Trade and Tariffs
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Microeconomics Lecture 10
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Absolute advantage
The ability to produce more of a good or service than a competitor using the same resources
Reminder* The opportunity cost of a good or service is…
what must be given up to acquire it
Comparative advantage
the ability to produce a good at a lower opportunity cost than competitors
True or False? No country can have a comparative advantage in the production of all goods
True
Autarky
a situation where a country does not trade with the world
Specialization
Each country allocates more resources toward producing what they are best at (and has the lowest opportunity cost)
Potential gain from specialization
There is now more of a good produced than when they operated under autarky
Countries/parties should specialize in the good they have ______ ______ in.
comparative advantage
Visual of the market under autarky
Price and quantity would be determined by domestic supply and demand
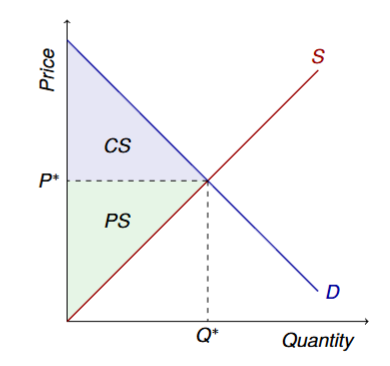
What is the small country assumption for Pw?
World supply is perfectly elastic at Pw
Visual of the market under free trade setting world price above the equilibrium price
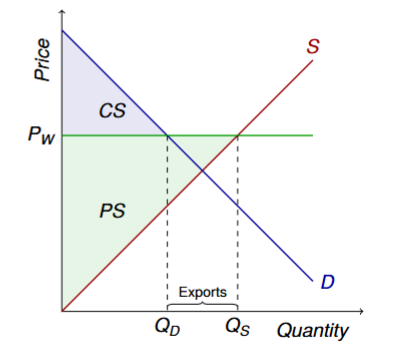
Formula for exports
Qs - Qd
What happens to surplus under a market with exports
Higher price benefits domestic sellers (PS ↑)
Higher price hurts domestic buyers (CS ↓)
Total surplus rises
Visual of the market under free trade setting world price below the equilibrium price
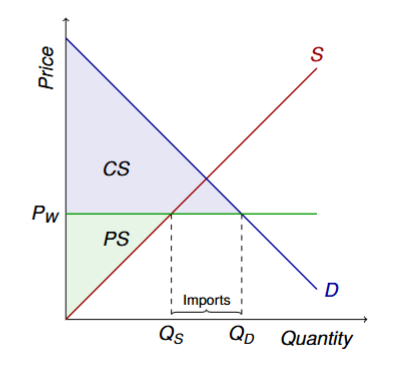
Formula for imports
Qd - Qs
What happens to surplus under a market with imports
Lower price hurts domestic sellers (PS ↓)
Lower price benefits domestic buyers (CS ↑)
Total surplus rises
Trade produces _______ and _______
winners and losers
How can winners compensate losers?
Workers exit declining industries, join rising ones
Lump sum taxes on winners, lump sum transfers to losers
A Pareto improvement
Tarrif
a tax on imported goods (and only on imported goods)
Why are taxes imposed?
To raise revenue
How do tarrifs affect the price of goods?
A tariff of $t increases the price of goods in the domestic market by t
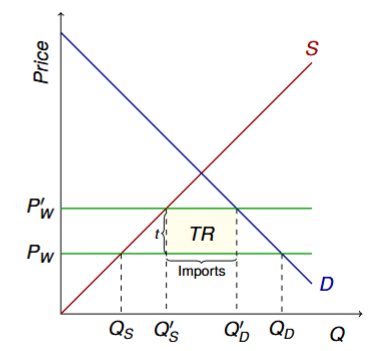
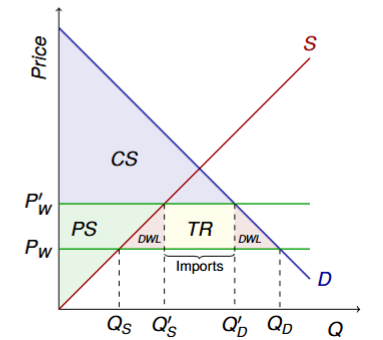
New world price after tariffs formula
P′w = Pw + t
When tariffs are imposed, what happens to production and consumption
Production rises, consumption falls
When tariffs are imposed, what happens to imports
Imports fall
How much revenue does the government generate from tarrifs? (formula)
t × Qimport (Qimport = Q′d − Q′s)
Benefits of tariffs
Tariffs are easy to enforce
Popular in countries with low state capacity
What happens to surplus when tariffs are imposed?
CS ↓
PS ↑
TR ↑
TS ↓
red triangles are DWL
How can tariffs be harmful?
More than narrow protectionist tariffs (e.g., on steel)
They tax goods with no (or few) domestic producers
They tax inputs into production
They are regressive
They reduce long-run economic growth
What is the impact when large countries impose tariffs
Large countries imposing tariffs similar to a regular tax
World price falls from PW to PS
Burden of tariffs is now shared

What affects who bears the burden of the tariff?
Burden of tariffs depends on relative elasticity of demand/supply
