Class 10 - Intervention Overview
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
Intervention
When a clinician acting in a professional capacity attempts to change a client’s behavior, thoughts, social circumstances, or everyday function.
What is the most common intervention?
Psychotherapy
Name 3 other interventions that are adjuncts to psychotherapy.
Psychoeducation
Biofeedback
Cognitive Training
Psychotherapy
Psychological techniques administered by trained professionals to help clients address psychological problems
How many “brand name” psychotherapies are there?
at least 600
Are all “brand name” psychotherapies scientific?
No, there are many that lack a scientific basis and consist of pseudoscience.
What are the six categories that psychotherapies can fit under based on evidence?
Psychodynamic
Humanistic
Cognitive, Behavioral, Cognitive-Behavioral
Mindfulness/Acceptance-based
Social Systems
Transdiagnostic
Base Rates
How common a given condition is in the population
What are the most commonly diagnosed disorders
Anxiety (19.1% - US 2023 Data)
Depression (8.3% - US 2023 Data)
What is the prevalence of disorders throughout the lifespan?
Prevalence of disorders peak in early adulthood and declines over time
When do most disorders first emerge?
During adolescence and young adulthood
What age range to most people receive their first mental disorder diagnosis?
11 to 15 (~30%)
True or False: Emergence time varies by disorder/
True
When do anxiety symptoms tend to appear?
Early on in life (childhood)
When do OCD symptoms tend to appear?
mid-adolescence
When do Mood Disorder symptoms tend to appear?
late-adolescence
When do Personality Disorders and Schizophrenia symptoms tend to appear?
Adulthood
What is the pattern of prevalence rates of mental illness by race?
Prevalence of disorders varies slightly by race & ethnicity (likely due to a conbo of stress and vulnerability differences from culture, discrimination, etc.)
What is the number one reason for people to not seek therapy?
Access: cost, coverage, and logistics
What is the second reason for people to not seek therapy?
Stigma
What is the third reason for people to not seek therapy?
Negative Beliefs about Therapy
Who benefits most from therapy?
Mixed findings on demographics (sex, gender, race/ethnicity, social class); there is no type of person that would benefit more than another
Better therapy outcomes appear with clients who have more:
Motivation
Confidence that therapy can work
Willingness to experience unpleasant thoughts, emotions, and sensations
Autonomy to choose from various treatment options
Which therapists are most effective (in general)?
more training and experience = better outcomes
better interpersonal skills = better outcomes
communicators, relationship builders, self-monitors
What are factors common to all therapies?
Common v. Specific Factors
Psychoeducation
Homework/Practice
Therapy Interfering Behaviors
General Therapy Stages
Common v. Specific Factors
When a treatment works- Is it the treatment’s special ingredients or is it just common factors that benefit everyone?
example: EMDR - effective for trauma and anxiety disorders b/c you tell someone abt trauma, not because of the use of eye movement
What contributes most to treatment success?
Client variables and extra-therapeutic events (40%)
What other factors contribute to treatment success?
Therapeutic relationship (30%)
Expectancy and Placebo Effects (15%)
Technique and Model Factors (15%)
What does Common Factors Therapy focus on?
The therapeutic relationship
Motivation (to learn or change)
Corrective experiencing (learning)
Insight (understanding)
Self-efficacy (doing)
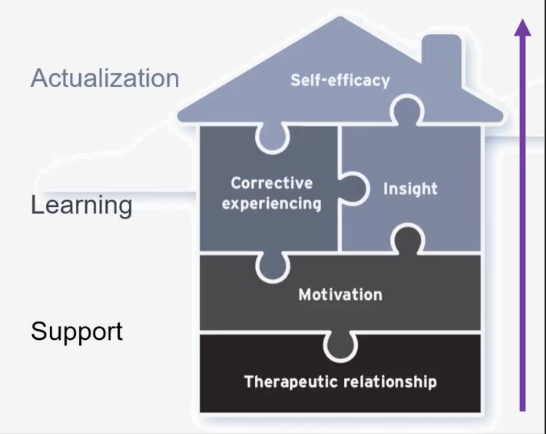
House of Common Factor Therapy
Support - things you need before anything else happens (Therapeutic Relationship & Motivation)
Learning - Teaching (Corrective Experiencing & Insight)
Actualization - what should stick after therapy; applying what they learned (Self-Efficacy)
Therapeutic Relationship/Alliance
Emotional bond built on trust, empathy, and collaboration to promote client well-being
shared understanding of therapy tasks and goals
changes over time; build slowly and can weaken/strengthen
Most treatment models view this as necessary, but not sufficient for success
Who are the therapists that view the therapeutic relationship as the active ingredient in treatment?
Humanistic Therapists
True or False: Therapeutic alliance is consistently predictive of treatment success.
True
Do we know why therapeutic alliance is consistently predictive of treatment success?
No, we aren’t sure why.
Reverse causation is sometimes possible
Early treatment success can strengthen the alliance
Insight
A client’s understanding of themselves and their problems
Psychoeducation
The process of providing knowledge, information, and resources about a specific mental health condition, concern, or treatment
all the therapies have this to a degree
usually early on in a treatment
Homework/Practice
Specific tasks or exercises assigned by a therapist to a client to be completed between treatment sessions
extension of the work down during session
“medicine dose”
more common in 2nd and 3rd wave treatments
Therapy Interfering Behaviors
Any actions that disrupt the therapeutic process
can be intentional or unintentional (i.e. cancelling, leaving early, not participating, not doing homework)
General Model of Treatment
Initial Assessment
Collaborate to Develop Treatment Plan
Follow treatment plan and learn skill
Apply skills outside of therapy
Monitor progress and make adjustments
Meet goals and terminate therapy
Stages of Change
Precontemplation = not ready to change
Contemplation = acknowledging there is a problem but not yet ready or sure they want to change
Preparation = getting ready to change
Action = taking active steps to cahnge
Maintenance = maintain the new status quo
Relapse = resumption of old behaviors
comes from motivational interviewing (substance abuse concerns)
we are always in a stage of change regarding whatever behavior we think of
if you have a problem to solve, figure out where you are on this wheel!
What does DBT stand for?
Dialectical Behavior Therapy
Dialectical Behavior Therapy
Designed for the most disordered, reactive, and high-risk patients
Goals for therapy depend on the stage the client is in
Stages of DBT
Severe Behavioral Dyscontrol - Getting in Control: of behaviors that are life-threatening; threats to treatment; major threat to quality of life with commitment, skills, and contingencies
Quiet Desperation - Getting in Touch: Exposure (PTSD Work); Cognitive Restructuring Working to reduce suffering
Problems in Living - Getting a Life: Identifying & working towards life goals & increasing self-respect
Incompleteness - Peak Experiences: spiritual fulfillment; expanded awareness; capacity of sustained joy
Termination (Graduation!)
End treatment with empathy and optimism
Reinforce learning, skill acquisition, and insight
Generate relapse prevention plan if necessary
Identify signals of when to return for “booster” therapy
Good Relapse Prevention Plans include:
Known triggers, stressors, or high-risk events
Tools and technique for coping with stress and triggers
A maintenance plan for important activity of daily life
Communication ideas for family and love ones
Flags for knowing when to return for more treatment
What are the ethical considerations in intervention guided by?
APA Ethical Principles of Psychologists and Code of Conduct
5 General Principles
10 Ethical Standards
151 Rules
Key Ethical Concerns for Therapists
Confidentiality - must maintain client’s privacy
Competence - must practice only within area of expertise
Informed Consent - client must know what they are signing up for
Conflict of Interest - must maintain therapeutic boundaries
Nonmaleficence - must avoid or minimize harm to others