Bio 111 Final
1/128
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam 1, 2 and Chapters 25 Review questions and Chapter 26 slides 13, 15, 16, 17, 18, 22 and Chapter 35/35 review questions
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
129 Terms
The genetic traits passed from one generation to the next are tightly associated with the biomolecule ________?
DNA
The organization of life is ascending level of complexity (from simplest to most complex can be represented by _______?
Molecule - Cell - Organism - Species - Population - Community - Ecosystem - Biosphere
Which of the following systems is the best example of homeostasis in living organisms?
pH Buffers
A hypothesis must be _______?
A statement that we should be able to test
A scientific theory ______
Is a widely accepted and supported by several forms of evidence.
Which represents the lowest degree of certainty in a scientific investigation?
Hypothesis
A Scientist testing the effects of a fertilizer on “soybean-yield” applies to a first group of 50 soybean plants that fertilizer in the Spring. A second group of 50 soybean plants does not receive the treatment. Following into the Fall, the number of soybeans produced by each plant is counted. Which of the following is the Control Group for this experiment?
The second group of soybean plants
A scientist testing the effects of an herbicide on “apple yield”, sprays a group of 15 apple trees with the herbicide in the Spring. A second group of 15 apple trees does not receive the herbicide treatment. Following into the fall, the number of apples harvested from each tree is counted. What is the dependent variable of this experiment?
The number of apples produced by the tree.
A Scientist testing the effects of an herbicide on “apple yield”, sprays a group of 20 apple trees with the herbicide in the Spring. A second group of 20 apple trees does not Receive the herbicide treatment. Following into the fall, the number of apples harvested from each tree is counted. What is the independent variable of this experiment?
The use of herbicide
Scientists perform __________ in order to __________ a given ________.
Scientists perform _EXPERIMENTS_ in order to _TEST_ a given _HYPOTHESIS_.
In an atom, electrons spin around the nucleus (arranged in orbitals) and provide the atom its physical identity characteristic. (True/False)
False
The atomic mass (mass number) of an atom is determined by- _______?
- by the sum of protons and neutrons
All living organisms are classified taxonomically (classification system used in Biology) into three major groups called Domains of Life. The Domain Eukarya is subdivided into what?
Kingdoms
Subdivided into Kingdoms
An atom that carries a net charge (either + or -) because loosing or gaining electron(s) is called a(n)?
Ion
The type of chemical bond between sodium and chloride in a table salt (NaCl) is: _______?
Ionic
Table salt (NaCl) is Ionic.
Which of the following molecules is NOT a sterol or steroid?
Glycerol
What is an example of a prokaryotic cell?
The intestinal bacterium cell E. coli.
A population of organisms is composed of individuals of ____? (what?)
The same species sharing the same resources.
Which compound is hydrophobic? (Non-polar)?
Cholesterol
(non-polar compound)
Which of the following is TRUE about water?
Hydrogen bonds old water molecules together making water more cohesive.
Which of the following would NOT be characteristic of a living organism?
Uniformity of size and form; size and form is permanent.
Which group of molecules is the most abundant in the cell plasma membrane?
lipids, specifically phospholipids
All eukaryotic cells contain subcellular structures that preform specific cellular functions that are called _______?
Organelles
In nutritional terms, _______ is the group of lipids most harmful to human health when consumed.
Trans-fats
(trans-fat is the group of lipids)
Eukaryotic cells have their DNA enclosed in the ________?
Nucleus
(DNA enclosed in the nucleus)
One of the generalizations of the Cell Theory is that _______?
All living organisms are made up of cells
(Cell Theory is that all living organisms are made up of cells)
Which of the following scientists is accountable for designing the first microscope?
Anton Van Leeuwenhoek
________ are subatomic particles of the atom with no electrical charge and located in the nucleus.
Neutrons
(Neutrons are subatomic)
Which type of microscope has the most powerful magnification and resolution?
Electron Microscope
Which of the following cells features is absent in a bacterial cell?
Nucleus
(Nucleus is absent)
One molecule of glucose combines with one molecule of fructose to form the disaccharide Sucrose. This takes place during a _____ chemical reaction.
Dehydration
(Takes place during)
Which of the following organelles is correctly matched with its function?
Mitochondria: ATP production
(Organelles)
The rough endoplasmic reticulum is a network of folded membranes studded with _________ which give them a lumpy appearance.
Ribosomes
(Folded membranes)
Many liquid detergents like bleach dissolved in water have pH greater than 9.0, therefore these are _______.
Bases
(pH)
Substance “X” when dissolved in water releases hydrogen ions into solution, therefore, this substance is __________.
An acid
(Hydrogen ions)
Which of the following cellular structures is common in both Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic cells?
Ribosomes
A molecule that removes H+ (Hydrogen ions) when mixed in water is ______?
Basic
All these are polysaccharides EXCEPT:
Triglycerides
C10H20O10 is likely to be a _________?
Carbohydrate
During the process of digestion, _________ chemical reactions will breakdown proteins into building blocks of amino acids.
Hydrolysis
(Chemical reactions)
Which cell organelle/structure is responsible for protein synthesis?
Ribosomes
Intermediate filaments, microfilaments and/or microtubules are typical components of the following cell structures, EXCEPT:
Golgi apparatus
Polymers of amino acids with a tertiary structure and associated specific biological function are called ____?
Proteins
The four most common elements in your body are ________?
Hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and carbon.
The biological function of many proteins is determined by their _______?
Tertiary structure or 3-D structure
The building blocks of RNA molecules are ______?
Nucleotides
_____ is described as the shipping center of the cell because of its function of collecting, sorting, packaging and distributing proteins and lipids produced in the endoplasmic reticulum.
Golgi Apparatus
(Shipping center)
_______ is the cell organelle of photosynthesis.
Chloroplast
(Organelle)
_________ are intercellular vesicles containing hydrolytic digestive enzymes.
Lysosomes
(digestive enzymes)
A supplement company selling a diet pill claims that its product is effective in controlling weight. Its CLAIM is based on previous studies done in people. They conducted a “blind study” with a control group of 100 individuals (randomly chosen) and an experimental group of another 100 individuals (all physically fit with a daily routine of exercising in a gym) The control group received a placebo pill while the experimental group received the diet pill. Every month the weight for all participants were monitored. Results showed after one year that the experimental group were able to maintain their body weights when compared to the control group. Is the experimental design of this study appropriate that could support the company’s claim about this diet pill? (TRUE or FALSE)
False
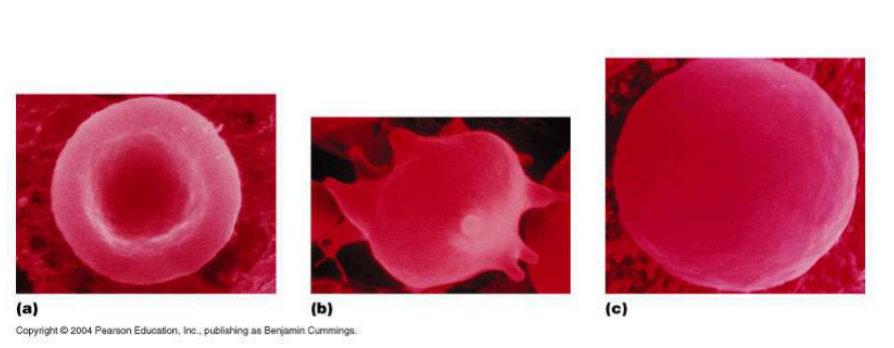
Which red blood cell is under hypotonic conditions?
C
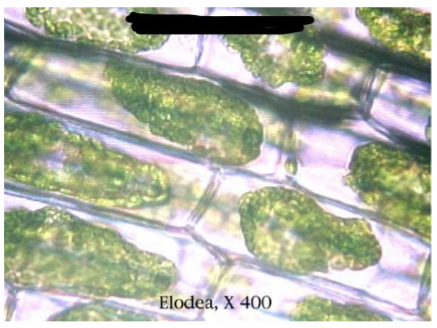
Which tonicity condition do these Elodea cells represent?
Hypertonic
Osmosis is briefly defined as:
Movement of water molecules across
A net movement of molecules or ions from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration until equilibrium is attained is called:
Diffusion
Intestinal cells absorb glucose via facilitated/passive transport. What would happen if all the mitochondria (“powerhouse organelle”) within these intestinal cells were destroyed?
Glucose adsorption would not be affected.
A Cellular example of exocytosis is:
Secretion of the hormone insulin.
When neurons (Nerve cells) release their neurotransmitters, they release them by secretory vesicles fusing with the plasma membrane thereby emptying their contents into an area that can stimulate some response. What type of cellular transport is occurring as the vesicle forms and then surfaces on the cell’s plasma membrane?
Exocytosis
A channel membrane protein that transports a specific molecule against its concentration gradient and thus using energy (ATP) to achieve this an example of:
Active transport
What structure(s) in the cell membrane will directly influence the process of osmosis?
Aquaporins
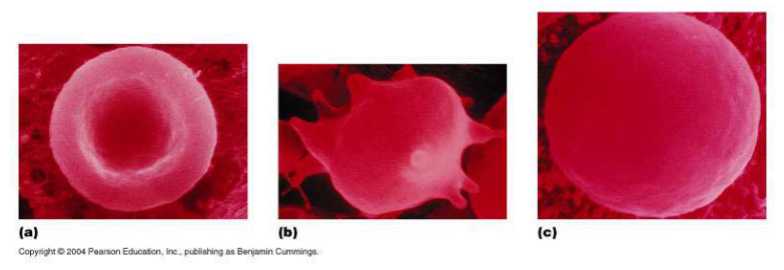
Which red blood cell is under hypertonic conditions?
B
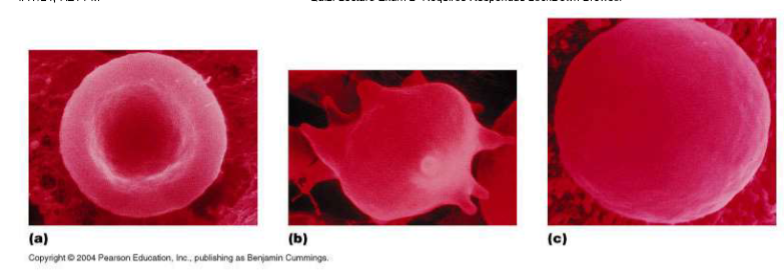
Which red blood cell is under isotonic conditions?
A
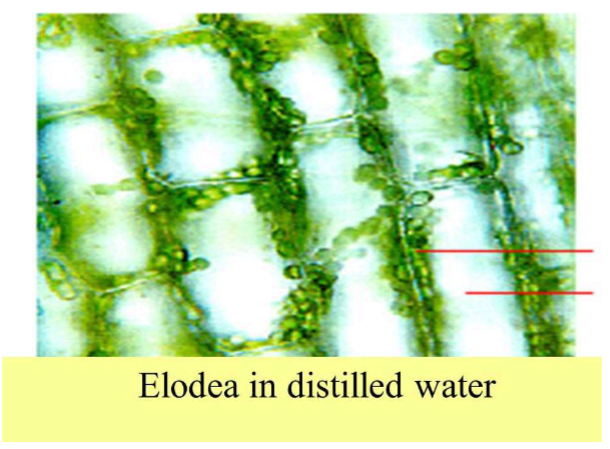

What tonicity conditions do these Elodea cells represent?
Hypotonic
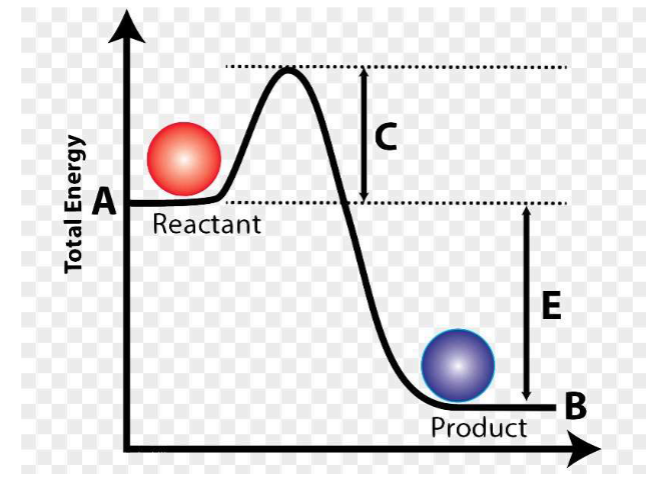
What does the letter C represent on this image?
Activation energy
Which of the following statements are CORRECT about the nature of enzymes?
Most enzymes are proteins
The conversion of solar energy into chemical energy losing heat as unusable energy during photosynthesis is a perfect example of:
Second law of thermodynamics
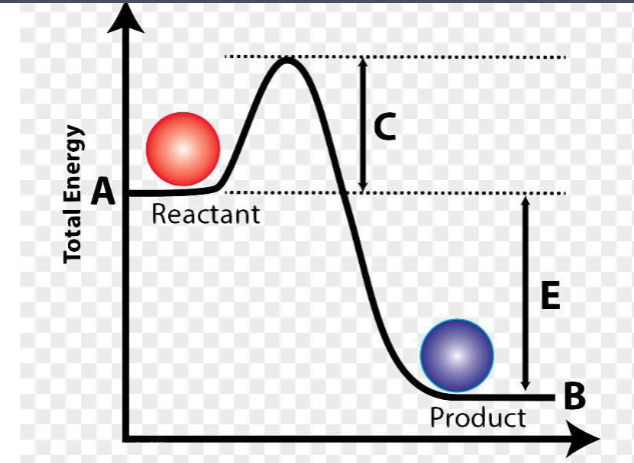
What does letter E represent on this diagram?
The difference is potential energy between the reactant and the product

The figure below represents a metabolic pathway. What happens if Enzyme2 is defective and nonfunctional?
Substrate Y would not be metabolized
In feedback allosteric inhibition of a metabolic pathway, where does the allosteric inhibitor bind to?
To the enzyme in the first reaction
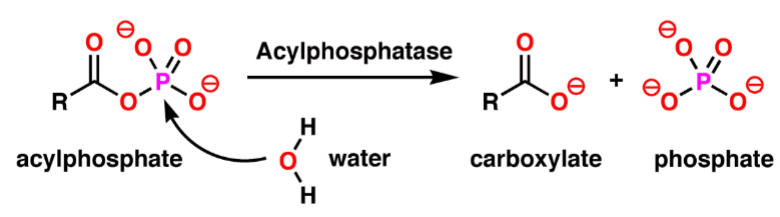
What is the enzyme in this chemical reaction?
Acylphosphatase
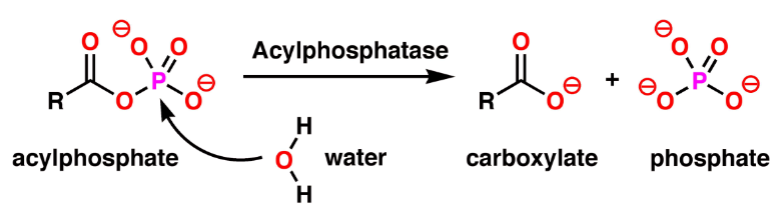
What is a product on this chemical reaction?
Carboxylate
According to the first law of thermodynamics, Energy_____?
Cannot be neither created nor destroyed
The part of the enzyme into which the substrate fits is called the _________?
Active site
When neurons (nerve cells) release their neurotransmitters, they release them by secretory vesicles fusing with the plasma membrane thereby emptying their contents into an area that can stimulate some response. What type of cellular transport is occurring as the vesicle forms and then surfaces on the cell’s plasma membrane?
Exocytosis
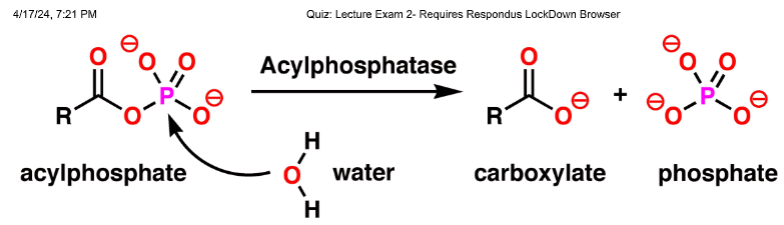
What is the substrate in this chemical reaction?
Acylphosphate
What biomolecule produces the highest number of ATP per molecule (higher yield) during cellular respiration?
A fatty acid containing 20 carbons
Which of the following is the correct sequence of events in aerobic cellular respiration?
Glysolysis, preparatory reaction, kreb’s cycle, electron transport system
The process of catabolizing a fatty acid by converting it first into AcetylCoA and then entering the Kreb’s cycle is known as ______?
Beta oxidation
Which of the following is an incorrect math of process to location?
Preparatory reaction - cristae of mitochondria
Cellular respiration is the opposite of what other cellular process?
Phosotsynthesis
The number of ATP produced during aerobic cellular respiration from one glucose molecule is ________
36-38
The final acceptor for hydrogen ions and electrons in aerobic cellular respiration is_______
Oxygen gas
Which hormone “turns on a switch” in the body of a pregnant human to burn fat molecules as the primary source of ATP production?
hCG
What would happen if NAD+ were not available for cellular respiration?
There will be a great reduction in the number of ATP formed
Where in the cell does glycolysis occur?
Cytoplasm
A family took their newborn to the doctor. They were worried something was wrong because the baby seemed to be in constant pain. He had large amounts of lactic acid accumulating in his muscle cells. Doctors figured out that the child had a rare disease in which mitochondria are barely present in skeletal muscle cells. Which of the following statements explains what they found?
The muscle cells had been going through fermentation
Glycolysis and the Kreb’s cycle are similar in that they both produce ______
NADH and ATP
When glucose is broken down to CO2 and H2O ______ energy is released and converted into ________
Chemical potential ATP
The Calvin Benson cycle is also known as:
Light independent reaction
The light-dependent reactions act much as a battery to power the reactions of the Calvin Benson cycle. This energy is stored as _______
ATP and NADPH
During hot and dry days, C3 plants use a different and alternative metabolic pathway to fix carbon into the Calvin Benson Cycle through an intermediate produced called Glycolate. This process is called:
Photorespiration
The O2 given off during photosynthesis is derived from which compound?
Water
The end product of the Calvin Benson cycle reaction is _________
Glucose
A plant leaf relies on a structure called ________ to perform exchange of gases such as O2, CO2 and H2O vapor.
Stomata
The Calvin Beson cycle takes place in ______ of the chloroplast.
Storma
Which of the following organisms can perform photosynthesis?
Algae
Which of the following events does not take place in the light reactions (light-dependent reaction) of photosynthesis?
Generation of glucose from CO2 and H2O
Inside the chloroplasts, chlorophyll is found in the _________
Thylakoid membrane
As climate change leads to drier and drier summers in the southeastern United States, more and more homeowners find that they have crabgrass growing in their yards. The reason for this is that _____________
Crabgrass is a type of C4 plant
A plant uses CAM photosynthesis is most likely to be successful in what type of environment?
Hot, dry
The light reactions produce ______, which are used in the Calvin Benson cycle. The Calvin Benson cycle produces _____, which are in turn used in the light reactions.
ATP and NADPH: ADP and NADP+