Upper Respiratory System Anatomy
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These question-and-answer flashcards cover key structures, histology, functions, and clinical correlations of the upper respiratory system, including the nose, paranasal sinuses, pharynx, and larynx.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
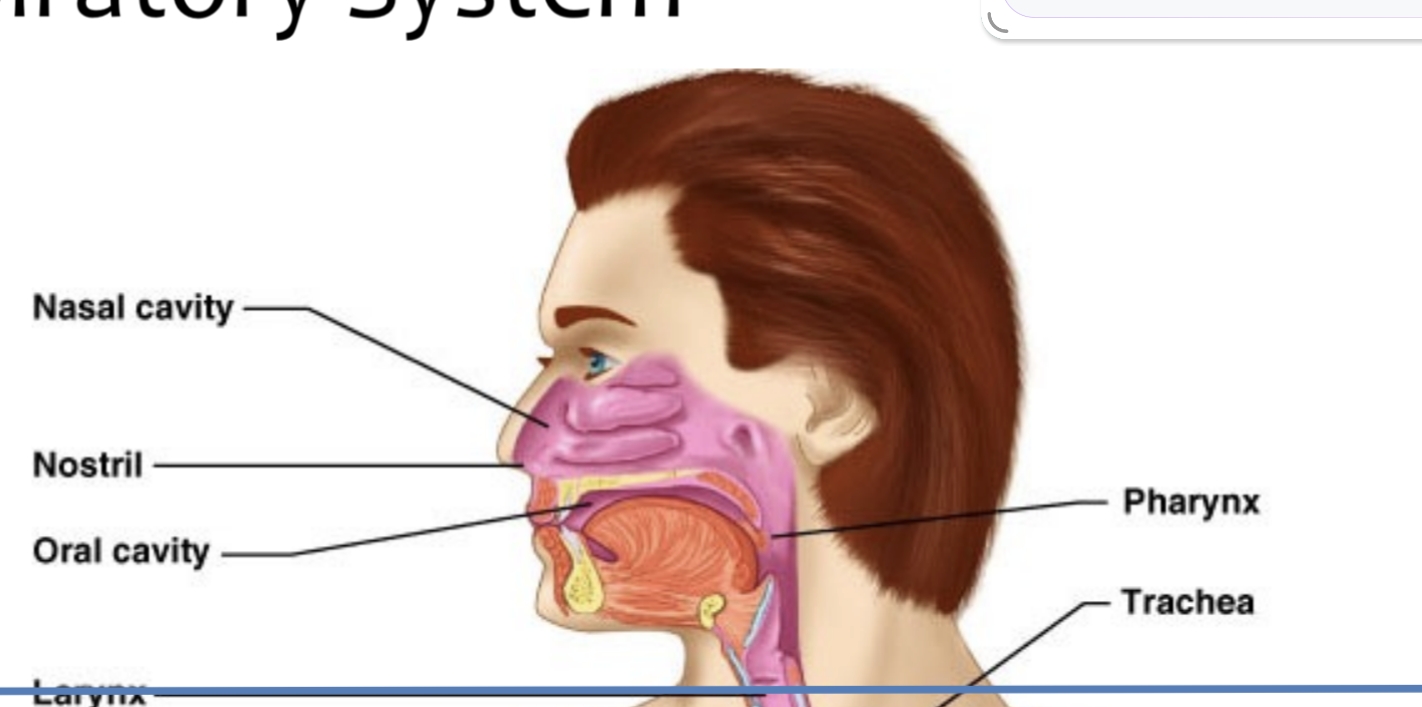
Nose cavity,Nostrill, oral cavity,Pharynx
Which structures make up the upper respiratory tract?
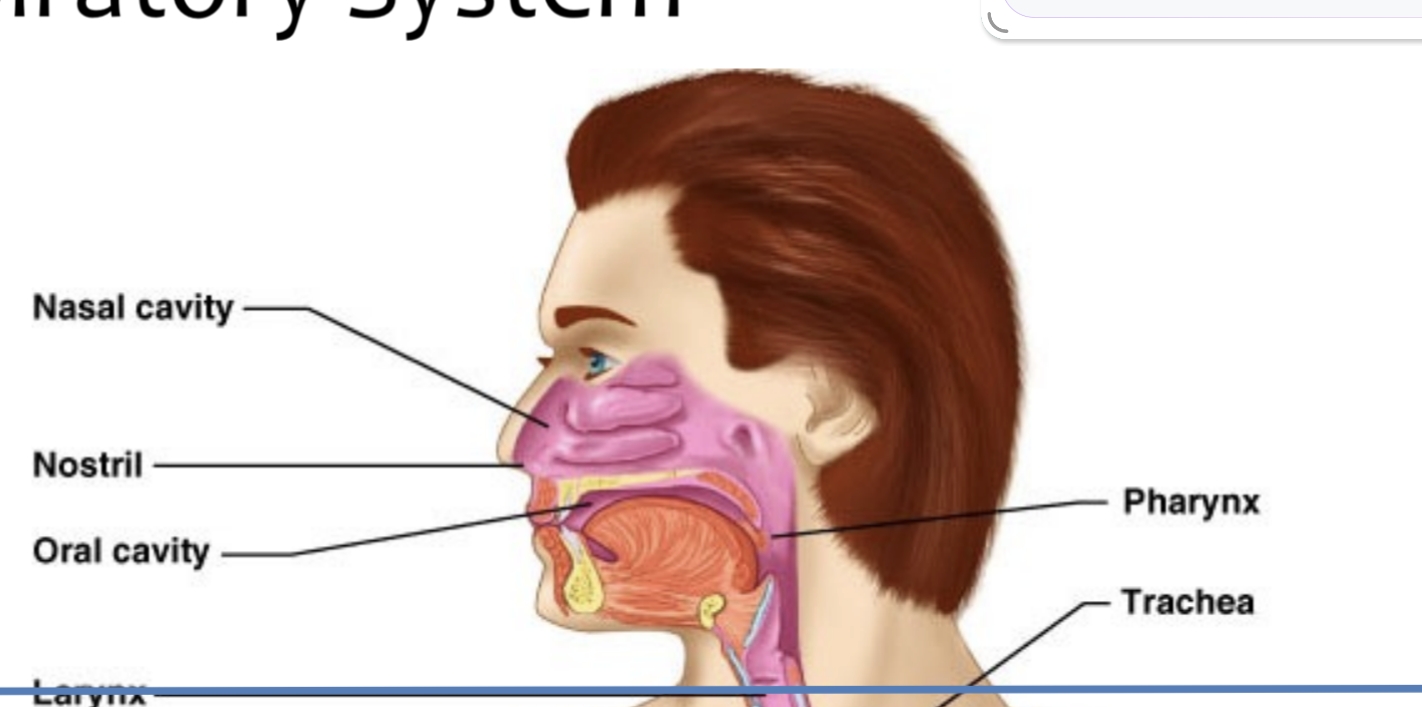
Conducting portion (nose to terminal bronchioles) and respiratory portion (respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts, alveoli).
What are the two functional portions of the respiratory system?
Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium with goblet cells (respiratory mucosa).
What type of epithelium lines most of the conducting portion of the upper airway?
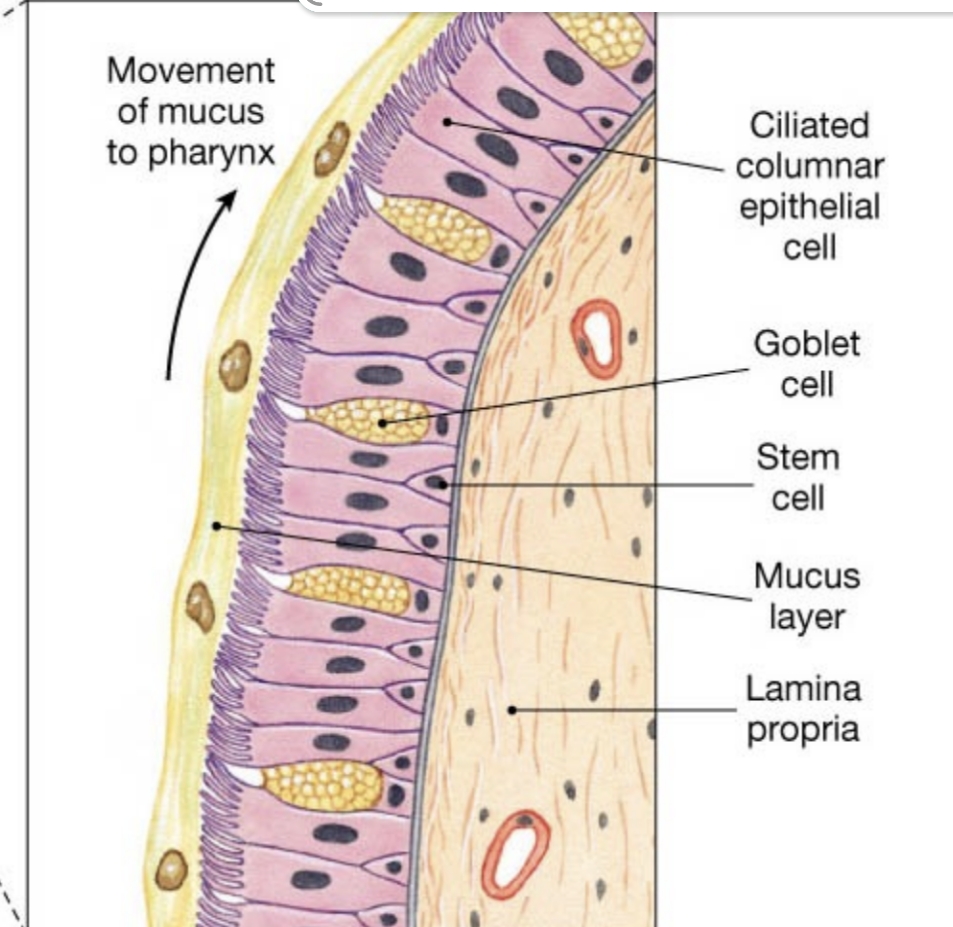
Cilia move mucus laden with trapped dust and contaminants upward toward the pharynx for swallowing or expulsion.
What is the role of the mucociliary escalator?
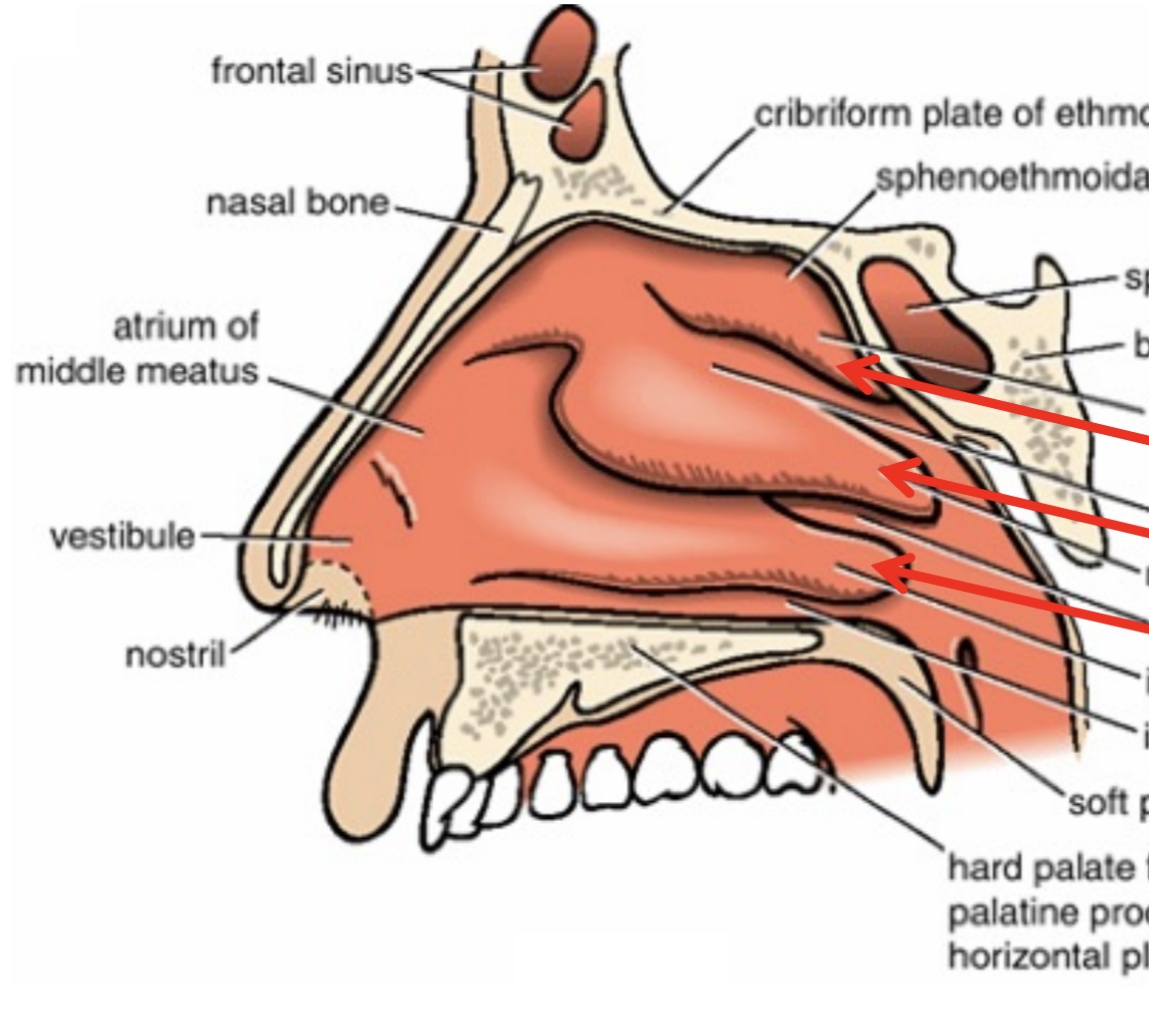
Superior concha, middle concha, inferior concha.
Name the three projections on the lateral wall of the nasal cavity.
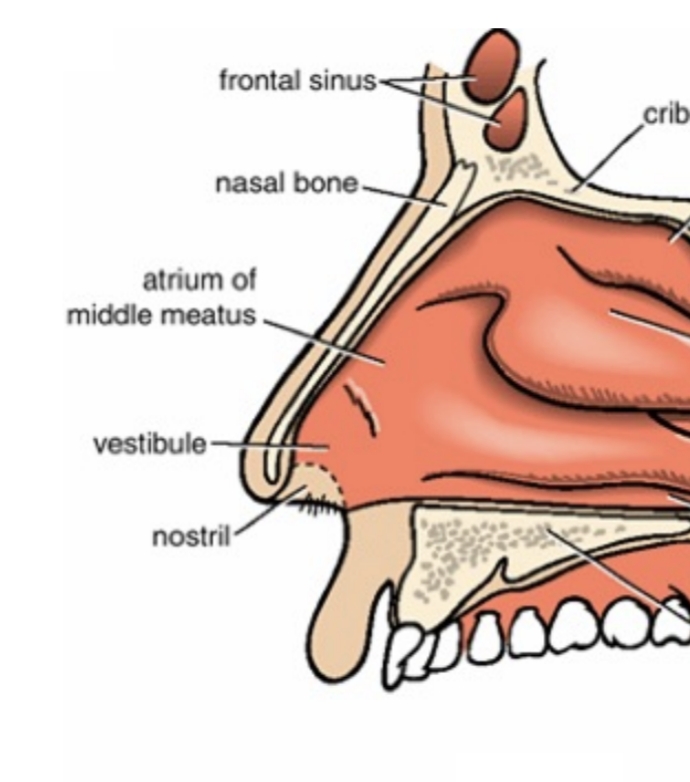
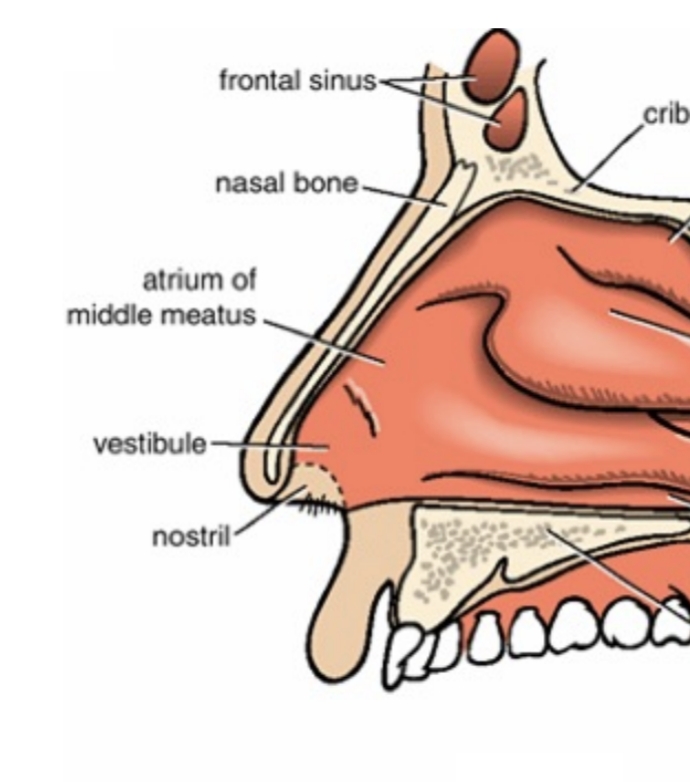
The air passage located beneath each nasal concha.
What is a meatus in the nasal cavity?
Increase air turbulence, ensuring inspired air contacts the mucous membranes for warming, humidifying, and filtering.
What is the function of the nasal conchae?
Stiff guard hairs located in the nasal vestibule that trap large particles and insects.
What are vibrissae and where are they found?
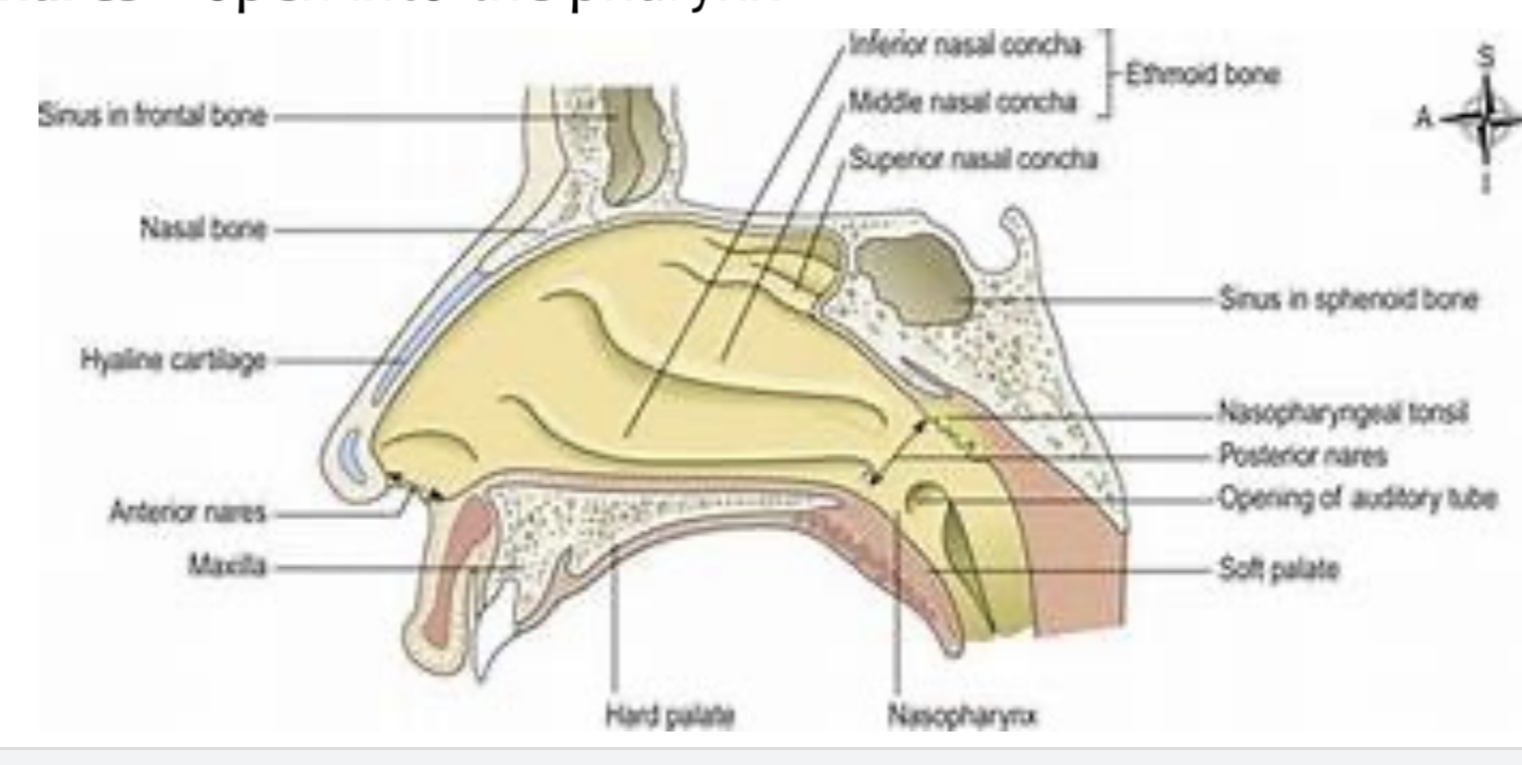
Hyaline cartilage.
Which type of cartilage forms most nasal cartilages?
The epiglottis
Which cartilage of the upper airway is composed of elastic cartilage?
Frontal, ethmoidal, sphenoidal, maxillary.
List the four paranasal sinuses.
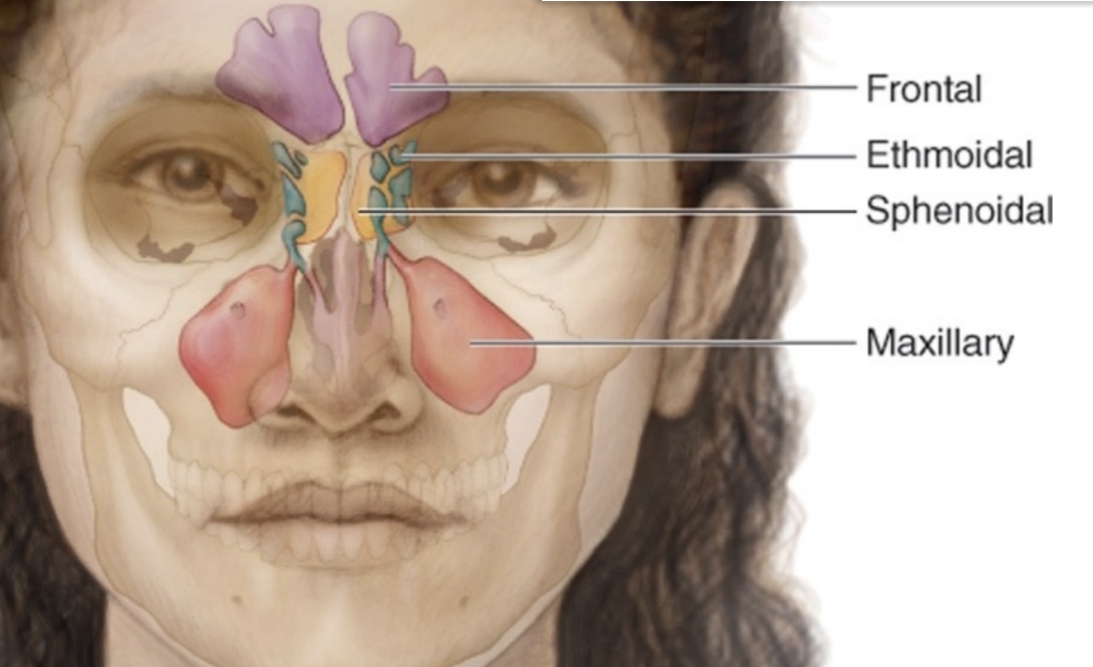
Decrease skull weight, warm/moisten/filter air, add resonance to the voice.
Give three functions of the paranasal sinuses.
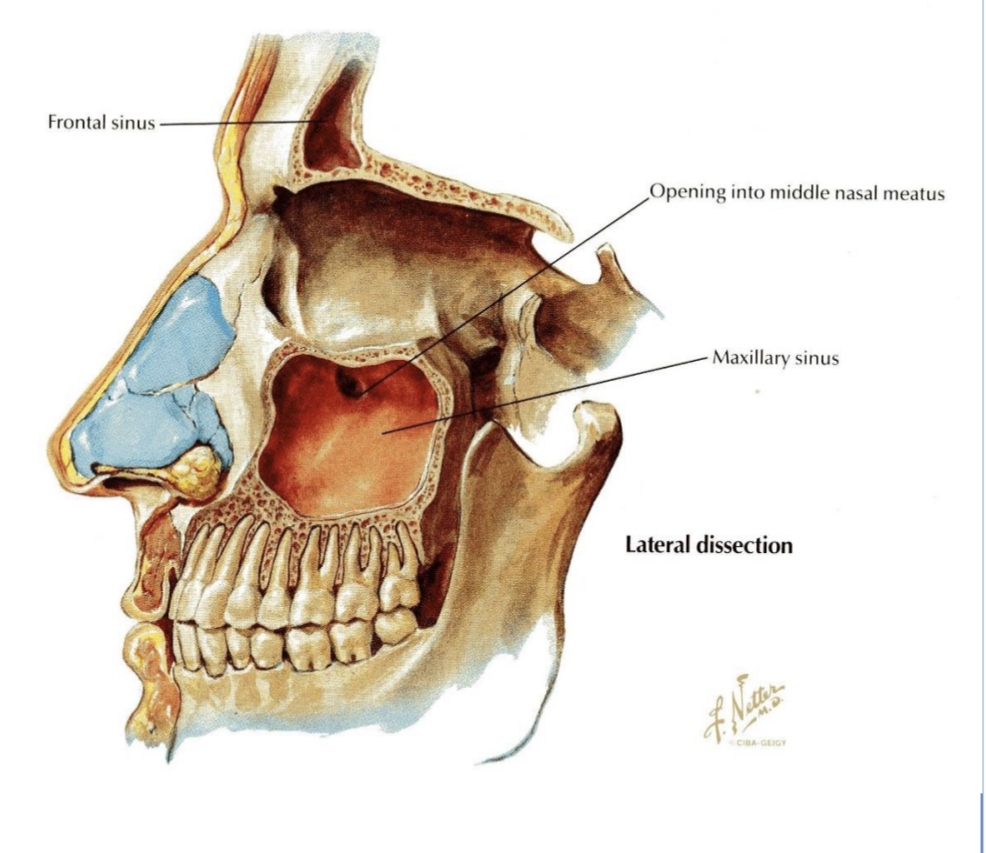
Middle nasal meatus via the semilunar hiatus.
Into which meatus does the maxillary sinus drain?
Roots of the first and second premolars, third molar, and sometimes the canine.
Which teeth roots may project into the maxillary sinus, potentially causing sinusitis after infection?
Into the sphenoethmoidal recess above the superior concha
Where does the sphenoidal sinus open?
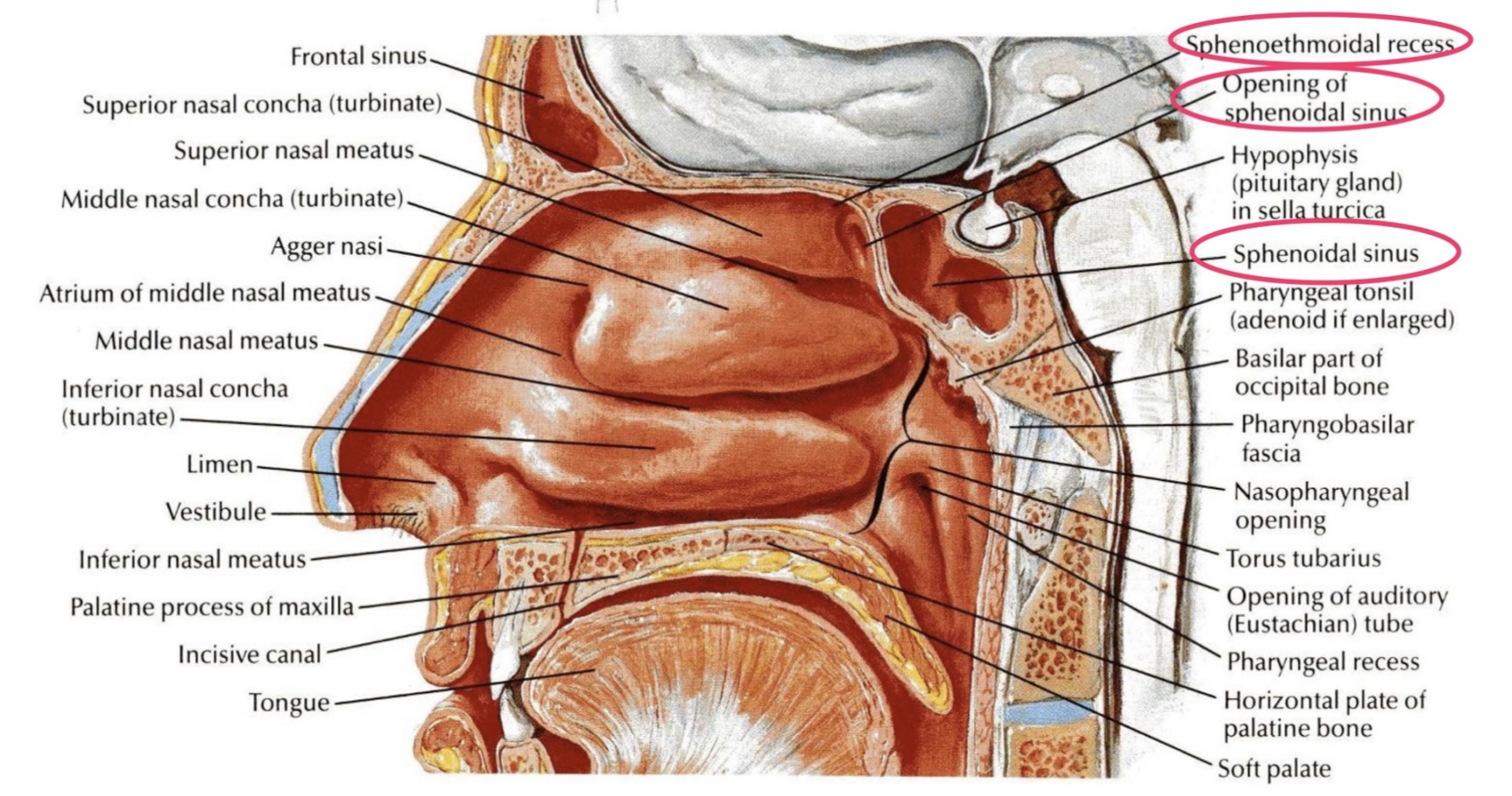
Posterior ethmoidal nerves.
Which nerves supply the mucosa of the sphenoidal sinus?
Anterior group → infundibulum; middle group → middle meatus (bulla ethmoidalis); posterior group → superior meatus.
How are the ethmoidal air cells grouped and where do they drain?
Nasopharynx, oropharynx, laryngopharynx.
Name the three regions of the pharynx from superior to inferior.
Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium.
What epithelium lines the nasopharynx?
Pharyngeal tonsil (adenoids).
Which tonsil is located on the posterior wall of the nasopharynx?
Into the lateral walls of the nasopharynx.
Where do the auditory (Eustachian) tubes open?
From the superior border of the epiglottis to the inferior border of the cricoid cartilage (C6).
Between which anatomical boundaries is the laryngopharynx located?
Non-keratinised stratified squamous epithelium
.Which epithelium lines the laryngopharynx?
Prevents food entering lower airway, conducts air, and produces sound.Prevents food entering lower airway, conducts air, and produces sound.
What are the primary functions of the larynx?
3 unpaired (thyroid, cricoid, epiglottic) and three paired (arytenoid, corniculate, cuneiform)
.How many cartilages form the laryngeal framework and how are they categorized?
Thyroid cartilage (laryngeal prominence).
Which laryngeal cartilage forms the Adam’s apple?
Cricoid cartilage.
Which laryngeal cartilage forms a complete ring around the airway?
The true vocal cords (vocal folds) and the rima glottidis (opening between them).
What is the glottis?
Posterior cricoarytenoid muscles.
Which muscles abduct (open) the vocal cords?
Lateral cricoarytenoid and transverse/oblique arytenoid muscles.
Which muscles adduct (close) the vocal cords for phonation?
Vestibule (supraglottic), ventricle (between vestibular and vocal folds), infraglottic cavity (below vocal folds).
What are the three divisions of the laryngeal cavity?
Vocal folds contain vocal ligaments and produce sound; vestibular folds protect the vocal folds and play no role in phonation.
What distinguishes the vocal folds from the vestibular folds?
Stratified squamous epithelium (to withstand vibration)
.Which type of epithelium covers the true vocal cords?
The epiglottis.
During swallowing, which structure covers the laryngeal inlet to prevent aspiration?
Inflammation of the vocal cords leading to hoarseness or loss of voice.
What is laryngitis and what symptom does it commonly cause?
The extrinsic muscles connecting the larynx to the hyoid bone (e.g., suprahyoid muscles).
Which muscles elevate the larynx during swallowing?
The rima glottidis at the level of the true vocal cords.
What is the narrowest part of the laryngeal cavity in adults?
Thyrohyoid membrane
.Which ligament connects the thyroid cartilage to the hyoid bone?
The cricothyroid ligament (membrane).
Which ligament is pierced during an emergency cricothyrotomy?
A recess lateral to the laryngeal inlet in the laryngopharynx; common site for food lodgement and potential mucosal injury.
What is the piriform fossa and why is it clinically significant?