1.2.3 Price, Income and Cross Elasticities of Demand
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
What is Elasticity theory mean?
Elasticity theory looks at the sensitivity of one variable in relationship to another.
What does Elastic mean?
Elastic means that the quantity demanded or supplied changes a lot when the price changes.
Eg) When price goes up a little people would buy less so demand is ELASTIC.
Eg) Ice Cream people would buy less if price rises (Luxuries)
What does Inelastic mean?
Inelastic means that the quantity demanded or supplied doesn’t change much when the price changes.
Eg) When price goes up or down people still buy the same amount so demand is INELASTIC.
Eg) Electricity people still use it even if price goes up (Needs)
What is Elasticity Coefficient?
An Elasticity coefficient is the measure of the response of one variable to changes in another variable.
What does the Price Elasticity of Demand measure?
It measures the responsiveness of demand to a change in price.
What is the Formula for Price Elasticity?
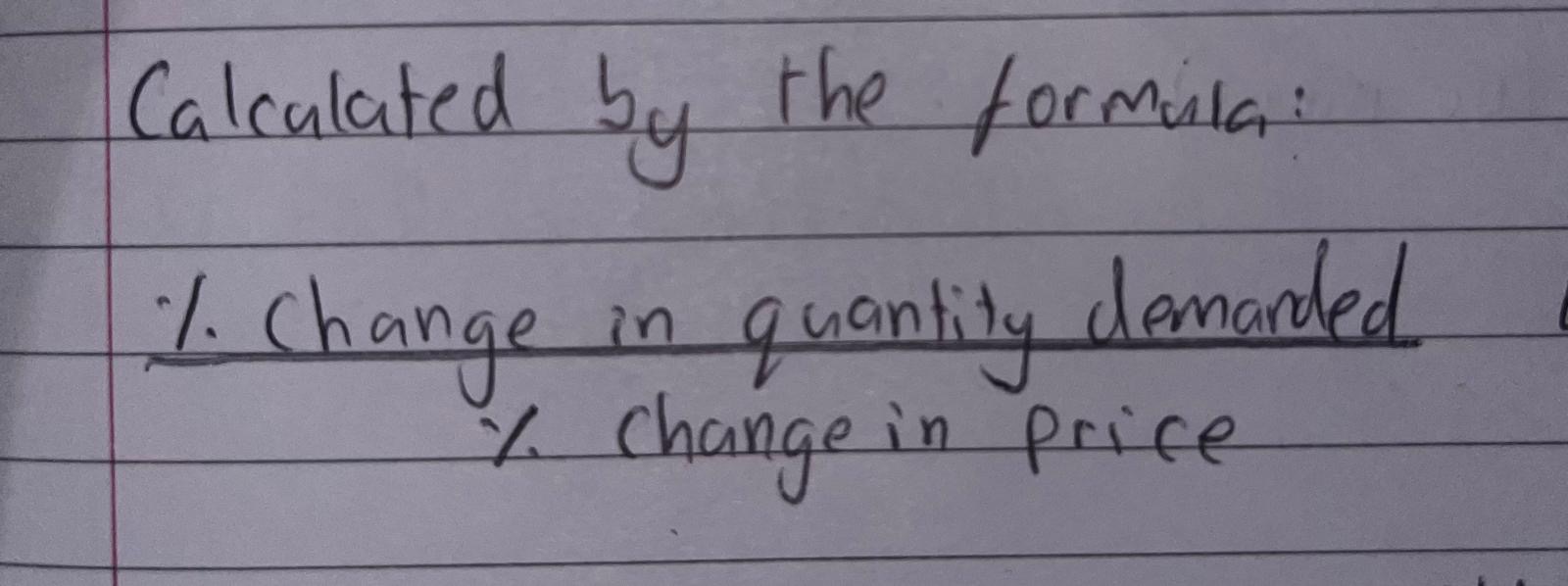
How to calculate PED?

How does Perfectly Inelastic Look like and what is the Coefficient?
Perfectly Inelastic product will have a PED coefficient of 0.

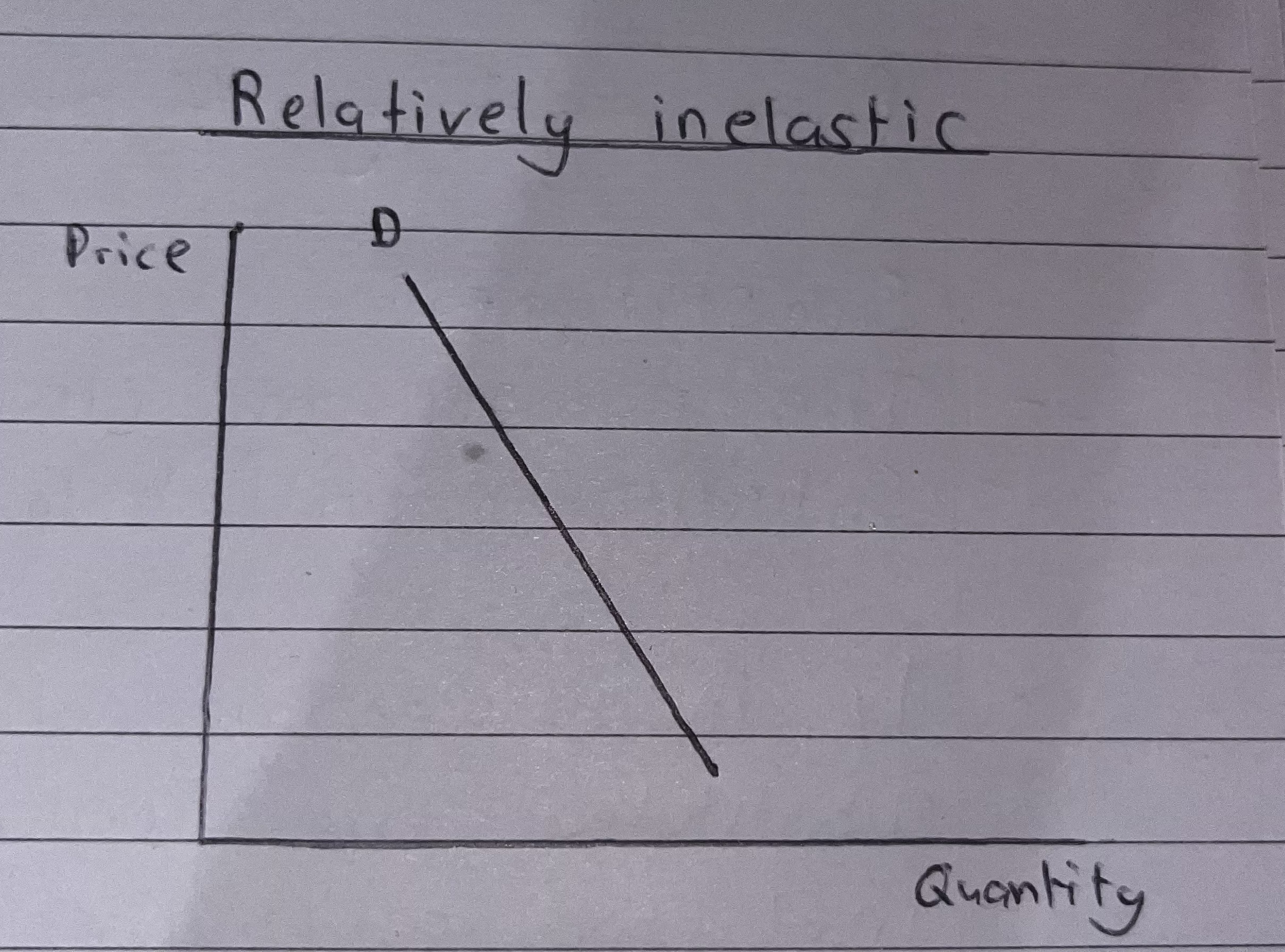
How does Relativity Inelastic Look like and what is the Coefficient?
A Relatively inelastic product will have a PED coefficient between 0 and -1
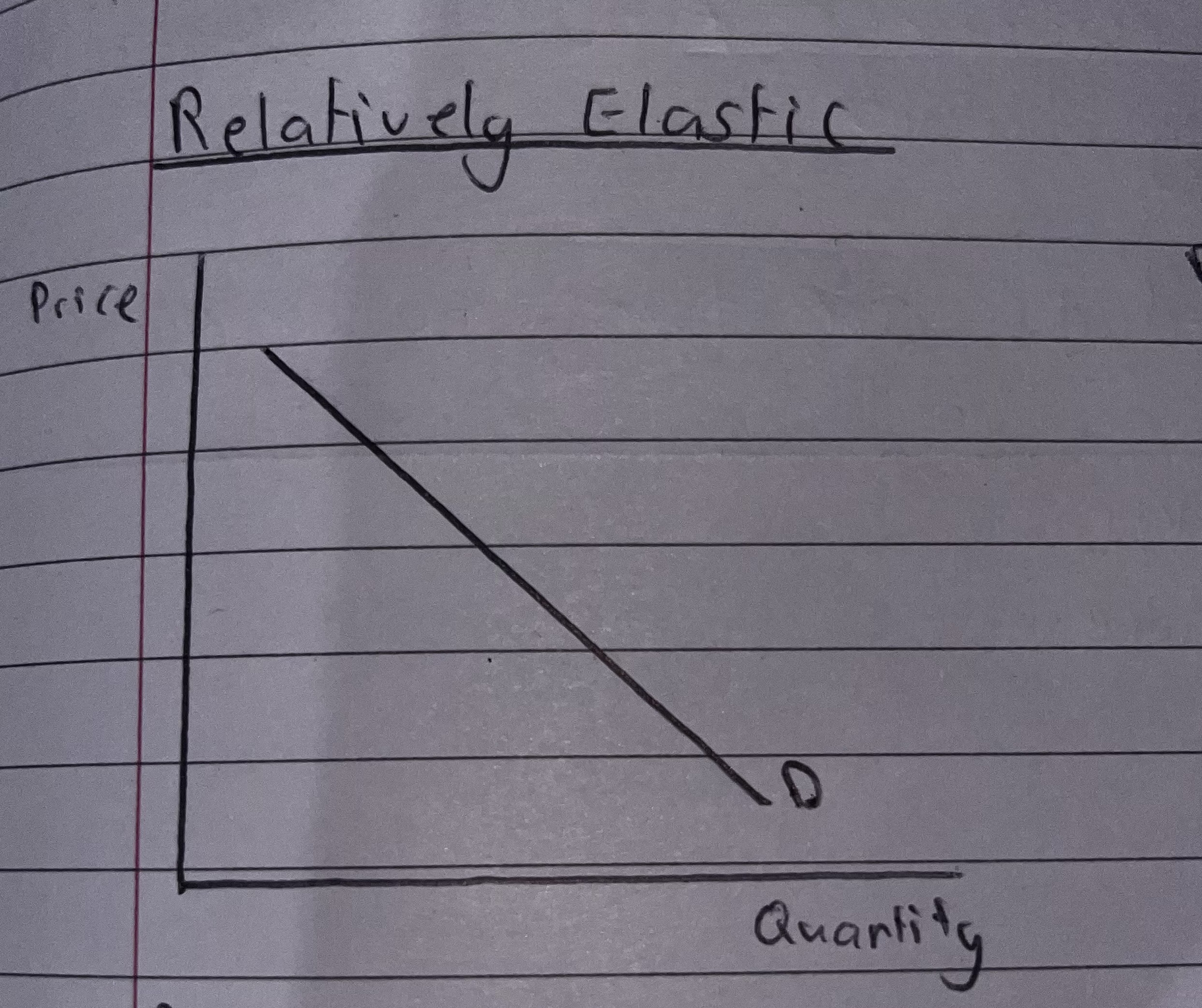
How does Relatively Elastic Look like and what is the Coefficient?
Relatively Elastic product will have a PED coefficient between -1 and infinity.
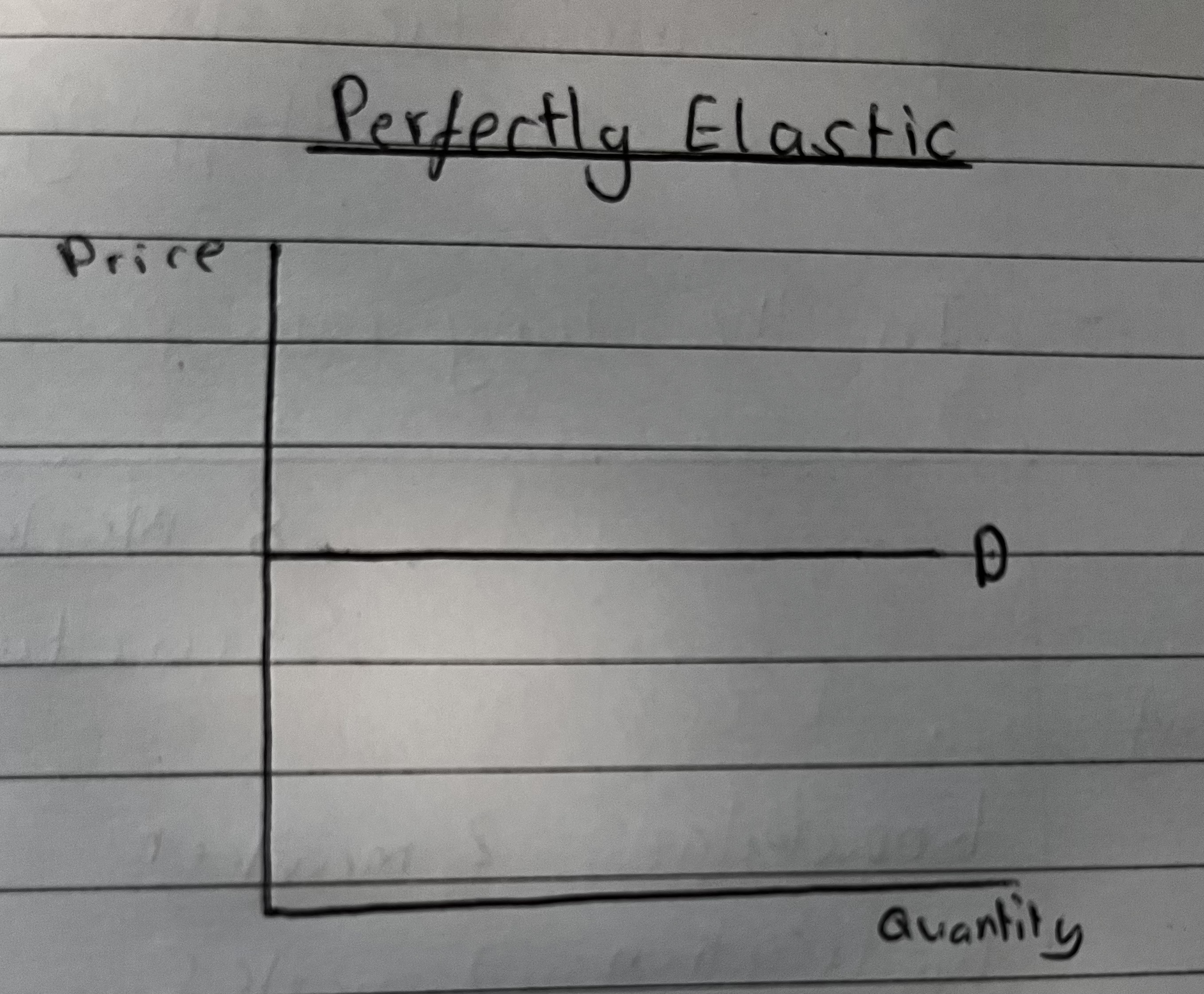
How does Perfectly Elastic Look like and what is the Coefficient?
A Perfectly Elastic product will have a PED product will have a PED coefficient of infinity.
If PED is greater than > 1 (elastic) what happens to price and revenue?
When price goes up, total revenue goes down
If PED is less than < 1 (inelastic) what happens to price and revenue?
When price goes up, total revenue goes up
What are the factors affecting PED?
Substitutes
Time (LR & SR)
What is Substitutes?
The number and closeness of available and it helps determine PED.
What is there is lack of available substitutes?
The product is likely to be very inelastic and vice versa. (Opposite)
Why are Short Run products are likely to be more price inelastic?
As consumers find it difficult to change their shopping habbits.
Why are Long Run products are likely to be more price Elastic?
As consumers have more time to changer their behaviour.