Quiz 4
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
What is the process of two cell estradiol production?
Thecal cells produce T that diffuse into granulosa cells → gran. cells have FSH receptors → binding of FSH causes synthesis of enzymes that turn T to estradiol
What is an LH surge? What does it do?
A cascade of events that leads to
Ovulation (follicular rupture and expulsion of oocyte)
Luteinization of the follicular cells- formation of CL
Maturation of oocyte
resumption of meiosis
LH surge affects on oocyte
resumption of meiosis in oocyte
Final synthesis of proteins and mRNA in oocyte
CL function
Secrete Progesterone and oxytocin
required for pregnancy maintenance
stimulates mammary dev.
controls ovarian cycle (inhibit ovulation/estrus)
Formation of CL
Continuation of follicular maturation
form from theca/granulosa cells
gran. cells become large luteal cells
theca cells become small luteal cells
What are the 4 steps of angiogenesis
basement membrane breakdown
production of angiogenic factors by granulosa cells
mitosis and migration of endothelial cells
capillary tube formation
Corpus Hemorragicum vs Corpus albicans
Hemorragicum: forms when follicle bursts and lets blood in. CH is formed from the combination of blood, theca cells, and granulosa cells
Albicans: when CL degenerates = scar tissue (white body)
Drop in progesterone leads to…an increase leads to…
Drop: increase in LH pulses and estradiol
Increase:
blocks estrus
inhibits LH surge
decrease uterine contractions
prepare uterus for pregnancy
Estradiol functions:
increase LH receptors in follicle
granulosa cell mitosis
estrus (sexual receptivity)
LH surge
uterine contractions
increase progesterone receptors in endometirum
Draw out the process of the Female gametogenesis
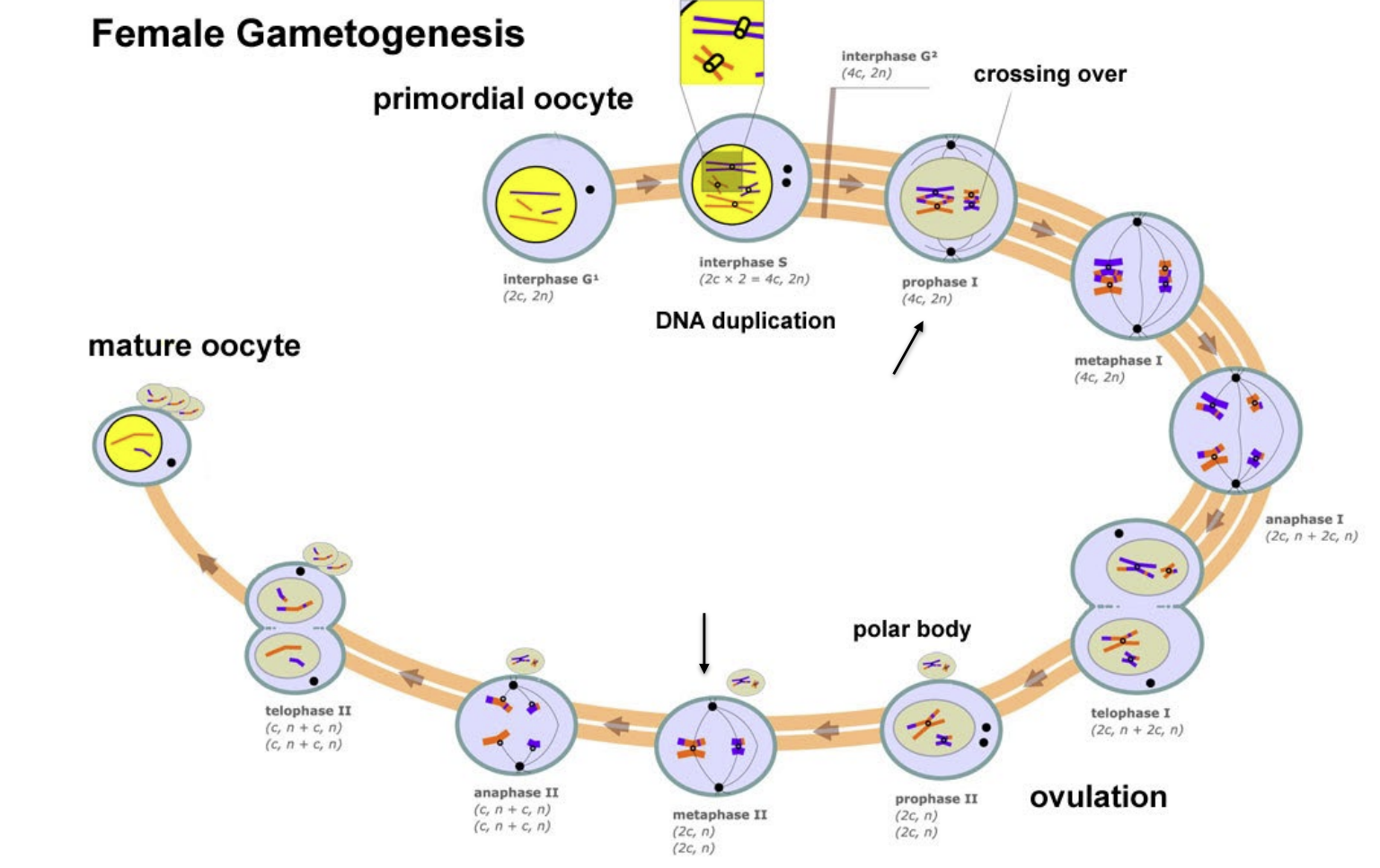
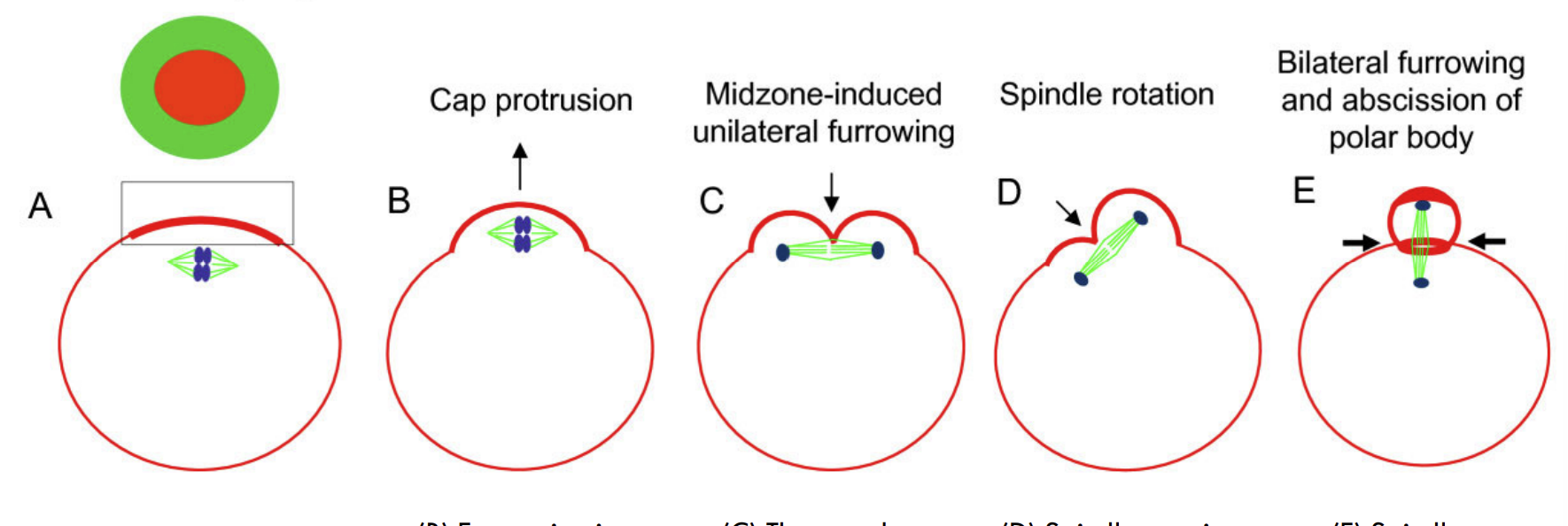
What is the polar body? What does extrusion of the polar body indicate?
small cytoplasmic exclusion body formed to enclose excess DNA during meiosis.
Extrusion of first polar body indicates completion of first meiotic division
Chromosome-induced cortical cap/ring
What do oocytes instruct cumulus cells to perform
They instruct the oocytes to perform Glycolysis, AA uptake, and Cholesterol Biosynthesis under the direction of the oocyte-secreted factors (GDF9, FGF8)
Oocyte metabolism
Cumulus cells start maturation in the first polar body → one of the substrates that can be used by the cumulus cells is glucose → a lot of active metabolism within the oocyte in the cumulus cells.
How is glucose used?
Used to go through glycolysis → regulated by oocyte-secreted factors (OSF) → glycolysis uses fatty acids to generate ATP