Igneous Rocks
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
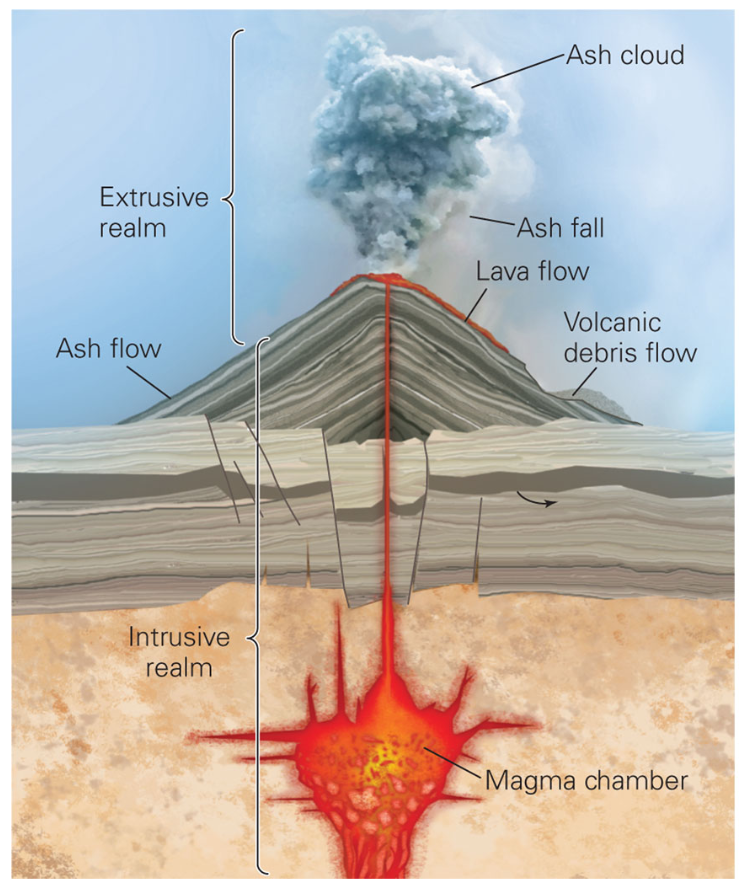
Extrusive vs. Intrusive realm
Extrusive: above surface (ex. lava) → cools on surface
Intrusive: below surface (ex. magma) → cools below surface
What is classifying igneous rocks based on?
Texture
Fine or coarse (depending on how quickly magma cooled)
Mineral content
Depends on the origin & chemical evolution of the magma
Reflects the chemical & cooling history of the rocks
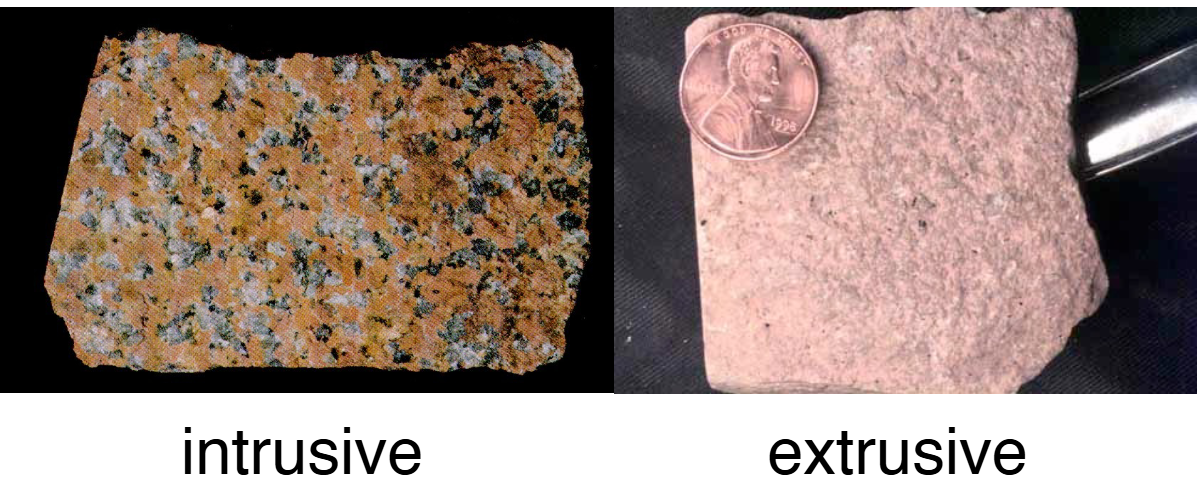
Texture: extrusive vs. intrusive
Extrusive: can’t see individual minerals (cooled at surface)
Intrusive: can see each individual mineral (bad at moving heat below surface)

6 minerals that are >95% of igneous rocks
Mafics (Mg-Fe): olivine, pyroxene, hornblende (amphibole)
Aluminosilicates (Si-Al-O): feldspar (plagioclase & K-spar), quartz, micas
3-4 of these minerals are common in each type of igneous rock
Silicate tetrahedron structure
SiO₄⁴⁻
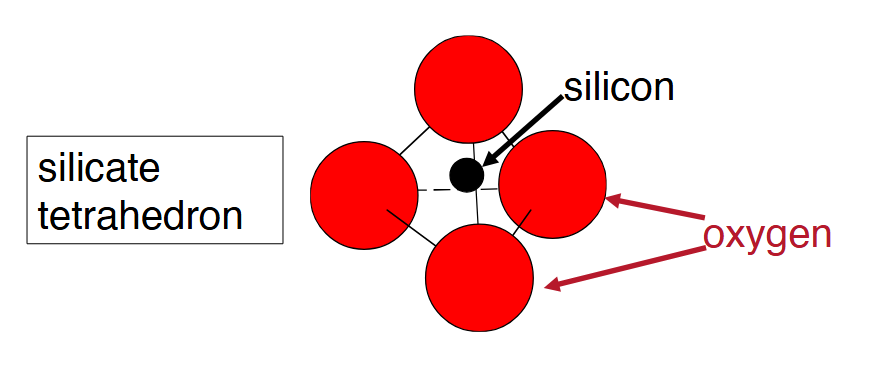
Silicate minerals
All have silicate tetrahedra as part of structure
Some have many metal ions attached to the tetrahedral
Others are made of 3-dimensional framework of tetrahedral
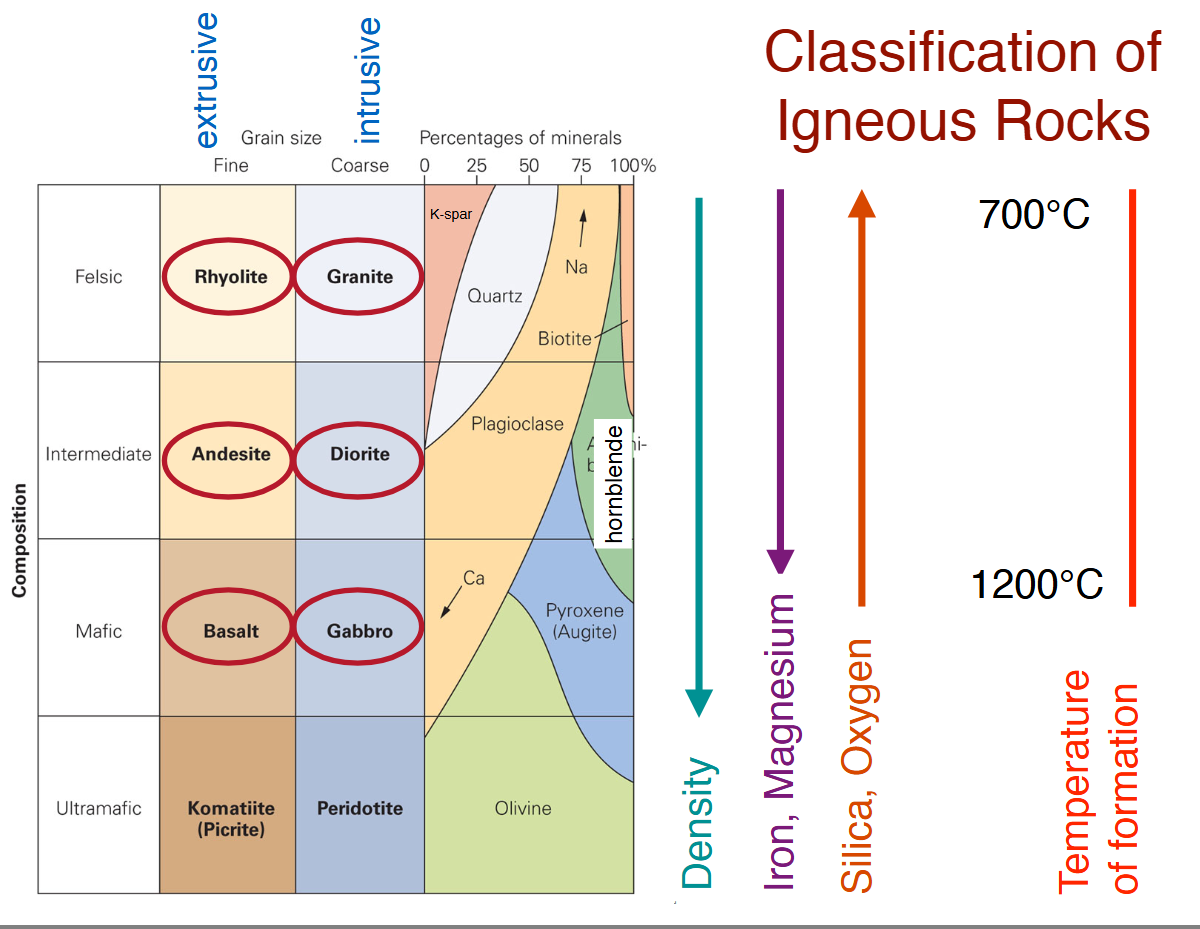
Broad classification of igneous rocks
Felsic - Si + O
Intermediate - between the 2
Mafic - Mg + Fe
Fine vs. Coarse grained

Mafic rocks
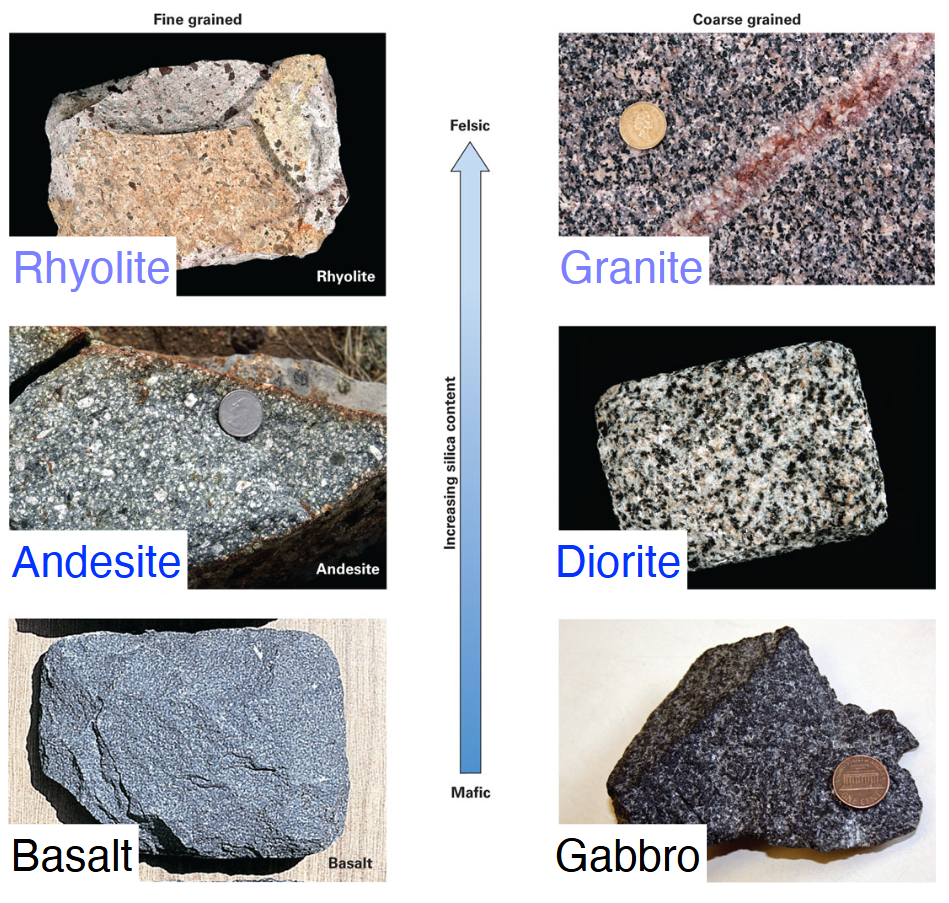
Gabbro:
Intrusive
Cooled slowly
Coarse-grained
Basalt:
Extrusive
Cooled quickly
Fine-grained
Same chemical & mineralogical composition as olivine, feldspar, & pyroxene

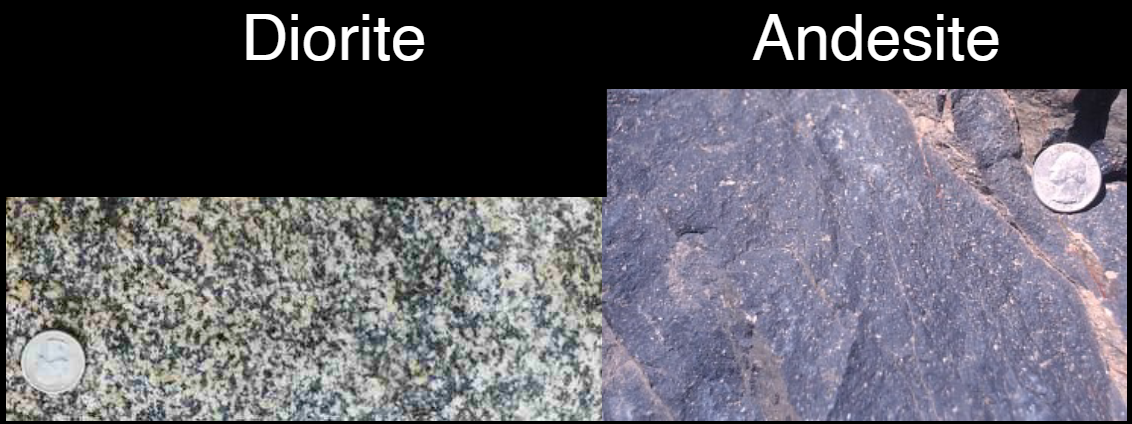
Intermediate rocks
Diorite:
Intrusive
Cooled slowly
Coarse-grained
Andesite:
Extrusive
Cooled quickly
Fine-grained
Same chemical & mineralogical composition as feldspar, hornblende, & mica
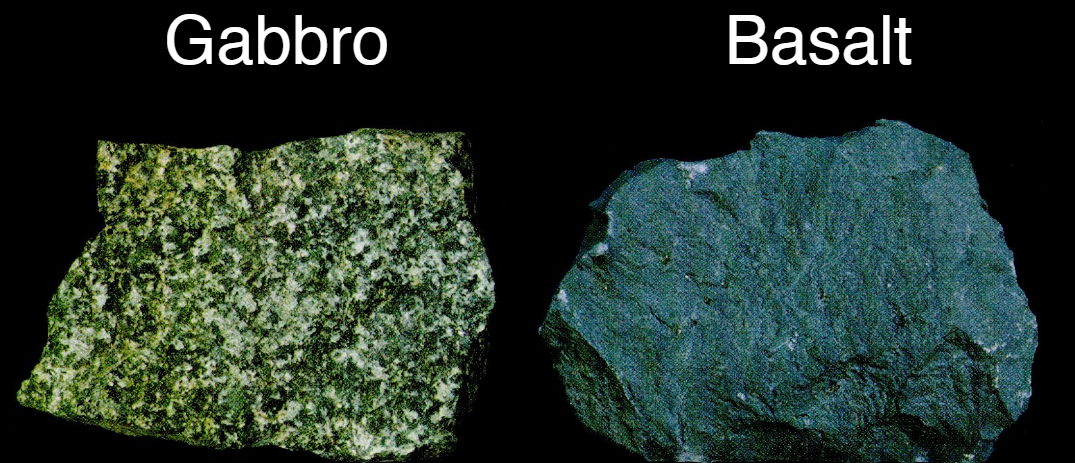
Felsic rocks
Granite:
Intrusive
Cooled slowly
Coarse-grained
Rhyolite:
Extrusive
Cooled quickly
Fine-grained
Same chemical & mineralogical composition as mica, feldspar, & quartz
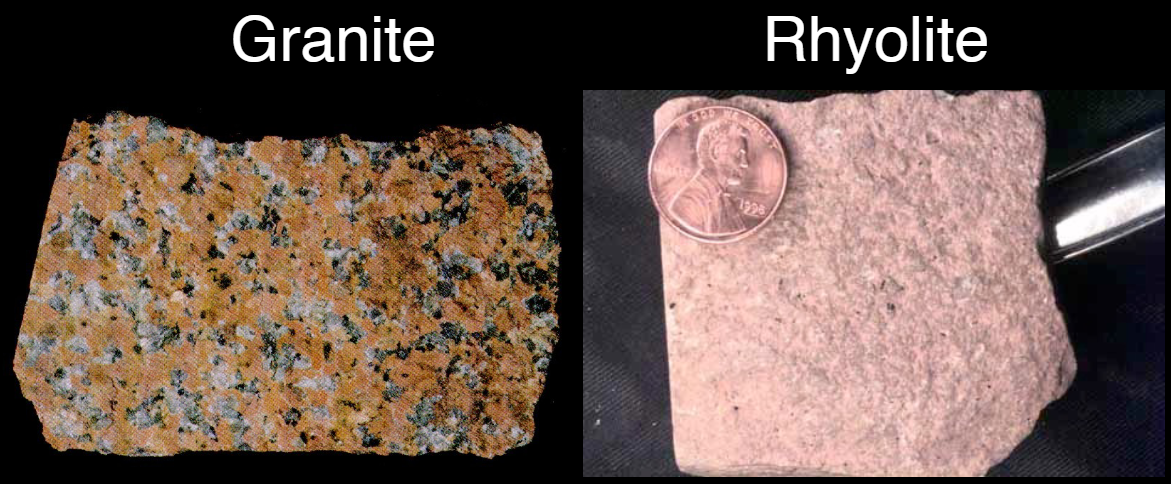

Rock families (3)
Basalt-Gabbro
Mafic rocks
Make up the ocean crust (ex. Hawaiian islands, hotspots, basalt plateaus)
Andesite
Intermediate rocks
Volcanic island arcs, active continental margins like the Andes, subduction zones
Granite-Rhyolite
Felsic rocks rich in quartz, feldspar, few mafic minerals
Granite & granodiorite most common form of continental crust
Occurs primarily on the continents
Textures of Igneous rocks
Phaneritic: intrusive & can see many minerals in a row
Porphyritic: different mineral sizes in a rock with larger K-feldspar “phenocrysts”
Aphanitic: extrusive & can’t see minerals (came out of volcano & cooled really quickly)
Porphyritic: larger amphibole phenocrysts
They have the same chemical/mineralogical composition but different cooling rates

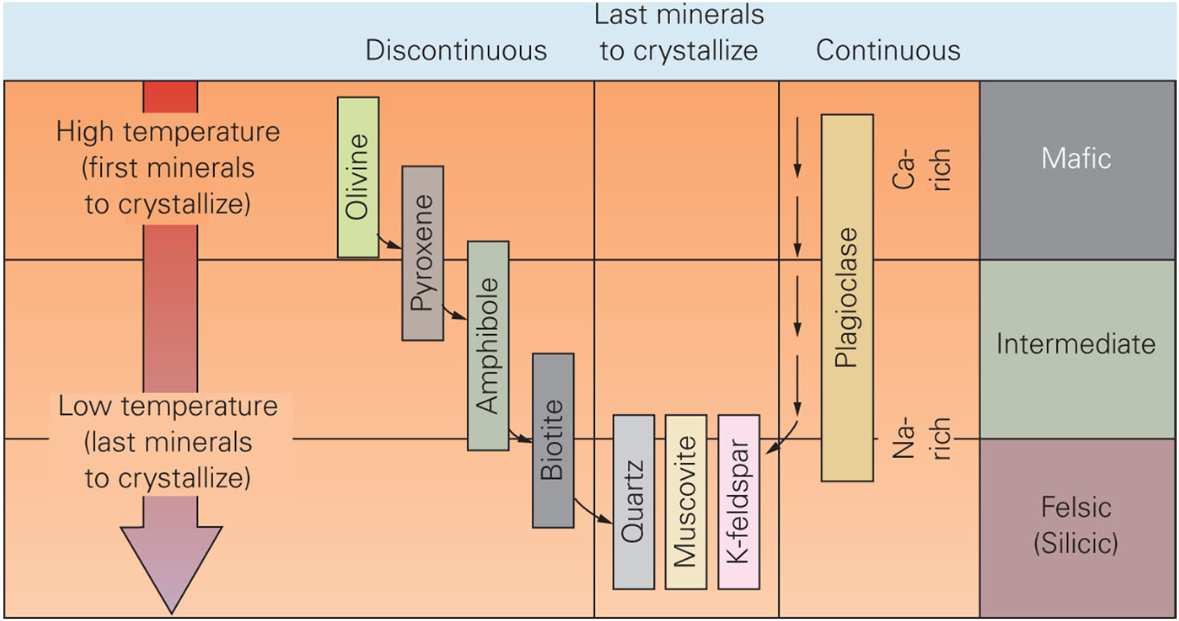
Bowen’s Reaction Series
Describes the specific sequence in which minerals crystallize from cooling magma. Different minerals form at distinct temperatures, from high-temperature - iron-rich, mafic minerals - (e.g., olivine) to lower-temperature - silica-rich, felsic minerals - (e.g., quartz).
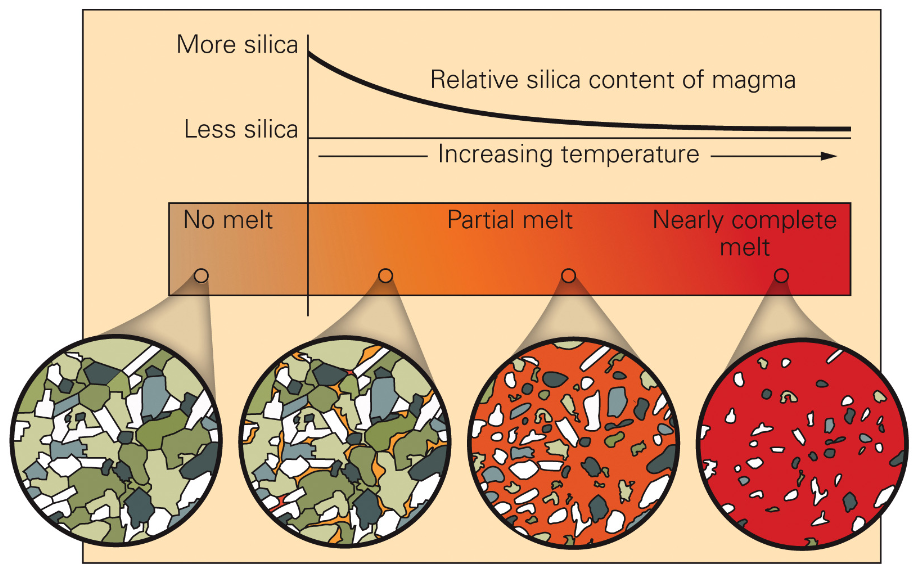
Partial Melting
Makes the melt silica-enriched because felsic minerals melt first
Always makes a more felsic magma than the rocks you start with
Different types of magma
Partial melting of upper mantle (felsic) rocks make basaltic (mafic) magma
Sedimentary rock + basaltic oceanic crust make andesitic (intermediate) magmas at subduction zones (ex. Andes)
Melt of sedimentary, igneous, & metamorphic crustal rocks make granitic (felsic) magma - only found on the continents (subduction zones)
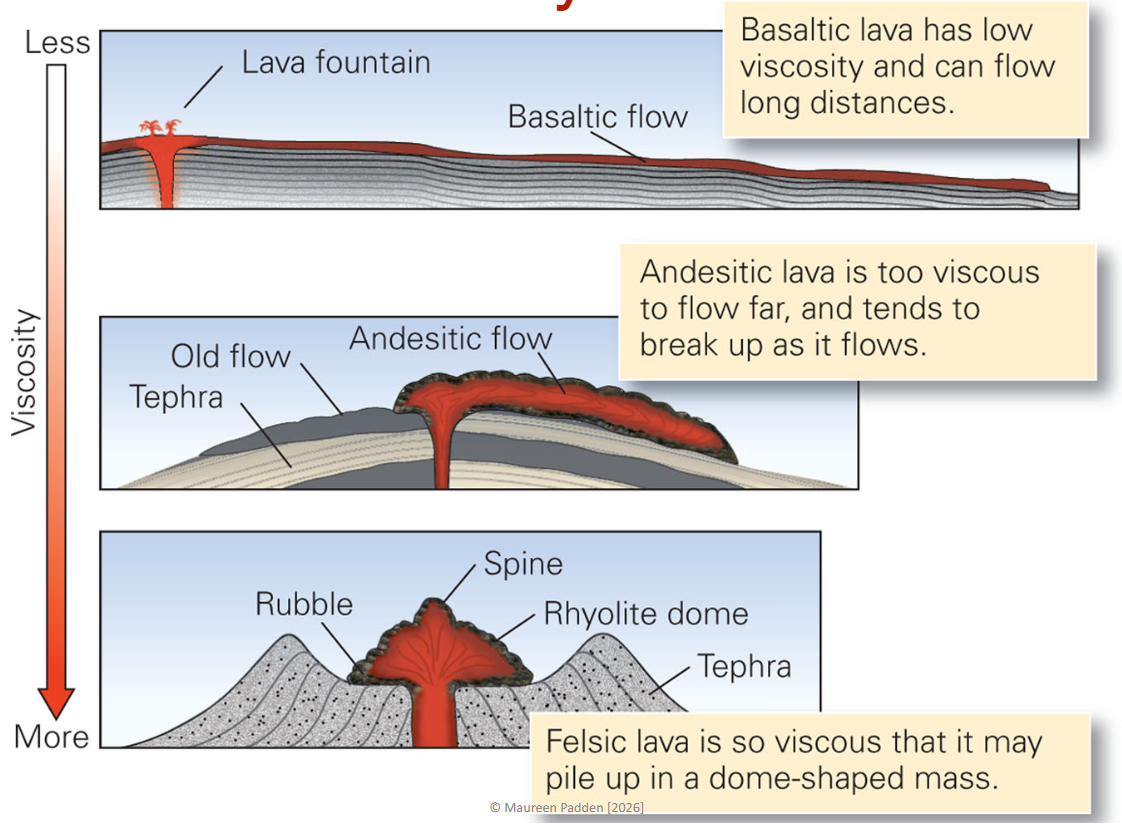
Lava Viscosity
Mafic → Felsic with low → high viscosity
Viscosity ∝ silica content
Silica tetrahedra link to each other, causing higher viscosity
25% increase in silica (basalt to rhyolite) causes 10^5 viscosity increase
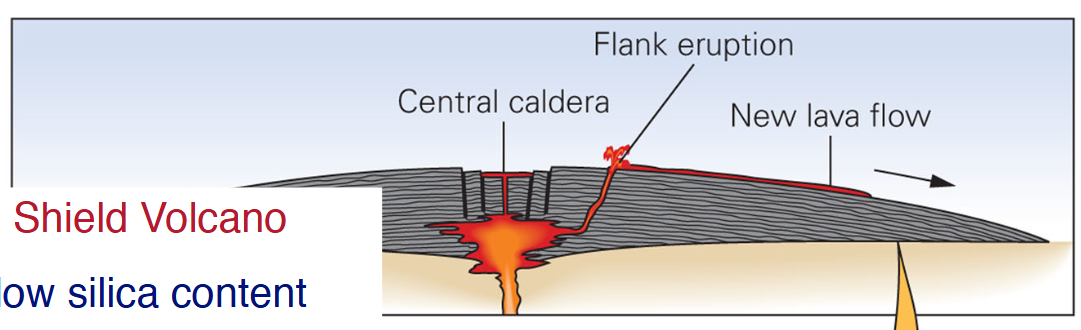
Shield Volcano
Low silica content, low viscosity, runny lava placid eruptions
Mafic volcanoes which are the biggest on earth due to the lava flowing down, forming a small hillC
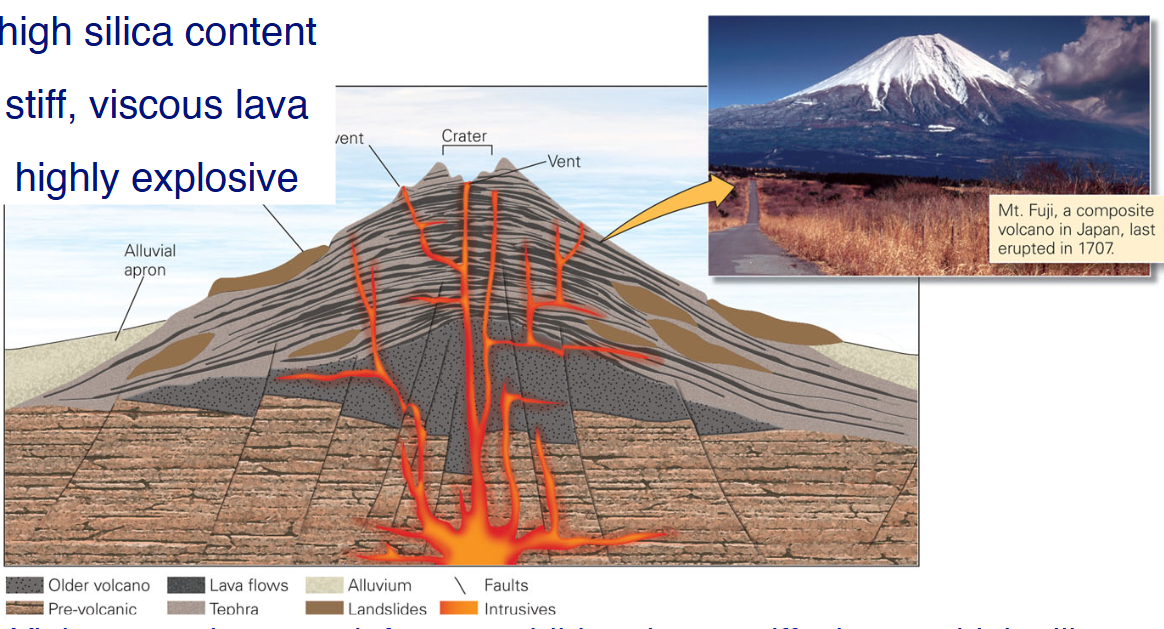
Composite Volcano
High silica content, stiff, viscous lava, highly explosive
Felsic volcanoes
Violent eruptions from gas buildup due to stiff, viscous, high-silica magmas (rhyolite)
“Cone” shape is made from debris (“ash”: small rock pieces) that falls out near volcano vent
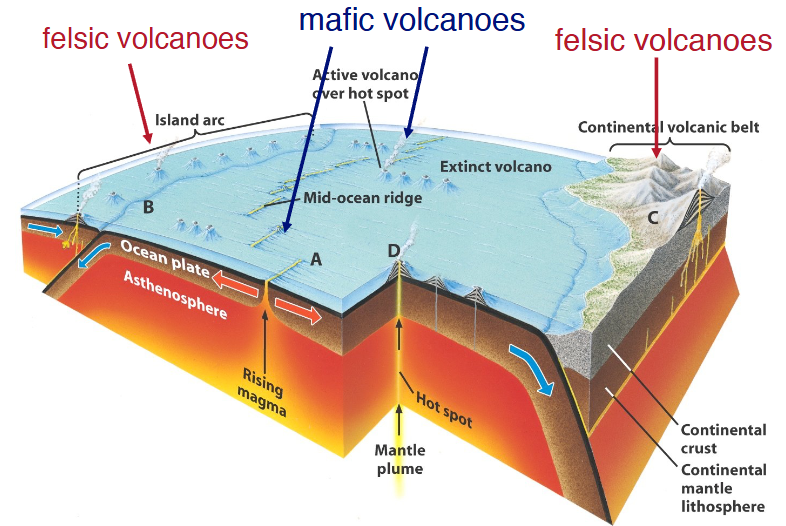
Tectonic setting of volcanoes (2)
Felsic volcanoes: ocean-ocean/continent subduction with barely an age difference; partial melting makes felsic & intermediate rocks; either makes island arcs or continental volcanic belt
Mafic volcanoes: formed by the eruption of low-viscosity, Mg and Fe rich magma from the partial melting of the mantle at hot spots or divergent plate boundaries. These hot, runny, and gas-poor lavas erupt effusively, flowing easily to build broad, gentle-sloped shield volcanoes or cinder cones.
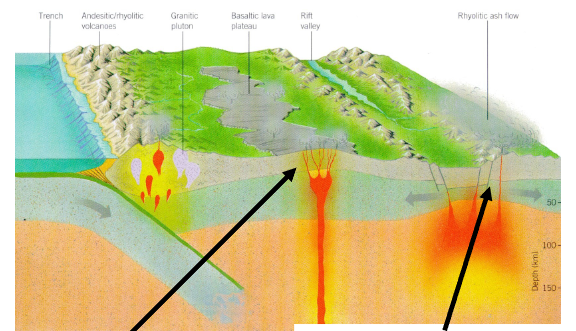
Tectonic setting of igneous activity
Mantle flood basalts (mafic) rise through continental crusts
Mantle hot-spots under the continental crust cause melting of Si-Al crust = rhyolite (felsic)
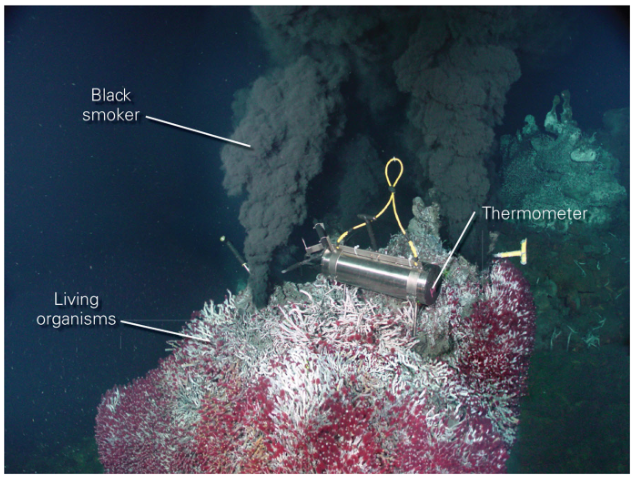
What does volcanism look like at MORs (divergent boundaries)?
Whole different ecosystem that doesn’t need light with microbes that depend on sulfite (& other minerals) from the magma underneath that’s “superheating” the water
Types of basaltic lava
Pahoehoe: ropy/smooth & flows easily with top solid surface that cools while the underneath still melts
aa lava: thicker, forms blocks that tumbles over itself
Hazards: vog (volcanic smog), forest fires, asphalt (toxic when melted) on road melts
Mount St. Helens
Convergent boundary volcano
Right before: Gas pressure in magma chamber pushed out against the volcano, causing a bulge on the north flank
After: mini volcano (volcanic plug) formed in the middle due to cooled lava with the side of the mountain blown out
How high can eruption plumes get?
~ 2 km
2 types of volcanic flows
Pyroclastic: deadly, fast-moving clouds of volcanic ash & gas
speed > 200 km/h
temp > 800 degrees C
feature of rhyolitic (felsic) volcanoes
Lahars: mix of ash & water from glacier volcanoes which melts the ice immediately when erupted
Which flow is faster & travels the farthest?
Lahars travel slower but travel the farthest
Yellowstone rhyolite cliffs
formed by explosive volcanic eruptions and lava flows
How do you check the status of a volcano?
GPS size & shape
Earthquakes
Gas pressure
Temperature
Pumice blocks
From volcanic eruptions with high volcanic activity & made of solidified, highly porous (many holes/gas bubbles) volcanic foam (often rhyolite or dacite).
How are minerals in an igneous setting from a melt related by cooling speed & size?
They are large if formed slowly (vice versa)
Large Igneous Provinces relevance
Are basalt
Associated with mass extinctions
Gas released affects the climate, etc.
Basaltic Lava - Flood basalts
Very fluid that erupts on flat terrain & spreads out in sheets
Can be thick units covering huge area as in Columbia plateau
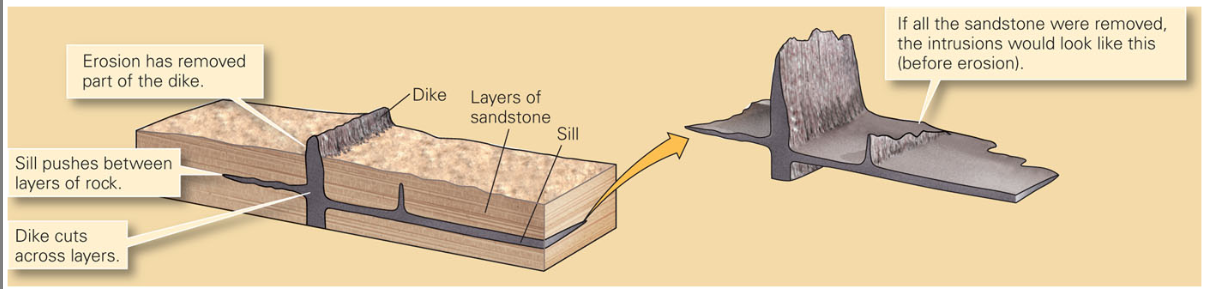
Intrusion types
Concordant (sills): within layers (horizontal)
Discordant (dikes): cuts across (vertical)
Batholiths
Huge features (made of granite) at the crustal scale