Biology Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
Overall reaction of photosynthesis
6CO2+6H2O --sun--> C6H12O6+6O2
How do the overall reactions of photosynthesis and cellular respiration compare?
It gives off oxygen and uses carbon dioxide in photosynthesis. It's slightly more complicated but does it without moving parts.
Where does energy for photosynthesis come from?
Sunglight energy
What plant pigments are involved in photosynthesis?
Chlorophyll
Explain why chlorophyll appears green to us in terms of what happens to different wavelengths of light that strike a chlorophyll molecule.
It is really absorbing every color except green and reflect green so we can see it. Green has the longest wave length so the least energy, therefore, the plant uses the other colors for energy.
How does the amount of energy in light change as the wavelength changes?
The longer the wavelength, the less energy. The shorter the wavelength, the more energy.
Which colors of light are most effective for photosynthesis? Why?
Purple mainly and Red because it is reflected by the chlorophyll
In what organelle of a plant does photosynthesis take place?
Chloroplasts
What are the two stages of photosynthesis?
Light reactions then the Calvin Cycle
In which part of the chloroplast does each stage occur?
Light reactions in the thylokoid. Calvin cycle in the stroma.
What happens to the water molecules in the light reactions?
They're split and oxygen is released while hydrogen and electrons are used.
What photosynthesis waste product is formed in the light reactions?
Oxygen (O2)
What two products of the light reactions are used up in the Calvin Cycle?
NADPH and ATP
What happens to carbon dioxide molecules in the Calvin Cycle reactions?
Combined with NADPH and ATP to form sugar
How can cells store the sugar that is produced in photosynthesis?
Starch
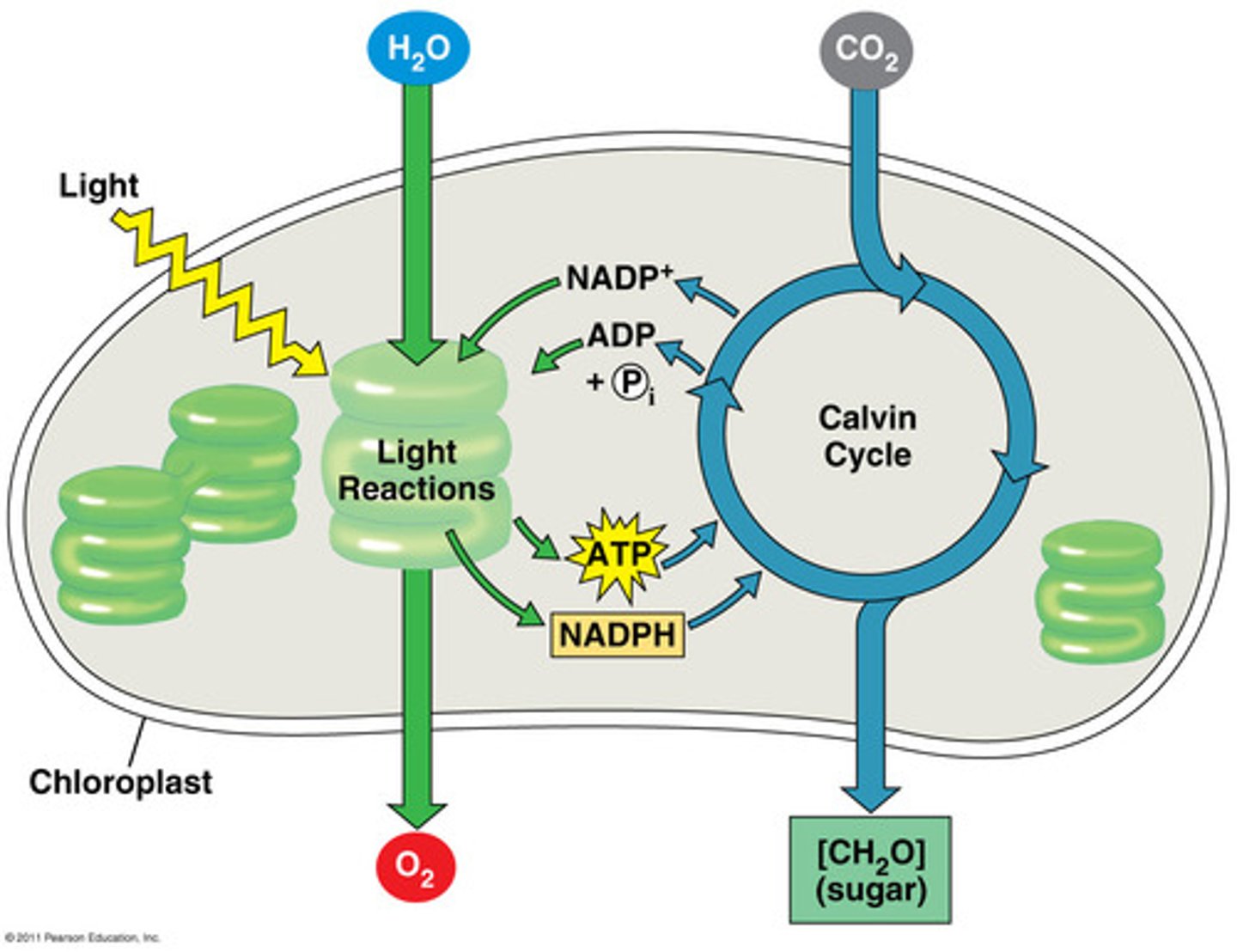
Label the two stages during photosynthesis...
Thylakoids, granum, stroma, light reactions, calvin cycle, light, H2O, sugar, CO2, NADPH, ATP, NADP+, O2, ADP+P
Label the structure of a leaf...
cuticle, upper epidermis, palisacle mesophyll, air space, lower epidermis, spongy mesophyll, guard cell, stoma, vein

Cuticle
Outermost layer, prevents water loss
Upper Epidermis
outer layers, protects middle cells
Palisacle Mesophyll
Contains chloroplasts
Air Space
Where CO2 and O2 exchange in the plant
Spongy Mesophyll
contains chloroplasts
Guard Cell
opens and closes stoma
Stoma
opening and where CO2 enters and O2 exits
Vein
water and nutrients go up to the leaves and sugar transports to the roots
Stroma
Thick fluid between grana
Thylakoid
site of photosynthesis
Granum
stack of thylakoids
Light hits the chlorophyll and makes what?
NADPH and ATP
What is the basic reaction for Cellular respiration?
C6H12O6+O2 ----> CO2+H2O+ATP+Heat
What are the reactants of cellular respiration?
glucose and oxygen
What the products of cellular respiration?
Carbon Dioxide, water, ATP
Why is ATP needed for the body?
Chemical work, mechanical work, transport work
Three stages of cellular respiration
Glycolosis, Krebs cycle, Electron transport chain
Glycolosis
Occurs in cytoplasm; net gain of 2 ATP and 2 pyruvic acids and 2 NADH energy carriers will be used in ETC
Krebs Cycle
Occurs in the mitochondria; net gain of 2 ATP and waste product of CO2 and 8 NADH and 2 FADH2 to be used in ETC; the cycle occurs with double because of two previous pyruviac acids
Electron Transport Chain
occurs in the mitochondria; charged electron carriers (NADH and FADH2) release their electrons; net gain of about 34 ATP and waste product of H2O
Total net gain from 1 round of cellular respiration
about 38 ATP
What is different in yeast cells?
If you give them sugar, it'll release CO2 and make alcohol instead of lactic acid
chlorophyll
Pigment inside the palisade and spongy cells that allows the plant to do photosynthesis
Autotrophic or heterotrophic organisms do photosynthesis?
Autotrophic
Purpose of photosynthesis
To produce sugar
What is the purpose of light in photosynthesis?
the light strikes the pigment molecules and chlorophyll; the absorbed light energy excites the electrons and allows the electrons to be passed along the chain further making the nadph and atp; it also splits water molecules
What three things are produced during the light dependent (light) reactions?
Oxygen, NADPH, and ATP
What is the role of water during the light reactions?
Gives hydrogen and electrons for photosystem II
What is produced during the light dependent Calvin cycle reactions?
sugar
Explain how the energy molecules (ATP and NADPH) are recycled?
It goes from light reactions to calvin cycle and back again after its energy is used
In what organelle does cellular respiration take place?
mitochondria
What is the purpose of cellular respiration?
provides energy in the form of ATP by converting oxygen and glucose into water, carbon dioxide and ATP (energy).
Summarize the purpose of the 3 stages of CR
glycolysis, krebs cycle, and electron transport occur to be most effective for humans through all types of work to create enough ATP
Describe how the energy made during the Krebs cycle is used during electron transport chain
8 NADH and 2 FADH2 facilitates transfer of electrons
How is the oxygen use during electron transport chain
oxygen is the "final electron acceptor." As electrons (usually represented as Hydrogen atoms) are passed down the chain, they lose their energy in the making of ATP. They have such little energy left, they are of no further use, and are donated to an oxygen atom to create a molecule of water.
What two substances go into the mitochondria for cellular respiration to occur and what 3 substances come out?
glucose and oxygen go in
water, 34 ATP, and CO2 comes out
Under what conditions (aerobic or anaerobic) does cellular respiration occur?
Aerobic because it requires oxygen to occur
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration work in a cycle. Draw the cycle and label the mitochondria and the chloroplast.
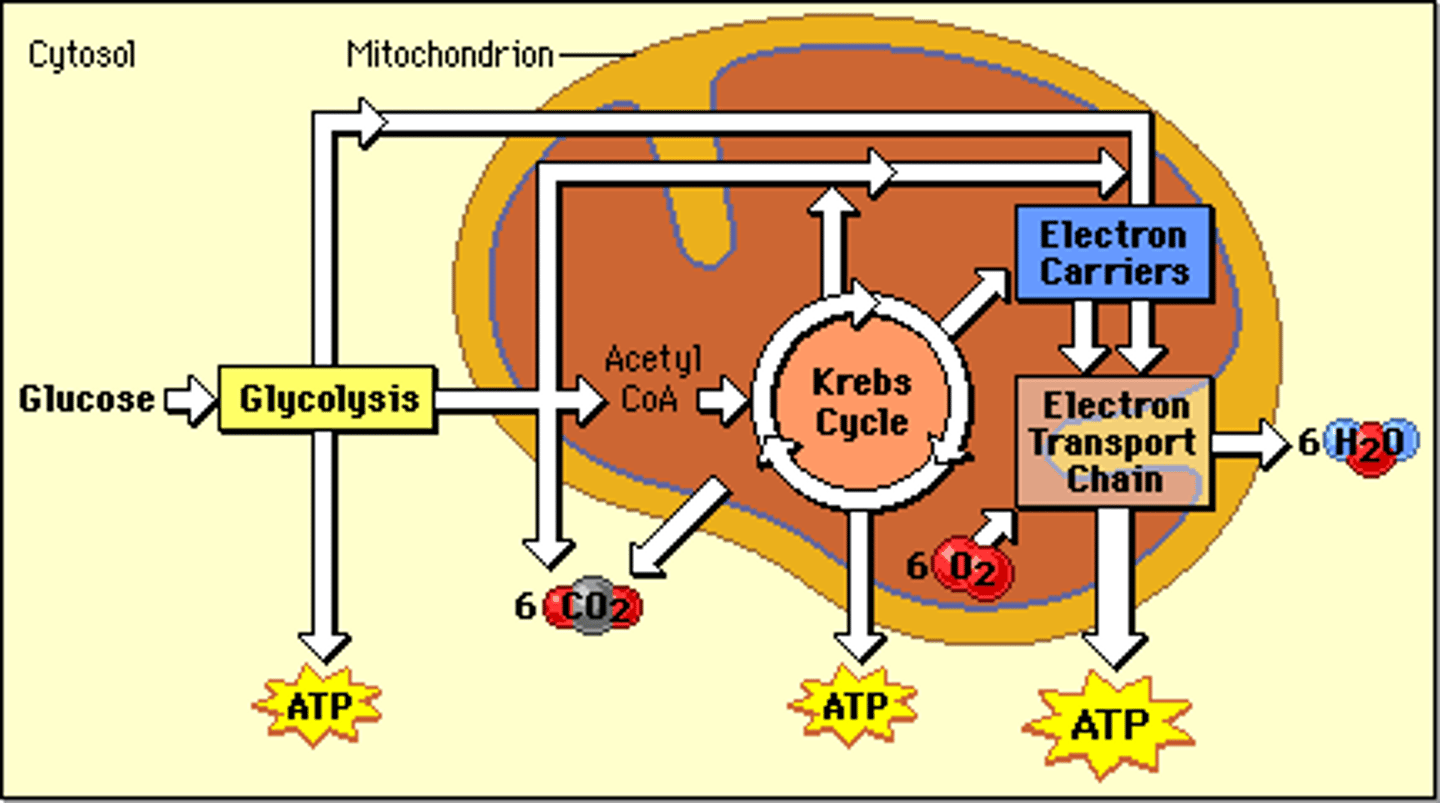
Where is the energy stored in an ATP molecule?
terminal bond between second and third phosphate
Cellular respiration
Chemical process where mitochondria break down food molecules to produce ATP, the three stages are glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain.
Glycolysis
occurs in the cytoplasm; net gain of 2 ATP and 2 pyruvate acids (2 NADH energy carriers to be used in ETC)
Krebs cycle (citric acid cycle)
occurs in mitochondria; net gain of 1 ATP and waste product of CO2 (8 NADH and 2 FADH2 to be used in ETC)
Light Reactions
energy from sunlight is absorbed by chlorophyll converted into stored chemical energy;
Calvin cycle
drive the assembly of sugar molecules from carbon dioxide using the chemical energy harvested during the light-dependent reactions;
Lactic acid fermentation
pyruvate is turned in lactic acid
Photosystem 2
Occurs 1st; electrons excited, water splits, makes oxygen- moves electrons
Photosystem 1
adds to nadp+ to make NADPH; following photosystem 1, ATP synthesis changes adp to atp
Matrix
Krebs cycle occurs here; inside the mitochondria;
Location of Chlorophyll
thlyakoids
Least effect on photosynthesis
light intensity
After 5 rounds of the Krebs Cycle, how much CO2 would be produced?
15 molecules (3 per round)
What is best absorbed by chlorophyll?
Violet THEN Red
Alcohol fermentation
two pyruvates are broken into two acetaldehyde and give off CO2 molecules; the aldehydes are then converted into two ethanol molecuels
Fermentation
a type of cell respiration that can occur in the absence of oxygen; depends on the organism to proceed in varying ways; only uses glycolysis and doesn't use the mitochondria; through the process of glycolysis sugar is split into two pyruvate molecules; the pyruvate molecules without oxygen are able to turn into lactic acid for example if our muscles aren't able to get enough oxygen; also, the bacteria in yogurt ferments
Yeast in fermintation
if you give yeast cells sugar, it'll release CO2 and make alcohol instead of lactic acid