Immune System Video and Reading Notes
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Who created the modern smallpox vaccine?
Edward Jenner
How did Edward Jenner create the vaccine?
Using pustules of cowpox was scratched on an individual’s skin
What are monoclonal antibodies?
commercially produced; type of antibody is mass produced in a lab
What are some pathogens can be treated by monoclonal antibodies?
rabies, anti-venom, cancer, Covid
What are some pathogens that can be diagnosed by monoclonal antibodies?
HIV, flu, COVID, strep (and pregnancy)
What animal is used to produce them (monoclonal antibodies) in labs?
mice
Hybridoma
fusion of B cell and tumor cell
Why are tumor cells needed to make monoclonal antibodies?
they divide rapidly
What hormone can be detected by monoclonal antibodies?
human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)
is blood or urine used for the most common type of pregnancy test?
Urine test
Why is there always a control on the test?
To show that the test is working properly/ not defective
What is the first step of a pregnancy test? (Positive result)
If hCG is present in urine, it attaches to free antibodies attached to a dye
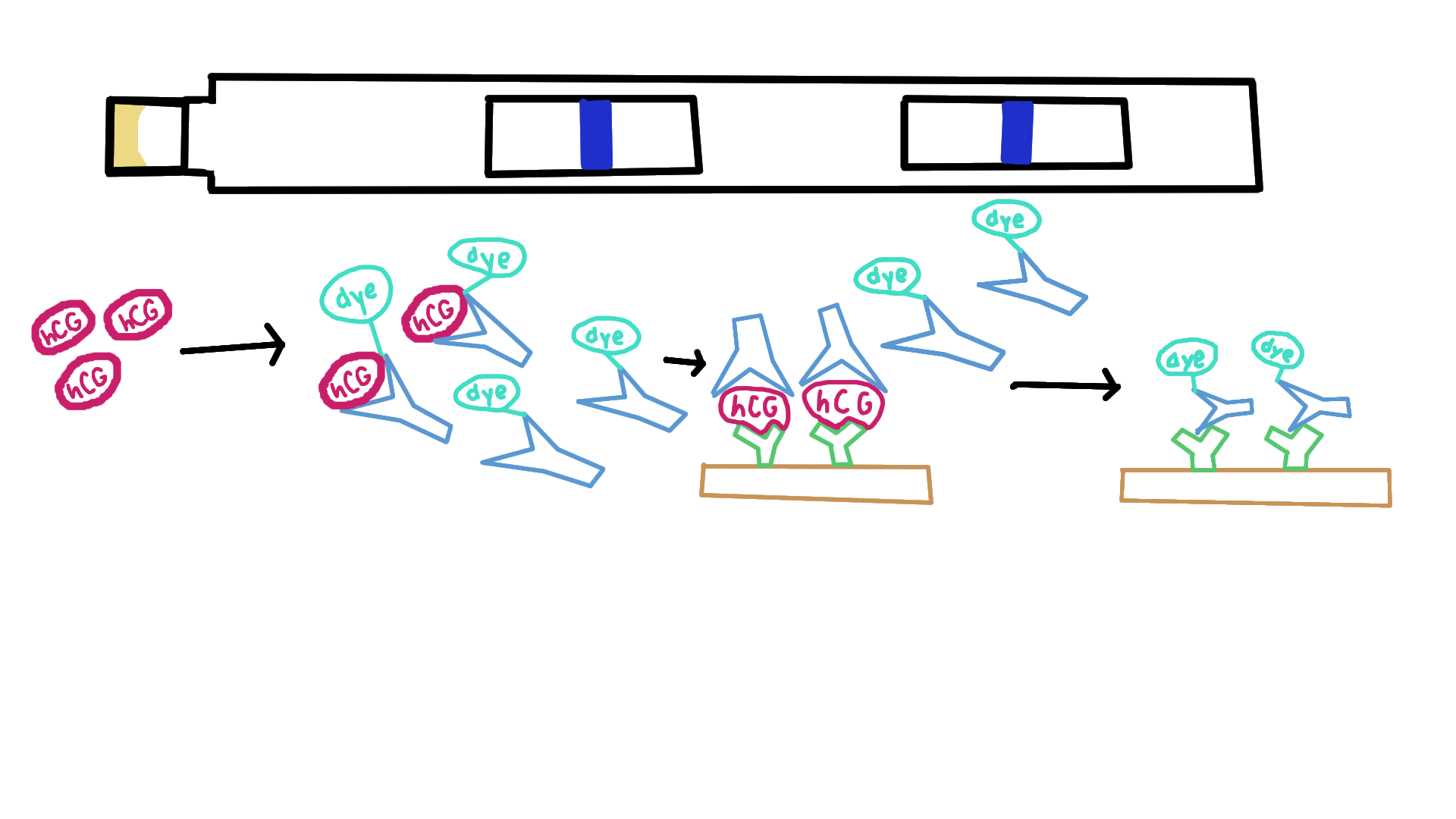
What is the second step of a pregnancy test? (Positive result)
hCG-free antibody complex moves up the stick (capillary action) → then binds to immobilized hCG antibodies to create a positve result in the first window (closest to urine)
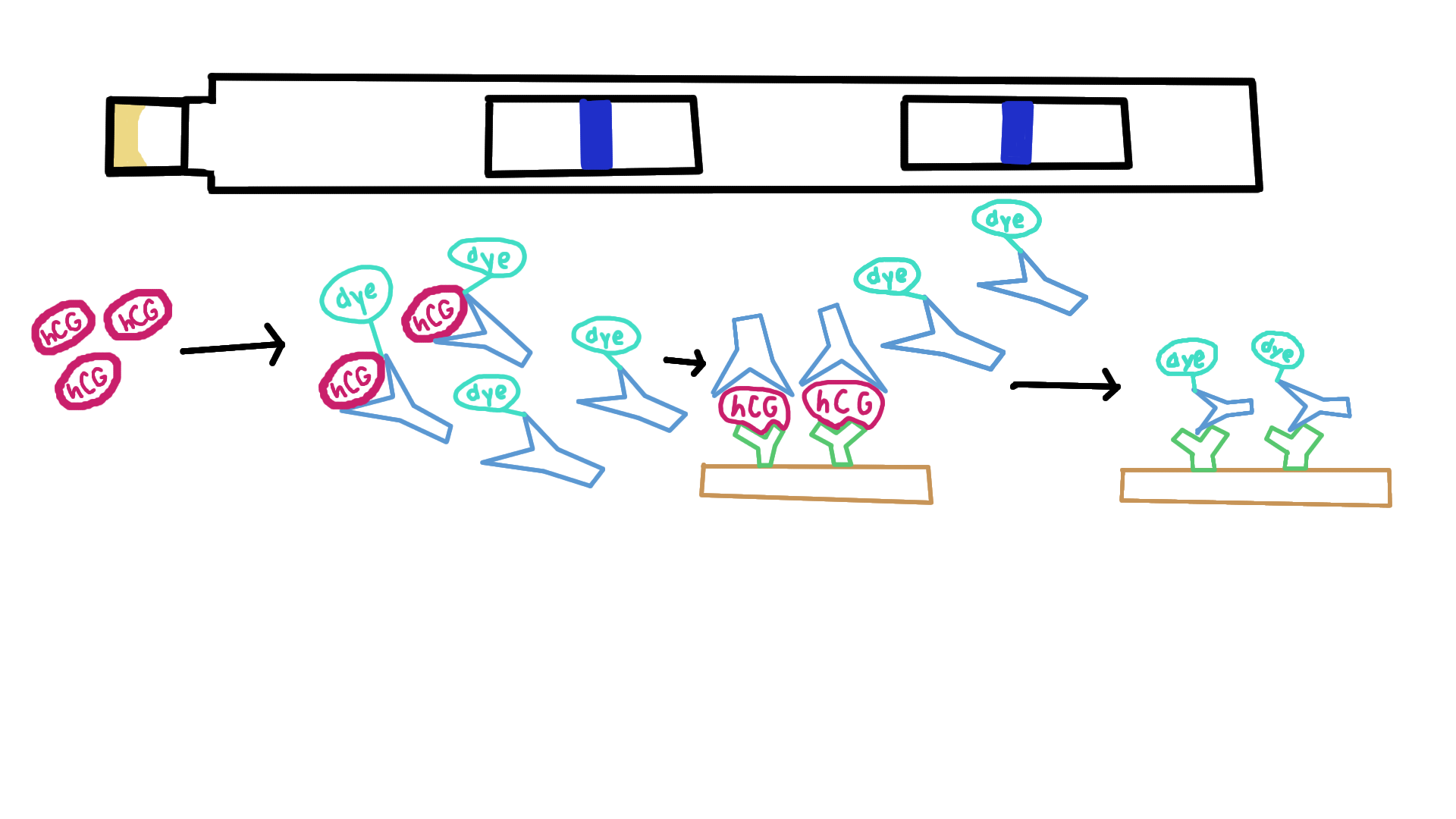
What is the third step of a pregnancy test?
Free antibodies with dye continue to move upwards and bind to immobilized antibodies that make the control mark in the second window
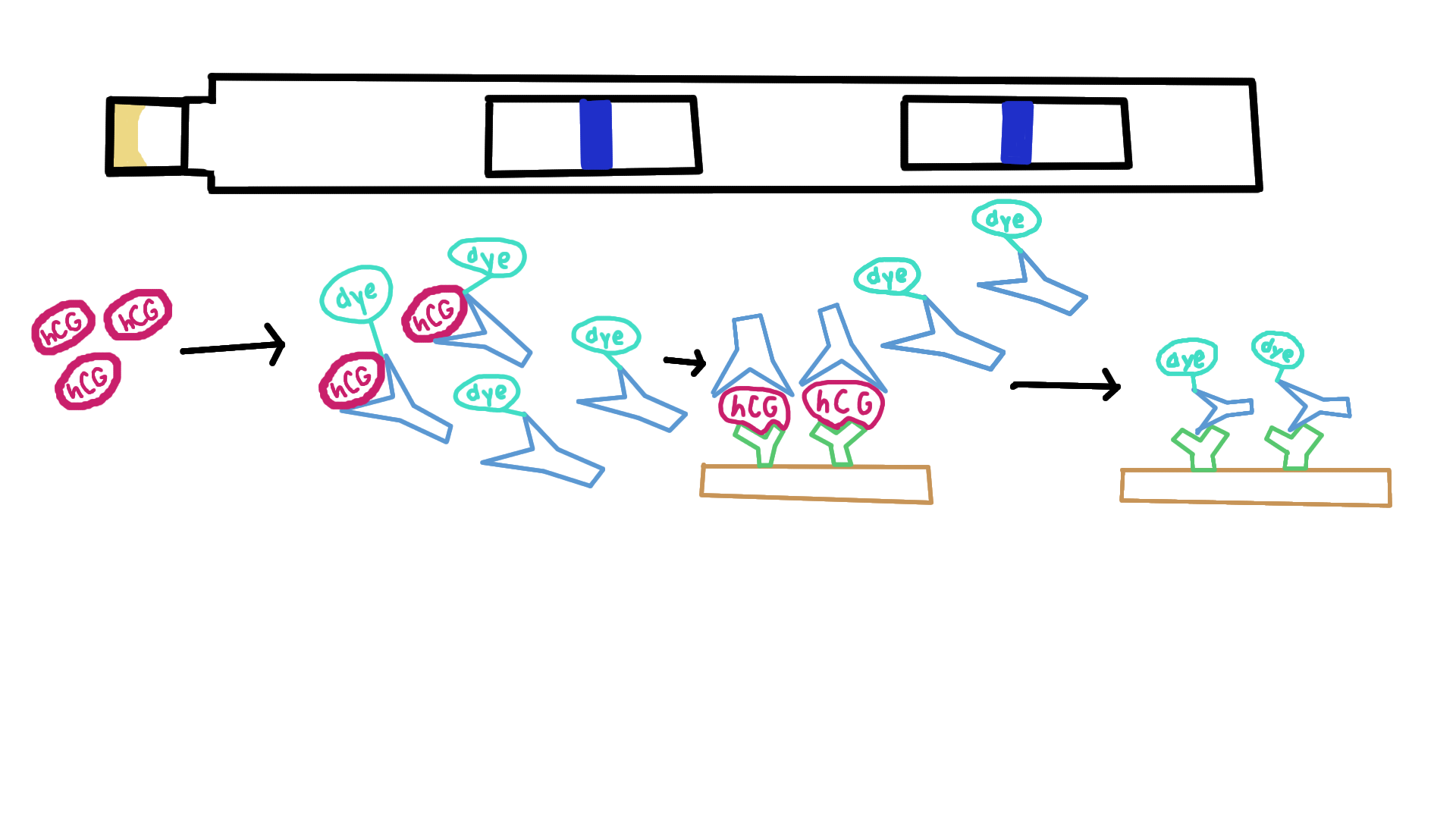
What happens between a pregnancy test and non-pregnant urine?
The urine won’t make a mark in the first window, but will still move up to cause the free antibodies to bind to immobilized antibodies that can make a control mark in second window
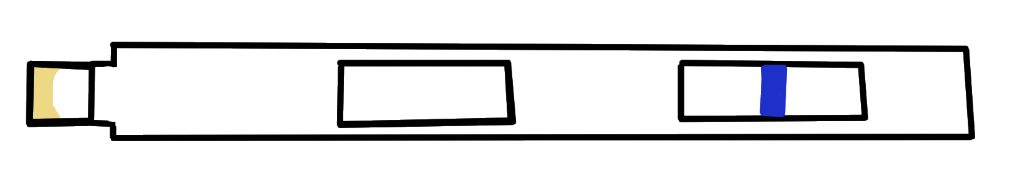
Why does non-pregnant urine not make a mark in the first window?
Because there’s no hCG
What is the full name of the HIV virus?
Human immunodeficiency virus
Does the virus HIV survive long outside a body?
doesn’t survive long
In what type of body fluids is HIV found?
found in blood, semen, vaginal fluids, rectal secretion, and breast milk
How is HIV spread (transmitted)?
sex without a condom (abrasions to the mucus membranes can cause minor bleeding)
sharing of hypodermic needles by intravenous drug users
transfusion of infected blood
blood factors like Factor VIII
childbirth and breastfeeding
What type of lymphocyte does HIV destroy?
helper T-cells
When is a person considered to be HIV positive?
when it’s detected that the immune system is making antibodies against HIV
AIDS
Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome
What is one of the rarer opportunistic infections/diseases that people with AIDS get?
Kaposi’s sarcoma
Why is Kaposi’s sarcoma a marker for HIV infection?
marks when antibody production becomes ineffective which allows infections to strike
What does it mean when the antibody production becomes ineffective?
Infections that could be fought by a healthy immune system
What is a retrovirus? (What does it contain?)
genes are made of RNA
What enzyme needs to be involved to produce DNA?
reverse transcriptase
Summarize some of the ways that antiviral drugs work on HIV
inhibit reverse transcriptase
others target the enzyme necessary for protein coat/ insertion of DNA into host cell’s chromosomes