Radiology6: Dental Trauma Lecture Notes
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A set of 50 flashcards covering key terms and definitions related to dental trauma.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Dental Trauma
Injury to the teeth and surrounding structures.
Etiology of Dental Trauma
Common causes include falls (65%), sports injuries, cycling accidents, motor vehicle accidents, and physical violence.
Luxation
Dislocation of a tooth or teeth.
Concussion
Injury where the tooth remains stable but experiences bleeding in the gingiva due to forces applied.
Subluxation
A condition where the tooth is mobile without displacement. Widened PDL
Intrusion
Tooth is pushed into the bone, depth of which affects prognosis.
Extrusion
Tooth is partially displaced from its socket.
Avulsion
Complete ejection of a tooth from the socket.
Resorption
Long-term effects of trauma leading to the breakdown of tooth roots.
Ankylosis
The fusion of the tooth root to the alveolar bone.
Fractured Tooth
Damage to the tooth structure including enamel, dentin, and possibly pulp.
Chipped Tooth
Fracture confined to enamel or dentin; pulp remains unaffected.
Complete AVulsion
When a tooth is completely displaced and may be replanted.
Partial Avulsion
Tooth is partially displaced but remains in the socket.
Subsequent Treatment
Follow-up treatment necessary after initial injury assessment.
Flexible Splint
A device used to stabilize teeth after trauma.
Immediate Treatment
Primary care given to a tooth after trauma occurs.
Pulp Vitality Testing
Assessing the health of the pulp after dental trauma.
Dental Radiographs
X-rays used to assess trauma to the teeth and jaw.
Gingival Laceration
Tearing of the gum tissue often resulting from dental trauma.
Periapical Radiograph
An X-ray that shows the whole tooth, its roots, and surrounding bone.
Lateral Luxation
Lateral displacement of teeth usually requiring repositioning.
Maxillofacial Trauma
Injuries affecting the maxilla and facial bone structures.
Alveolar Fracture
Fracture involving the alveolar bone that supports the teeth.
Mandibular Fracture
Break in the lower jawbone.
Condylar Fracture
Fracture of the condylar neck in the mandible.
Vertical Root Fracture
Fracture that runs vertically along the length of the root.
Horizontal Root Fracture
A fracture that runs horizontally across the root of a tooth.
Complicated Crown Fracture
A fracture that exposes the pulp tissue.
Uncomplicated Crown Fracture
A fracture that does not expose pulp.
Root Canal Treatment (RCT)
Endodontic treatment to remove infected pulp.
Storage Medium for Avulsed Tooth
Ideal solutions such as milk, HBSS, and saline to preserve a tooth until replantation.
Dental Guidelines
Protocols developed by associations for the treatment of dental injuries.
Bleeding in Gingiva
Common symptom after tooth concussion.
Intraoral Assessment
Clinical examination of the oral cavity for injuries.
Emergency Management
Procedures followed immediately after a dental trauma.
Ortho Repositioning
Orthodontic methods to move teeth back to proper alignment.
Chipping
Minor fracture of enamel.
Open Fracture
Fracture with exposure to the oral environment.
Bone Fracture
Fracturing of the bone surrounding the teeth.
Surgical Stabilization
Using surgical techniques to stabilize fractured bones.
CBCT
Cone Beam Computed Tomography used for detailed imaging of dental structures.
Displacement
Movements of teeth from their normal position following trauma.
Crown Fracture
Fracture involving loss of crown structure.
Vertical Fracture Identification
Detection based on characteristic patterns in radiographs.
Trauma Guidelines
Standards established for managing dental trauma cases.
Sports Injuries
Common cause of dental trauma among active individuals.
Concussion assessment
Take a PA. Test vitality with cold and retest after a period to see overall vitality.
subluxation follow up if:
discoloration pain and continued mobility
chipped tooth
only enamel and dentin
can be filled
can be crowned depening
fractured tooth
root canal if into pulp
vitality test if no pulp availible
can repair with bonding or crown.
root fracture
vertical or horizontal
outcome depends on location and mobility
mobility means extract
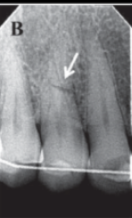
horizontal root fracture
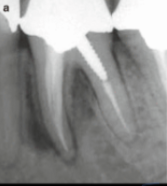
vertical fracture
vertical root fracture
not always visualized but shows j shape lucency
extraction typical
imaging for fractures
PA to CBCT
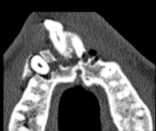
alveolar fracture
alveolar fracture
difficult to visualize on 2D
bone with tooth fractured
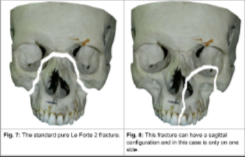
fractured maxilla