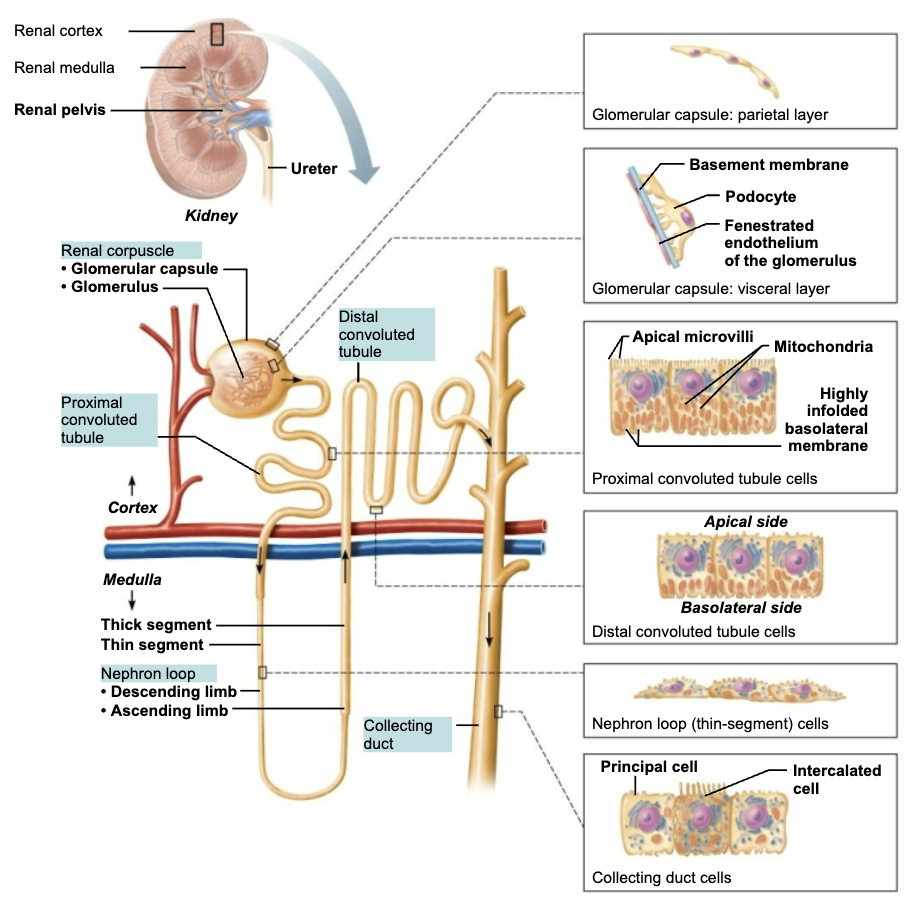
(25.2) Nephrons
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Describe the function of Nephrons
The structural and functional units that form urine
> 1 million/kidney
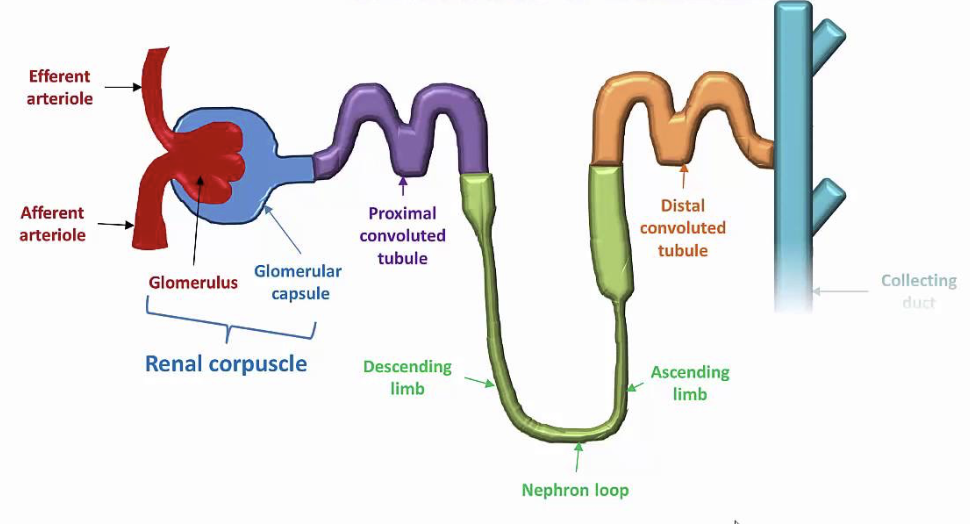
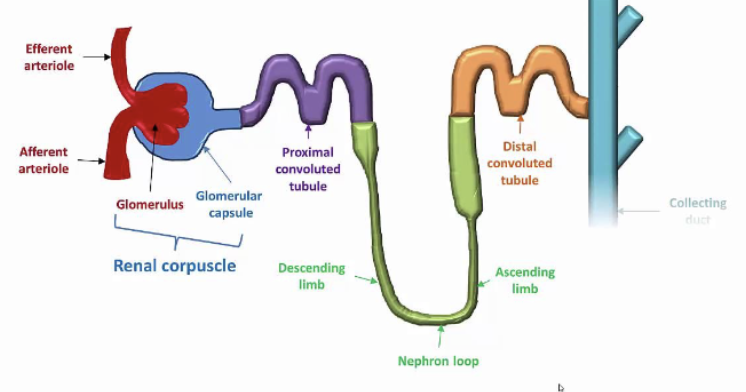
Describe the structure of the Nephron
Two main parts:
Renal corpuscle
Renal tubule
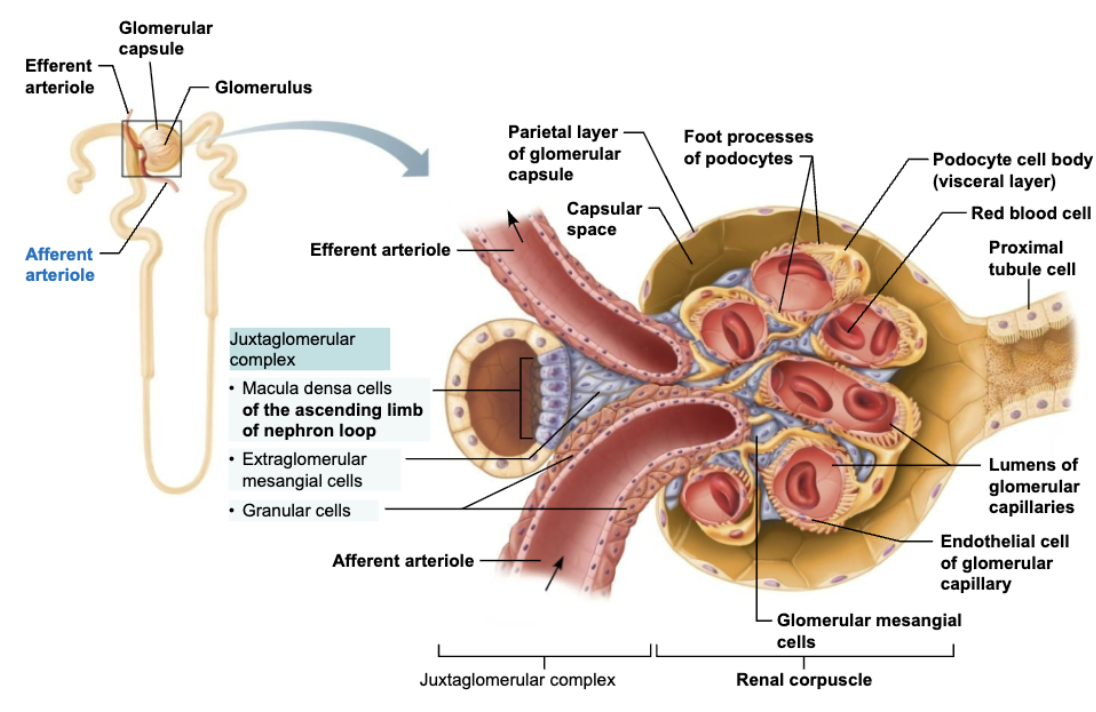
Describe the Structure and Function of Regions of the Renal Corpuscle
Glomerulus
STURCTURE
Tufts of capillaries composed of fenestrated endothelium
FUNCTION
Highly porous capillaries (fenestrated)
Allows for efficient filtrate formation
Glomerular capsule (Bowman’s capsule)
STURCTURE
Parietal layer → simple squamous epithelium
Visceral layer → clings to glomerular capillaries; branching epithelial podocytes
FUNCTION
Cup-shaped hallow structure surrounding glomerulus
Role of Filtrate
Plasma-derived fluid that renal tubules process to form urine
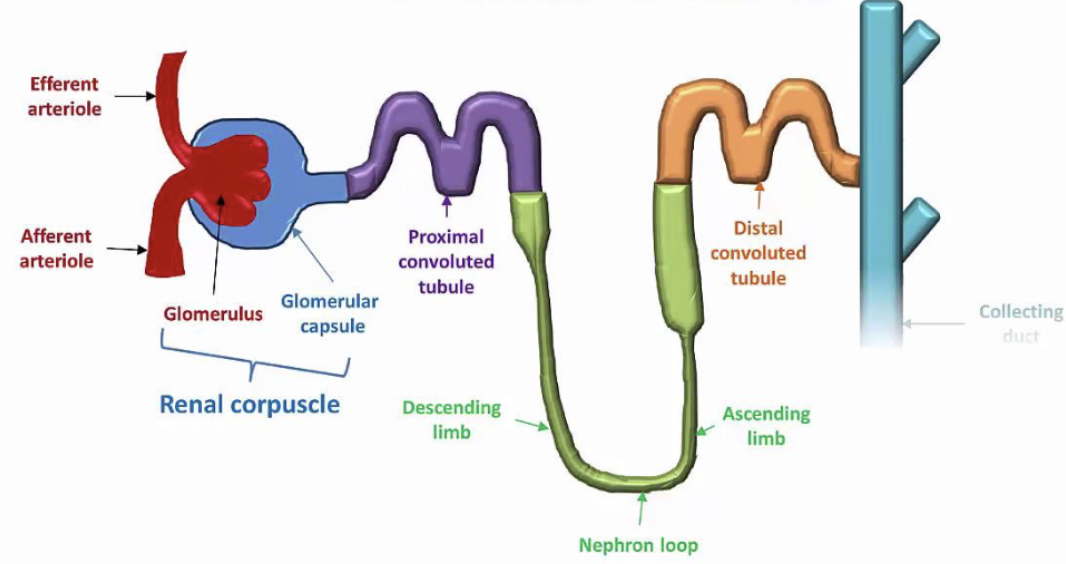
Describe the structure and function of Regions of the Renal Tubule
STRUCTURE
3cm (1.2 in) long
Single layer of epithelial cells
FUNCTION
Each region has its own unique histology and function
Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT)
Nephron loop
Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT)
Collecting ducts
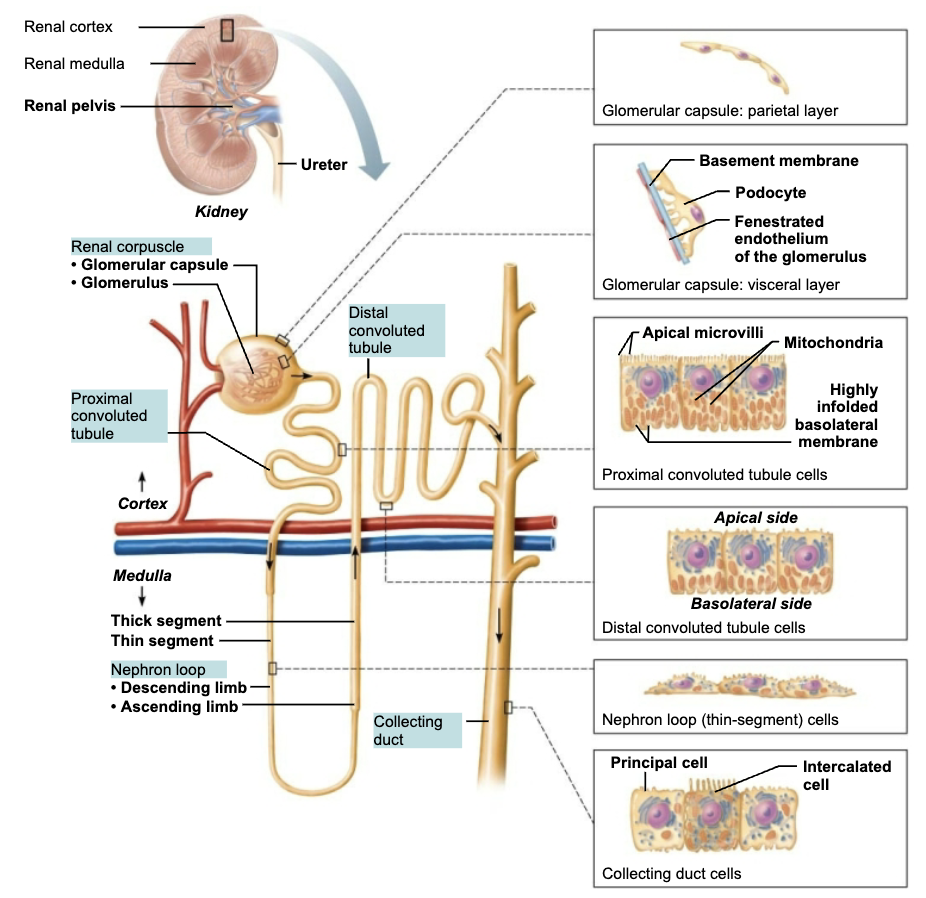
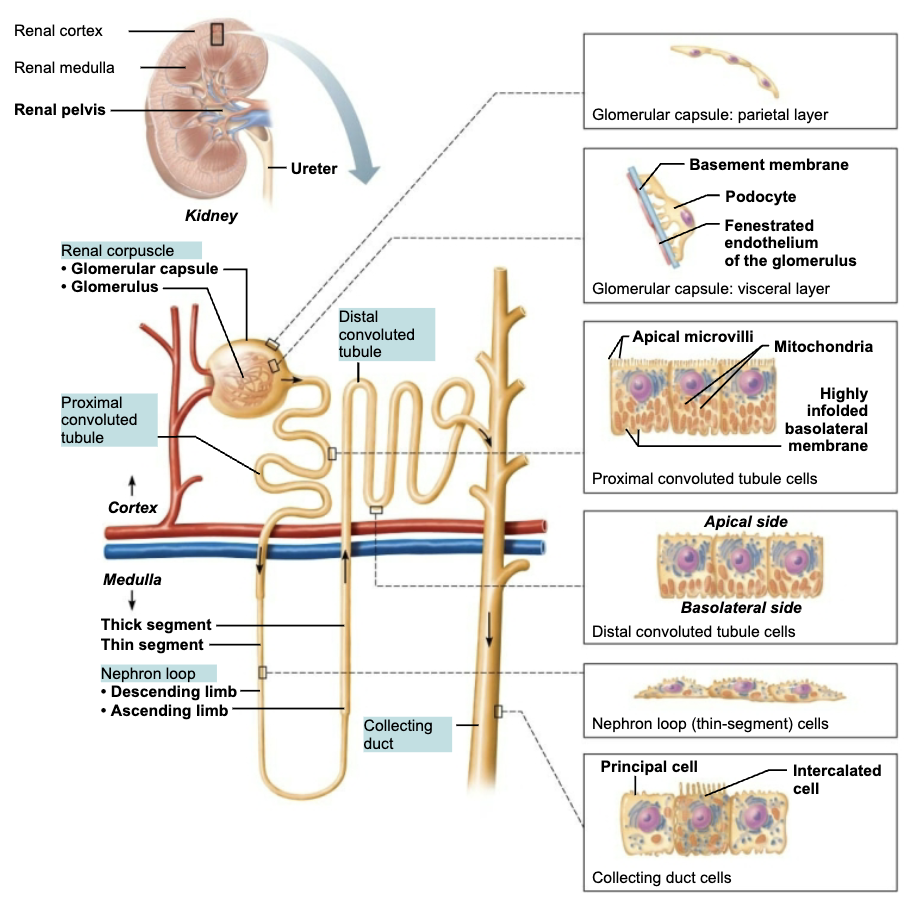
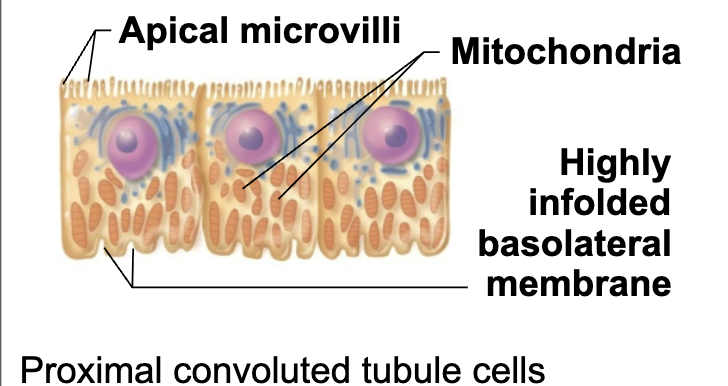
Structure and Function of Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT)
Region of the Renal Tubule (1/4)
STRUCTURE
Confined to cortex
Cuboidal cells with dense microvilli that form brush border
FUNCTION
Increase surface area
Reabsorption & secretion
Structure and Function of Nephron loop
Region of the Renal Tubule (2/4)
Loop of Henle
STRUCTURE
Middle segment
U-shaped structure consisting of two limbs
Descending limb
Ascending limb
FUNCTION
Plays a vital role in the kidney’s ability to form dilute or concentrated urine
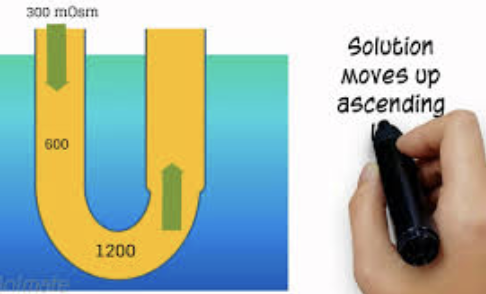
Distinguish between Descending limb & Ascending limb
Descending limb
Proximal part of descending limb is continuous with proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)
Distal portion also called descending thin limb
Ascending limb
Thick ascending limb
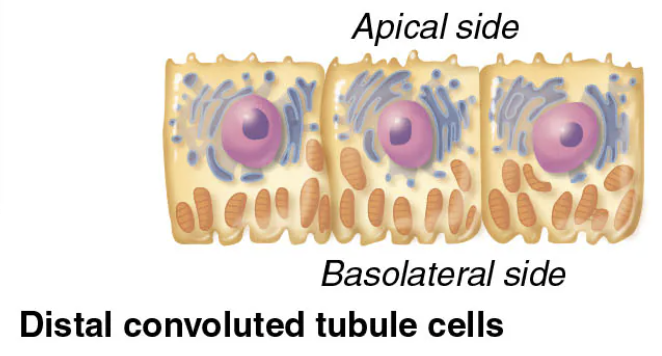
Structure and Function of Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT)
Region of the Renal Tubule (3/4)
STRUCTURE
Confined to cortex
FUNCTION
MORE SECRETION than reabsorption
Structure and Function of Collecting Ducts
Region of the Renal Tubule (4/4)
STRUCTURE
Run through medullary pyramids
FUNCTION
Receive filtrate from many nephrons
Ducts fuse together to deliver urine through papillae into minor calyces
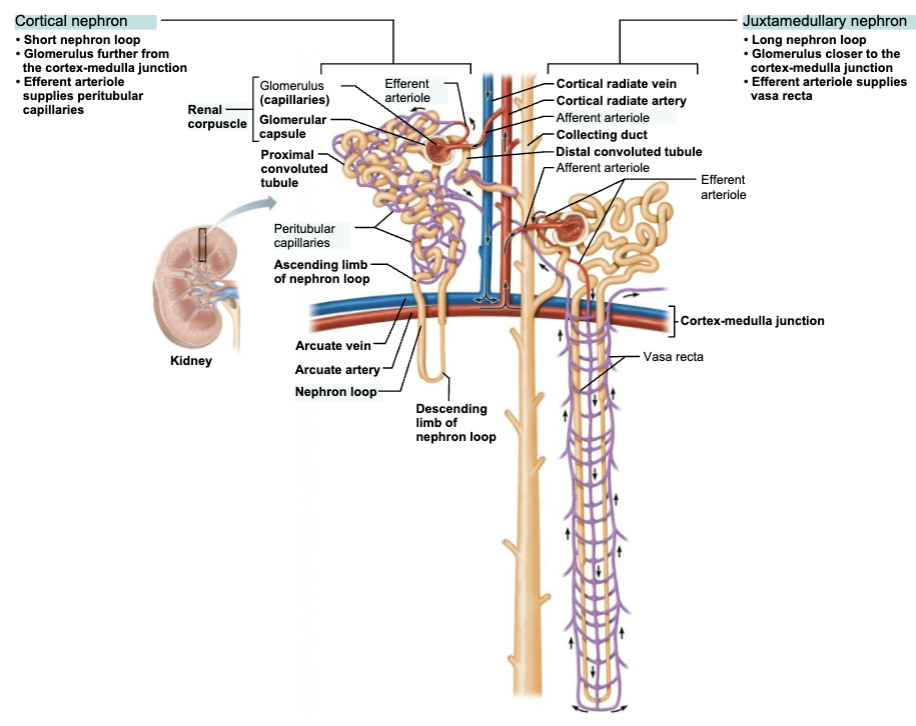
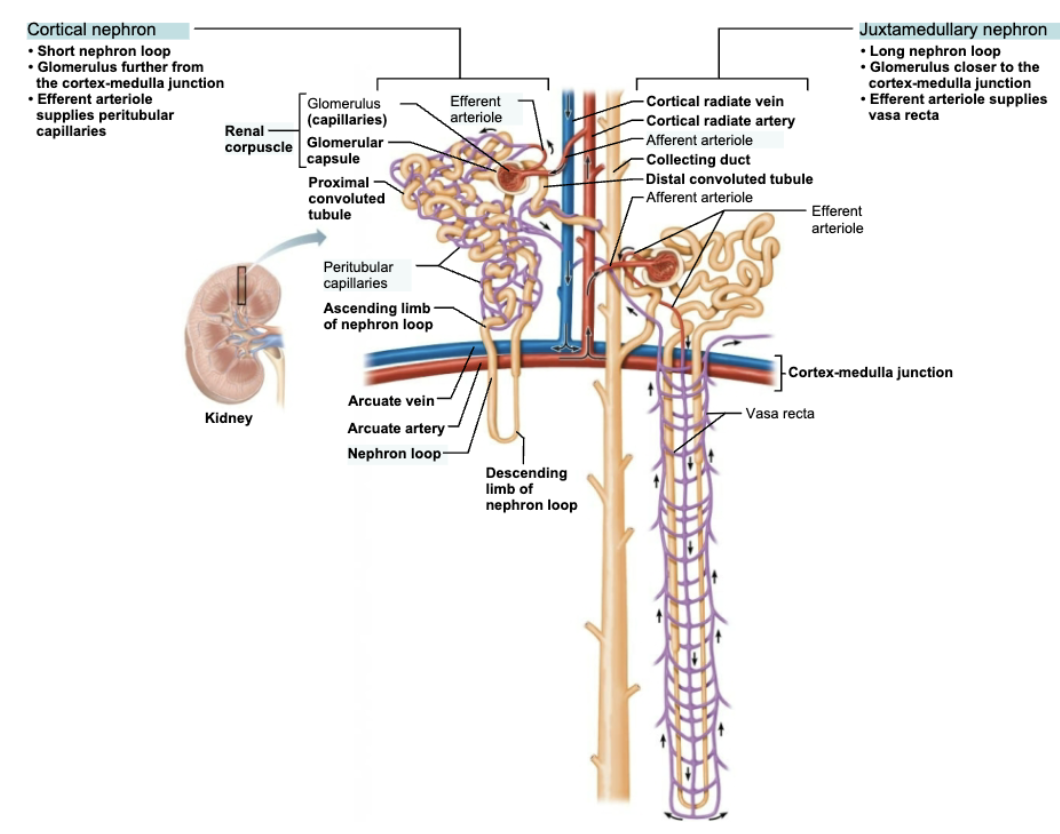
Name the Major Groups of Nephrons
Cortical nephrons
Make up 85%
Almost entirely in cortex
Juxtamedullary nephrons
Long nephron loops deeply invade medulla
Ascending limbs have thick and thin segments
Important in production of concentrated urine
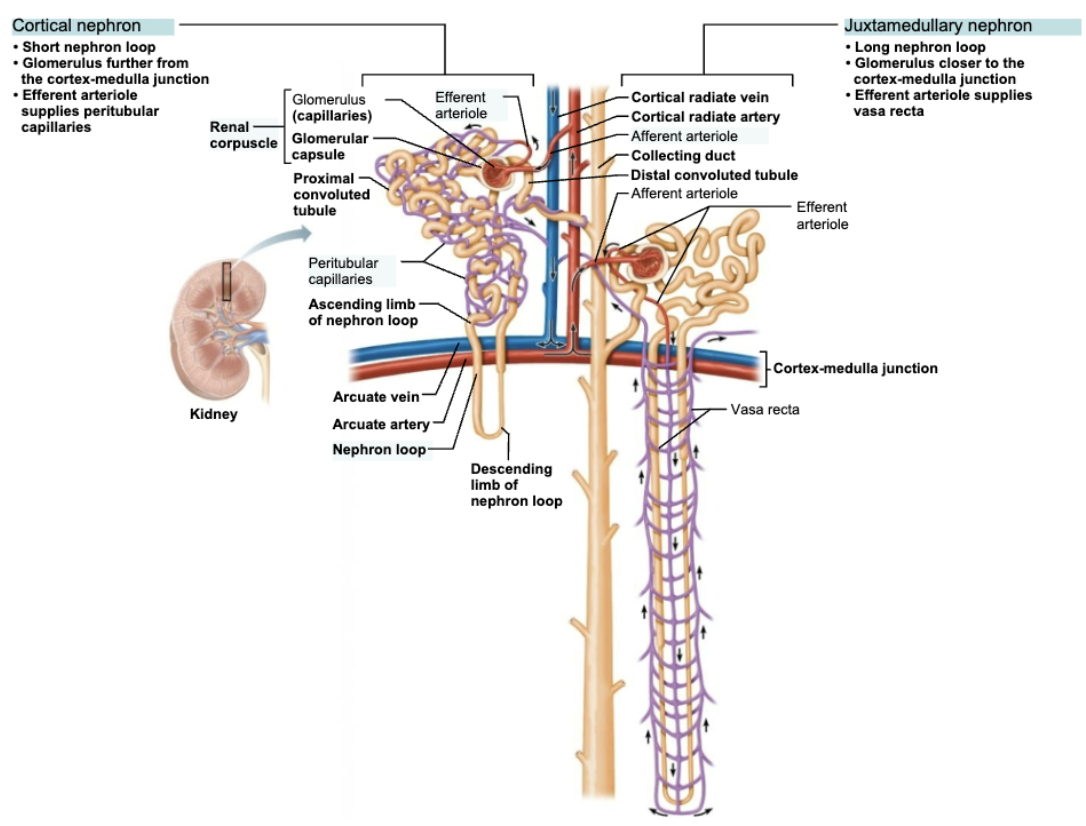
Compare and constast Cortical vs Juxtamedullary Nephrons Structure
Cortical nephrons
Almost entirely in cortex
Short nephron loop
Glomerulus further from the cortex-medulla junction
Efferent arteriole supplies peritubular capillaries
Juxtamedullary nephrons
Long nephron loops deeply invade medulla
Long nephron loop
Glomerulus closer to the cortex-medulla junction
Efferent arteriole supplies vasa recta
Name the Capillary Bed(s) associated to Cortical nephrons
Glomerulus
Peritubular capillaries
Name the Capillary Bed(s) associated to Juxtamedullary Nephrons
Glomerulus
Vasa recta
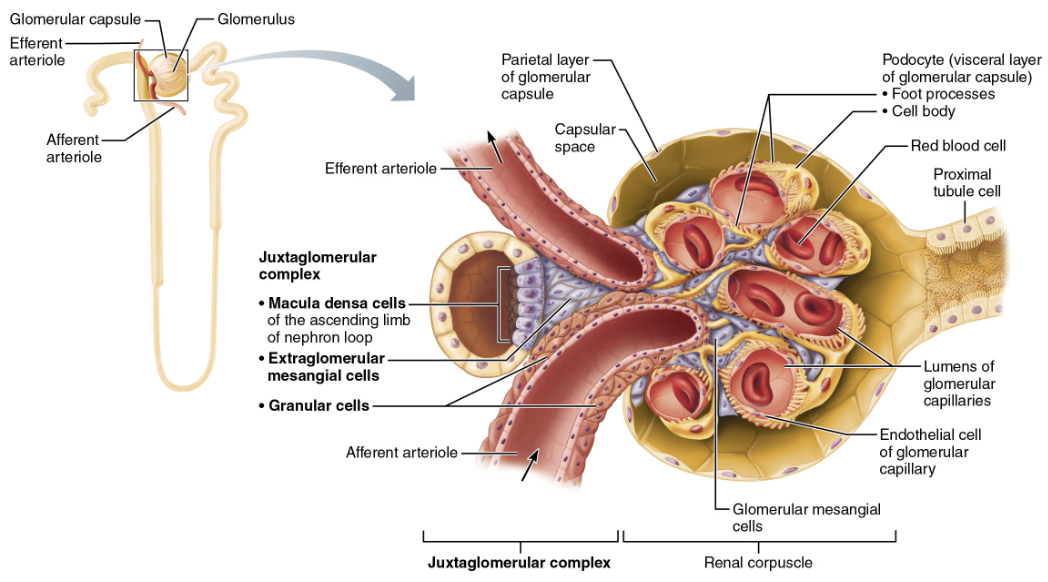
Describe Location and Function of Glomerulus Capillaries
LOCATION
Cortical & Juxtaglomerular Complex (JGC) → Renal Corpusle
FUNCTION
Capillaries are specialized for filtration
Different from other capillary bends because they are fed and drained by arteriole
Afferent arteriole enters glomerulus and leaves via efferent arteriole
T/F: Blood pressure in glomerulus is low
→ FALSE
Blood pressure in glomerulus is HIGH → Afferent arterioles are larger in diameter than efferent arterioles
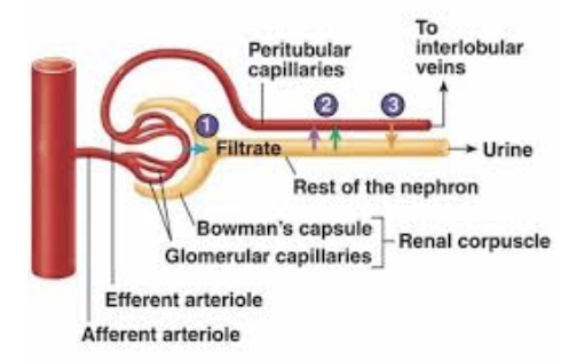
Describe Location and Function of Peritubular Capillaries
LOCATION
Cortical Nephron → Renal Tubule
STRUCTURE
Arise from efferent arterioles → Empty into venules
Cling to ajacent renal tubules in cortex
FUNCTION
Low-pressure, porpus capillaries adapted for absorption ot water and solutes
Describe Location and Function of Vasa recta
LOCATION
Juxtaglomerular Complex (JGC)→ Renal Tubule
STRUCTURE
Long, thin-walled vessels parallel to long nephron loops to Juxtamedullary Nephrons
Arise from efferent arterioles serving Juxtamedullary Nephrons
FUNCTION
Formation of concentrated urine
SUMMARY of Nephron Capillary Beds
Glomerulus
LOCATION
Cortical & Juxtaglomerular Complex (JGC) → Renal Corpusle
STRUCTURE
Different from other capillary bends because they are fed and drained by arteriole
Afferent arteriole enters glomerulus and leaves via efferent arteriole
FUNCTION
Capillaries are specialized for filtration
Peritubular Capillaries
LOCATION
Cortical Nephron → Renal Tubule
STRUCTURE
Arise from efferent arterioles → Empty into venules
Cling to adjacent renal tubules in cortex
FUNCTION
Low-pressure, porous capillaries adapted for absorption of water and solutes
Vasa recta
LOCATION
Juxtaglomerular Complex (JGC)→ Renal Tubule
STRUCTURE
Arise from efferent arterioles serving Juxtamedullary Nephrons
Long, thin-walled vessels parallel to long nephron loops to Juxtamedullary Nephrons
FUNCTION
Formation of concentrated urine
Role of Afferent & Efferent Arteriole
Afferent Arteriole
Supplies blood to the glomerulus of a nephron.
Efferent Arteriole
Drains blood from the glomerulus of a nephron
Explain Structure and Function of Juxtaglomerular Complex (JGC)
LOCATION
Each nephron has one Juxtaglomerular Complex (JGC)
STRCTURE
Involves modified portions of:
Distal portion of ascending limb of nephron loop
Afferent arteriole
FUNCTION
Important in regulating rate o filtrate formation and blood pressure
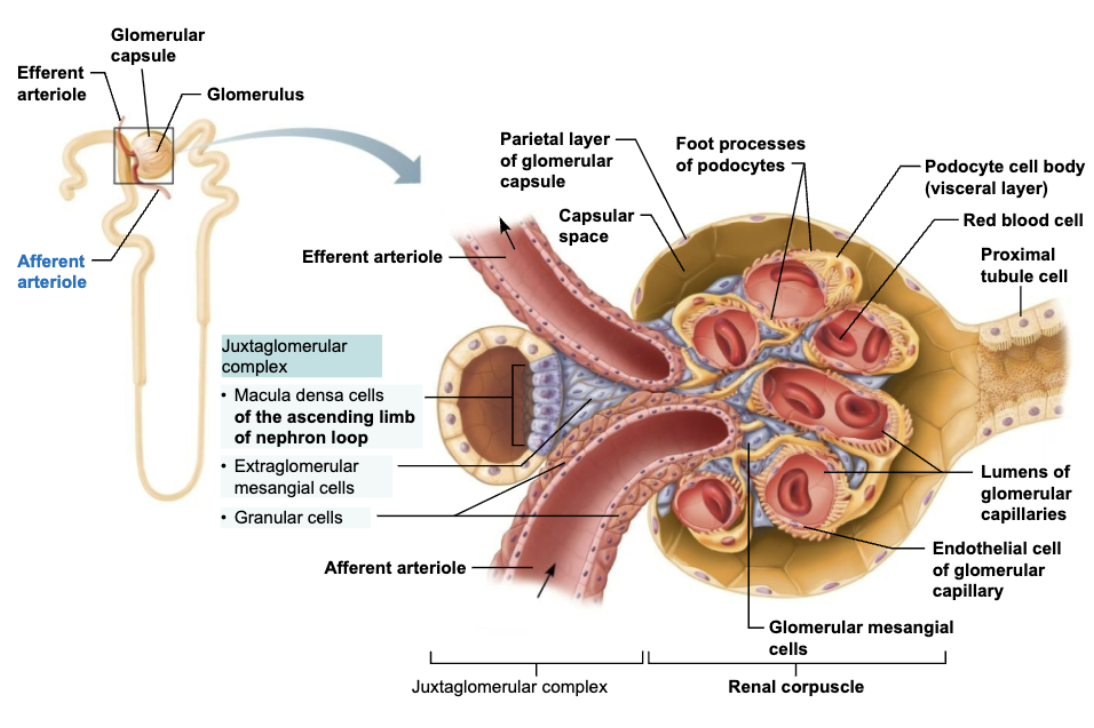
Name the Cell Populations in JGC
Macula densa cells
Granular cells
Explain Structure and Function of Macula densa cells
Juxtaglomerular Complex
STRUCTURE
Closely packed cells of ascending limb
FUNCTION
Contain chemoreceptors that sense NaCl content of filtrate
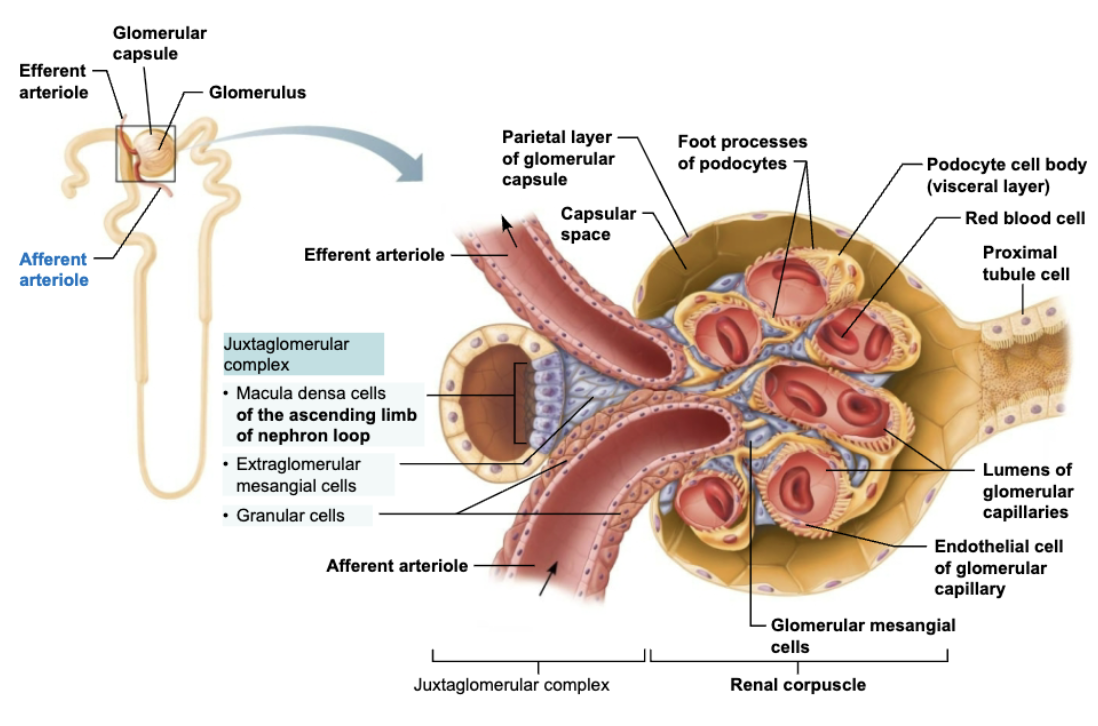
Explain Structure and Function of Granular cells
Juxtaglomerular Complex
STRUCTURE
Enlarged, smooth muscle cells of arteriole
FUNCTION
Act as mechanoreceptors to sense BP in afferent arteriole
Contain secretory granules that contain renin