symptoms: smooth, enlarged lymph nodes called buboes (groin, armpit, neck)
- muscular pain, severe headache, If bacteremia or septicemia happens, you have death of tissues which turn black
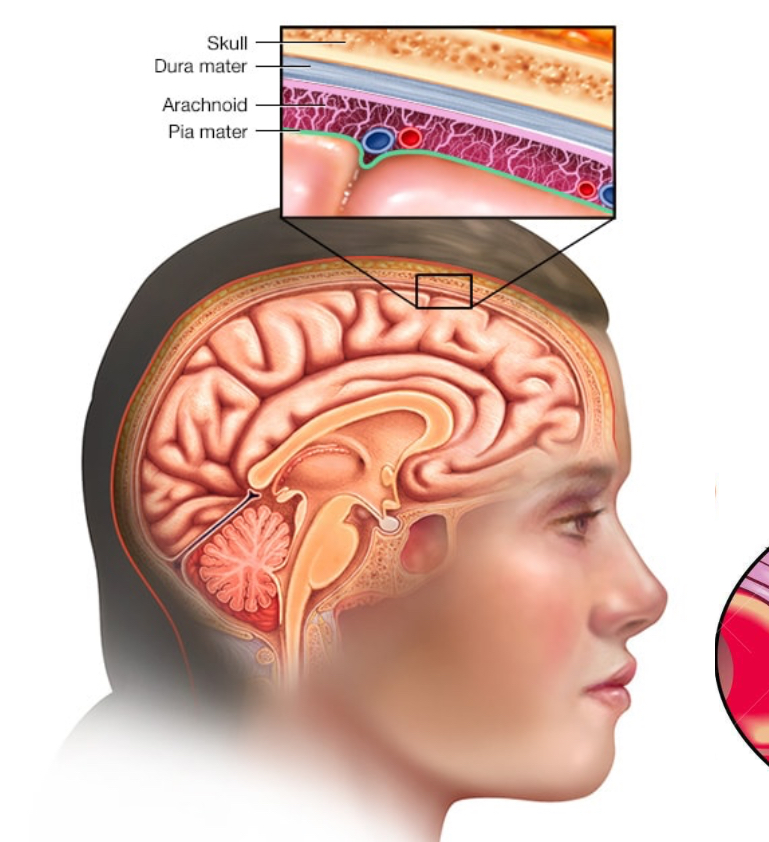
Meningitis
Agent: H. influenzae
Transmitted through air
Signs and symptoms: – Increased white blood cells in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Inflammation of meninges causes severe headache, light sensitivity, nausea, pain
Loss of brain functions: drowsiness, confusion, irritability
If brain infected, encephalitis (inflammation of the brain)
Deafness, blindness, drastic changes to patient’s behavior, coma, or death
Food-borne infections
Agent: Campylobacter jejuni
Leading cause of food-borne illness in US
Symptoms: diarrhea, abdominal cramps and fever, no vomiting
In the intestines, not stomach
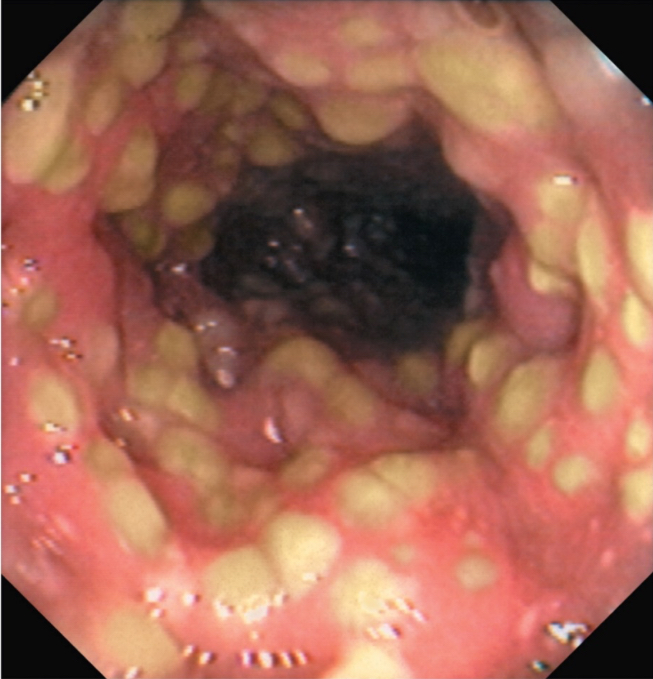
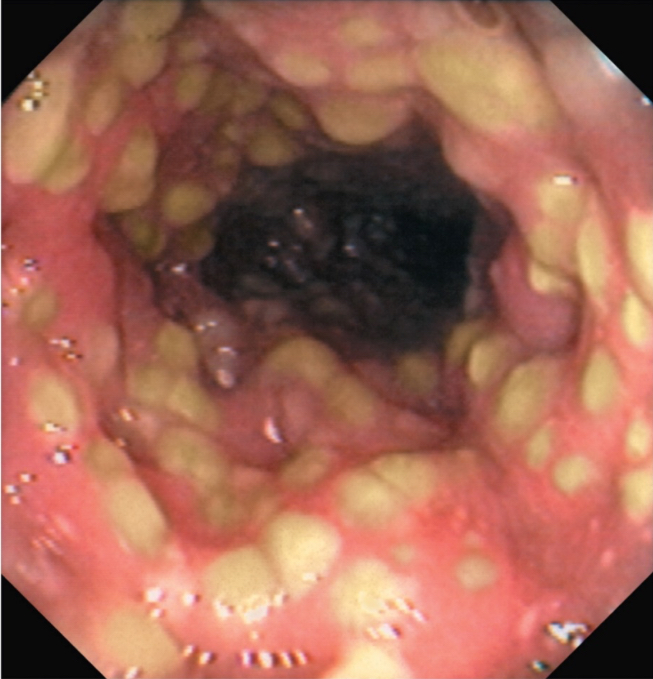
C. diff
Agent: Clostridium difficile
Signs and symptoms: 5-10 watery, foul-smelling bowel movements per day
—Inflammation and formation of intestinal lesions called pseudomembranes
Made of connective tissue, dying WBCs, and dead colon cells
Treatments: – Restoring the microbiome
“Modern infection”, increased with the use of antimicrobial drugs
Usually, stopping antimicrobial treatment is enough to restore the normal microbiome
•Probiotics
•Fecal transplants in severe cases
C. Diff
Intestinal lesions; Made of connective tissue, dying WBCs, and dead colon cells
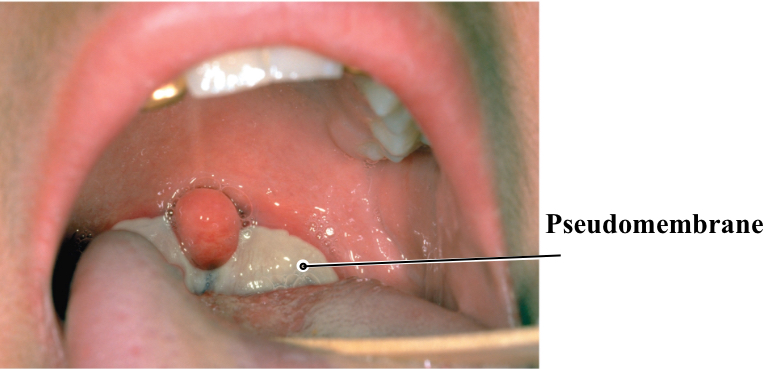
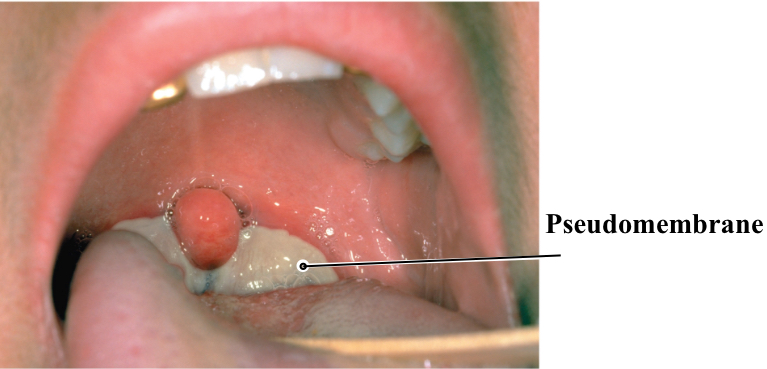
diptheria
Pseudomembrane made of: intracellular fluid, blood clotting factors, leukocytes, bacteria, and remains of dead cells
Tetanus and lockjaw
Agent: Clostridium tetani
Transmitted through: puncture wound
Signs and symptoms: Tightening of the jaw and neck muscles
-Sweating, drooling, grouchiness, and constant back spasms
-Spasms and contractions may increase and spread to cause curled arms, fists, and feet, and the body arches backwards as the heel and back of the head bend towards each other

Botulism
Agent: Clostridium botulinum
Toxin blocks the nerve signal that tells the muscle to contract (acetylcholine)
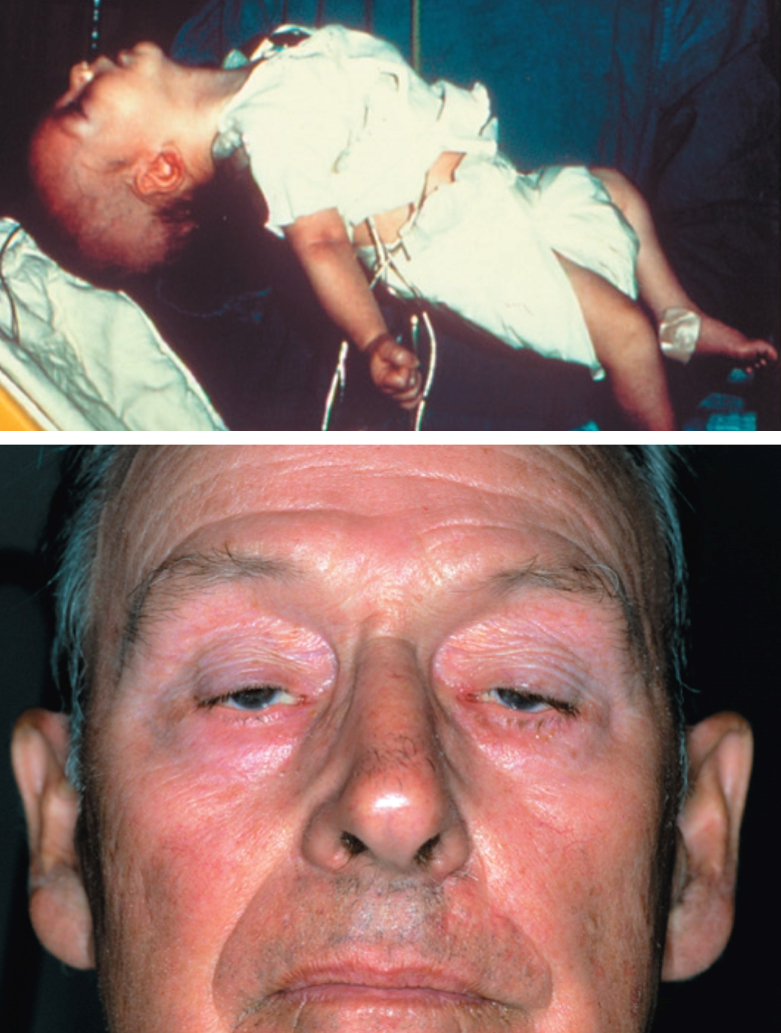
Gas Gangrene
Agent: Clostridium perfringens (anaerobic)
Symptoms: Intense pain at site of infection; blackening of infected muscle and skin; production of bubbles of hydrogen and CO2
– May break out with a frothy brownish liquid
– necrosis( tissue death)
Transmitted through contact with broken skin
Diabetics are susceptible
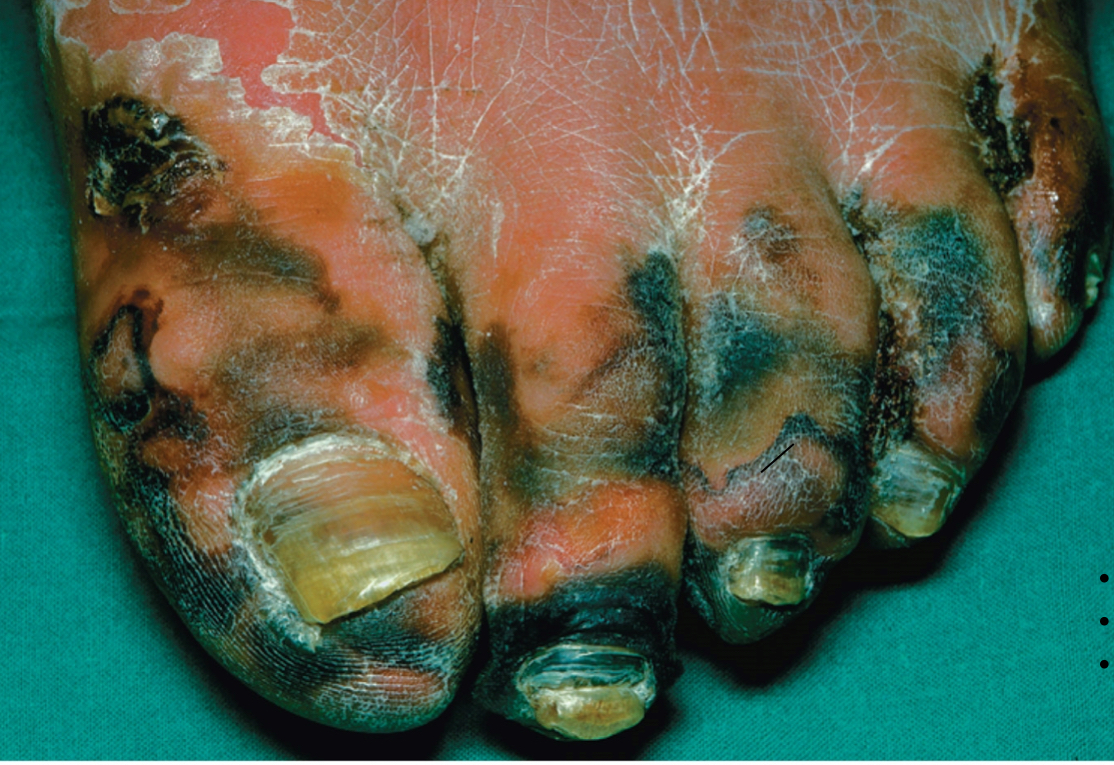
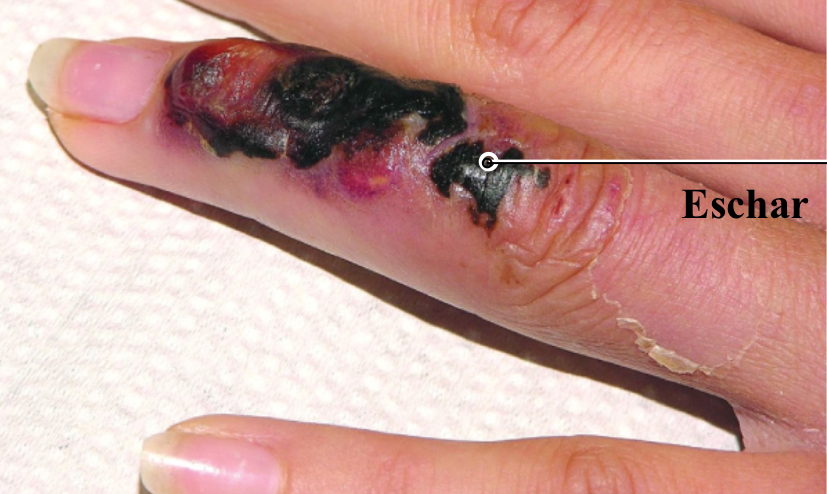
Cutaneous anthrax
Agent: Bacillus anthracis
Bacteria usually shed from an animal makes its way to broken skin; results in eschars or swollen, black, crusty ulcers
Inhalation anthrax
Agent: Bacillus anthracis
Inhalation(most severe from): common cold or flu- sore throat, mild fever, myalgia, mild cough, and malaise
progress to severe coughing, nausea, vomiting, fainting, confusion, lethargy, shock, and death

Impetigo and scalded skin syndrome
Agent: Staphylococcus aureus
Impetigo: small, flattened red patches usually on the face and limbs, usually on children
-Pus filled vesicles that break, forming a thick honey-colored crust
Scalded skin syndrome: separation of the outer layer of skin by the toxins released by Staphylococcus
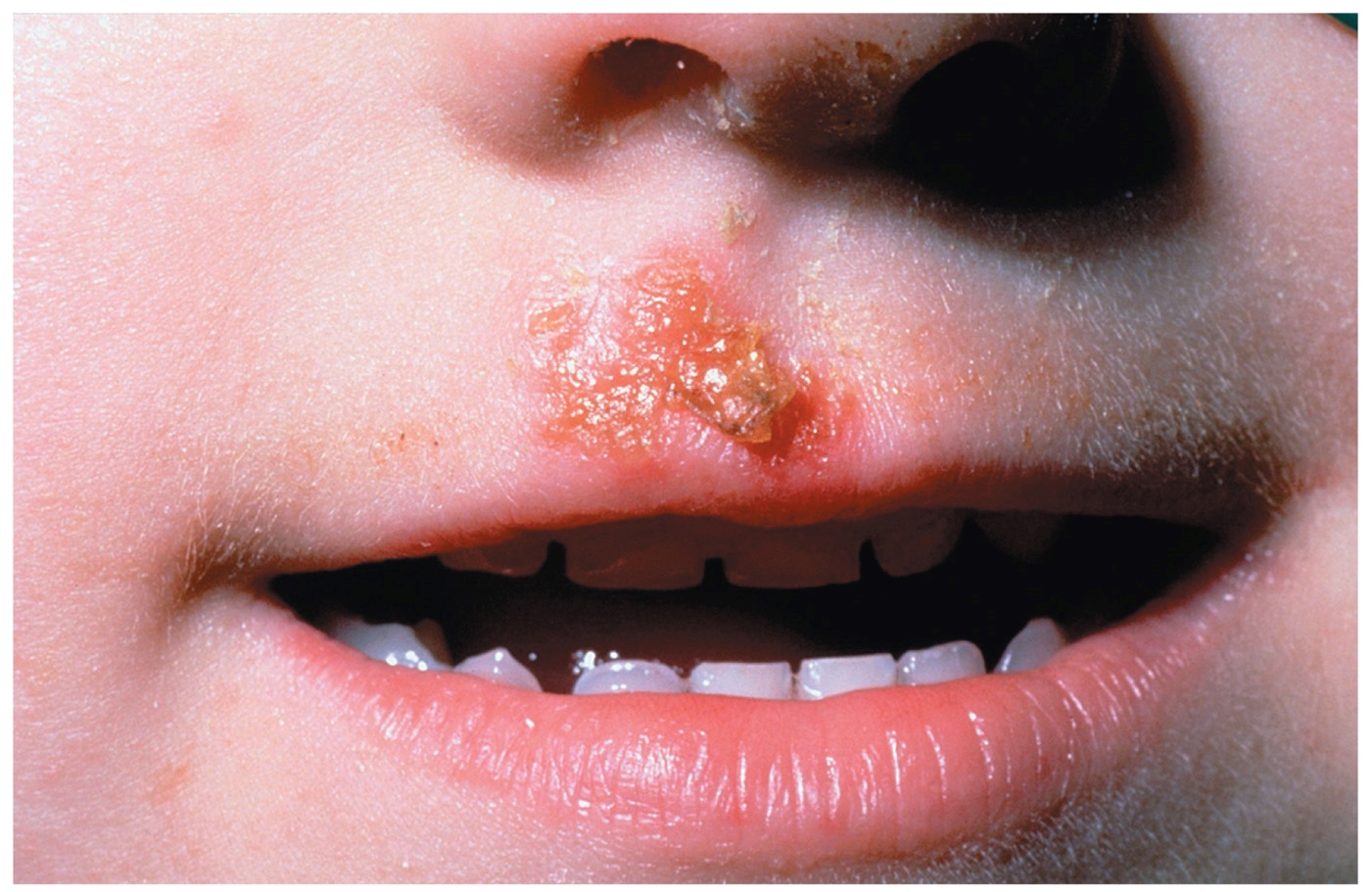
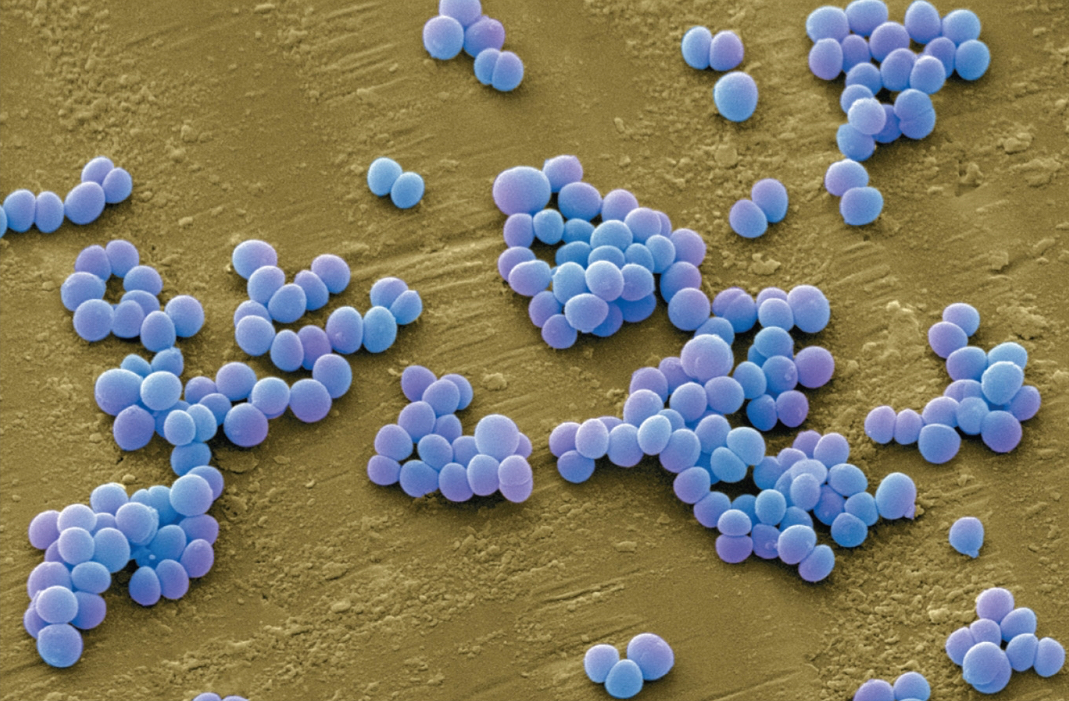
Identify which bacteria are commonly associated with methicillin resistance and what measures keep it in check:
Staphylococcus aureus
often become resistant against antimicrobial drugs; usually treated with vancomycin
— part of normal flora; a large amount is needed for infection
— Proper aseptic technique and cleansing keeps it in check
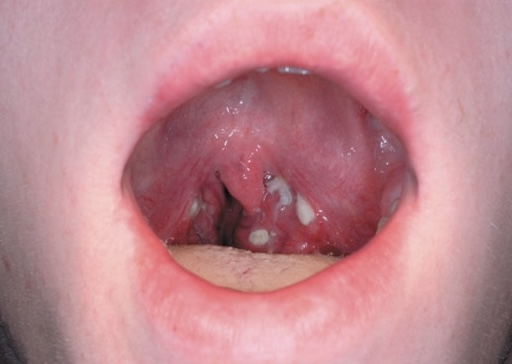
Strep throat and Scarlet Fever
Agent: Streptococcal pharyngitis:
Strep throat: inflamed back of pharynx, with swollen lymph nodes and purulent abscesses covering the tonsils; pain during swallowing; bad breath
•Scarlet fever- rash that begins on the chest and spreads through the body- tongue becomes strawberry read
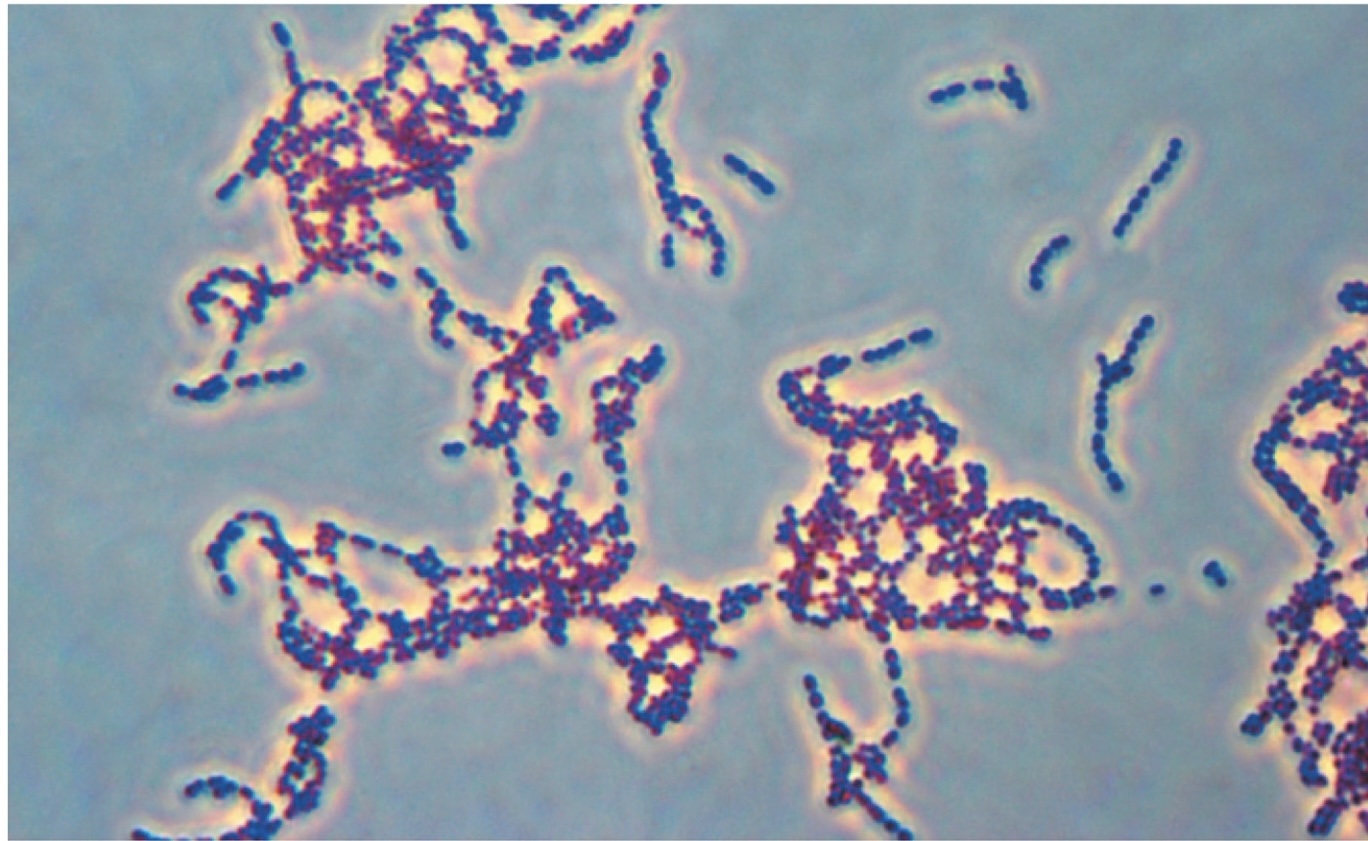
Streptococcus pyogenes
Streptococci shape (round and in strings)
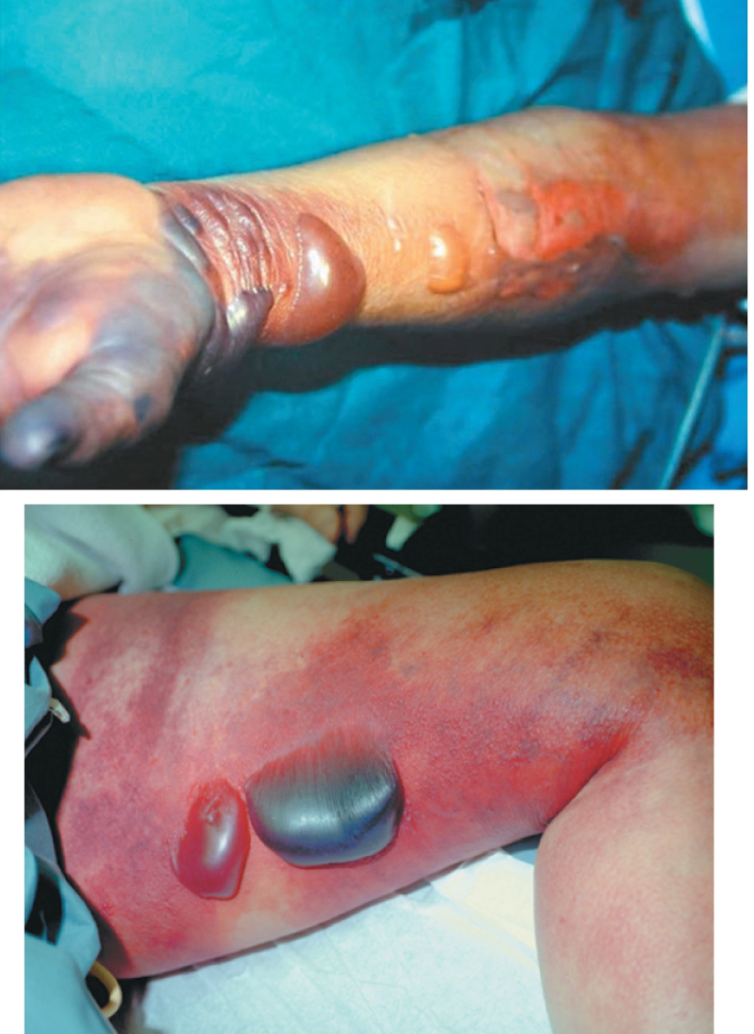
Necrotizing Fasciitis
Agent: S. pyogenes
Early: Hot, intensely painful sunburn-like rash
•Disproportionately more pain than how the rash appears
As it progresses:
•Fever, tiredness, muscle aches
•As tissue is destroyed, blood pressure drops, and patient becomes mentally confused and ultimately comatose
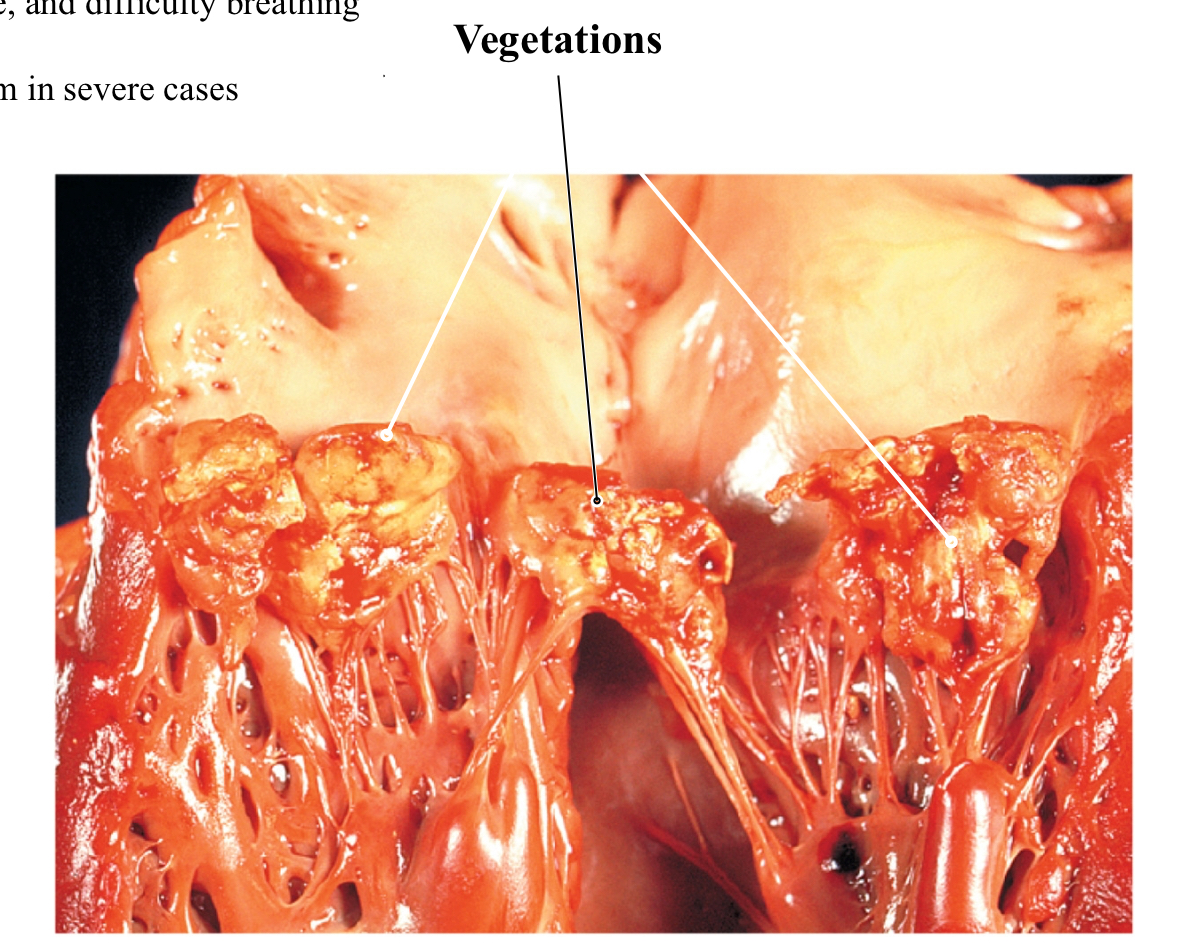
Endocarditis
Endocardium lines the heart chambers, valves, and vessels near the heart
-Bacteria along the linings trigger inflammation and the formation of vegetations
Vegetations- bulky masses of platelets and clotting proteins that surround the bacteria
Complications: IV drug use; Heart abnormalities; Suppressed immune system;
Increases risk for strokes as the vegetation can break off ( interrupt blood flow through brain)
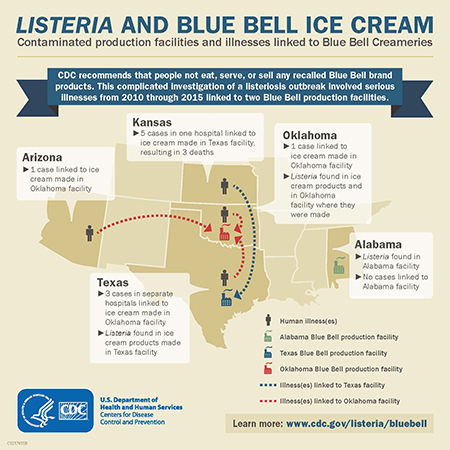
Listeriosis
Listeria monocytogenes
Transmitted: Foodborn or in utero Cold —Tolerance can allow the bacteria to survive and proliferate in refrigeration (Bluebell listeria)
complications that can result in fetuses that contract listeriosis:
abortion, stillbirth, bacterial meningitis
Tuberculosis
Agent: Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Acid fast- Cell walls contain mycolic acid, a waxy lipid
Grows slowly; Survive phagocytosis from immune cells; Can grow inside cells;
Resistant to Gram stains, detergents, common antimicrobial drugs, and drying out
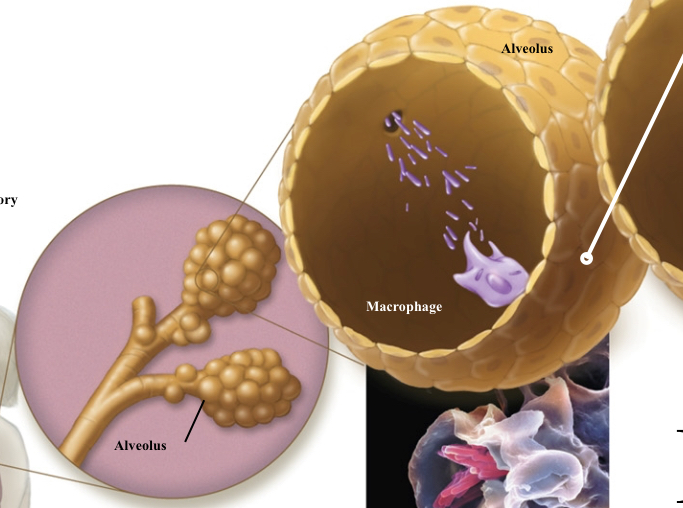
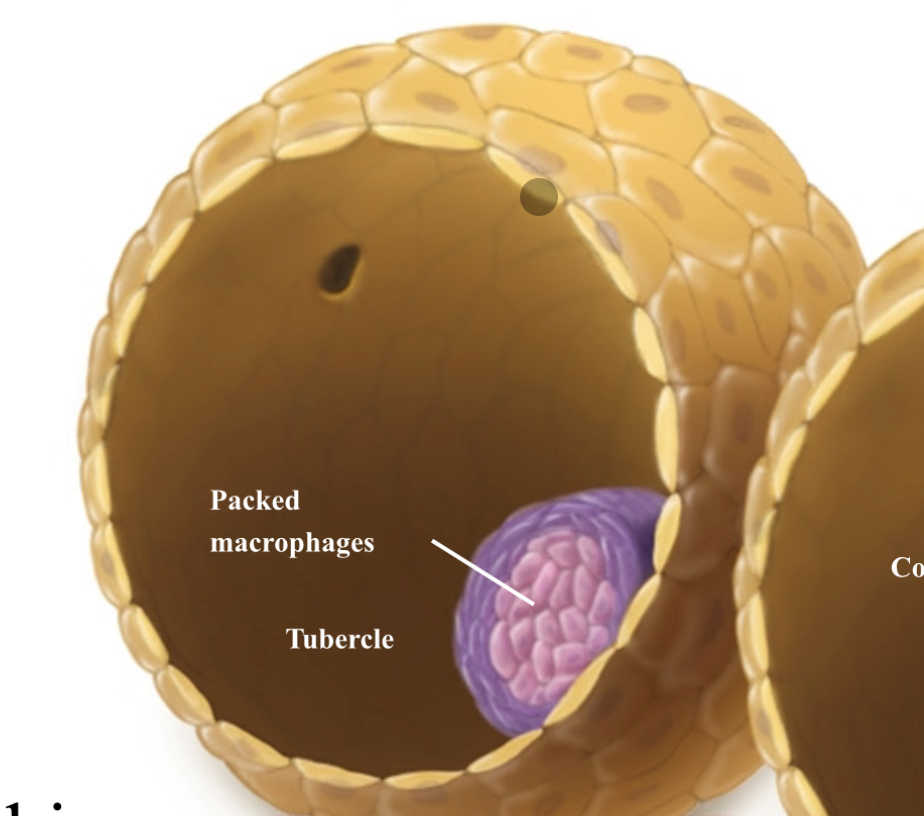
Explain how tuberculosis can result in tubercles
Macrophages call in more immune cells, causing a tubercle
Tightly packed macrophages surround the site of infection, forming a
tubercle over a two- to three-month period.
Diptheria
Agent: C. diptheriticae
C. diptheriticae has a lysogenic phage that codes for the diptheria toxin
Symptoms: sore throat fever pain
Pseudomembrane: intracellular fluid, blood clotting factors, leukocytes, bacteria, and remains of dead cells
Explain where diptheria gets the ability to make diptheria toxin from
C. diptheriticae has a lysogenic phage that codes for the diptheria
Toxin: Prevents polypeptides from being made and causes cell death
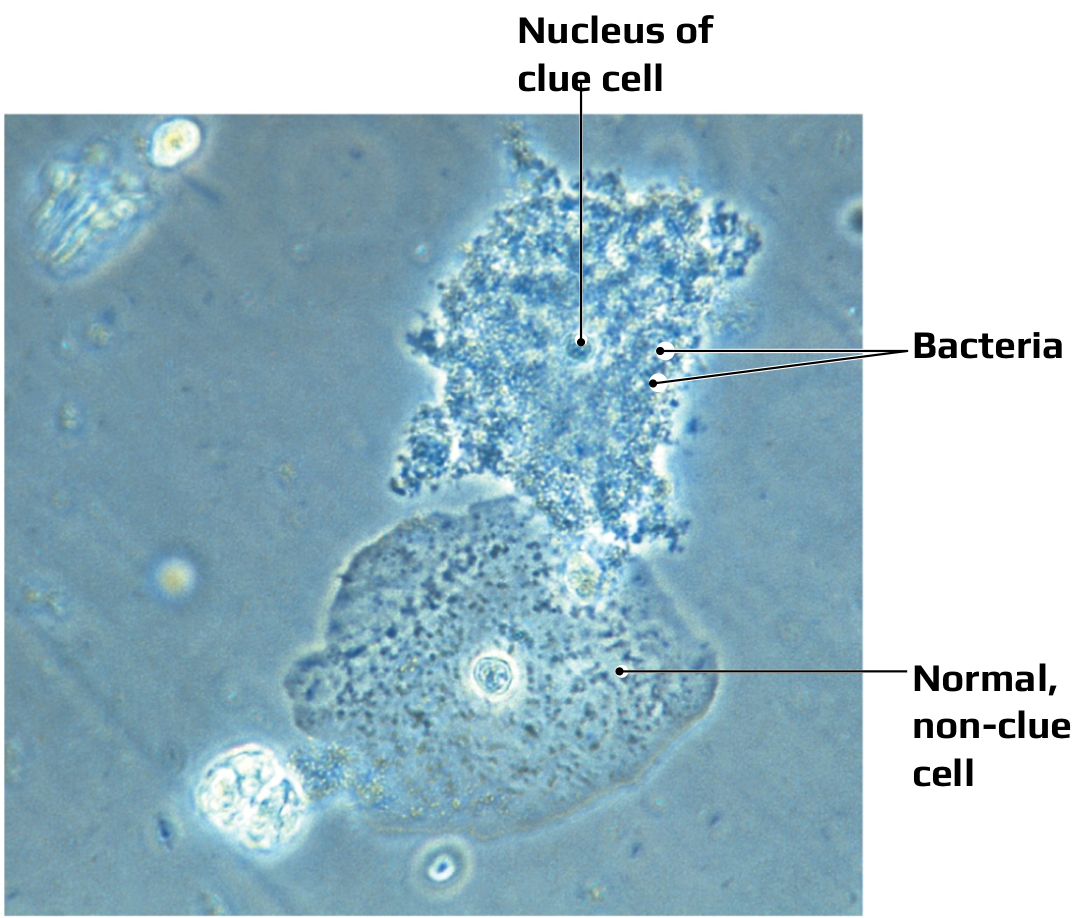
bacterial vaginitis/vaginosis
Agent: Gardnerella vaginalis,
Signs and symptoms: White vaginal discharge with a “fishy” odor; Itching and irritation of the vaginal opening;
Clue cells differentiate from vaginal candidiasis
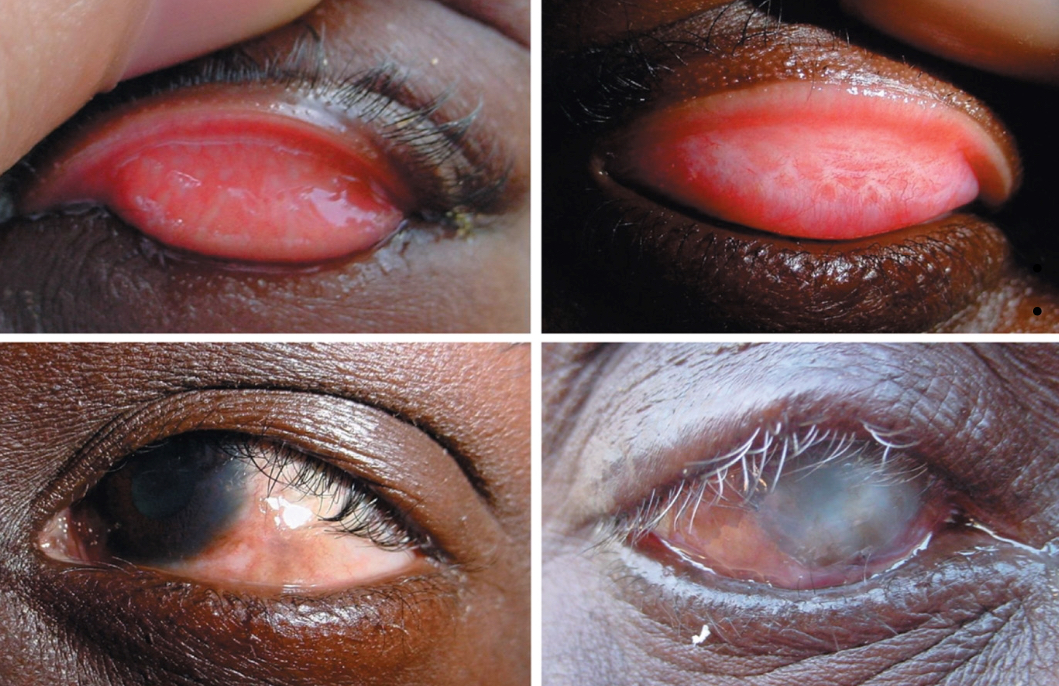
Trachoma
Agent: Chlamydia trachomatis
Sign and symptoms: Scarring of the conjunctiva and cornea;
Eyelashes turn inwards, cornea is scratched and irritated by the eyelashes
genital chlamydia
Agent: Chlamydia trachomatis
(Asymptomatic in women) Damage to reproductive tissues can cause sterility
– Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
Lymphogranuloma venereum- transient genital lesion at the site of infection
•Followed by development of bubo
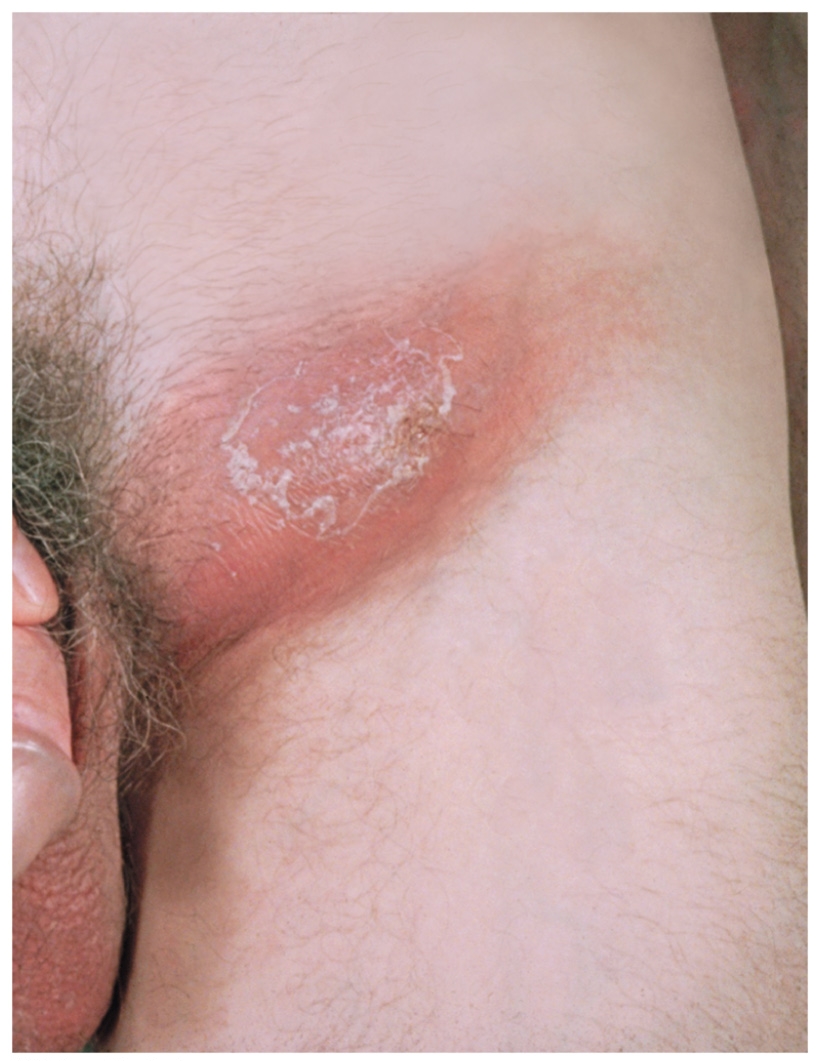
syphilis
Agent: T. pallindum
Primary phase: Small, painless, hard lesion known as a chancre (ulceration)
•Often unobserved
Secondary phase:
Widespread rash, sore throat, headache, mild fever, malaise, myalgia
Latent phase : usually ends here;antimicrobial drugs
.Tertiary phase: years later, untreated patients experience dementia, blindness, paralysis, heart failure, or syphilitic gummas( tumor like growth)
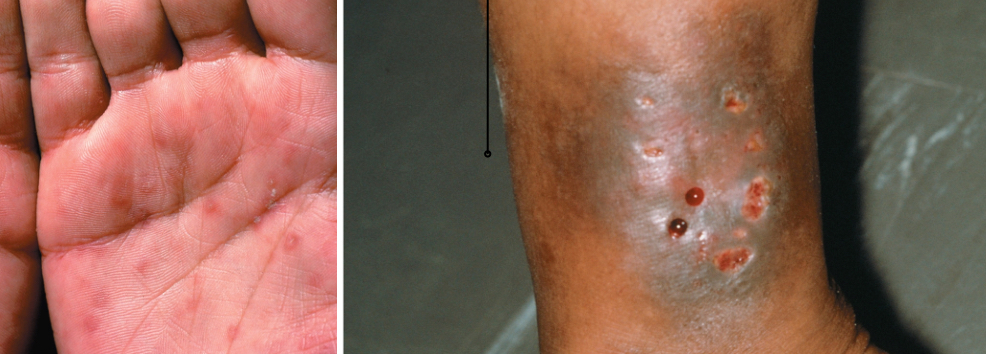
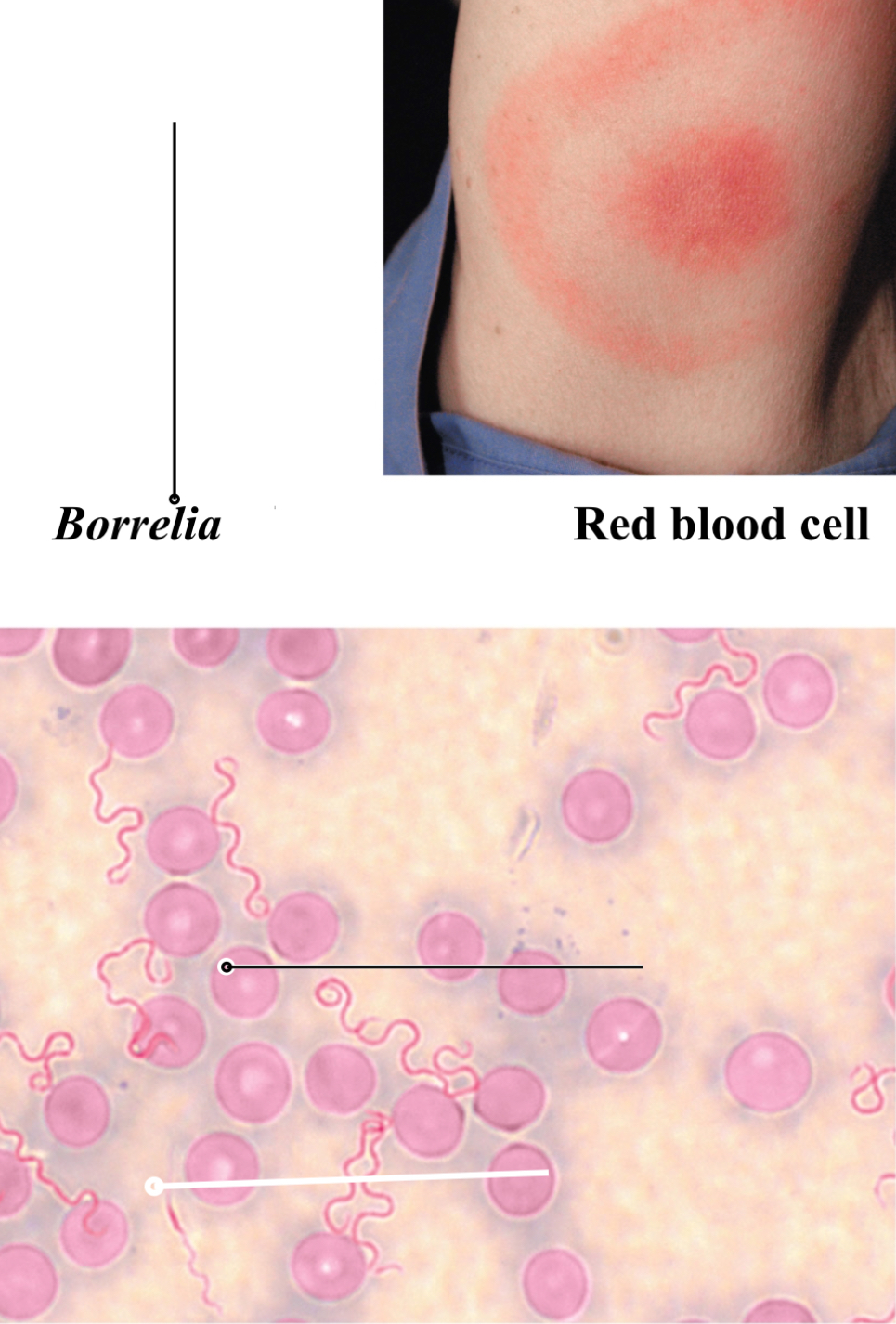
Lyme disease
Signs and symptoms: Bulls-eye lesion
Early: bulls-eye lesion, headaches, dizziness, stiff neck, severe fatigue, chills
Middle: 10% of patients experience neurological symptoms and cardiac dysfunction
Final: 80% of patients experience severe arthritis (may last years); rarely fatal
Vector: deer tick