Week 4 Fitness Appraisal
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
How do we express CRF values?
L per min: Litres of O2 used by the body each minute
ml/ kg/ min: Ml of O2 used by each kg of body weight each minute
METs; multiples of resting metabolic rate
What is the criteria of choosing an appropriate CRF test?
Age
Fitness level
Known health problems
Risk of CHD
Availability of needed equipment and personnel
What are the steps prior to testing?
Informed consent
Pre-participation and health screening
Referral to a health professional needed?
Review history for absolute and relative contraindications
Resting cardiovascular tests (BP, HR) and body composition
What are the general indications for stopping an exercise test?
Angina, systolic BP, excessive rise in BP, shortness of breath, wheezing, leg cramps, claudication, fatigue
HR and heart rhythm
Subject communication
Failure of testing equipment
What are the common measures to examine CRF?
HR
fitness indicator at rest and at submaximal levels
Duration
30s or 1 min at rest
10, 15, or 30s during exercise (longer is more accurate)
Take for 10 to 15 seconds postexercise.
Radial pulse typical
BP
SBP should rise with increasing workloads
Diastolic BP remains same or may decrease slightly
Proper cuff size and adherence to standard technique are imperative for accurate readings
RPE
Rating of perceived exertion gives subjective information regarding intensity of activity (Borg scale, 0 to 10 relative effort)
What are graded exercise tests (GXT)?
Tests with incrementally increasing workload
Maximal GXT (client stops cause of exhaustion)
Submaximal GXT (client stops at 85% of maximal HR)
Symptom limited GXT (clients stops due to discomfort or abnormal physiological responses)
What are the pros and cons of Bench Stepping, Cycle ergometers and treadmill GXT?
Bench stepping
Pros: low cost of equipment an portability,
Cons: Difficult to take measurements, limited number of stages for a given fitness level
Cycle Ergometer (appropriate rpm 50 - 60 low to avg, 70 to 100 rpm competitive)
Pros: HR and BP measurements relatively easy to take, safe for those with balance problems, instruments are moderately priced
Cons: Pacing difficult to regulate, leg fatigue may stop a client to stop before reaching VO2 max, each increment in intensity places greater relative load on a smaller person
Treadmill
Pros: Reproducible: treadmill maintains the speed, natural activity, acommodates all fitness levels
Cons: Temptation to use the handrail, lack of portability, difficult to take measurements (e.g., BP), expense of equipment
Influences VO2 max based on test, (Graded runnning > running at 0% grade)
What are the protocols for GXT?
Submaximal and maximal tests can use the same GXT protocol, but the criteria for test termination differ
Maximal tests effectively identify ischemic heart disease
Submaximal tests are useful in assessing fitness and are less expensive to administer
VO2 max estimated from a submaximal test is not as accurate as VO2 max obtained from a maximal test
What plays a role in Maximal GXT?
ACSM notes maximal testing is often not feasible in health and fitness testing
Criteria to verify a maximal effort
Plateau in VO2 max with increased workload
No HR increase with increased workload
Postexercise blood lactate greater than 8 mmol per L
Peak respiratory exchange ratio (RER) greater than 1.10
How do we predict VO2 max from submaximal test data?
HR response usually linear between 110 bpm and 85% HRmax
Standard error of estimate (SEE) = 5ml /kg /min
Very reliable for tracking progress over time, regardless of accuracy of estimated VO2 max
Estimation based on submaximal HR responses; important to not conditions that affect HR
How do we predict VO2 max from submaximal test data in graphing?
this method involves plotting HR responses (>110 bpm) to a GXT on a treadmill, cycle ergometer, or bench step
A line is drawn through the HR values and is extrapolated to the subject’s age predicted estimate of maximal HR
A vertical line is drawn to the x axis to estimate the work rate and VO2 the person would have achieved if it had been a maximal test
What factors affect responses HR, BP and RPE responses in a GXT?
Temperature, humidity
Amount of sleep before testing
Emotional state
Hydration status
Medications
TIme of day, last meal, Psychological environment
How do you estimate VO2 max from submaximal GXT on Cycle ergometer: Astrand and Rhyming Cycle Ergometer test?
1 work rate for 6min that results in a HR response between 125 and 170 bpm
The HR mean for the final 2 minutes is used to estimate VO2 max.
A nomogram or table can be used; the resulting value will require age correction.
What is the post test protocol?
Active cool down procedure → rest
Decrease intensity, active recovery for 3 min
Monitor vitals till subject feels comfortable in sitting rest
Remove cuff and monitor when close to pretest values
Instructions for 30 min before showering, warm water
Discuss results, making an appointment
What are the pros and cons of field testing?
Pros:
Moderate of high correlation of VO2 max
Use of natural activities
Ability to test large numbers in a short time
Cons:
Difficult to monitor physiological responses
Outcomes subject to other factors (motivation, environment)
Lack of graded or submaximal testing protocols
What is the mile walk test?
accomodates different ages and fitness levels
Walk as fast as possible measuring HR at the end of the mile
What is the 6 min walk test?
Use with individuals with reduced CRF
Test is self paced; participants walk as far as possible on a level surface in 6 minutes
Senior fitness test uses a rectangular walking path measuring 20 yards by 5 yards
What is a run test?
Run as fast as possible for 12 minutes or 1.5 miles.
Run test is one of the most common CRF tests (easy to administer repeatedly and at low expense)
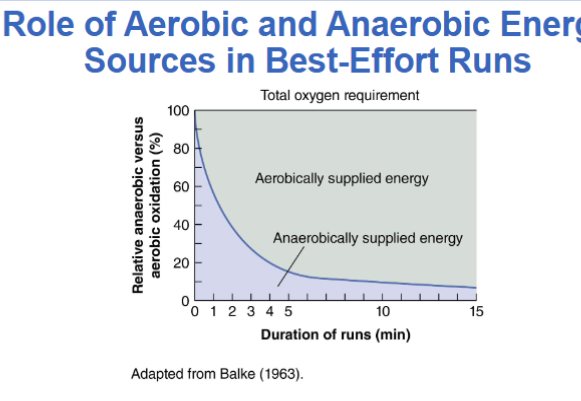
Run time for VO2 max test is 12 to 15 minutes to diminish the anaerobic contribution
Tends to underestimate VO2 max in children, and overestimates VO2 max in competitive runners and those who walk
What is the mile run for youth?
For youth 10 to 17 y/o, BMI and age are considered along with the mile run time to predict anaerobic capacity.
What is the PACER?
20m progressive shuttle run
Beginning pace of 5.3 mph and increasing 0.3 mph at each level
CRF based on number of 20m laps completed
Part of the FitnessGram testing battery for children
How do we estimate VO2 without doing an exercise test?
Estimate with simple variables: age, gender, body fatness or BMI and self reported activity