microbiology - exam 1
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
microbe
organism that requires microscope to be seen
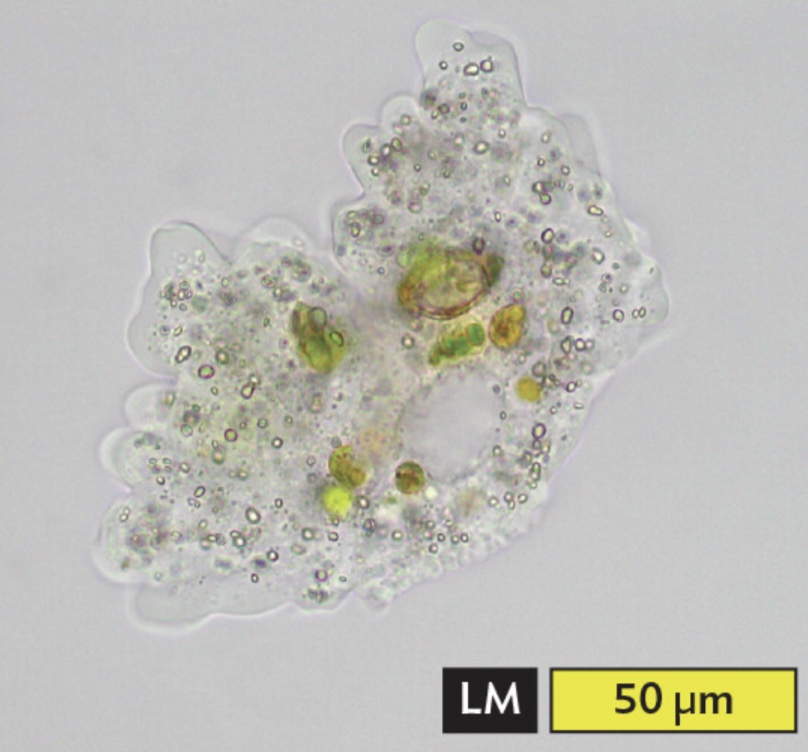

Pelomyxa sp., a large ameba
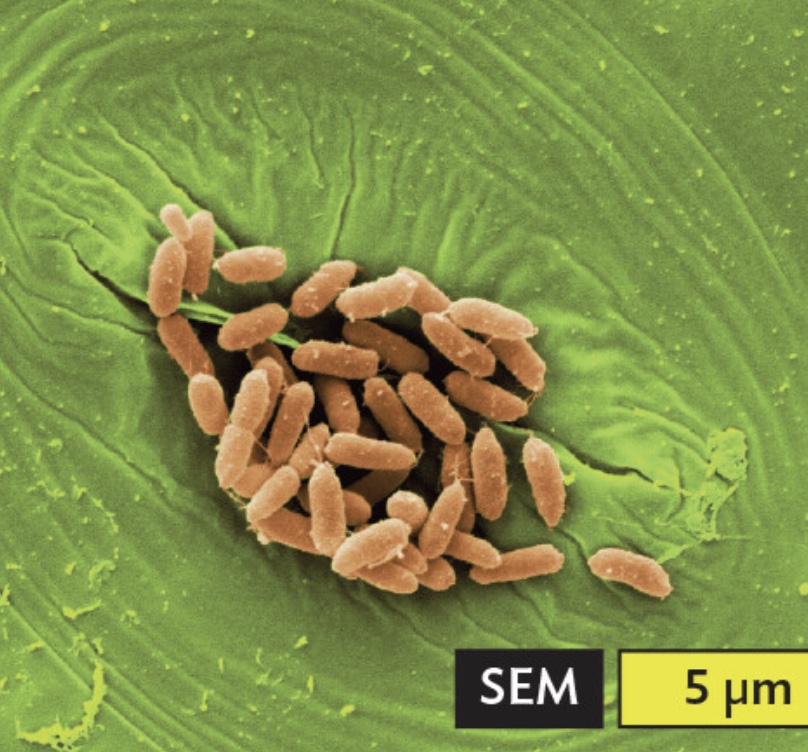
Escherichia coli bacteria
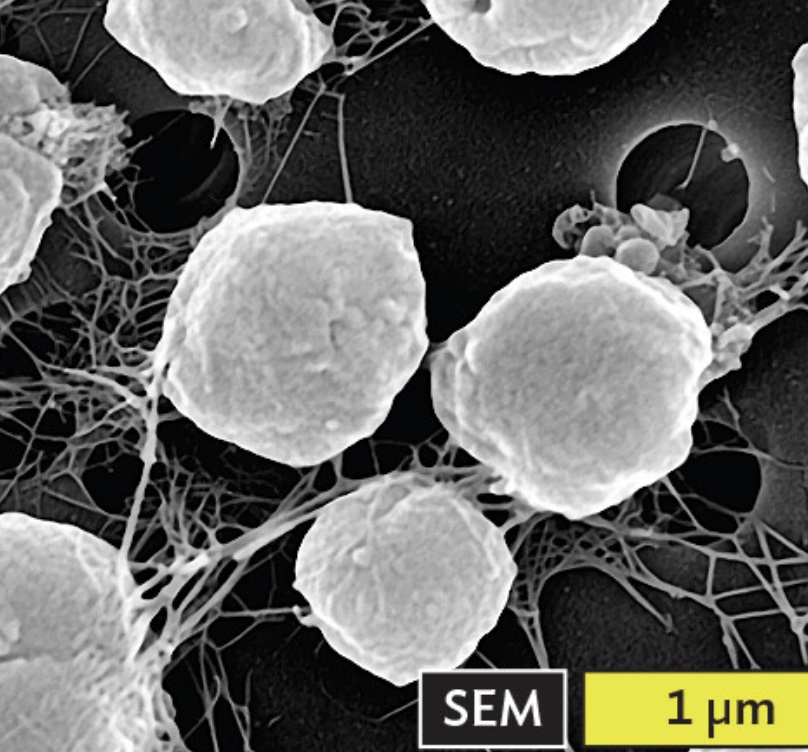

Methanocaldococcus jannaschii, archeaon
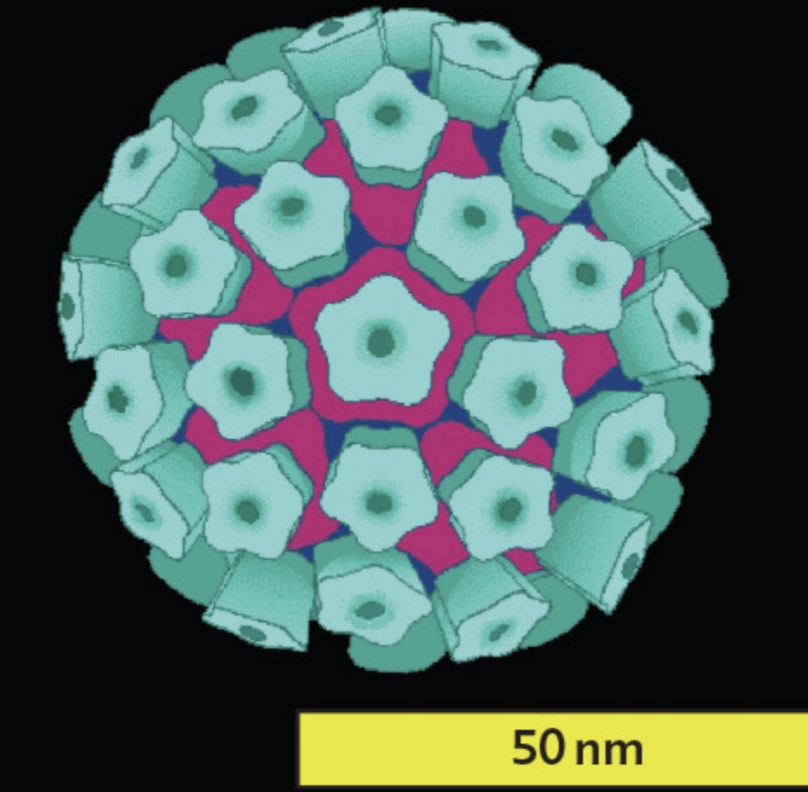
Human papillomavirus
pathogens/germs
microbes that cause disease
(bacteria, viruses, and fungi)
principal cause of human mortality
diseases caused by pathogens
microscope
instrument that uses one or more lenses to magnify the image in our eyes
first microscopist to publish a systematic study of world as see under a microscope
Robert Hooke
compound microscope + who created it
created by Robert Hooke
a magnifying instrument containing two or more lenses that multiply their magnification in series
Micrographia
the first publication that illistrated objects observed under a microscope
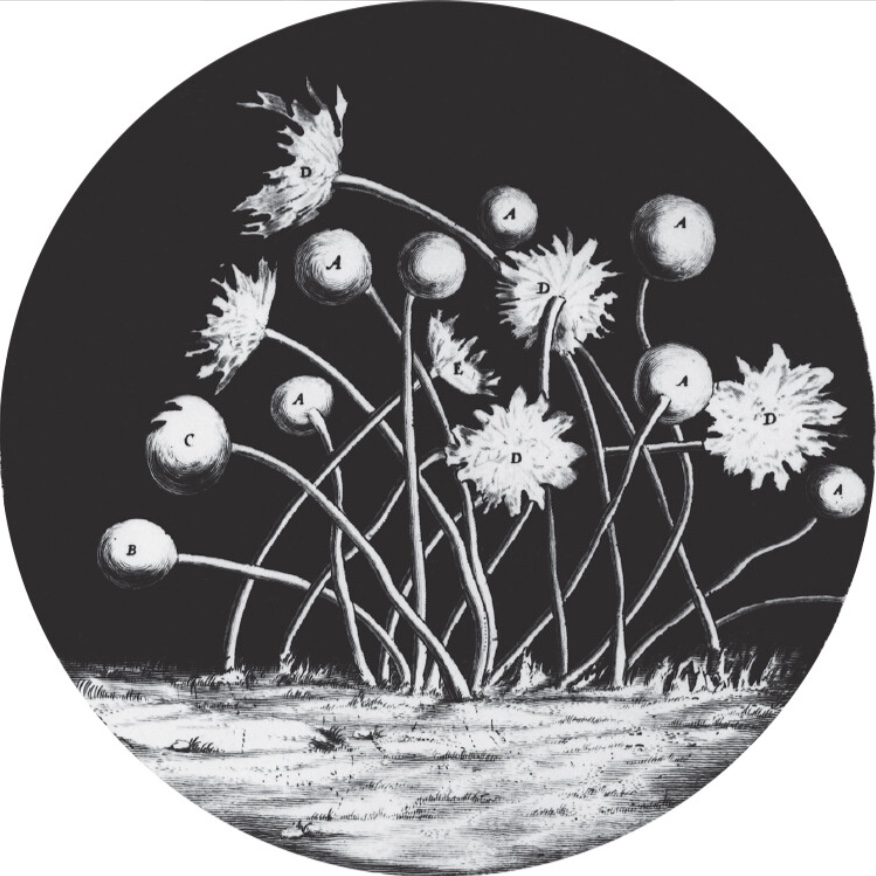

Illustration of mold sporangia, drawn by Hooke from his observations of objects with a compound microscope
who was the first to observe distinct units of living material, calling them “cells”
Hooke
first to observe bacteria with a single lens, first to observe single celled microbes
Leeuwenhoek
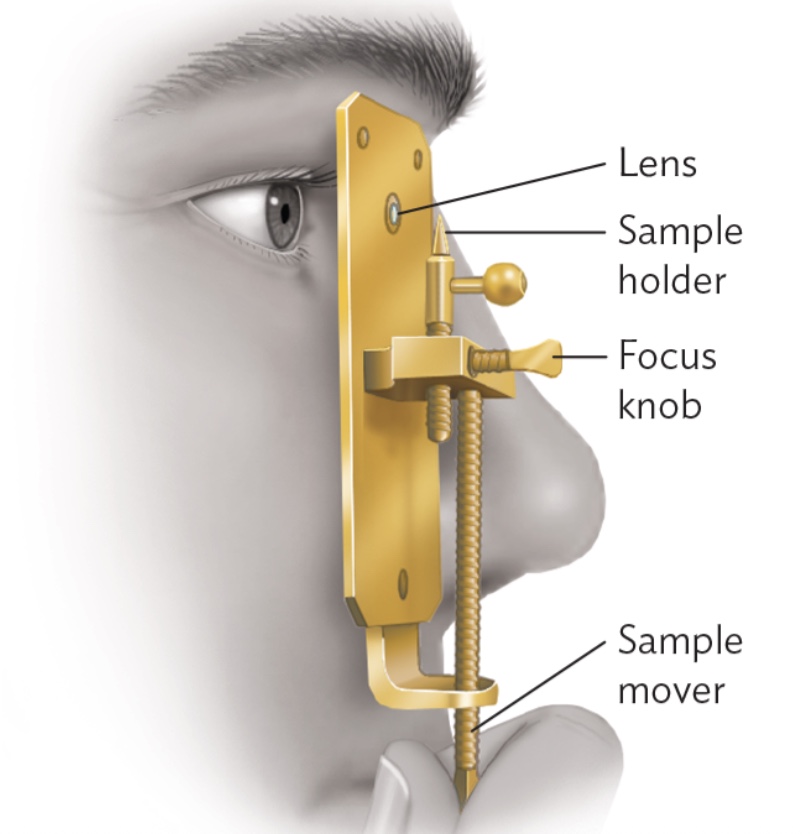
Leeuwenhoek’s microscope
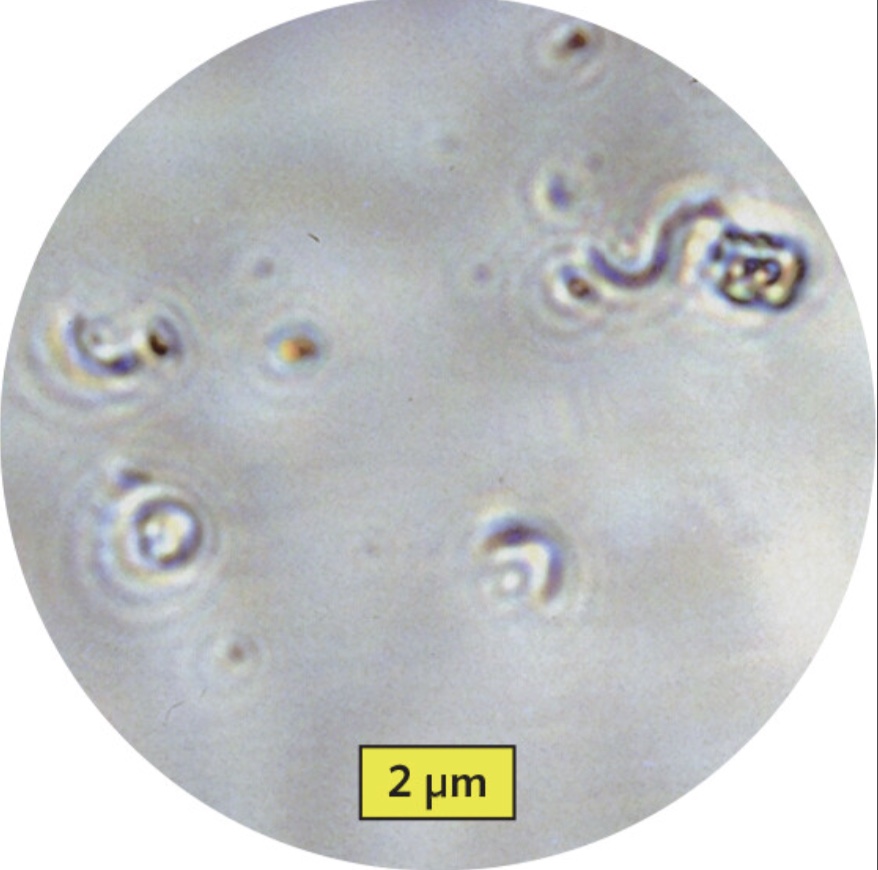
spiral bacteria viewed through a replica of Leeuwenhoek’s instrument
how are microbes classified
members of a species, according to shared set of genes and traits
fundamental basis for classifying all life forms
genome - a total DNA sequence content of organism
major trait distinguishing microbes
possession or lack of a membrane-enclosed nucleus
prokaryote
an organism whose cell or cells lacks a nucleus
eukaryote
an organism whose cell contains a nucleus
bacteria and archaea
prokaryotes
fungi, protozoa, and algae
eukaryotes
the 3 domains
bacteria, archaea, & eukarya
some archaea are extremophiles… what does that mean?
live in seemingly hostile environments
methanogens
archaea whose metabolism releases methane
what do archaea NOT do
cause disease
protozoa
a heterotrophic eukaryotic microbe, usually motile
algae
eukaryotic microbes containing chloroplasts that conduct photosynthesis
protists
a single-celled eukaryotic microbe, usually heterotrophic and motile
fungi
heterotrophic organisms, usually nonmotile, grow by absorbing nutrients from surrounding
parasites
organisms that live at the expense of a host they inhabit
viruses
noncellular microbe that contains a genome and can only replicate inside a host
how do viruses replicate
a virus particle contains genetic material that takes over the metabolism of a cell to generate more virus particles
how did humans use microbes before discovering them?
made food and used lithotrophs (rock-eating bacteria) to mine
the “golden age” of microbiology as a science
19th century (1847-1899)
antibiotics
a molecule that can kill or inhibit the growth of selected microorganisms
leading cause of death in children
microbial infections
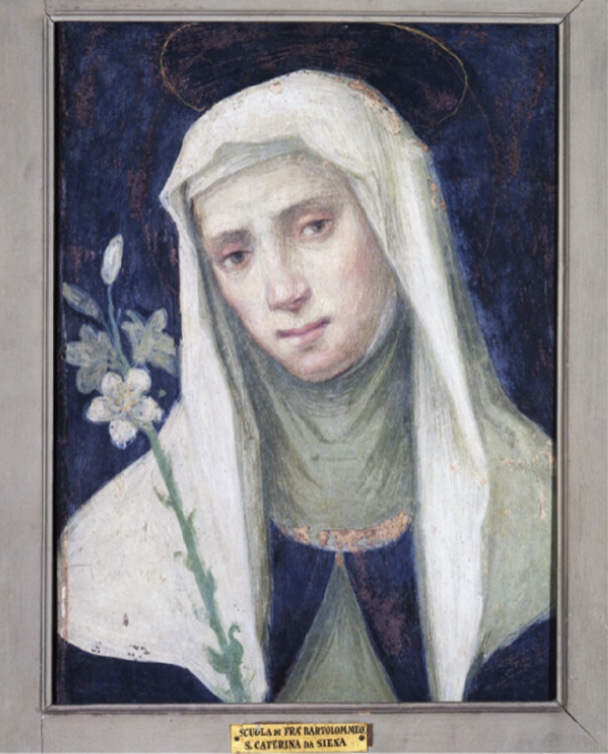

Catherine of Siena
patron saint of nurses, nursed victims of plague and leprosy
spontaneous generation
the theory that living microbes can arise spontaneously, without parental organisms
Lazzaro Spallanzani
disproved spontaneous generation of microbes by showing a sealed flask of meat broth sterilized by boiling failed to grow microbes & discovered cell fission by watching one microbe split into two
Louis Pasteur
disproved spontaneous generation with a swan-neck flask and discovered fermentation is actually caused by a living yeast
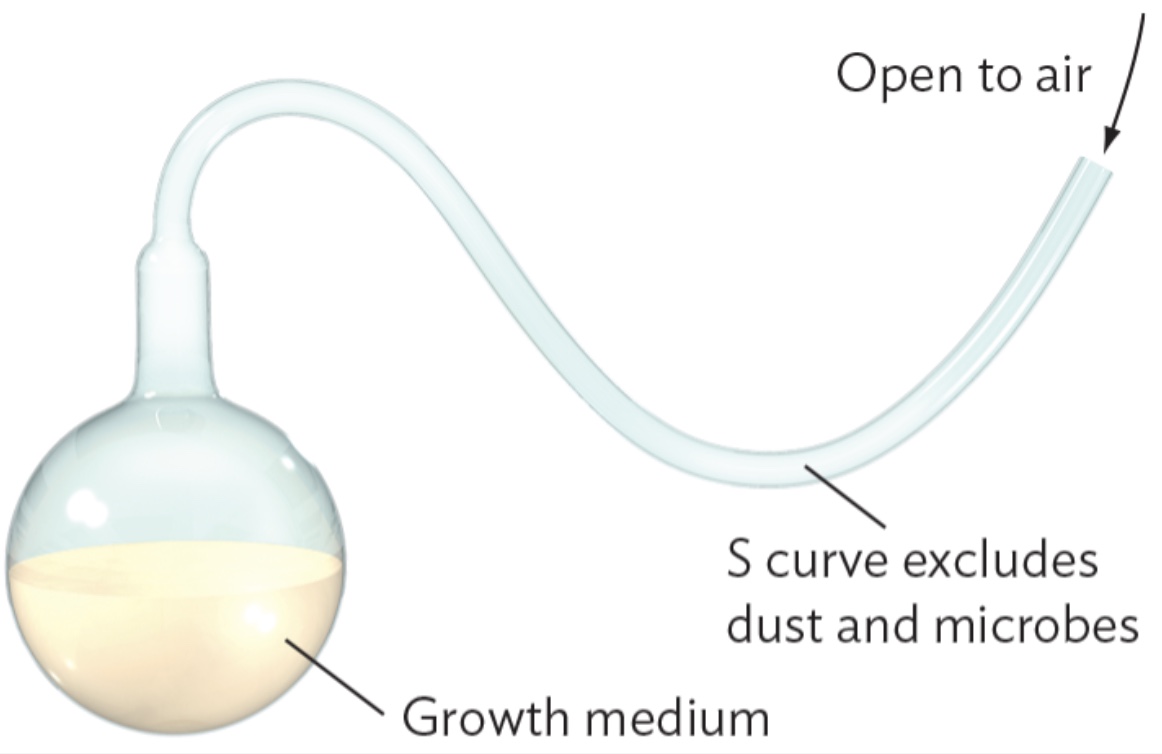
Pasteur’s swan-neck flask
After boiling, contents remained microbe free, despite access to air
John Tyndall
showed that repeated cycles of heat are necessary to elimate spores formed by certain kinds of bacteria
endospores/spores
heat-resistant form of bacteria