2D Vectors
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Scalar
Any positive or negative quantity that has magnitude only, without direction.
Scalar Examples
Length, Mass, Volume, Time, Etc.
Coplanar Vectors
Vectors that lie in the same plane in a three-dimensional space
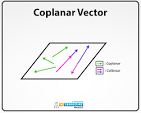
Collinear Vectors
Two or more vectors that are parallel to each other, regardless of their direction or magnitude

Concurrent Vectors
Vectors have lines of action that pass through same point
Collinear Forces
Forces that act along the same line of action, either in the same or opposite directions.
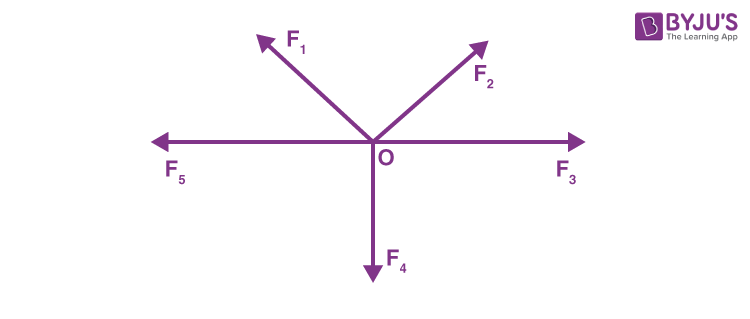
Coplanar Concurrent Forces
Forces that lie in the same plane and have lines of action that intersect at a common point.
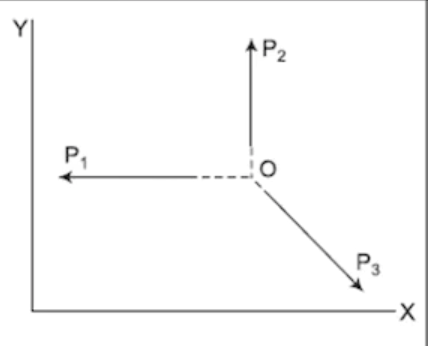
Coplanar Non-Concurrent Forces
Forces that lie in the same plane but do not intersect at a common point act independently of each other.
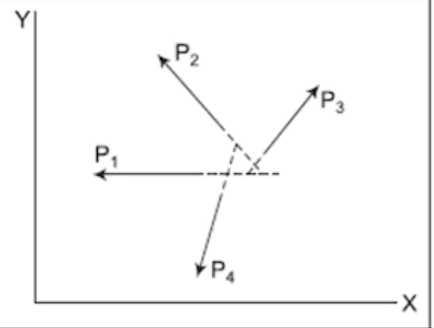
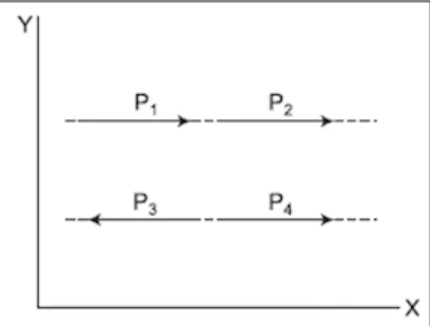
Coplanar Parallel Forces
Forces that lie in the same plane and act in parallel, either in the same or opposite directions, without intersecting.
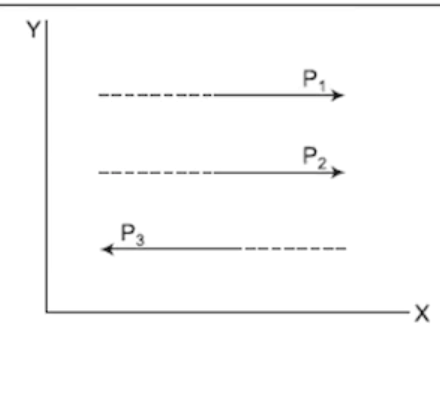
Non-Coplanar Concurrent Forces
Forces that act in different planes but intersect at a common point. They can result in a net force not confined to a single plane.
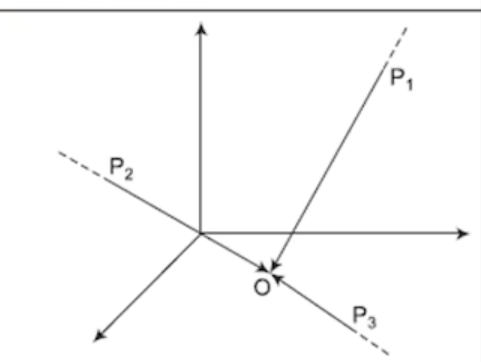
Non-Coplanar Non-Concurrent Forces
Forces that act in different planes and do not intersect at a common point. These forces can create complex motion and result in a net force not confined to a single plane.
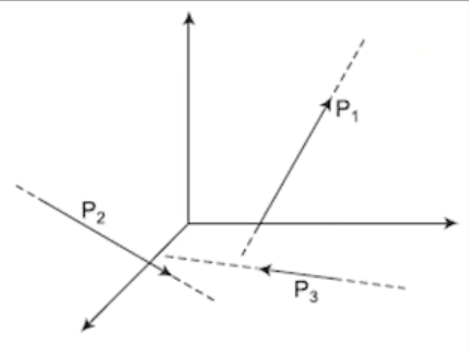
Non-Coplanar Parallel Forces
Forces that act in different planes and are parallel to each other, not intersecting at any point.
Force
Action of one body on another characterized by its point of application, magnitude, direction, line of action, and sense of the interaction between the two bodies. (Draw with arrow)
Principle of Transmissibility
A force may be applied anywhere along its line of action without changing its effect on the body it acts upon.