The kidney - excretion
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
Briefly explain the two functions of the kidney
excretion - removal of nitrogenous waste from the body
osmoregulation - the control of the water potential inside the body by maintaining water and solute conc.
Explain how nitrogenous waste is taken to the kidney for excretion
Proteins are broken down into amino acids which are transported to the liver where most are distributed around the body to build new proteins in cells. the excess is deaminated in the liver by removing the amino group and converting it to urea. It is then taken to kidney for excretion.
Explain the structure of the kidney
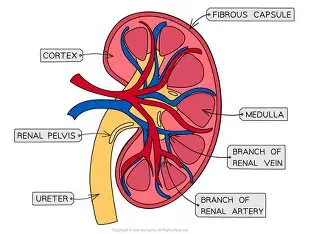
Draw and label the fine structure of the kidney nephron and what is a nephron
A nephron is an individual filtering unit

Explain ways to identify microscope slides of the cortex and medulla
cortex
glomerulus - lots of vessels
Bowmans capsule - large white curved
PCT - cuboidal cells
Medulla
No glomerulus or Bowmans
loop of Henle and collecting duct - lots of small circles
Where does ultrafiltration take place and how is it adapted for fast diffusion and how the filtrate is made
Bowman’s capsule and glomerulus
Its adapted for fast diffusion by
a high blood pressure - high hydrostatic pressure to counteract the water potential from lost of solutes in blood. This is done by: Efferent arteriole has a smaller diameter and lumen compared to afferent arteriole so the blood builds up in glomerulus and there is higher blood pressure. Also its under heart control - ventricular systole
Basement membrane of collagen and glycoproteins act as a molecular filter - selectively permeable
Capillaries have fenestrae which are pores in a thin walled endothelium one cell thick wall
podocytes - squamous epithelium cells that wrap around the capillary to lower diffusion pathway and the slits are filtration slits
Stages of ultrafilitration
fenestrae
basement membrane
podocyte filtrate gaps
bowmans capsule
This forms the fitrate of small mols like glucose, urea, ions, water, salts and amino acids
Explain what is selective reabsorption, where is it done and what are the PCTs adaptations and process
Selective reabsorption takes place in the kidney proximal covulated tubule of the the nephron. It is the reabsorption of useful products from the filtrate including
glucose and amino acids - by FD (co-transport with sodium (two for glucose and one for amino acid)) and sometimes secondary active transport - energy from diffusion of sodium ions down electrochemical gradient provides energy
ions - active transport or co-transport or FD
sodium - actively transported from cytoplasm of PCT into blood which means lower conc. grad. in the cytoplasm so diffuse via FD into cytoplasm with co-transport with glucose
water - osmosis
diffusion - some proteins and urea
ADAPTATIONS and process
The PCT includes columnar epithelium cells which have cilia that provide a large SA:V for absorption
they also have lots of mitochondria in their lumen for active transport
they also have basal channels in the strong basement membrane that have a large SA:V and concentrate a build up of mols to create conc. grad.
Tight junctions between cells of protein complexes prevent diffusion back of between mols.
Vasa recta vessels are close for short diffusion pathway and maintain conc. grad by taking away proteins
What will happen if glucose levels are too high in the blood
It means that there may not be enough transport proteins to reabsorb all glucose so it may be lost as urine
This is due to
type 2 diabetes - damage to insulin receptors
type 1 diabetes - lack of insulin from pancreas
How is water reabsorbed differently in parts of the nephron
The PCT (most of the water reabsorbed) and loop of Henle absorb the same amount of water no matter the conditions of the body but the collecting duct and DCT are selectively dependent on bodily needs
Explain the process of reabsorption of water in The Loop of Henle
In the ascending limb ions like CL and Na are pumped out by active transport to create a low WP grad. and due to impermeable walls no water leaves to maintain WP in the medulla intertitular fluid .
This means that when water flows down the desending limb water leaves via osmosis due to permeable walls down WP gradient as their is a low WP in medulla. - no ions leave.
This means at the hair pin there is a concentration gradient built up so FD out of loop
The vasa recta is close to loop of Henle and maintains low WP by moving water along
The low WP in medulla benefits DCT and collecting duct as more water can be removed based on ADH needs too and a concentrated urine is passed into pelvis and ureter.
Explain how nitrogenous waste is dealt with in different organisms
Reptiles, birds and insects produce uric acid that is highly concentrated and low toxic as they need to conserve water they they have no excess water
fish can excrete ammonia straight into the water as no need to store
plants convert ammonia with a-keto glutamate to make glutamine which can be used to transaminate into any amino acids so no need for excretion.