PDA III - Exam 4: Drug Abuse RW
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
What behaviors define addiction?
Compulsive drug seeking and drug abuse
Chronic condition consisting of remissions and relapses
What is the term for a diagnosis of addiction?
Substance use disorder
How is substance abuse disorder measured?
Measured on a continuum from mild to severe
How many criteria must a patient have to be diagnosed with a substance use disorder?
≥2 criteria
What is mild substance use disorder defined as?
2-3 criteria
What is moderate substance use disorder defined as?
5-6 criteria
What is severe substance use disorder defined as?
≥6 criteria
What are criteria for diagnosis of a substance use disorder?
Hazardous use
Social/interpersonal problems related to use
Neglecting major roles to use
Withdrawal
Tolerance
Used larger amounts/longer than planned
Repeated attempts to quit/control use
Much of time spent using and recovering
Physical/psychological problems related to use
Activities given up to use
Craving
What is the "continuum of drug use"?
A continuum of drug use
In terms of the amount, pattern, and consequences
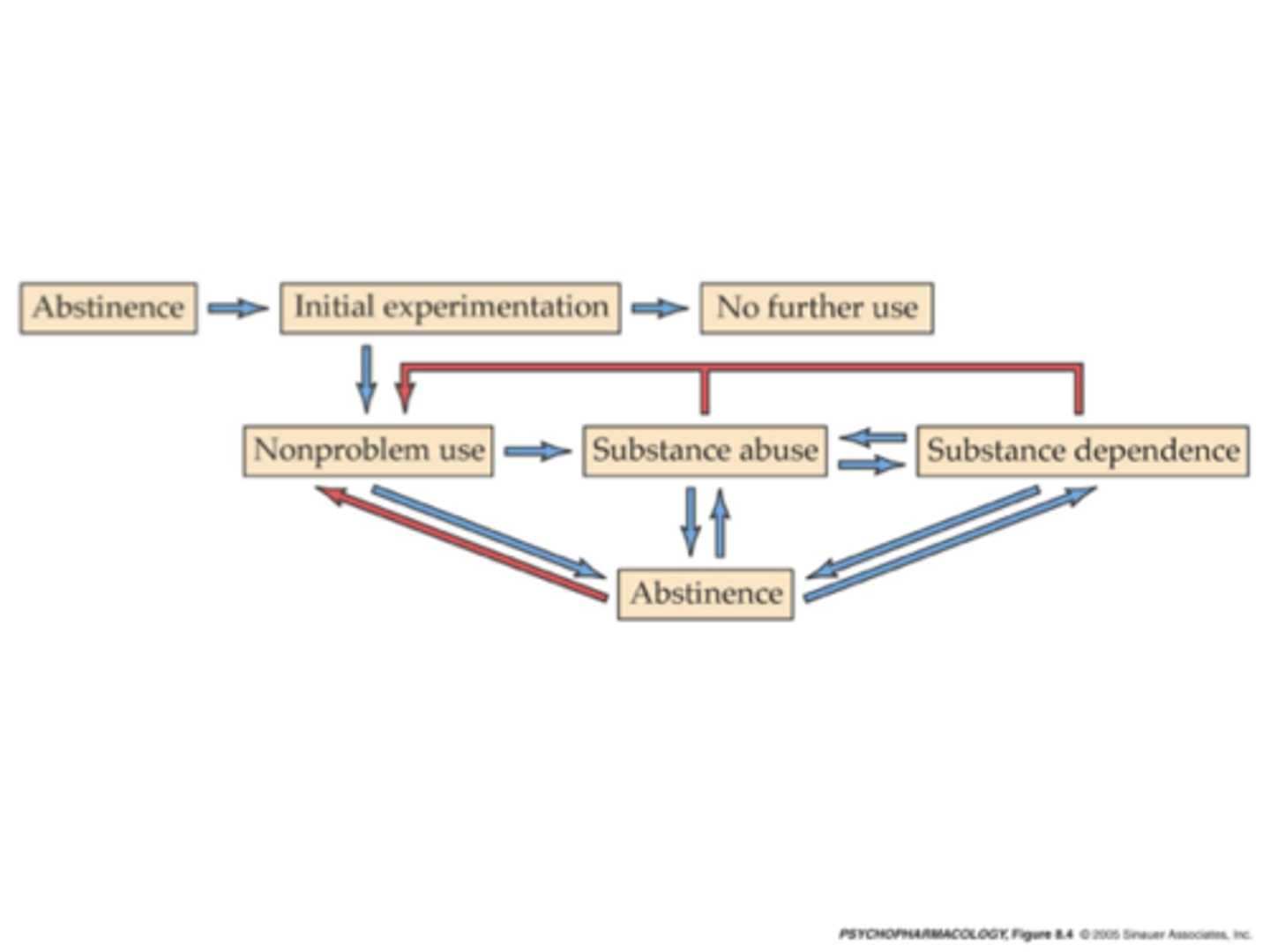
How do people move through the "continuum of drug use"?
When first use a drug can move anywhere along continuum
Even hard-drugs are not instantly/automatically addictive
People can move in all directions along continuum
People with drug addiction shift along the continuum, shifts vary greatly between people
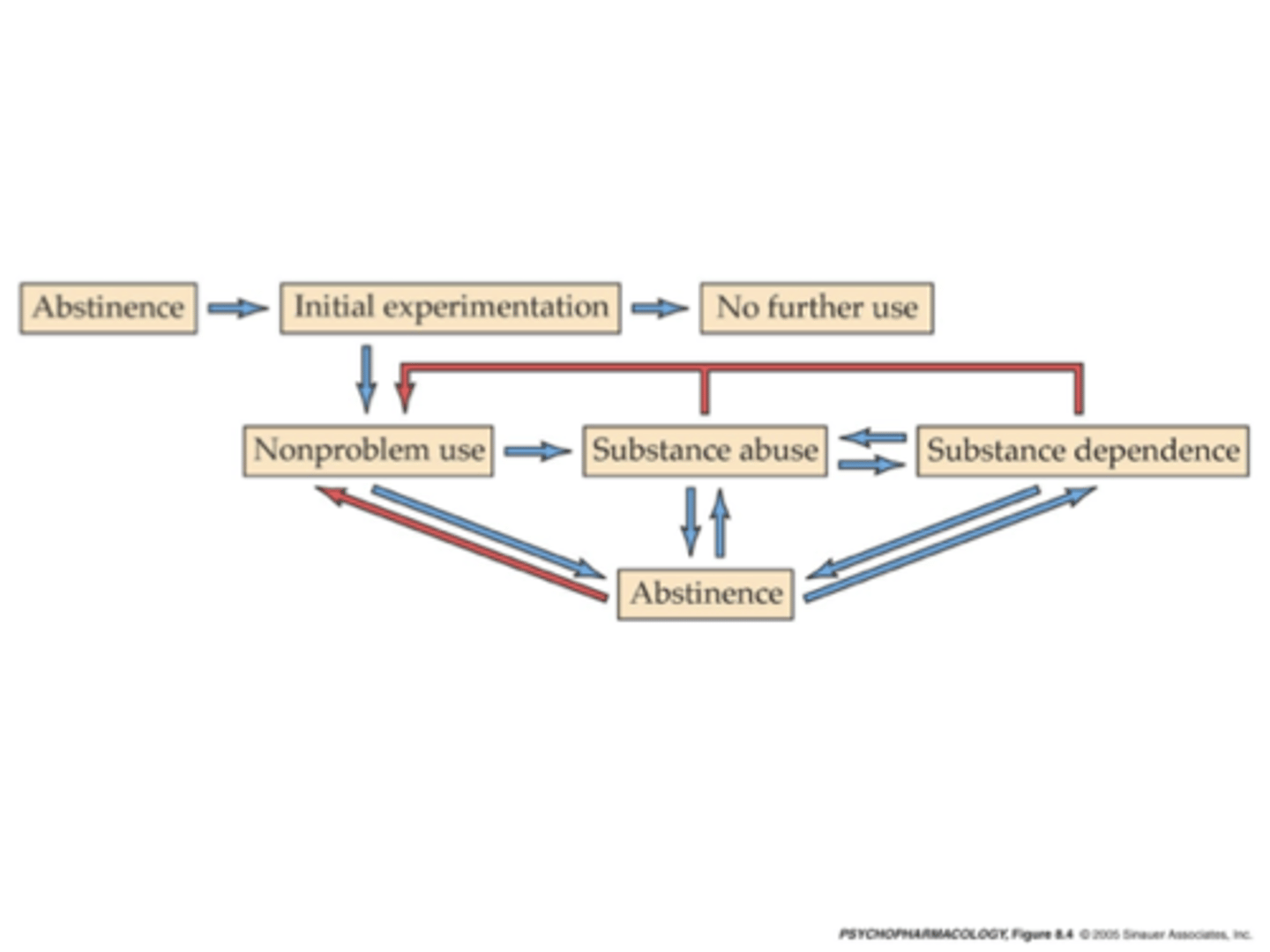
What type of disorder is drug addiction?
Drug addiction is a chronic-relapsing disorder
Pattern varies greatly from individual to individual
What is described by the Gateway Theory of drug use?
Use of "gateway" drugs leads to later use of more serious drugs
Strongly implies that experimentation with lesser drugs causes the eventual experimentation with harder drugs
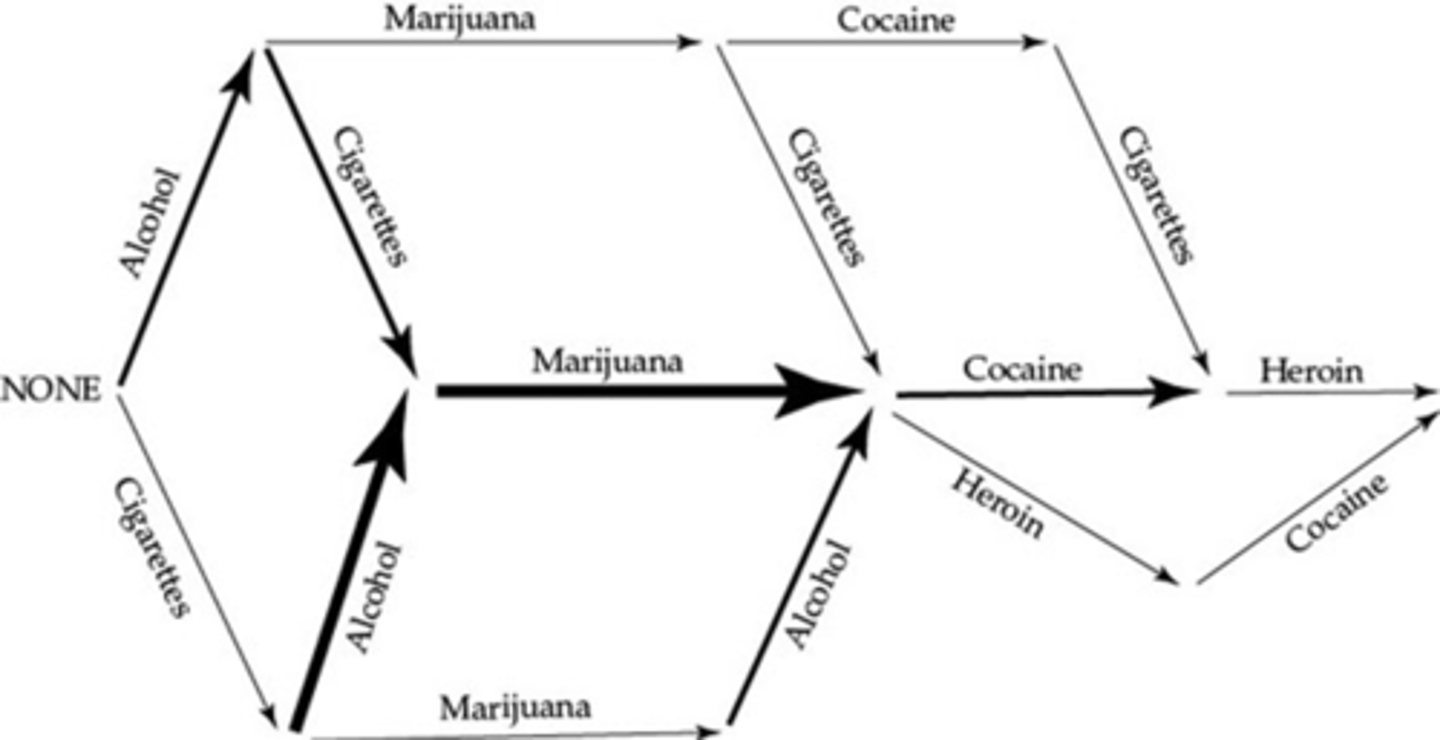
What are weaknesses of the Gateway Theory of Substance abuse?
Study relied on school surveys
(sampling bias)
Studies didn't prove causality
(post hoc, ergo propter hoc)
Other factors may cause use of one drug to reliably precede another
What is conditioned place preference?
Association of a space with a reward (drug)
What conditioned place preference experiment supports the gateway hypothesis?
Rats exposed to nicotine prefer cocaine more than unexposed rats
Nicotine made the cocaine more rewarding
increased cocaine seeking behavior
What is Pavlovian (classical) conditioning?
Associating of a response with a conditioned stimulus
Conditioned responses
Conditioning may contribute to drug abuse (seek drugs when come into contact with conditioned stimuli)
How can drug paraphernalia cause a conditioned response?
Associate rewarding effects of a drug with the drug paraphernalia

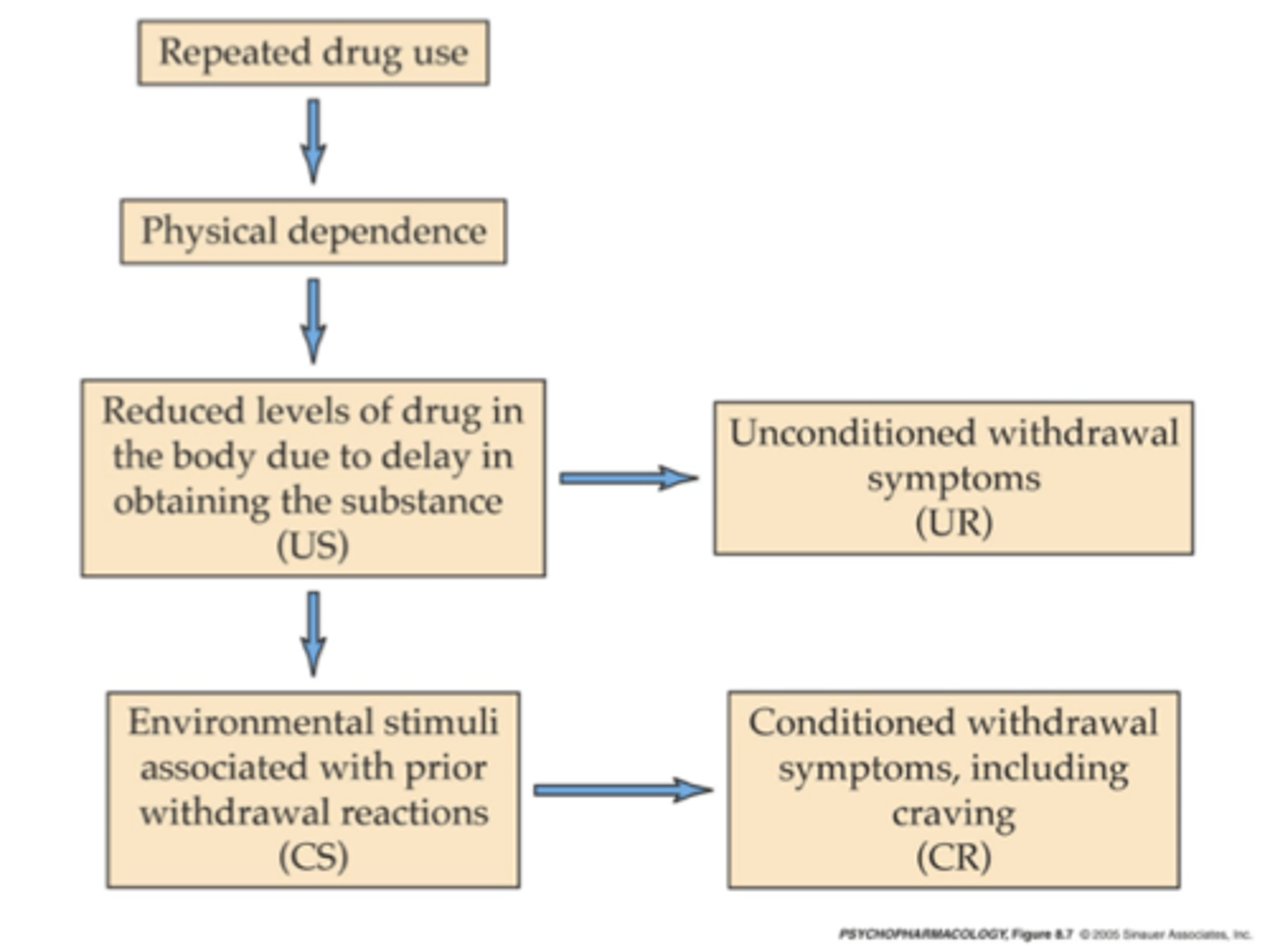
What is conditioned withdrawal?
Having withdrawal symptoms (or cravings for the drug) in places or situations the drug has been used in the past
Feel withdrawal even when no longer physically dependent
What is operant conditioning?
Behavior followed by reward or punishment
Reward inc. likelihood of behavior
Punishment dec. likelihood of behavior
What is the positive reinforcement model of drug abuse?
Euphoria from drug acts as reward
Positively reinforces future use
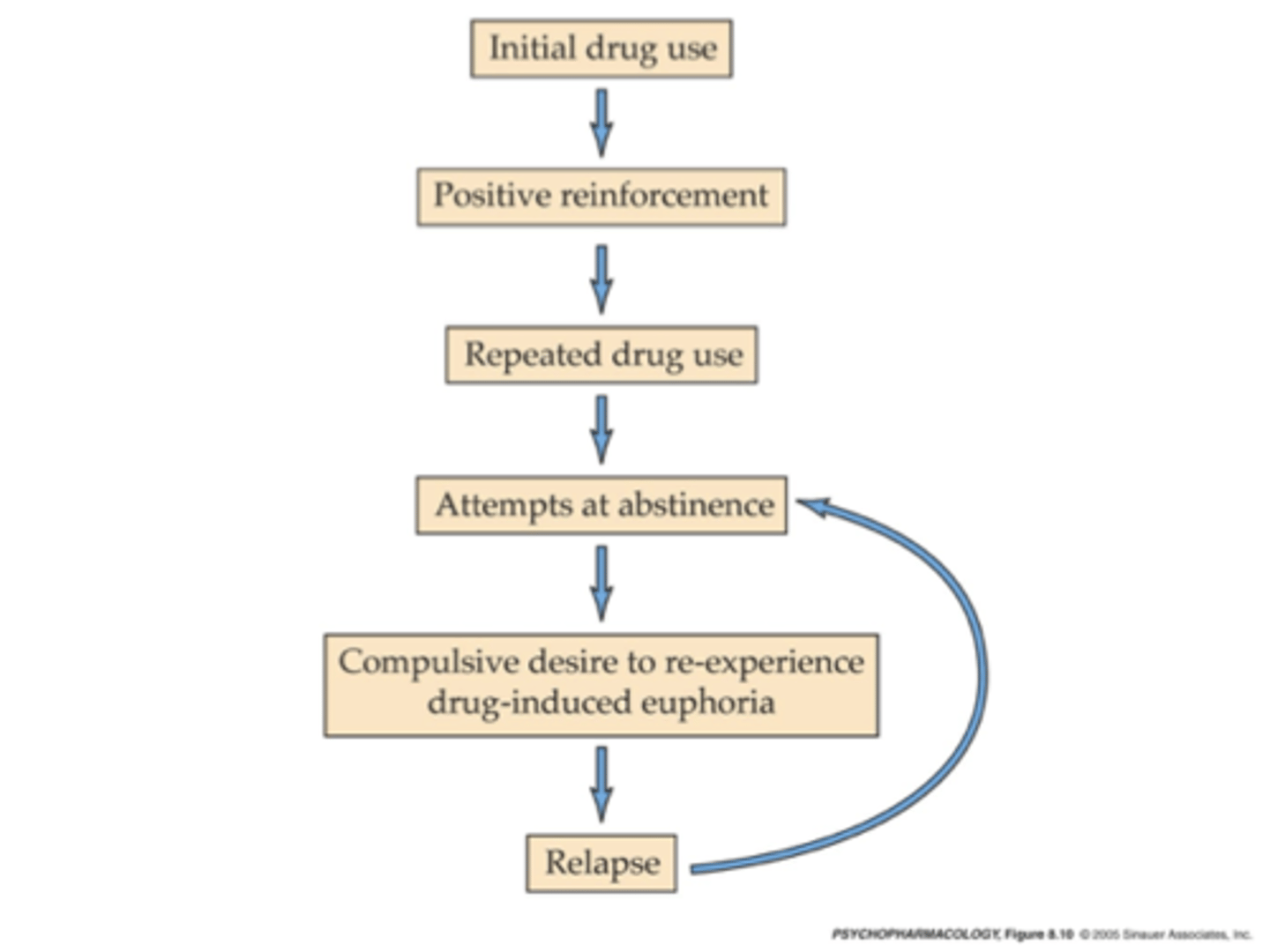
What is evidence for the positive reinforcement model of drug abuse?
Animals self-administering drugs
What is animal drug self-administration used to study?
Quantify how rewarding a drug is
Relationship between the rewarding properties and dose of a drug
What are shortcomings of the positive reinforcement model?
Drug craving increases
But, there is tolerance to the euphoria
What is delayed discounting?
The further in the future a stimulus is the less power it has over behavior
Minimizing punishment and making reward more powerful
Temporal discounting of delayed stimuli
Reason negative consequences of abuse don't counteract the positive reinforcement from drug-induced euphoria
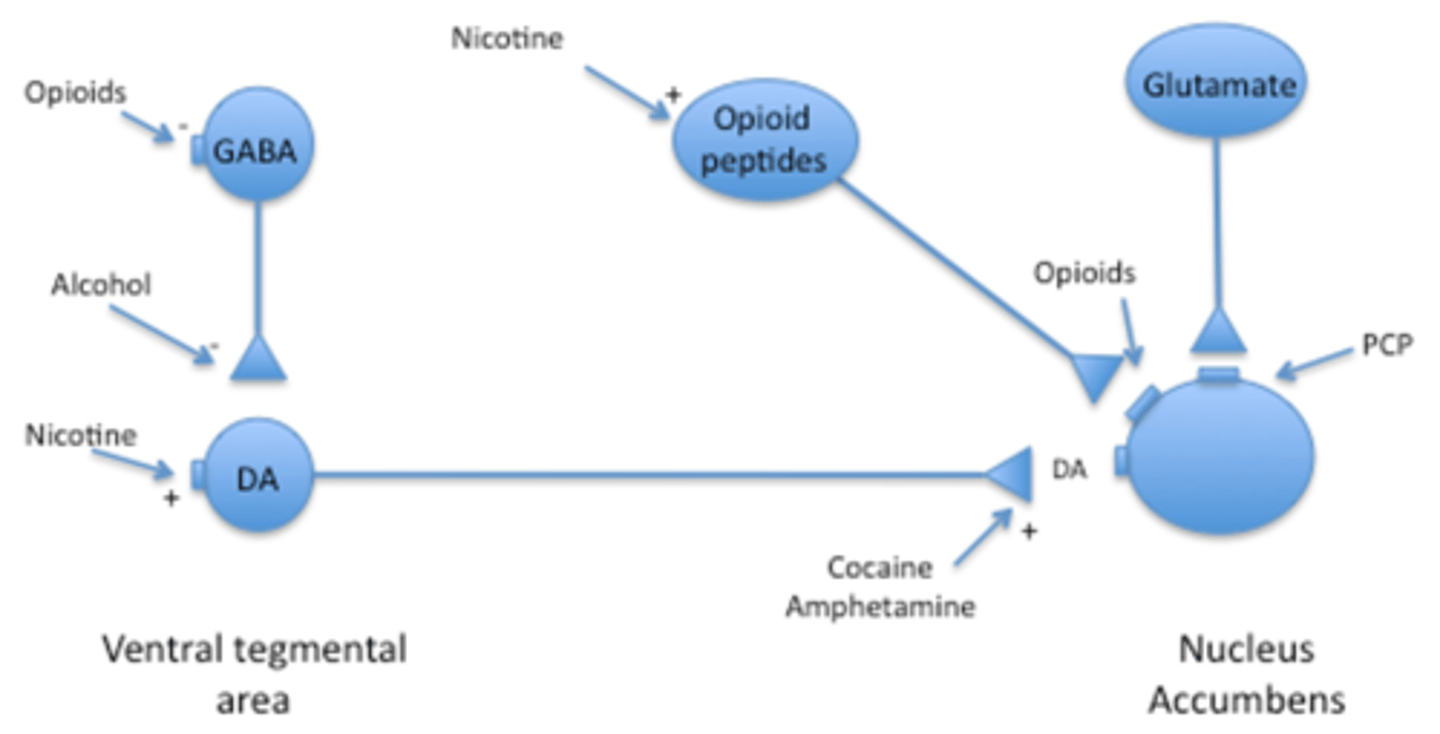
What are the main areas of the reward circuit?
Nucleus accumbens (NA)
Ventral tegmental area (VTA)
What are the other names for the nucleus accumbens?
Ventral striatum
Emotional striatum
How are the NA and VTA connected in the reward circuit?
Dopaminergic input from the VTA to the NA
Connection made by medial forebrain bundle
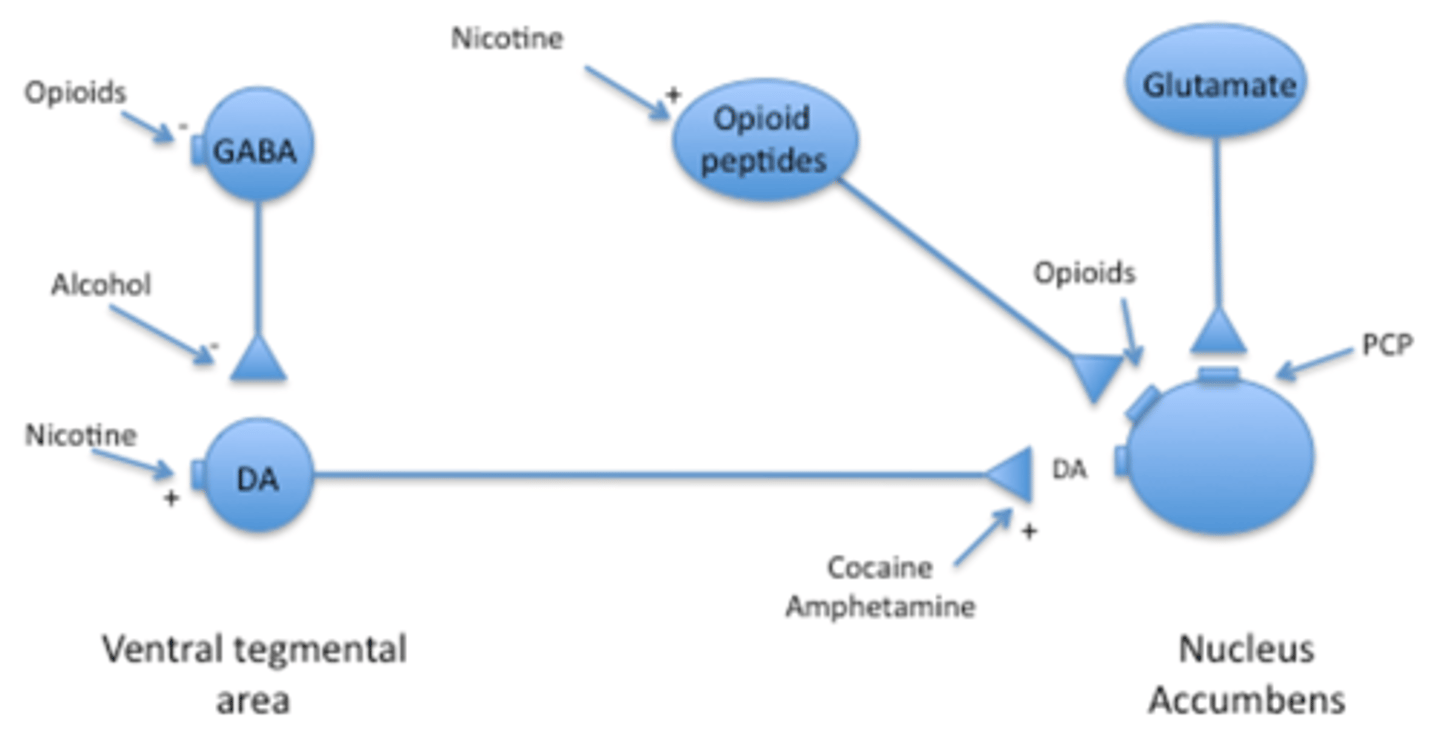
What are characteristics of DA receptors on nucleus accumbens neurons?
DA receptors in the nucleus accumbens are D2 (Gi)
When DA is release it inhibits the nucleus accumbens
Corresponding to subjective feeling of pleasure
How do opioids cause reward in the reward circuit by acting in the VTA?
GABA interneurons in the VTA are responsible for inhibiting the dopaminergic neurons
Inhibiting the reward circuit
Mu opioid receptors are inhibitory (Gi)
Found on GABA interneurons
Stim. of opioid receptors by opioids inhibits GABA neurons
Causes disinhibition
Activating the reward circuit
How do opioids cause reward in the reward circuit by acting in the nucleus accumbens?
Accumbens neurons have mu (Gi) receptors
Opioids act directly at nucleus accumbens and inhibit it
Pleasure signaling
How does alcohol cause reward in the reward circuit?
Inhibits GABA neurons in the VTA
(disinhibition)
Turning on the VTA
Causing reward
How does nicotine cause reward in the reward circuit?
Activates dopaminergic pathway
AND activates release of endogenous opioids in the nucleus accumbens
How does nicotine activate the dopaminergic pathway?
Nicotine stim.'s dopaminergic neurons of reward pathway
By action at nicotinic receptors in the VTA
DA neurons in VTA have ionotropic nicotinic receptors
Nicotine stim. nicotinic receptors
Na channels open
Na influx
Depolarization
DA release
How does nicotine cause release of endogenous opioids in the NA?
Nicotinic receptors present on opioid neurons
Nicotine stim. opioid receptors
Causes release of endogenous opioids in the nucleus accumbens
Leading to inhibition of the nucleus accumbens
Which causes reward/pleasure
How does cocaine cause reward in the reward circuit?
Blocks DA transporters
Increased DA levels in the nucleus accumbens
How does amphetamine cause reward in the reward circuit?
Increases DA release
Increased DA levels in the nucleus accumbens
How does PCP cause reward in the reward circuit?
Antagonizes inotropic Glu receptors on nucleus accumbens neurons
Blocking excitation of NA
Inc inhibition of NA
Pleasure
What is the effect of Glutamate neurons in the nucleus accumbens?
Glu excites the nucleus accumbens
Opposite of reward