ap psych unit 1
1/194
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
195 Terms
nature vs nurture
nature: hereditary (chromosomes, dna, inherited brain chemistry, genetic predisposition)
nurture: environmental factors (family interactions, education, where you live, in vitro exposures, diet)
Genetic Predisposition
an increased likelihood of developing a disease based on a person's genetic makeup
evolutionary perspective
-the study of the evolution of behavior and the mind, using principles of natural selection
-natural selection, adaptation, survival, reproductive success
natural selection
inherited traits that enable an organism to survive will be more likely passed on to succeeding generations
-ex: oppoable thumb, fear of heights
eugenics
-pseudoscientific view that the genetic makeup of the population can be improved by selective breeding;preventing reproduction by people with various disabilities
-selective breeding, selective sterilization
twin studies
-Assess the influence of heredity on expression of a behavior
studies of identical twins separated at birth
The extent to which they are different is likely due to "nurture" (environment)
studies on fraternal twins raised together
The extent to which they are different is likely due to "nature" (genetics)
family studies
research conducted among siblings, parents, or children to assess evidence for genetic links for characteristics or outcomes, often related to health or disease.
adoption studies
Investigates the relationships among genetic and environmental factors in the development of personality, behavior, or disorder by comparing the similarities of biological parent-child pairs with those of adoptive parent-child pairs.
the nervous system
-central nervous system (brain and spinal cord)
-peripheral nervous system (all other nerves)
central nervous system
-brain and spinal cord
-brain: body's "command central"
-Spinal Cord: sends messages from and to the brain; handles swift reflexes
peripheral nervous system
-everything NOT in the central nervous system
-somatic
-autonomic
somatic nervous system
-carries motor messages from brain to skeletal muscles through motor (efferent) neurons
-sends messages to the brain from sense organs to the brain through sensory (afferent) neurons
somatic neurons
-Same
-Afferent
-Motor
-Efferent
autonomic nervous system
controls glands and muscles of the internal organs involved in:
-respiration
-pupil dilation
-heart beat
-digestion
things within autonomic nervous system
-sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems
sympathetic nervous system
-fight or flight
-dilated pupils
-increases heart rate
-adrenaline production
-slows digestion
parasympathetic nervous system
-"parachute," returns body to homeostasis
-rest and digest
-pupil constriction
-slow heartrate
-stimulate saliva
-stimulate digestion
parts of neuron
-cell membrane
-cell body
-dendrites
-axon
-myelin sheath
-node of ranvier
-axon terminal
axon
carries a neural impulse away from cell body
cell body
neurotransmitters (chemical messengers of nervous system) are made here!
dendrites
receives incoming neural messages
myelin sheath
made up of glial cells: protects and speeds up neural transmission
terminal button
-vesicles containing neurotransmitters (the chemical messengers of the nervous system)
-synapse - space between two neurons; neurotransmitters are released into here
-receptor sites on dendrite of receiving neuron; neurotransmitters lock into these receptor sites and either open them up or keep them closed
direction of neural impulse
1. dendrites
2. soma
3. axon
4. axon terminal
synapse
space between two neurons
neurons
-Transmit information
-building blocks of nervous system
-ensory neurons (afferent), motor neurons (efferent), interneurons
-like Queen Bees they cannot feed or protect themselves
glial cells
-Structure
-Insulation
-Communication
-Waste transport
-like worker bees; not only do they provide structure and support, they play a role in learning, thinking & memory
reflex arc
-simple, automatic response to a sensory stimulus BEFORE sensory stimulus reaches the brain
-sensory neurons: send signal to brain
-spinal cord:
-intercepts signal and through interneurons sends info to …
motor neurons: contract muscles
neural transmission
the transfer of information between two neurons
what type of communication do neurons use
-Neurons use electrochemical signals to communicate with each other.
-Neurons release chemical transmitters at the synapses, the tiny gaps between neurons, that either excite or inhibit the receiving neuron from firing its own action potential.
what type of communication is used WITHIN the neuron
Electrical signals, called action potentials, send information from the cell body to the axon terminals. The speed of the signal is influenced by myelin, a fatty layer that insulates the axon
resting potential
Neuron at rest. The inside of the neuron's membrane is negative compared to the outside.
describe neuron action potential graph
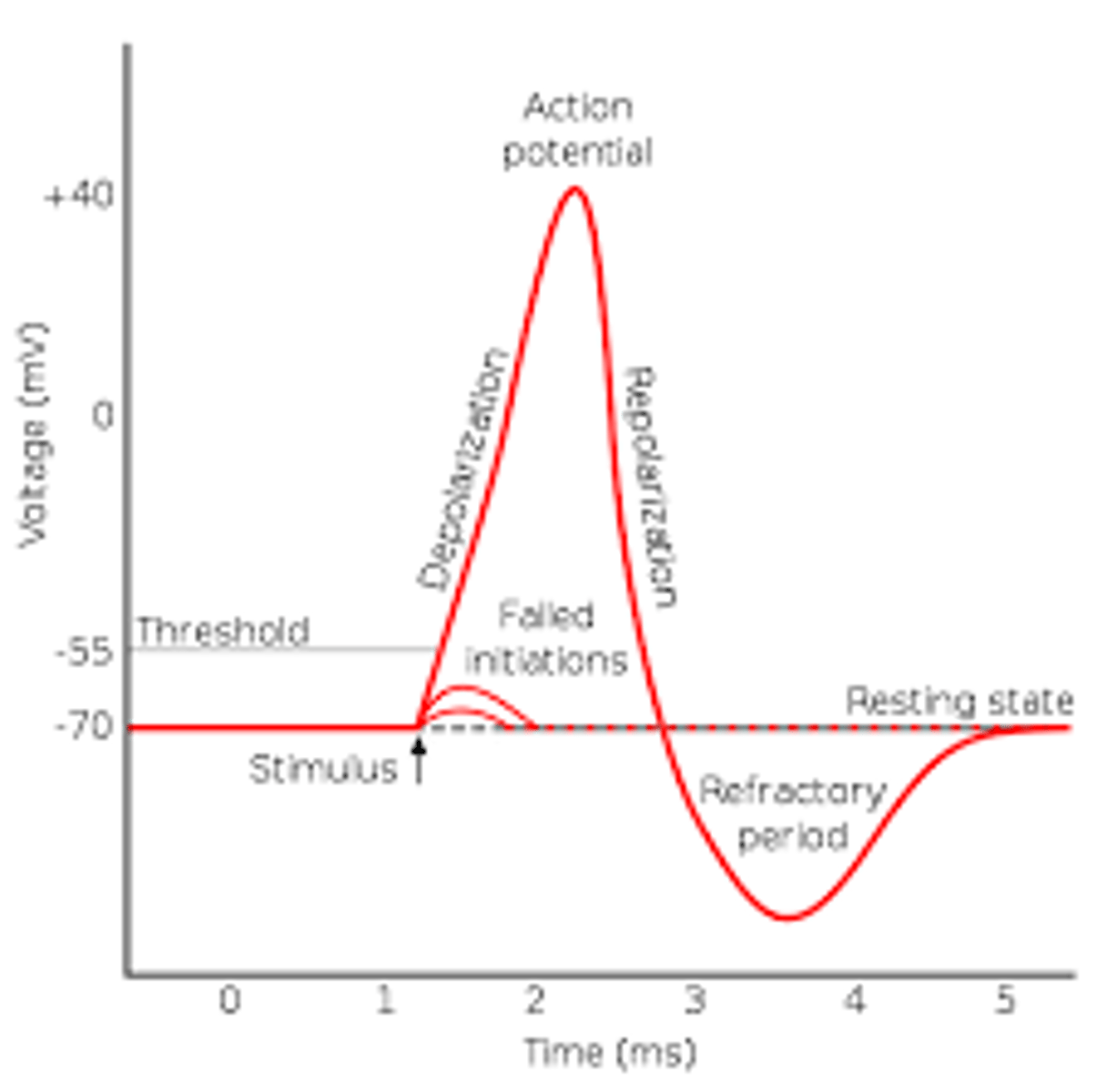
threshold
Minimum intensity needed to trigger an action potential (neural impulse)
action potential
-neural impulse
-Electrical charge that travels down the axon
depolarization
Movement of a cell's membrane potential to a more positive value
all or none principle
-a neuron's reaction of either firing (with a full strength response) or not firing
-like a dunk tank (you either get dunked nothing happens at all)
refractory period
A brief resting pause that occurs after a neuron has fired; subsequent action potential cannot occur until the axon returns to its resting state
neurotransmiters
-chemical messengers of the nervous system
FATE: 1. degraded by enzymes in synaptic space OR
2. reuptake THEN repackaged for reuse
reuptake
the reabsorption of a neurotransmitter by the sending (pre-synapatic) neuron
multiple sclerosis
-disease of the central nervous system
-myelin sheath is destroyed, causing a slow down of messages or even death of a neuron
-impacts vision, movement, cognition
myasthenia gravis
-affects neuromuscular system
-receptor sites on neurons responsible for muscle contraction are attacked by the immune system
-muscle weakness affects all muscles including organs
-impacts muscles and speech
excitatory neurotransmitters
-increase the chance that the next neuron in the chain will "fire" (achieve an action potential)
-example: if you get into an argument with a friend, you might find that your heart beats faster, your mind races; these are the results of excitatory neurotransmitters such as epinephrine (adrenaline)
inhibitory neurotransmitters
-decrease the chance that the next neuron in the chain will "fire" (achieve an action potential)
-example: after an argument, inhibitory neurotransmitters, such as GABA, help you to calm down and return to a more balanced state
slow actin neurotransmitters
-acetycholine
-norepinephrine
-dopamine
-serotonin
-endorphins
-substance P
acetycholine
-slow acting
-excitatory properties
-CNS: attention, learning, memory
-PNS: muscle contractions
-Deficit: dementia, paralysis
-Surplus: spasms, cramps
norepinephrine
-slow acting
-excitatory properties
-CNS: alertness, attention
-PNS: Fight or flight
-Deficit: depress mood, attention & focus issues
dopamine
-slow acting
-inhibitory and excitatory properties
-CNS: voluntary movement, regulation emotions, motivation, pleasure/reward
-Deficit: tremors and decreased mobility (Parkinsons)
-Surplus: Hallucinations (Schizophrenia)
serotonin
-slow acting
-inhibitory and excitatory properties
-CNS: mood, hunger, sleep, arousal
-PNS: modulates pain signals
-Deficit: depression
endorphins
-slow acting
-inhibitory properties
-Both CNS & PNS: Inhibit pain transmission
indirectly increase pleasure
-Deficit: pain
-Surplus: euphoria (but if induced chemically, a suppression of endorphin production)
substance P
-slow acting
-excitatory properties
-modulation of pain
-Surplus: chronic pain
fast acting neurotransmitter
-glutamate
-GABA
glutamate
-fast acting
-excitatory properties
-Most abundant excitatory neurotransmitter
-involved in memory
-Surplus: migraines, seizures, anxiety
GABA
-fast acting
-inhibitory properties
-Most abundant inhibitory neurotransmitter;
-significant role in sleep regulation
-Surplus: sedation, lack of coordination, memory impairment
-Deficit: anxiety, seizures (epilepsy), insomnia, Huntington's disease
hormones
-the chemical messengers of the endocrine system
-regulate growth, hunger, sleep, immune response, and sexual motivation
hormone examples and what they do
-adrenaline: fight or flight, adrenal glands
-leptin: hunger (supressant), stomach
-melatonin: sleep
-ghrelin: hunger (stimulation), rowling stomach
-oxytocin: labor, lactation, love
qualities of neurotransmitters
-location: nervous system (neurons)
-speed: fast-acting (miliseconds)
-duration: short lived and localized
-release mechanism: in response to action-potentials
qualities of hormones
-location: endocrine system (glands)
-speed: slower acting (seconds to minutes)
-duration: long lasting and affects whole body
-release mechanism: in response to signals from brain to glands
How are neurotransmitters released?
neurotransmitters are released into a synapse when an action potential reaches the terminal button.
psychoactive drugs
-Chemical substances that alter brain function by interacting with neurotransmitter systems
-agonist, antagonist, reuptake inhibitor
agonist drugs
-enhances the effects of a neurotransmitter
-IT CAN MIMIC A NEUROTRANSMITTER AT THE RECEPTOR SITES OF THE RECEIVING (POST-SYNAPTIC NEURON)
-note how an agonist (drug) fits like a key into a lock:
the "key" is the agonist, the "lock" is the receptor site on the receiving neuron
-the agonist has the similar properties to the neurotransmitter is it mimicking.
What do agonist drugs do?
Agonists either MIMIC a neurotransmitter action or BLOCK its reuptake
reuptake inhibitor
-type of agonist
-enhances the effects of a neurotransmitter by blocking its reuptake
antagonist drugs
-prevents the effects of a neurotransmitter
-the antagonist occupies the receptor site on the post- synaptic (receiving) neuron.
-it's like a key that fits into a lock but the lock won't turn and if the wrong key is in there, the right key can't do it's job
-the antagonist has just enough similar properties to the neurotransmitter to occupy the receptor site but it won't actually activate it and the site is now blocked
What do antagonist drugs do?
Antagonists block the actions of a neurotransmitter by occupying the receptor site on the receiving neuron.
stimulants
-increase neural activity
-caffeine, cocaine
caffeine as a stimulant
-Improved concentration, alertness, elevated mood, anxiety at high doses, disruptions in sleep
-most widely consumed!
cocaine as a stimulant
-increased energy, euphoria, and heightened alertness, but also significant risks such as anxiety, paranoia and a crash!
-acts as a reuptake inhibitor for norepinephrine (heightened alertness), dopamine (reward system), and serotonin (euphoria)
depressants
-decrease neural activity
-alcohol
Alcohol as a depressant
-Reduces anxiety and inhibitions
-Depresses activity in Prefrontal Cortex responsible for impulse control, and social behavior.
-Depresses activity in Cerebellum responsible for coordination & balance.
-Slows down motor and cognitive responses
-Poor Judgment, Social Misinterpretation, Overconfidence,
-Memory Lapses
-GABA agonist?
hallucinogens (psychedelics)
-Indirectly stimulates dopamine release
-Distortions in perception and/or cognition
-marijuana, LSD
THC/marijuana as a hallucinogen
-Mild hallucinations
-Increased sensitivity to sound and light
-Euphoria and Relaxation
-Anxiety and Paranoia
-Enhanced Creativity
-Depersonalization (out of body experience)
-Memory loss
LSD as a hallucinogen
-Vivid visual hallucinations
-Near death experiences
-Potential for Flashbacks
-Serotonin Antagonist
opioids
-Pain relievers
-They are endorphin agonists
-Neurons cease producing endorphins when opiates are present in the brain
negative outcomes of drug use
-tolerance: Requiring larger doses to achieve the same effect
-addiction: Disease involving physical and/or psychological dependence
-withdrawal: Symptoms associated with stopping use
biopsychology
The scientific study of the links between biological (genetic, neural, hormonal) and psychological processes
biopsychosocial
The scientific study of the links between biological, psychological and social factors impact mental health and disease
neuroplasticity (plasticity)
The brain's ability to build new pathways, strengthen existing ones in response to new information or when necessary to compensate for damage to parts of the brain.
using case studies to understand baiin function
-Cases like Phineas Gage and H.M., are examples of using unusual situations to understand how brain damage affects areas and to develop theories of neurotypical cognition.
-Essentially, the people used had brain lesions (whether by accident or medical necessity) and, through them we learned more about specific functions of the brain.
EEG (electroencephalogram)
Noninvasive tool to see brainwave activity; useful to diagnose seizures and sleep disorders (shows brain function)
fMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging)`
A brain imaging technique that measures blood flow and oxygenation to show which areas of the brain are active. Can see effects of strokes, help plan surgeries and treatment (shows brain structure and function)
lesioning
An individual who has had areas of their brain destroyed (lesioned) out of medical necessity or by natural means can be studied to see the effects of that damage on cognitive and behavioral functions (HM, Phineas Gage).
hemispheric specialization
Studies of people who have had their hemispheres separated (by cutting nerves in the corpus callosum) to stop seizures from spreading can be examined to learn how each hemisphere functions independent of the other one.
left hemisphere
-Language
-Logic
-Motor control of right side
-Receives sensory signals from right side
right hemisphere
-Abstract thought
-Recognize faces
-Motor control of left side
-Receives sensory signals from left side
Contralateral Hemispheric Organization
The property of the brain that causes the brain hemispheres to represent the opposite side of the body
brain stem/hindbrain
Arousal, attention & vital life functions
reticular activating system (RAS)
-attention and arousal
-sensory filter, controls attention
-controls consciousness
-motivation to engage in rewarding behavior
medulla
-vital life functions
-crossover point for signals coming in from each side of the body
-breathing
-heart rate
-involuntary reflexes (sneezing, swallowing, cougining, vomiting)
-crossover point for signals coming in from each side of the body
cerebellum
-coordinates sequences of movement (with basal ganglia)
balance
-formation of implicit memories*
cerebral cortex
-divided into two hemispheres and includes the limbic system (thalamus, hypothalamus, pituitary gland, hippocampus, amygdala), corpus callosum, and the lobes of the cortex
limbic system/forebrain
emotion, drives & memory formation
thalamus
-sensory "relay" station
-directs incoming messages (except SMELL) to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla
hypothalamus
-Keeps body regulated/maintains homeostasis
-Eat / Drink
-Fight / Flee
-Fornicate
-Sleep / Wake
-Body temperature ("Fahrenheit)
-Governs Endocrine System (Pituitary Gland)
-Linked to emotion and reward
-the 4 f's: fight/flight, feeding, fahrenheit, fornication
hippocampus
-learning, memory, converting short term to long term memories
-Critical to the formation of new, explicit (conscious) memories.
episodic memories vs semantic memories
episodic: personal events or experiences (a concert you attended, what you did on vacation)
semantic: facts, general knowledge (the sky is blue, EVs run with less noise than gas run cars)
amygdala
-emotion
-Controls emotional responses such as fear and aggression and stores those along with memories.
-Damage would reduce emotional responses
-Stimulation would elicit fear and aggressive responses
pituitary gland
-controlled by hypothalamus
-"master gland"
-regulates the activity of other endocrine glands
-secretes hormones including prolactin, oxytocin