Biotechnology: Lecture 8 - Drugging innate immunity – Complement Therapeutics
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Give an overview of the complement system pathway
C4: C3 (passive) → C3a + C3b (active)
C3b targets surface of pathogens → conformational change → attracts other complement proteins → cascade → C3 convertase
opsonization: labels for phagocytosis
C3 convertase → C5 convertase recruits more proteins → membrane attack complex → membrane C5b9 pores (lysis)
C3 convertase activates more C3 proteins (amplification)
Activation of C3a + C5a → anaphylatoxins
C3a activates immune cells (chemotaxis)
Give an overview of the classical complement system pathway
(IgG + IgM bind to pathogen) binds to C1
C1 binds → conformational channge → activation
C1 cleves C4 + C2 → C3 convertase
Activates the complement system
Give an overview of the mannose-binding lectin (MBL) complement system pathway
MBL/ ficolin detects carbohydrates on surface of pathogens
conformational change → C4 + C2 → C3 convertase
Activates the complement system
Give an overview of the alternative complement system pathway
spontaneous hydrolysis: C3 → C3b
distinct C3 convertase
Activates the complement system
Natural complement regulators
C1 inhibitor: Inhibits C1r and C1s, blocks MASP
CR1: degradation of C3b and C4b (classical & alternative)
MCP: promoting cleavage of C3b and C4b by Factor I
DAF: Accelerates decay of C3 and C5 convertases
CD59: Blocks MAC formation by inhibiting C9 polymerization
C4bp: inactivate C4b, dissociates C3 convertases
No regulation: MAC on own cells
Tissue damage in autoimmune disease
deposition of autoimmunoglobulin and immune complexes in affected organs
Vicious cycle’: complement activation and inflammation → tissue damage → C activation
complement not always cause of disease, exacerbates condition and sustains proinflammatory cycle
Physiological roles of complement
Direct killing of invading bacteria, infected cells
Initiation/enhancement of inflammation at sites of injury or infection
Cell activation: triggering of oxidase response and other cell activation events
Enhancement of phagocytosis
Immune complex handling
B cell activation, adaptive immunity
considerations when designing anti-complement therapeutics
Point of inhibition
C3?
C5? (Start of the terminal pathway, pre-C5a)
MAC formation?
Abundance of Target proteins
Most abundant: C3 (~1mg/ml in serum)
Acute phase response: don’t know how much protein to target
Long term systemic complement inhibition
bacterial infections?
immune complex disease?
Cost of generating biological reagents
short half-life, more expensive
bacterial expression vs. eukaryotic
What are some successful anti-complement therapeutics
sCR1: Avant Therapeutics
Anti-C5: Alexion Pharmaceuticals
APL-2: Apellis
Types of anti-complement therapeutics
Biological reagents based on mammalian (human) naturally occurring regulators (e.g. sCR1/TP10)
Antibody based therapeutics (e.g. anti-C5, Soliris)
Small molecule inhibitors/ naturally occurring compounds (e.g. Compstatin)
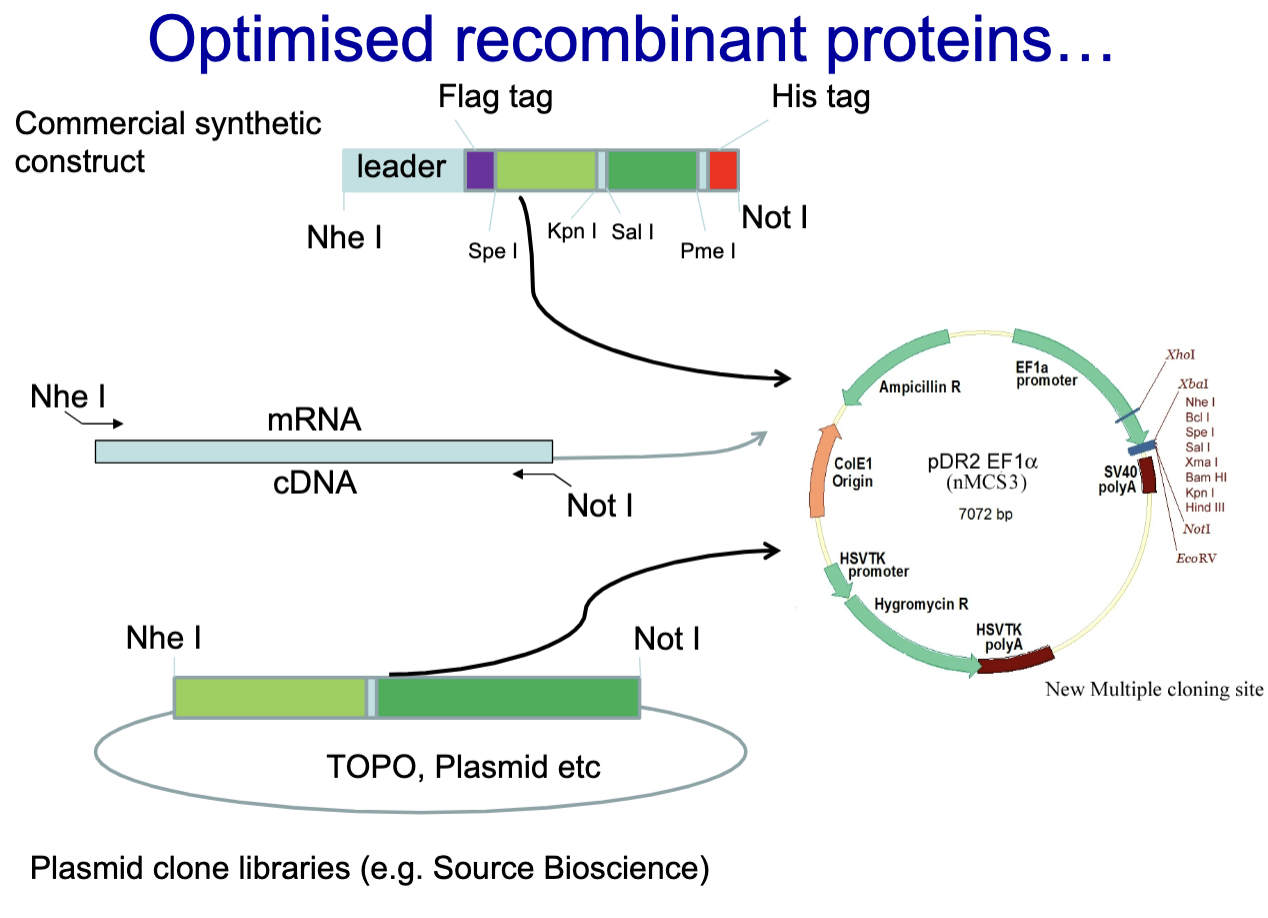
Generating optimized recombinant proteins
Commercial Synthetic Construct
mRNA is isolated and reverse transcribed into cDNA
Plasmid clone library
Inserted into plasmids using restriction enzymes (Nhe I and Not I).
Recombinant plasmids are used to transform bacteria or transfect mammalian cells for protein production
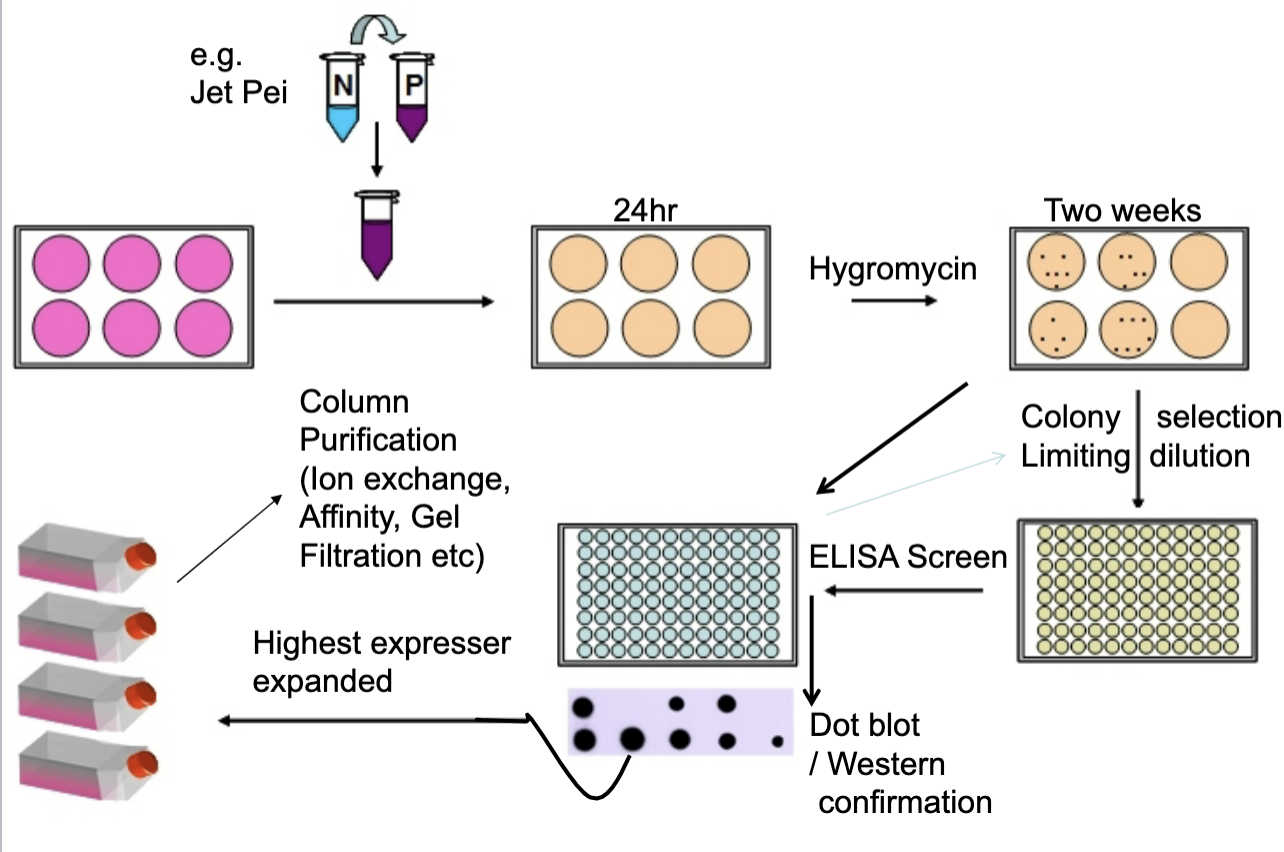
Transfection of Mammalian Cells ( CHO, HEK, etc)
Transfection: introduce plasmid DNA
Initial Expression: cells begin to express the recombinant protein
Antibiotic Selection (Hygromycin): hygromycin resistance = sucessful transfection
Colony Isolation (Limiting Dilution): each well contains cells derived from a single colony
Screening (ELISA & Dot Blot/Western Blot): measures the amount and confirms identity
Clone Selection and Expansion: highest expressing clone is chosen
Protein Purification: Ion exchange/ Affinity chromatography, Gel filtration
1st generation recombinant complement inhibitor: sCR1 (TP10)
soluble form of Complement Receptor 1 (CR1)
Inhibits complement activation by accelerating decay of C3 and C5 convertases
Human clinical trials: myocardial infarction, ARDS (acute
respiratory distress syndrome), transplantation
Ischaemia-reperfusion (many tissues), rats/mice
Experimental demyelination (MS), rats
Experimental myaesthenia gravis, rats
Xenotransplantation (pig-primate)
Antigen arthritis (rats)
2nd generation recombinant complement inhibitor
modifying protein function to become more drug like
enhancing potency, specificity, half-life, and clinical efficacy
Adding Fc domains increases serum half life
APT070 in arthritis: anchors to cell membranes and inhibits C3 convertases
Ways to extend half life
Fuse to antibody
PEGylation: modification of lysine residues in the protein with polyethylene glycol (PEG)
increases size: reduces renal clearance and proteolysis
increases solubility
Albumin-binding domains (Streptococcal protein G)
Half-life doesn't always matter
Tailed reagent
Location at membrane
Systemic inhibition
Advantages of monoclonal antibodies
increase half life
‘natural’ product, body is tolerant to them
(target C5) does not affect opsonisation
humanise mouse mAbs
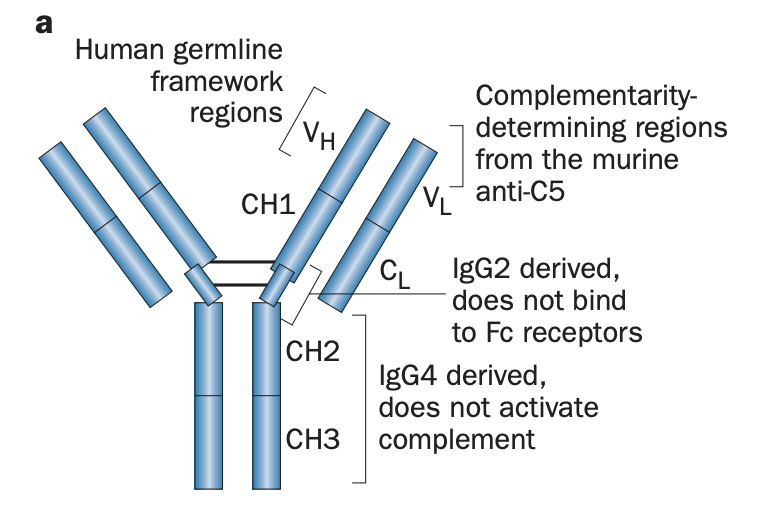
describe structure of Eculizumab (Zuber et al, 2012)
humanised mAb
derived from the murine antihuman C5 antibody
CDR = mouse anti-human C5 IgG
FR = human germline
hinge region =.human IgG2 (does not bind Fc receptors)
CH2–CH3 = human IgG4 (unable to activate complement)
modifications minimize immunogenicity and prevent pro-inflammatory responses mediated by the IgG Fc portion
describe function of Eculizumab
Binds to C5
blocks C5 convertase from binding (steric hindrance)
cannot be ceaved into C5a and C5b (MAC)
cleared from system
what alteraction were made to Ravalizumab?
changed 2 amino acids in CDR to loosen binding
Tyr - 27 - His
Ser - 57 - His
when pH changed from 6 to 7, antibody releases from C5
Ag degraded but Ab can be recirculated
changed 2 amino acids in Fc to enhance binding
Tyr - 27 - His
Ser - 57 - His
half life = >30 days (longer than Eculizumab)
extended dosing interval
Recombinant anti-C5: scFv and minibodies
(Marzari et al, 2002)
C5 cleavage site of C5 = common target for neutralizing human mAbs: in vitro and in vivo
isolation of an anti-C5 scFv Ab from a human phage display library
Ab inhibits activation of C5 and the terminal complement complex implicated in cell and tissue damage
Engineered into a minibody, has enhanced binding due to dimerisation
Problems with C5 inhibitors
No terminal pathway = risk of infection with encapsulated bacteria
Neisseria species
immunized patients with polyvalent meningococcal vaccine (2 weeks before)
Children treated with eculizumab should also be vaccinated against Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae type b
Extravascular Haemolysis = anaemia
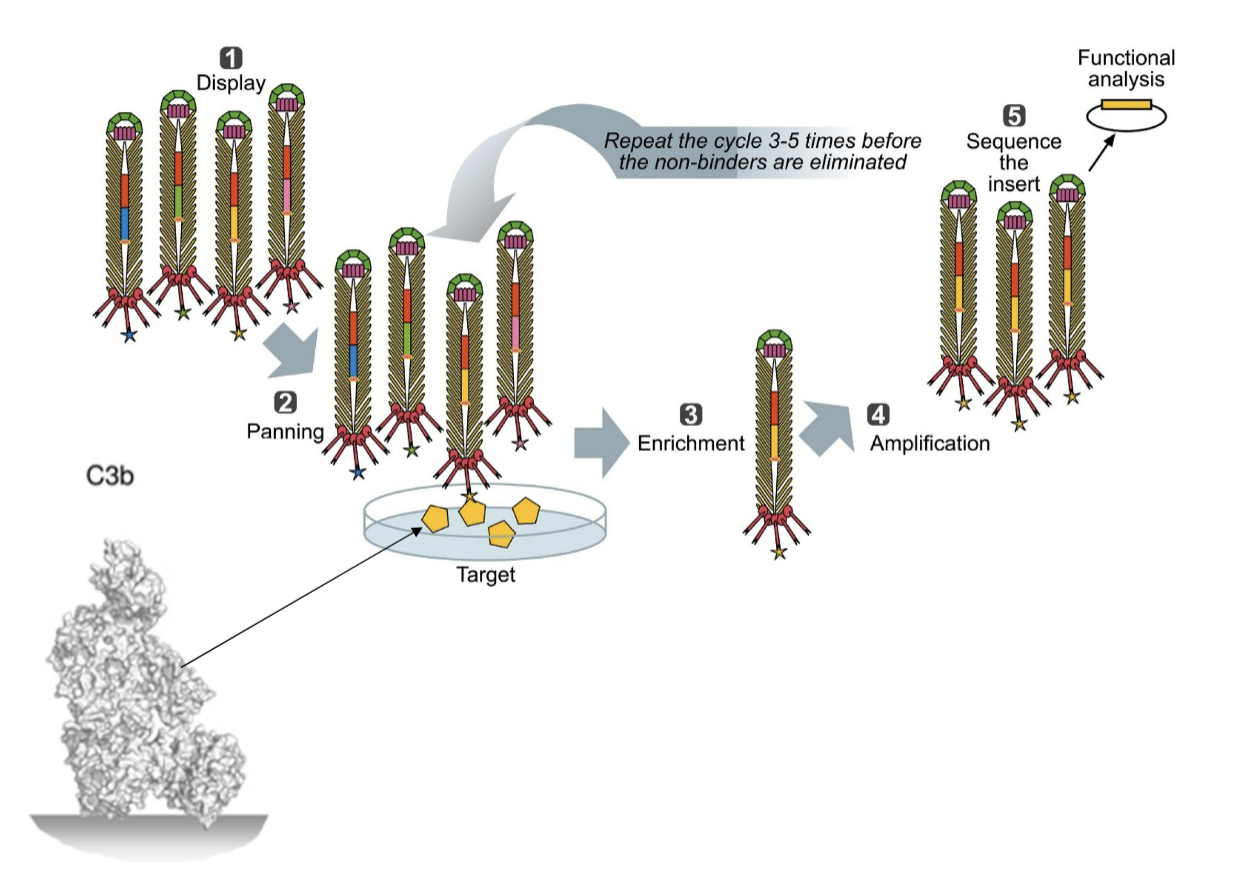
Small molecule inhibitors: Compstatin and derivatives (Lambris et al)
All based on a ~13-residue cyclic peptide,
binds to C3 and inhibits the cleavage of C3 to C3a and C3b
highly potent and selective C3 inhibitor
Compstatin Phage display
Target = C3b
Also checked for ability to block lytic attack (sheep red blood cells)
How does Compstatin function (MAstellos et al, 2015)
binds to C3+C3b and prevents convertase interacting
binds between MG4 and MG5
stops complement activation
small peptide = cheap to make
half life is an issue
Compstatin Derivatives
Compstatin derivatives have been shown to be safe and effective in a series of ex vivo and in vivo experiments
many diseases are targeted.
But serum half-life was initially poor.
Apellis attached a PEG moiety to 2 copies of APL-1 = APL-2 (pegcetacoplan)
increase half life
Clinically, the most successful derivative to date
druggable: interactions are fairly low affinity so rely on avidity
Novel uses for Compstatin (Cp40)
Toothpaste: block gum disease and tooth decay
Natural reagents from other species: Ticks
Ectoparasites: feed on blood
Complement-inhibitory activities identified in salivary glands of soft tick (Ornithodoros moubata)
Recombinant protein (OMCI) inhibits terminal pathway of human complement at C5 stage
Inhibits in many species: easier in lab
Short half life; resynthesis of C5 by liver is restoring complement levels
quickly
Other small molecule inhibitors
3D53: a macrocyclic compound, binds the C5aR
potent, selective, orally active
potent inhibition in vivo in many rat models of human disease: neutropenia/sepsis, arthritis, immune-complex dermal inflammation, and ischemia-reperfusion injury
K76COOH: partially oxidized derivative of natural terpenoid K-76
inhibits production of C5a
FUT-175: synthetic broad-specificity serine protease inhibitor.
Potently inhibits both coagulation and complement proteinases inhibits C1s, factor D
BCX-1470: serine protease inhibitor, inhibits factor D, C1s
Selective inhibition of the membrane attack complex of complement by low molecular weight components of the aurin tricarboxylic acid synthetic complex
LN023 – Factor B
Oral drug x2 a day
reversible FB blocker
Alternate pathway specific – blocking C3/C5 convertase
protect against rheumatoid arthritis, C3G and PNH
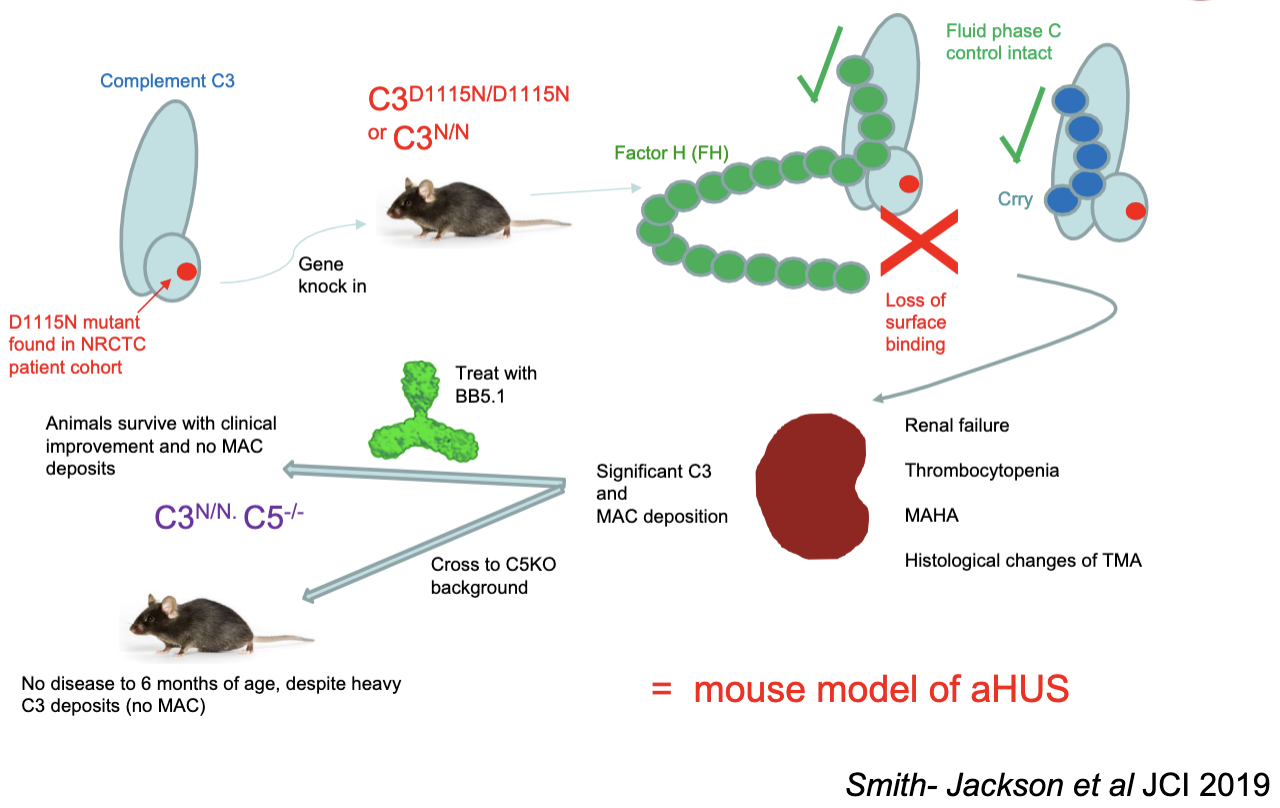
The C3 GOF mouse model of aHUS
Idorsia Pharmaceutics Ltd: hC5a R antagonist
Blocks C5 receptor - stops its signalling immune cells
Protected mice on diet with it
reduction of MAC
what starts the Alternative pathway of complement activation?
spontaneous hydrolysis
name two cell membrane bound regulators of complement
DAF (CD55) Decay Accelerating Factor: Disrupts C3/C5 convertases
CD59 (Protectin): Inhibits the Membrane Attack Complex (MAC)
name the first licenced terminal pathway blocking monoclonal antibody
Eculizumab, 2007
what type of molecule is compstatin and how was it found
Small molecule inhibitor
Phage display screening