Oxygenation - Med Surg II
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/139
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
140 Terms
1
New cards
respiration vs. ventilation
* respiration = act of breathing in and out (exchange of gases)
* ventilation = the **movement of air** in and out of alveoli
* ventilation = the **movement of air** in and out of alveoli
2
New cards
which 2 diseases affects gas exchange?
COPD!!
pulmonary embolism
3
New cards
diseases that affect ventilation
* asthma
* cystic fibrosis
* anaphylaxis
* pneumothorax
* pneumonia
* cystic fibrosis
* anaphylaxis
* pneumothorax
* pneumonia
4
New cards
which disease specifically affects RESPIRATION (gas exchange)?
* PULMONARY EMBOLISM!!
5
New cards
how does COPD affect lung compliance?
* in COPD, the lungs will keep getting more expanded, but not fully squeeze back to normal :((
6
New cards
normal VQ scan results
* ventilation 4L air/minute
* perfusion 5L blood/minute
* REMEMBER THAT PERFUSION is higher than ventilation
* perfusion 5L blood/minute
* REMEMBER THAT PERFUSION is higher than ventilation
7
New cards
VQ scan - usually done to verify what? what other test can be done?
* VQ scans are used to verify a suspected PE
* a CT with contrast can also be done to check this
* a CT with contrast can also be done to check this
8
New cards
CT with contrast - CONTRAINDICATIONS!!
* severe contrast allergy
* unable to get a 20 G IV
* pregnancy
* renal disease with low GFR and NOT on hemodialysis (unable to get rid of contrast!!)
* unable to get a 20 G IV
* pregnancy
* renal disease with low GFR and NOT on hemodialysis (unable to get rid of contrast!!)
9
New cards
PaO2 - normal range? Is it possible to have a PaO2 higher than 100? How does this happen?
* normal range = 80-100
* you can get a PaO2 over 100 if the patient receives too much oxygen → INVESTIGATE WHY IT IS LOWER !!!
* you can get a PaO2 over 100 if the patient receives too much oxygen → INVESTIGATE WHY IT IS LOWER !!!
10
New cards
normal SaO2 for COPD? if on oxygen, when should you start to wean them off? why?
* normal SaO2 = 88-90 for COPD
* if on oxygen and they get to 96%, you start to wean them off because they can become RELIANT on it (NO BUENO)
* if on oxygen and they get to 96%, you start to wean them off because they can become RELIANT on it (NO BUENO)
11
New cards
O2 + hemoglobin = ?
oxyhemoglobin
12
New cards
what is PaO2?
the volume of O2 dissolved in the plasma
13
New cards
diagnostic procedures for respiratory disorders
* PFTs
* ABGs
* pulse ox
* cultures
* sputum studies
* chest x-ray
* CT scan
* MRI
* pulmonary angiography
* VQ scan
* bronchoscopy
* thoroscopy
* thoracentesis
* ABGs
* pulse ox
* cultures
* sputum studies
* chest x-ray
* CT scan
* MRI
* pulmonary angiography
* VQ scan
* bronchoscopy
* thoroscopy
* thoracentesis
14
New cards
hypoxemia - symptoms
* dizziness
* anxiety/SOB
* decreased LOC/mental status (LATER ON)
* cyanosis (blue lips/fingernails)
* headache
* clubbing nails
* anxiety/SOB
* decreased LOC/mental status (LATER ON)
* cyanosis (blue lips/fingernails)
* headache
* clubbing nails
15
New cards
Do you need an order for oxygen? What amount is a nurse legally allowed to give WITHOUT an order?
* oxygen is a medication, NEED AN ORDER
* WITHOUT an order, a nurse may administer 2 L of O2
* WITHOUT an order, a nurse may administer 2 L of O2
16
New cards
why is the amount of oxygen given to COPD patients VERY important to note?
COPD patients hold on to CO2 so their drive to breathe is a low pO2 (88-92 is THEIR normal); therefore if pt gets too much O2, the drive to breathe is knocked out, causing their CO2 to rise even higher causing acidosis (NO BUENO!!)
17
New cards
COPD (what is meant by “less is more”)
keeping them on LESS oxygen is MORE beneficial in the long run (maintains their drive to breathe)
18
New cards
what is the max amount of O2 one can administer via nasal cannula? what happens if you go over?
* 6L is the max you can give; going over will NOT increase the amount of oxygen going in (POINTLESS AF)
19
New cards
venti mask - why is it very beneficial?
VERY specific with the amount of oxygen being given, ensuring one doesn’t over/underdo it
20
New cards
non-rebreather - why is it very beneficial?
ESSENTIALLY BREATHING PURE OXYGEN (does not allow you to breathe anything but oxygen)
* this is the step just below intubation
* this is the step just below intubation
21
New cards
ABCs - what is meant by this? what should you NOT do?
* PRIORITIES - airway, breathing, circulation
* do NOT add to the question by making up airway issues (ex: airway for COPD vs. airway for hip fracture (no relationship whatsoever))
* do NOT add to the question by making up airway issues (ex: airway for COPD vs. airway for hip fracture (no relationship whatsoever))
22
New cards
OSA - risk factors
* LARGE NECK CIRCUMFERENCE!!
* genetics
* genetics
23
New cards
OSA - patient presentation (hint: 3 S’s)
* sleepy during the day
* snoring
* significant other sent them to get checked out (OMG LMAO SO FUNNY)
* snoring
* significant other sent them to get checked out (OMG LMAO SO FUNNY)
24
New cards
OSA - diagnostic
SLEEP STUDY!!
25
New cards
OSA - medical management (2)
* CPAP (continuous positive air pressure (into pt; patient still breathes on their own)
* BiPAP (blows air and forcefully has them expel a breath too (REALLY good for COPD patients!!)
* BiPAP (blows air and forcefully has them expel a breath too (REALLY good for COPD patients!!)
26
New cards
OSA - surgical intervention? when is this usually done?
* removal of the tonsils
* usually only done in pediatrics (not for adults)
* usually only done in pediatrics (not for adults)
27
New cards
OSA - nursing education
* ENFORCE LUNG COMPLIANCE!! (to encourage lung expansion)
28
New cards
cancer of the larynx - patient presentation
* hoarse voice
* FEELS like swollen lymph nodes (but no pain)
* Air way is being blocked!!!
* FEELS like swollen lymph nodes (but no pain)
* Air way is being blocked!!!
29
New cards
cancer of the larynx - 2 diagnostics
* CT to show mass
* biopsy to confirm cancer
* biopsy to confirm cancer
30
New cards
cancer of the larynx - surgical intervention?
TOTAL LARYNGECTOMY!! (removal of the upper airway)
31
New cards
cancer of the larynx - #1 cause
SMOKING!!
32
New cards
tracheostomy vs. laryngectomy
* tracheostomy = surgical opening to access the tracheal lumen WITH the entire larynx remaining intact
* laryngectomy = surgery where ENTIRE larynx is removed and the trachea is brought to the skin as a stoma, which no longer has any anatomical connection with the oropharyngeal cavity and digestive tract
* laryngectomy = surgery where ENTIRE larynx is removed and the trachea is brought to the skin as a stoma, which no longer has any anatomical connection with the oropharyngeal cavity and digestive tract
33
New cards
laryngectomy - communication?
* work with speech therapist!! (esophageal speech / artificial electric larynx)
34
New cards
pleural effusion - risk factors
* fluid overload
* laying down/not moving (for long periods of time)
* laying down/not moving (for long periods of time)
35
New cards
pleural effusion - lung sounds?
* DIMINISHED!!!! (NOT crackles)
36
New cards
pleural effusion - diagnostic?
CHEST X-RAY!!!
37
New cards
pleural effusion - nursing management
* INCENTIVE SPIROMETER!!
* ambulation!!
* promote lung expansion
* ambulation!!
* promote lung expansion
38
New cards
pleural effusion - 3 draining techniques
* chest tube (if severe)
* thoracentesis
* pleur-x catheter (LONG TERM!! patient is able to drain fluid by themselves)
* thoracentesis
* pleur-x catheter (LONG TERM!! patient is able to drain fluid by themselves)
39
New cards
pleural effusion - pleur-x catheter (nursing considerations)
* MAINTAIN STERILITY!!
* provide patient education!
* AT HOME? - patient will always have a home care nurse to monitor them and provide education
* provide patient education!
* AT HOME? - patient will always have a home care nurse to monitor them and provide education
40
New cards
empyema - what is it?
pleural effusion that has become infected (due to lack of sterility, bacteria build, or patient has pneumonia, etc)
41
New cards
empyema - patient presentation
* infection (fever; elevated WBC; tachycardia; low BP; lung symptoms such low SaO2)
42
New cards
empyema - medical management
* antibiotics
* fluid drainage (think about the pleural effusion drainage techniques!)
* fluid drainage (think about the pleural effusion drainage techniques!)
43
New cards
pneumothorax - what is it?
air in the thoracic cavity, collapsing the lung
44
New cards
pneumothorax - 4 types
* simple/spontaneous (usually occuring in tall skinny males)
* traumatic (gunshot, stabbing, etc)
* hemothorax (blood in thoracic cavity)
* surgery (open heart surgery (EXPECTED); bilateral chest tubes are placed after surgery to fix lungs)
* traumatic (gunshot, stabbing, etc)
* hemothorax (blood in thoracic cavity)
* surgery (open heart surgery (EXPECTED); bilateral chest tubes are placed after surgery to fix lungs)
45
New cards
what is a good indication that a pneumothorax has occurred?
chest x-ray indicates heart and trachea migration (on x-ray, BLACK indicates air, white is structures)
46
New cards
what is used to temporarily fix a pneumothorax prior to inserting a chest tube?
a catheter needle (to expel air)
47
New cards
chest tubes - assessment
1. make sure chest tube is SECURE!! (they move excessively and are uncomfy); make it a priority keep it secure with FOAM TAPE!!
1. assess tubing to ensure there’s no kinks/clots
2. drainage system = UPRIGHT at all times!!
3. drainage system = BELOW level of chest
4. assess for crepitus (RICE CRISPIES!!); caused usually by an air leak
5. suction? - need an order
6. CHECK FOR AIR LEAKS (look for bubbles)
48
New cards
chest tube emergency management (3 bedside supplies)
1. foam dressing/tape (at insertion site to prevent air from leaking)
2. hemostats (to clamp off chest tube; if tubing disconnects from chamber system, air can easily get into the chest cavity)
3. Vaseline gauze with a covering (XEROFORM)
1. prevents air from leaking in AT the insertion site
49
New cards
pulmonary embolism (risk factors)
DVT (clot breaks off and goes to lungs)
orthopedic surgeries (anesthesia, decreased mobility, laying down)
cerebral palsy
clotting disorders
smoking
birth control users/pregnant women
INCREASED ESTROGEN LEVELS, which increases clotting factors
obesity
50
New cards
pulmonary embolism - symptoms
* SOB (air flow is good, but NO GAS EXCHANGE!!!)
* diminished lung sounds / cyanosis
* increased HR and BP
* impending doom (I feel like I am going to die)
* diminished lung sounds / cyanosis
* increased HR and BP
* impending doom (I feel like I am going to die)
51
New cards
saddle PE? what is it
a VERY large blood clot that prevents blood flow to BOTH lungs (very unlikely to live from it)
52
New cards
d-dimer - what is it?
a test that indicates if there is a blood clot in the body (NOT specific)
53
New cards
pulmonary embolism - what test will look normal ?
CHEST x-ray (shows structures, not vessels) - NOT RELIABLE :(
54
New cards
pulmonary embolism - diagnostics
* d-dimer (indicates blood clot SOMEWHERE in body)
* __**CT chest with contrast (check kidney function to ensure pt can get rid of contrast; start on heparin drip if clot is confirmed!!)**__
* VQ scan (HIGH ventilation, low perfusion)
* ABG (shows respiratory alkalosis (hyperventilation))
* ECG (sinus or tachycardia; right sided heart failure symptoms also start occurring)
* __**CT chest with contrast (check kidney function to ensure pt can get rid of contrast; start on heparin drip if clot is confirmed!!)**__
* VQ scan (HIGH ventilation, low perfusion)
* ABG (shows respiratory alkalosis (hyperventilation))
* ECG (sinus or tachycardia; right sided heart failure symptoms also start occurring)
55
New cards
PE (d-dimer, CXR, VQ scan, respirations, heart rate, pulse ox, and temp results) - CHART
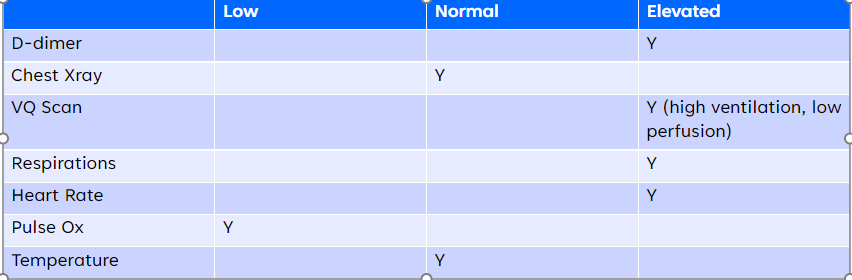
56
New cards
pulmonary embolism - prevention
* ambulation / mobility
* SCDs
* subq heparin / lovenox (to prevent); heparin drip (clot detected, prevents it from getting BIGGER/adhere to wall preventing migration)
* SCDs
* subq heparin / lovenox (to prevent); heparin drip (clot detected, prevents it from getting BIGGER/adhere to wall preventing migration)
57
New cards
atelectasis - what is it
(alveoli collapse due to BLOCKED AIR PASSAGE)
58
New cards
atelectasis - #1 risk factor
SURGERY
59
New cards
atelectasis - nursing education/prevention?
use incentive spirometry!!!!
60
New cards
atelectasis - symptoms
chest pain, SOB, shallow respirations
61
New cards
atelectasis - complication
CAN BECOME PNEUMONIA (increased mucus in collapsed lung leads to infection)
62
New cards
what is the #1 cause of death from an infectious disease?
PNEUMONIA!!
63
New cards
pneumonia - diagnostic test?
SPUTUM CULTURE!!
64
New cards
pneumonia - 4 types
1. CAP
2. HAP
1. VAP
3. Aspiration
65
New cards
CAP - when does it usually develop?
usually after a recent illness (PREDICTABLE!!)
66
New cards
what is the most commonly acquired pneumonia?
CAP
67
New cards
2 most common organisms that cause CAP
1. strep-pneumo
2. H-flu
68
New cards
HAP - what is it
pt. admitted in hospital for AT LEAST 48 hours, and then pneumonia develops
69
New cards
HAP - are they caused by the same organisms involved in CAP?
NOOOO, which is why sputum cultures are SOOO important
70
New cards
VAP - what is it?
a pneumonia the forms due to lack of hand hygiene/sterility on a ventilated patient, who has been on the ventilator for AT LEAST 48 hours
71
New cards
aspiration pneumonia - 2 populations at risk?
1. stroke (swallow reflex is weakened; CONFIRM GOOD SWALLOW EVAL before giving anything PO)
2. parkinson’s
72
New cards
aspiration pneumonia - what is it?
* food you eat goes into the lungs, preventing gas exchange; as well, vomiting while laying down can cause it too
73
New cards
CAP/HAP/VAP/aspiration pneumonia (risk factors) - CHART
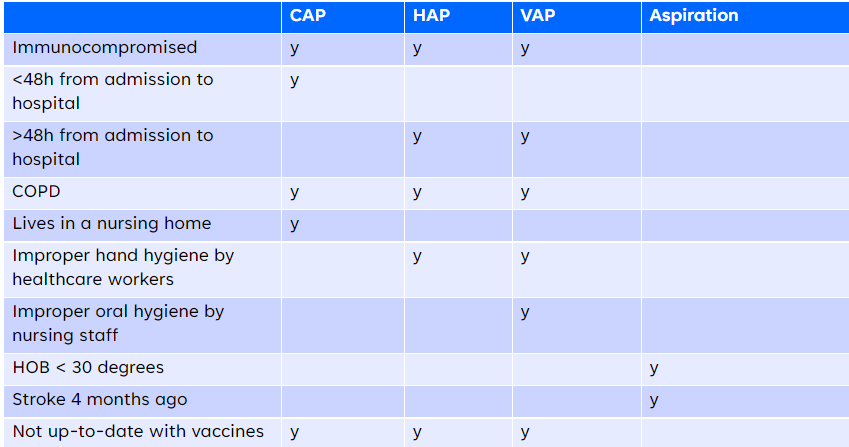
74
New cards
CAP/HAP/VAP/aspiration pneumonia (symptoms) - CHART
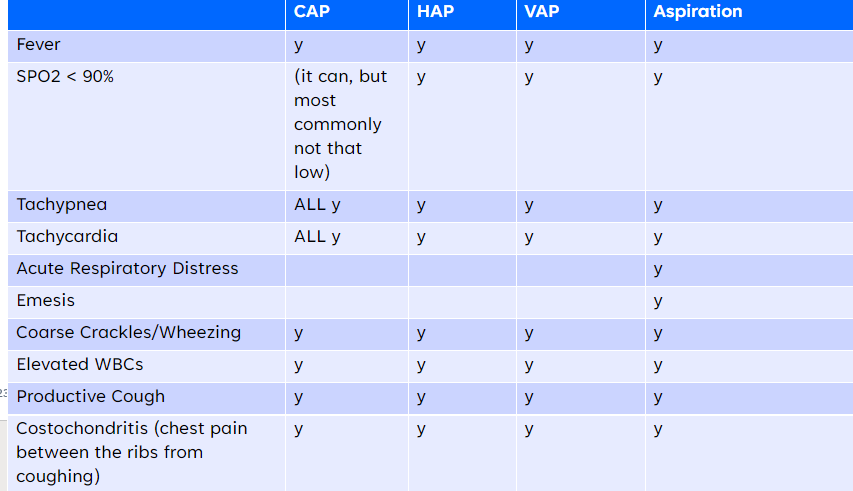
75
New cards
pneumonia - nursing considerations (WITHOUT an order)
* Oxygenation monitor
* Adequate fluid intake (help with dehydration / loosen secretions)
* Elevate head of bed
* Incentive spirometry
* Ambulation (to promote lung expansion
* Encourage coughing / deep breathing / suctioning
* Adequate fluid intake (help with dehydration / loosen secretions)
* Elevate head of bed
* Incentive spirometry
* Ambulation (to promote lung expansion
* Encourage coughing / deep breathing / suctioning
76
New cards
pneumonia - anticipated provider orders
* Antibiotics!!!
* IV fluids
* Chest x-ray
* Sputum culture (need an order to send it, but can collect it without an order) (NEEDS TO BE COLLECTED BEOFRE ANTIBIOTIC ADMINISTRATION, as it can alter results)
* Antipyretic to lower the fever!!!
* IV fluids
* Chest x-ray
* Sputum culture (need an order to send it, but can collect it without an order) (NEEDS TO BE COLLECTED BEOFRE ANTIBIOTIC ADMINISTRATION, as it can alter results)
* Antipyretic to lower the fever!!!
77
New cards
COVID-19 - what specific PPE must be worn ?
N95 mask!!!
78
New cards
COVID-19 - specific finding to confirm diagnosis?
* ground glass opacities (in a CT scan)
79
New cards
COVID-19 - risk factors
* older age
* obese
* immunocompromised
* underlying lung disease patients
* obese
* immunocompromised
* underlying lung disease patients
80
New cards
COVID-19 - hypoxia management
* continuous cardiorespiratory monitoring (rapid decompensation is prevalent!!)
* encourage patient to self-prone as often as possible/tolerated
* supplemental oxygen (nasal cannula; non-rebreather; CPAP; and if still not enough, ET intubation)
* encourage patient to self-prone as often as possible/tolerated
* supplemental oxygen (nasal cannula; non-rebreather; CPAP; and if still not enough, ET intubation)
81
New cards
pulmonary edema - what is it?
abnormal accumulation of fluid in the alveoli, lung tissue, or both; NO GAS EXCHANGE occurs
82
New cards
pulmonary edema - causes
* congestive heart failure (already fluid overloaded)
* damage to pulmonary lining (from trauma for example)
* damage to pulmonary lining (from trauma for example)
83
New cards
pulmonary edema - symptoms
* PINK FROTHY SPUTUM!!
* very crackly lung sounds
* low pulse ox
* very crackly lung sounds
* low pulse ox
84
New cards
pulmonary edema (what will you see in a CXR)
LOTS OF WHITE (fluid)
85
New cards
what is the #1 cancer death in the US?
LUNG CANCER!!
86
New cards
lung cancer has a 5-year survival rate. what does this mean?
from the time of diagnosis to 5 years later, only 5% are still alive
* why? THEY DON’T STOP SMOKING
* why? THEY DON’T STOP SMOKING
87
New cards
lung cancer - patient presentation
* chronic cough
* sputum
* pulse ox will STILL LOOK NORMAL if they don’t have COPD (same symptoms as COPD!!)
* sputum
* pulse ox will STILL LOOK NORMAL if they don’t have COPD (same symptoms as COPD!!)
88
New cards
lung cancer - what is the good news for pt who are long term smokers?
CAT scans can be administered (insurance included) to catch lung cancer early (lose dose radiation/contrast)!!!
89
New cards
lung cancer - 2 diagnostic tests
1. biopsy (to prove cancer)
2. bronchoscopy (to verify place of cancer)
90
New cards
lung cancer - medical managment
SYMPTOM management :)
91
New cards
4 treatments for ALL cancers? how is the type of treatment decided?
4 treatments:
* surgery
* chemo
* radiation
* palliative
* patient / provider decide what treatment they want, depending on the stage of cancer they’re in
* surgery
* chemo
* radiation
* palliative
* patient / provider decide what treatment they want, depending on the stage of cancer they’re in
92
New cards
staging of all cancers (0-4)
* stage 0 = Precancer (found a polyp)
* stage 1 = on surface of organ (remove it and you’re good)
* stage 2 = invading deeper from the surface
* stage 3 = spread to the surrounding lymph nodes (feel for swelling); this is HOW cancer metastasizes
* stage 4 = more than one organ has cancer :(
* stage 1 = on surface of organ (remove it and you’re good)
* stage 2 = invading deeper from the surface
* stage 3 = spread to the surrounding lymph nodes (feel for swelling); this is HOW cancer metastasizes
* stage 4 = more than one organ has cancer :(
93
New cards
bronchoscopy - 2 medications used? what are their purposes?
* lidocaine (to numb the gag reflex / prevent pain during procedure)
* atropine (to prevent hypotension (caused by hitting vagal nerve); keep the heart rate up; DRY SECRETIONS (preventing aspiration))
* atropine (to prevent hypotension (caused by hitting vagal nerve); keep the heart rate up; DRY SECRETIONS (preventing aspiration))
94
New cards
bronchoscopy - postop nursing considerations
* monitor O2 status
* monitor HR/BP
* AVOID FOOD AND FLUID UNTIL GAG REFLEX IS BACK
* monitor for lung collapse (tracheal deviation and other symptoms)
* monitor for any bleeding (minor hemoptysis is expected)
* monitor HR/BP
* AVOID FOOD AND FLUID UNTIL GAG REFLEX IS BACK
* monitor for lung collapse (tracheal deviation and other symptoms)
* monitor for any bleeding (minor hemoptysis is expected)
95
New cards
what is the third leading cause of death in the US?
COPD
96
New cards
COPD - what is it?
a disease state characterized by chronic airflow limitation that is irreversible (chronic bronchitis and emphysema)
97
New cards
COPD - why do patients have the barrel chest?
* patients are able to have lung expansion, but no ability to squeeze to exhale (lungs get BIGGER and BIGGER overtime)
98
New cards
emphysema - what happens?
alveolar walls are destroyed, resulting in impaired gas exchange; overtime this will ead to chronic hypoxemia and CO2 retention
99
New cards
emphysema - do they have a high or low CO2? why?
HIGH CO2, because their ability to exhale is impaired, causing them to retain more CO2
100
New cards
how to facilitate breathing for patients with emphysema?
position them into a tripod position