NR 222 Exam #1 Chamberlain
1/156
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
157 Terms
CHAPTER 1
Nursing Today
Benner's Model of Novice to Expert
Novice
Advanced beginner
Competent
Proficient
Expert
ANA definition of nursing
the protection, promotion, and optimization of health and abilities, prevention of illness and injury, alleviation of suffering through the diagnosis and treatment of human response, and advocacy in the care of individuals, families, communities, and populations
ANA Standards of Nursing Practice
Assessment
Diagnosis
Outcomes Identification
Planning
Implementation
Coordination of Care
Health Teaching + Health Promotion
Consultation
Prescriptive Authority + Treatment
Evaluation

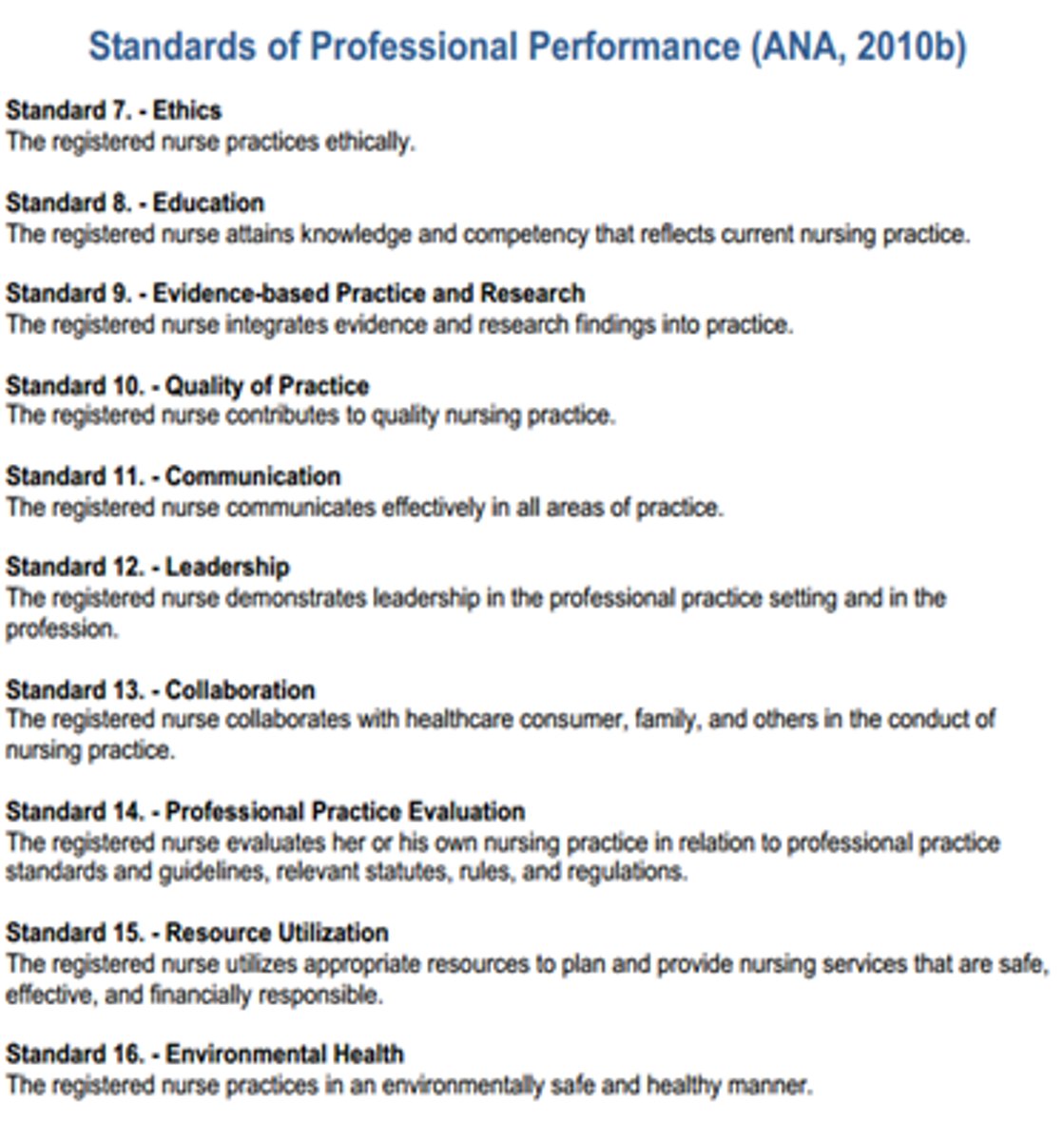
ANA Standards of Professional Performance
Ethics
Education
Evidence-Based Practice
Quality of Practice
Communication
Leadership
Collaboration
Professional Practice
Resources
Environmental Health
Autonomy
Essential element of professional nursing that involves the initiation of independent nursing interventions without medical orders.
Advanced Practice Registered Nurse (APRN)
Most independently functioning nurse; has masters degree in nursing
Clinical Nurse Specialist (CNS)
An APRN who is an expert clinician in a specialized area of practice
Nurse Practioner (NP)
Are prepared to provide direct client care in primary care settings, focusing on health promotion, illness prevention, early diagnosis, and treatment of common health problems
Certified Nurse-Midwife (CNM)
An APRN who is also educated in midwifery and is certified by the American College of Nurse-Midwifes
Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetist (CRNA)
An APRN with advanced education in a nurse anesthetia accredited program
Nurse Educator
works primarily in schools of nursing, staff development departments of health care agencies, and patient education departments
Nurse Administrator
manages patient care and the delivery of specific nursing services within a health care agency
Nurse Researcher
conducts evidence-based practice and research to improve nursing care and further define and expand the scope of nursing practice
Florence Nightingale
Founder of modern nursing; started first organized program to train nurses; first practicing nurse epidemiologist; connected sanitation with cholera and dysentery
Clara Barton
Nurse during the Civil War; founder of the American Red Cross

Mary Mahoney
First professionally trained African American nurse

Mary Adelaide Nutting
First professor of nursing at Columbia University Teachers College in 1906.

Compassion fatigue
described as physical, emotional, and spiritual exhaustion resulting from seeing patients suffer, leads to a decreased capacity to show compassion or empathize with suffering people
Burnout
Occurs when perceived demands outweigh perceived resources
Lateral violence
Aggressive and destructive behavior or psychological harassment of nurses against each other
Genomics
Study of whole genomes, including genes and their functions
CHAPTER 2
Health Care Delivery System
Health Services Pyramid
Managing health instead of illness
Emphasis on wellness
Injury prevention programs

Primary Health Care
Focuses on improved health outcomes for an entire population; includes primary care and health education, proper nutrition, maternal/child health care, family planning, vaccines, and control of diseases
Intensive Care
Patients receive close monitoring and intensive medical care
Psychiatric Facilities
Patients who suffer emotional and behavioral problems such as depression, violent behavior, and eating disorders often require special counseling and treatment in psychiatric facilities
Rural Hospitals
Located in a county that has a low population density
Restorative Care
Care that helps persons regain their health, strength, and independence
Home Care
Provision of medically related professional and paraprofessional services and equipment to patients and families in their homes for health maintenance, education, illness prevention, diagnosis and treatment of disease, palliation, and rehabilitation
Rehabilitation
Restores a person to the fullest physical, mental, social, vocational, and economic potential possible
Extended Care Facility
A facility that provides health care and help with the activities of daily living to people who may be physically or mentally unable to care for themselves; this type of care may last from days to years
Skilled Nursing Facility (SNF)
Includes administration of IV fluids, wound care, long term ventilator management, and rehab
Continuing Care
For people who are disabled, functionally dependent, or suffering a terminal disease
Assisted Living
A living arrangement for elderly people that combines privacy and independence with medical supervision
Respite Care
A type of care provided for caregivers of homebound ill, disabled, or elderly patients; gives the normal care-takers time off
Adult Day Care
A program for impaired adults that attempts to meet their health, social, and functional needs in a setting away from their homes
Hospice
Allows patient to live with comfort, independence, and dignity while easing the pains of terminal illness
IOM Competencies
Patient Centered Care
Work in Interdisciplinary Teams
Use Evidence-Based Practice
Apply Quality Improvement
Use Informatics

Ten Rules of Performance in a Redesigned Health Care System
1. Care is based on continuous healing relationships
2. Care is individualized based on patient needs and values
3. Patient is the source of control, participates in decision-making
4. Knowledge is shared, info flows freely
5. Decision making is evidence-based
6. Safety is a system property and focused on reducing errors
7. Transparency is necessary through sharing info with patients and families
8. Patients needs are anticipated
9. Waste is continuously decreased
10. Cooperation and communication among clinicians are priorities
Quality Health Care
The degree to which health services for individuals and populations increase the likelihood of desired health outcomes and are consistent with current professional knowledge
Pay for performance programs
Designed to promote quality, effective, and safe patient care by physicians and health care organizations
Quality improvement strategies that reward excellence through financial incentives to motivate change to achieve measurable improvements
Six Sigma
A data-driven approach for improving quality by removing defects and variations in processes
Patient-Centered Care
Recognize the patient or designee as the source of control and full partner in providing compassionate and coordinated care based on respect for patient's preferences, values, and needs
Magnet Recognition Program
Recognition by the American Nurses Credentialing Center that an organization provides quality nursing care
Nursing-sensitive outcomes
Patient outcomes and nursing workforce characteristics that are directly related to nursing care such as changes in patients' symptom experiences, functional status, safety, psychological distress, registered nurse job satisfaction, total nursing hours per patient day, and costs
Nursing Quality Indicators
Outcomes of nursing care, identified by the American Nurses Association, that address patient safety and quality of care

Nursing informatics
Uses information and technology to communicate, manage knowledge, mitigate error, and support decision making
Telemedicine
Involves the use of video, audio, and computer systems to provide medical and/or health care services
Vulnerable populations
Collection of individuals who are more likely to develop health problems as a result of excess risks, limits in access to health care services, or being dependent on others for care
CHAPTER 6
Health and Wellness
Healthy People 2020
A set of disease prevention and health promotion objectives for Americans to meet during the second decade of the new millennium
Health
A state of complete physical, mental, and social well-being, not merely the absence of disease or infirmity.
Health beliefs
A person's ideas, convictions, and attitudes about health and illness
Positive health behaviors
Activities related to maintaining, attaining, or regaining good health and preventing illness
Negative health behaviors
Inculde practices actually or potentially harmful to health such as smoking, drug or alcohol abuse, poor diet and refusal to take necessary medications
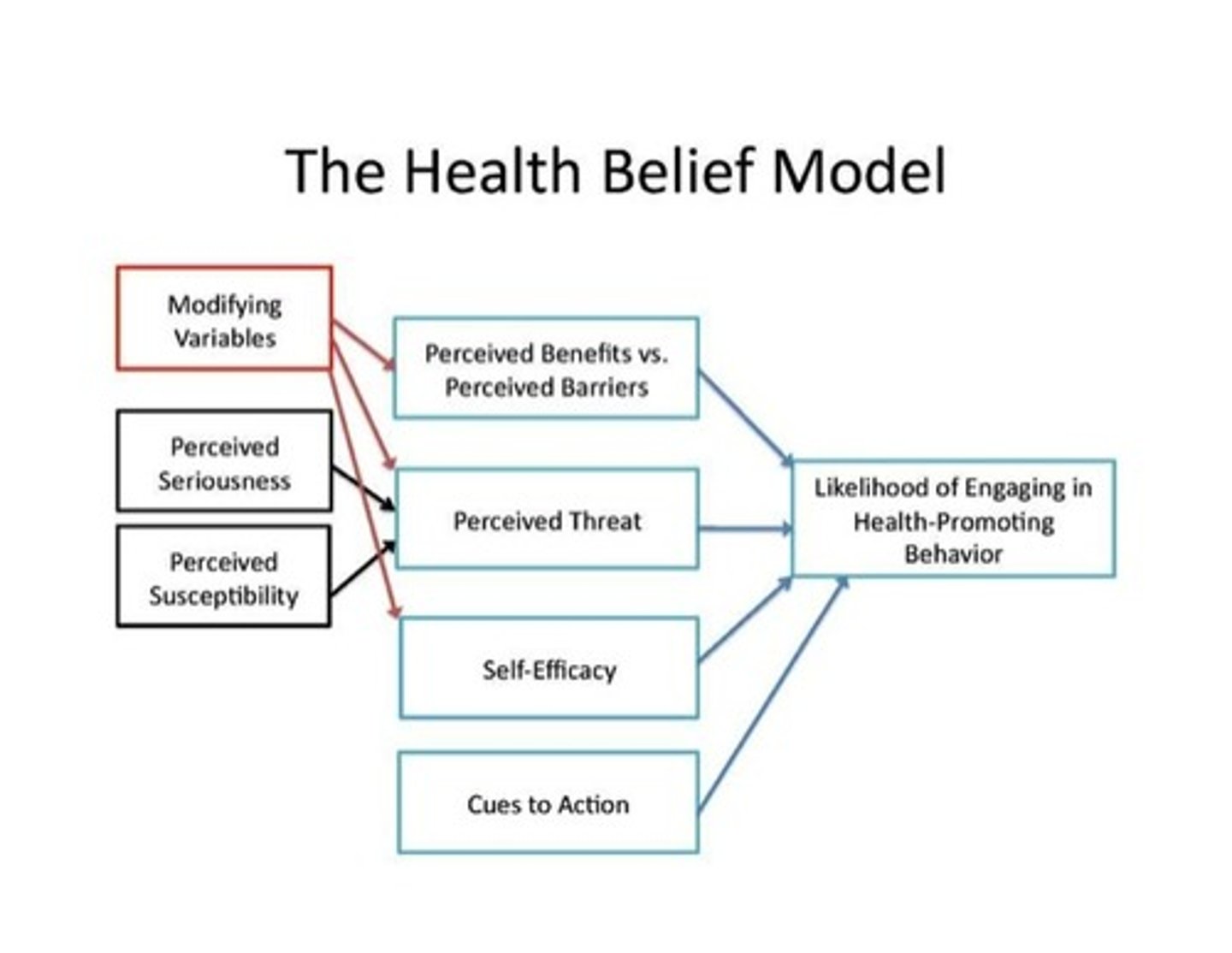
Health Belief Model
Addresses the relationship between a person's beliefs and behaviors
Health Promotion Model
Directed at increasing a patient's level of well-being
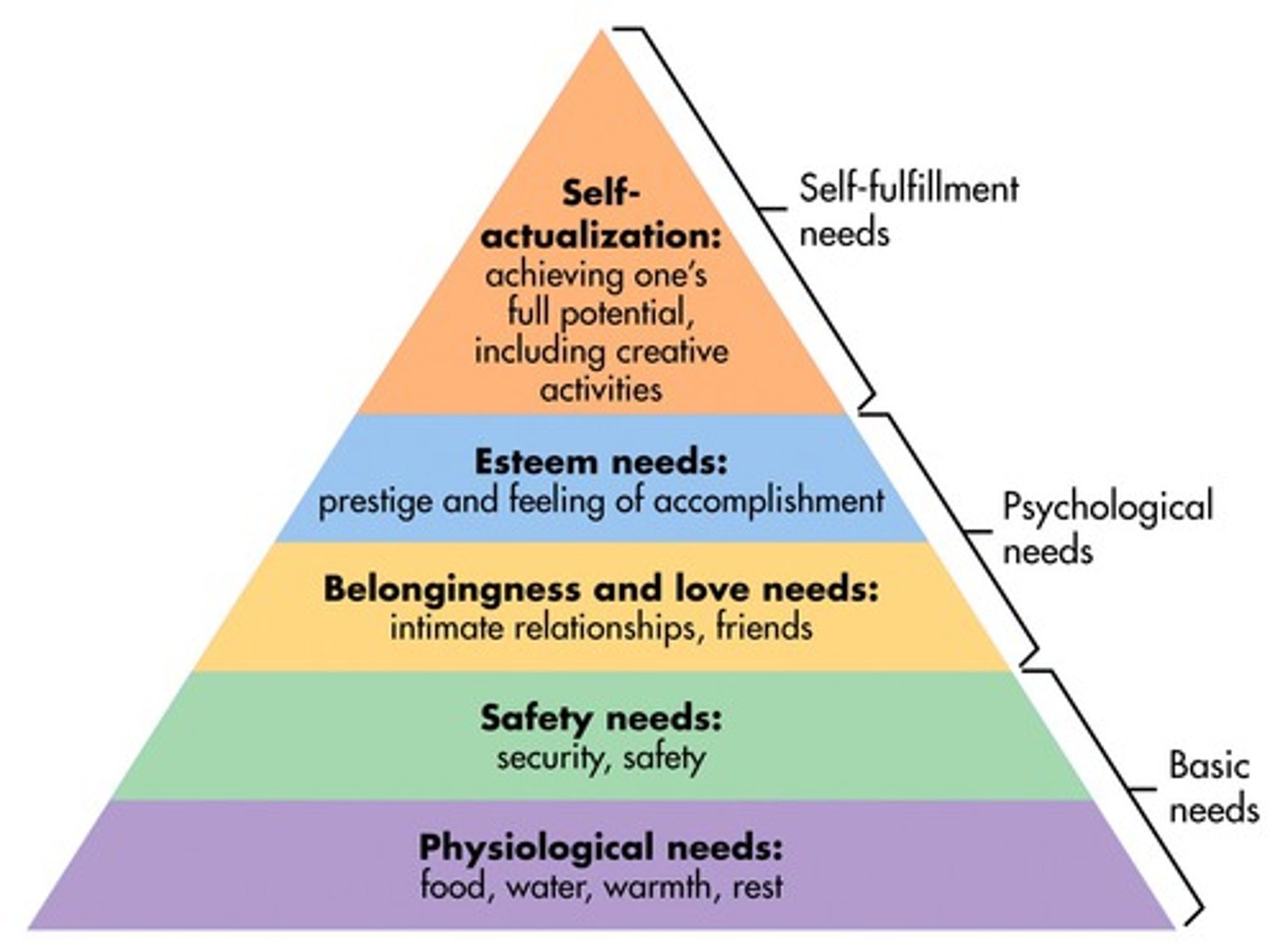
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
Physiological
Safety
Love + Belonging
Self Esteem
Self-actualization
Holistic Health Model
Attempts to create conditions that promote optimal health

Internal Variables that Influence Health
Developmental stage, intellectual background, perception of functioning, emotional factors, spiritual factors
External Variables that Influence Health
Family practices, socioeconomic factors, cultural background
Health promotion
The process of enabling people to increase control over, and to improve, their health
Illness Prevention
Health education programs or activities directed toward protecting patients from threats or potential threats to health and minimizing risk factors
Passive Health Promotion Strategies
Ex. Fluoride in water, fortified foods
Active Health Promotion Strategies
Ex. weight reduction, smoking-cessation
Levels of Preventive Care
Primary, secondary, tertiary
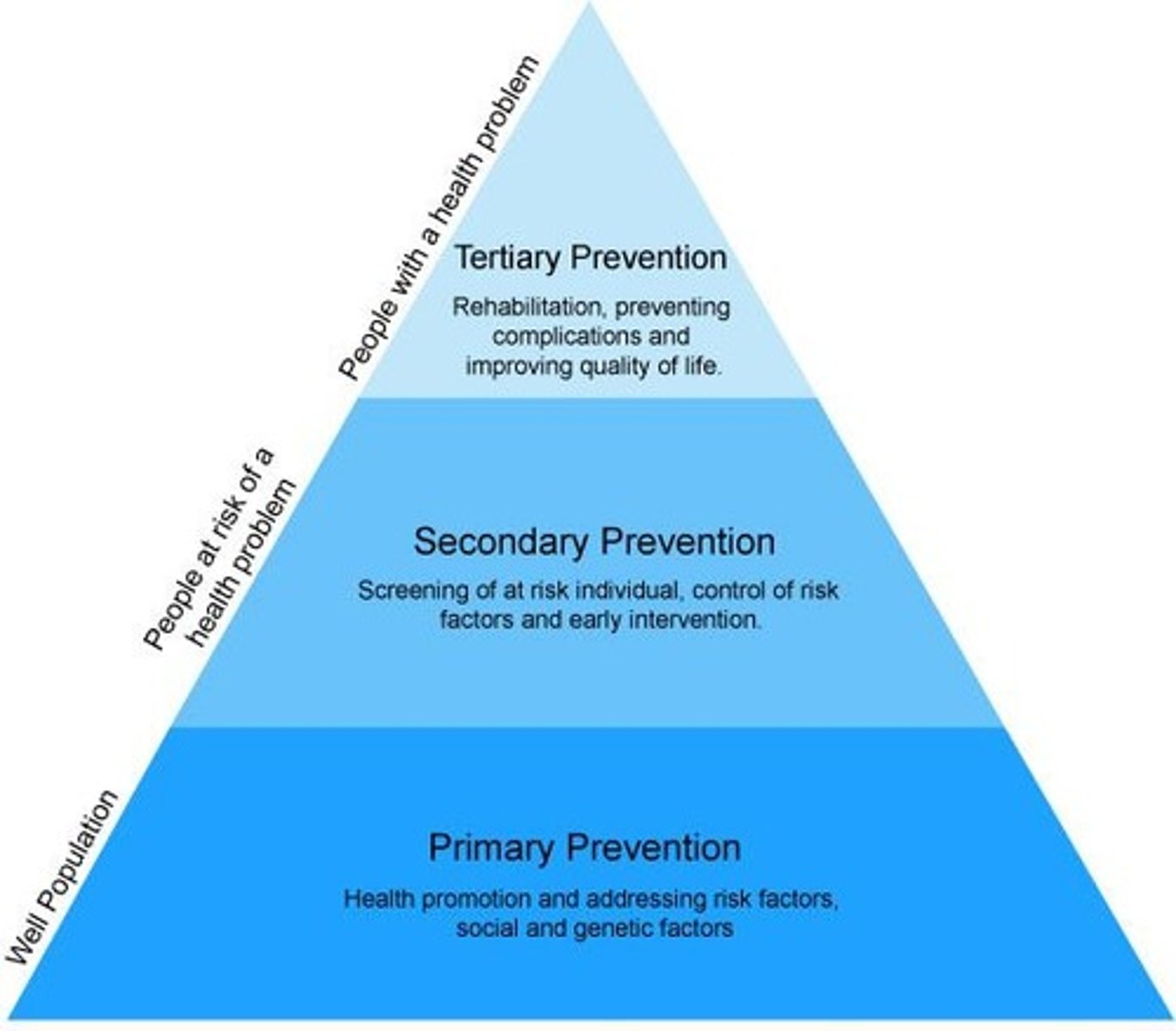
Primary Prevention
True prevention, precedes disease or disfunction and applied to patients considered physically and emotionally healthy
Includes: health education, vaccines, nutritional programs, fitness activities
Secondary Prevention
Focuses on individuals who are experiencing health problems or illnesses and are at risk for developing complications or worsening conditions
Tertiary Prevention
Occurs when a defect or disability is permanent or irreversible; involves minimizing the effects of long-term disease or disability by interventions directed at preventing complications and deterioration
Risk Factor
Any situation, habit, or other variable such as social, environmental, physiological, psychological, developmental, intellectual, or spiritual that increases the vulnerability of an individual or group to an illness or accident
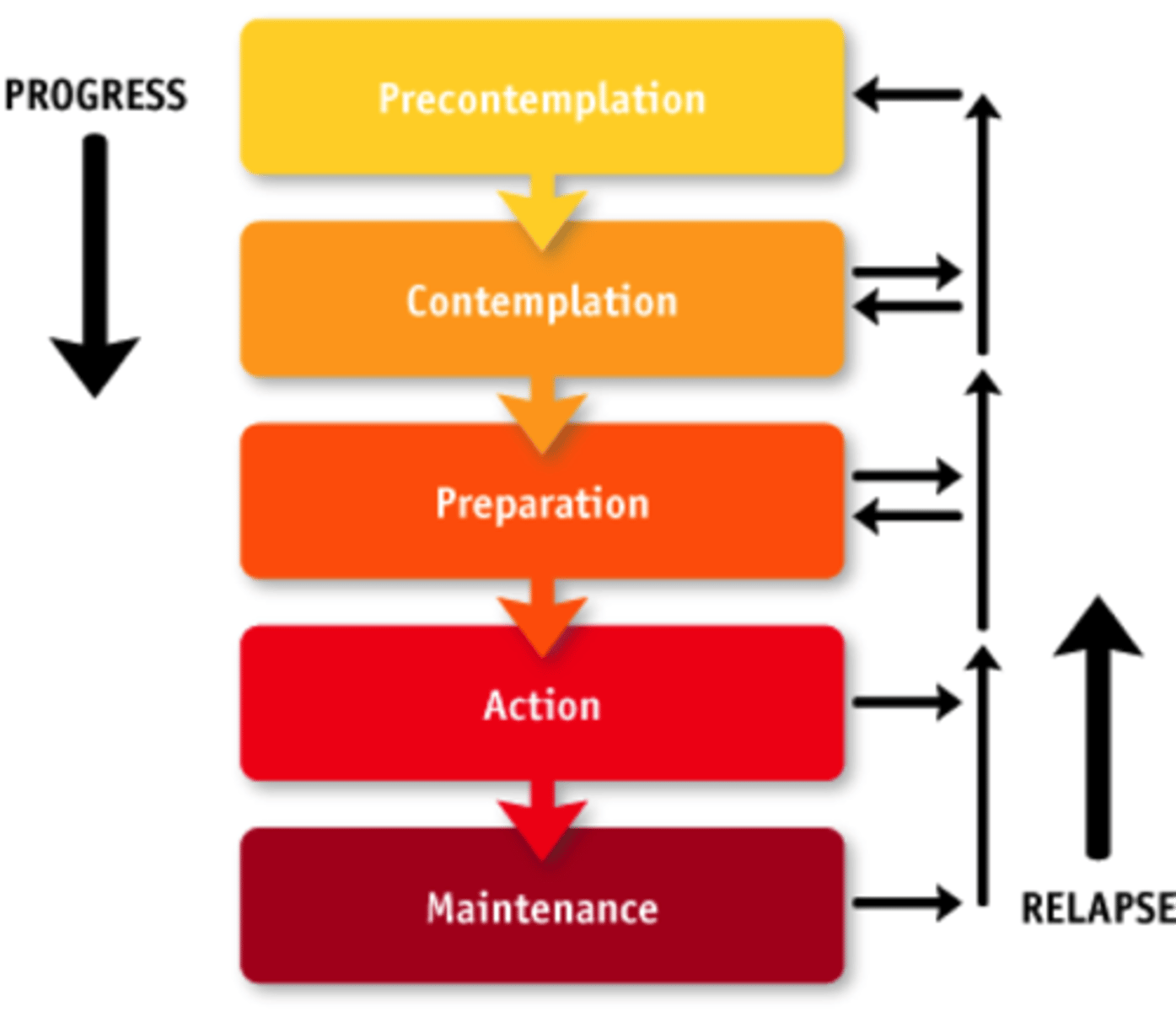
Transtheoretical Model of Change
1. Precontemplation
2. Contemplation
3. Preparation
4. Action
5. Maintenance
Illness
A state in which a person's physical, emotional, intellectual, social, developmental, or spiritual functioning is diminished or impaired
Acute Illness
A sudden illness from which a person is expected to recover
Chronic Illness
Persists longer than 6 months, is irreversible, and affects functioning in one or more systems
Illness Behavior
Ways in which people monitor their bodies, define and interpret their symptoms, take remedial actions, and use the health care system.
CHAPTER 16
Nursing Assessment
Nursing Process
Assessment
Diagnosis
Planning
Implementation
Evaluation

Nursing Assessment
Systematic and continuous collection and analysis of information about the client
Two Steps:
1. Collect info from primary source (pt) and secondary sources (family, friends, health prof, records)
2. Interpret and validate data to ensure complete database
Critical thinking and the assessment process
Cue
Information that you obtain through use of the senses
Inference
Your judgement or interpretation of these cues
Health perception-health management pattern
Describes patient's self-report of health and well-being; how patient manages health (e.g., frequency of health care provider visits, adherence to therapies at home); knowledge of preventive health practices
Nutritional-Metabolic Pattern
Describes patient's daily/weekly pattern of food and fluid intake (e.g., food preferences or restrictions, special diet, appetite); actual weight; weight loss or gain.
Elimination Pattern
Describes patterns of excretory function (bowel, bladder, and skin)
Activity-Exercise Pattern
Describes patterns of exercise, activity, leisure, and recreation; ability to perform activities of daily living
Sleep-Rest Pattern
Describes patterns of sleep, rest, and relaxation.
Cognitive-Perceptual Pattern
Describes sensory-perceptual patterns; language adequacy, memory, decision-making ability
Self-Perception-Self-Concept Pattern
Describes patient's self-concept pattern and perceptions of self (e.g., self-concept/worth, emotional patterns, body image)
Role-Relationship Pattern
Describes patient's patterns of role engagements and relationships
Sexuality-Reproductive Pattern
Describes patient's patterns of satisfaction and dissatisfaction with sexuality pattern; patient's reproductive patterns; premenopausal and postmenopausal problems
Coping-Stress Tolerance Pattern
Describes patient's ability to manage stress; sources of support; effectiveness of the patterns in terms of stress tolerance
Value-Belief Pattern
Describes patterns of values, beliefs including spiritual practices, and goals that guide patient's choices or decisions
Problem-Focused Patient Assessment
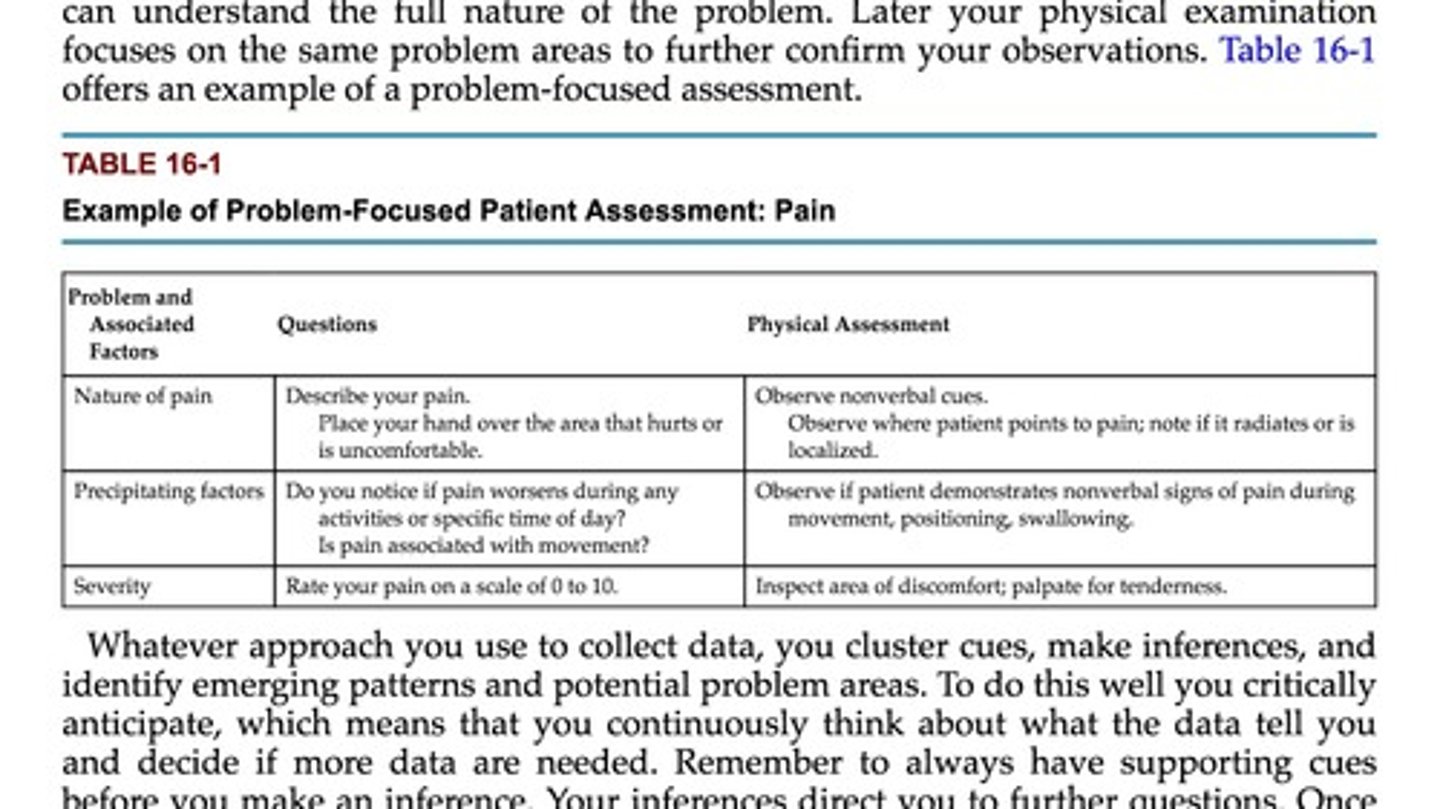
Subjective Data
Things a person tells you about that you cannot observe through your senses; symptoms
Includes patient's feelings, perceptions, and self-reported symptoms
Patient-Centered Interview
Requires: courtesy, comfort, connection, confirmation
PQRST
Provokes
Quality
Radiate
Severity
Time
Interview Techniques
Observation
Open-ended questions
Leading question
Back channeling
Probing
Direct close-ended questions
Concomitant Symptoms
Does the patient experience other symptoms along with the primary symptom? For example, does nausea accompany pain?
Review of Systems (ROS)
A systematic approach for collecting the patient's self-reported data on all body systems.