Glycolysis Steps
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
Preparatory phase
first five steps
Preparatory phase’s energy
uses 2 ATP
Payoff Phase
second five steps
Payoff Phase Energy Usage
4 ATP, 2 NADH made
Glycolysis Overall Energy
uses 2 ATP
makes 2 NADH, 4 ATP
total: 2 NADH, 2 ATP made
Hexokinase is what enzyme class
transferase
Hexokinase refers to what step
Step 1
Reagents for Hexokinase
Glucose
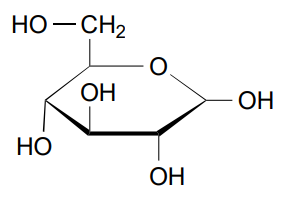
Products for Hexokinase Step
Glucose-6-Phopshate (G6P)

Hexokinase Step’s energy
endergonic due to the use of ATP (-4.0 kcal/mol)
Hexokinase Reaction Formulas
Glc + Pi → Glc-6-P
ATP →ADP + Pi
Once glucose has been phosphorylated
it cannot leave the cell (can’t traverse the membrane)
after step 1!
Phosphohexose Isomerase is what enzyme class
isomerase
Phosphohexose Isomerase refers to what step
2
Phosphohexose Isomerase’s reagents
Glucose-6-Phosphate
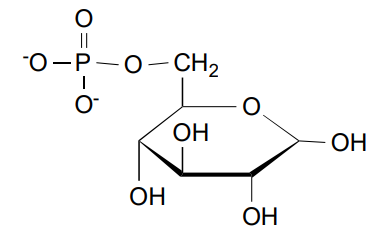
Phosphohexose Isomerase’s product
Fructose-6-Phosphate

Phosphohexose Isomerase’s Energy
Endergonic due to the 6 membered ring becoming a 5 membered ring (+0.4)
∆G⁰’ Formula
∆G⁰’ = -RTlnKeq
Phosphofructose Kinase-1 (PRK-1)’s Enzyme Class
transferase
Phosphofructose Kinase -1 (PFK-1) refers to what step
3
Phosphofructose Kinase -1’s reagaent
Fructose-6-Phosphate
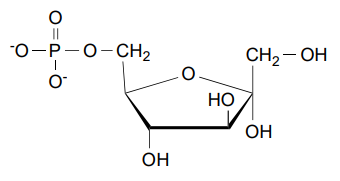
Phosphofructose Kinase -1’s product
Fructose- 1,6- Biphosphate (FBP)
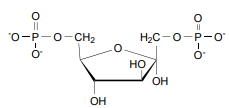
Phosphofructose Kinase -1’s Energy
Exergonic due to use of ATP -3.4 kcal/mol
use ATP to make ADP
Phosphofructose Kinase -1’s Formulas
F6P + Pi → FBP
ATP → ADP + Pi
Aldolase is what enzyme class
synthase/lyase
Aldolase refers to what step
4
Aldolase’s reagent
Fructose-1,6-Biphosphate (FBP)
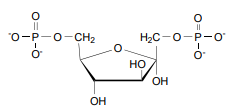
Aldolase’s products
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (GAP) and Dihdroxyacetone Phosphate (DHAP )

Aldolase’s Energy
Endergonic due to sigma bonds becoming pi bonds
+5.7 kcal/mol
Step 4’s products ___ in the pathway
move forward
This is important because they will move forward in the next steps in glycolysis and FBP will continue to react to take these products place.
Triose Phosphate Isomerase (TIM) is what enzyme class
isomerase
Triose Phosphate Isomerase refers to what step
5
Triose Phosphate Isomerase ’s reagent
Dihydroxyacetone Phosphate (DHAP)
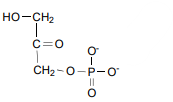
Triose Phosphate Isomerase’s product
Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate (GAP)
Triose Phosphate Isomerase’s Energy
endergonic due to a ketone becoming an aldehyde (+7.5 kcal/mol)
Step 5’s Products _____ in the Glycolysis pathway
move forward
This is important because they will move forward in the next steps in glycolysis and FBP will continue to react to take these products place.
GAP Dehydrogenase is what enzyme class
oxidoreductase
GAP Dehydrogenase is used in what step
6
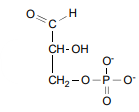
GAP Dehydrogenase’s reagent
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate

GAP Dehydrogenase’s product
1,3- Biphosphoglycerate (BPG) & NADH (2)
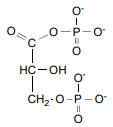
GAP Dehydrogenase’s energy
+1.5 kcal/mol
Mercury inhibition
Inhibits Step 6.
Shuts down the reaction by interacting with the Sulfur molecule
Arsenate Inhibition
can replace the Pi as a substrate for GAP DH. The resulting product of arseno analog is unstable and falls off. Step 7 is skipped, which is very bad because Step 7 makes ATP.
GAP Dehydrogenase's Formulas
GAP + Pi → BPG +2e-
NAD⁺ + 2e- → NADH
GAP Dehydrogenase’s Oxidation and Reduction
GAP is oxidized to BPG. NAD⁺ is reduced to NADH.
Phosphoglycerate Kinase is what enzyme class
Transferase
Phosphoglycerate Kinase refers to what step
step 7
Phosphoglycerate Kinase’s reagents
1,3- Biphophoglycerate (BPG)

Phosphoglycerate Kinase’s products
3-Phosphoglycerate & 2 ATP!!
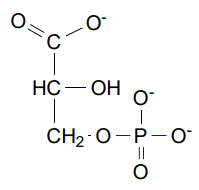
Phosphoglycerate Kinase involves
Substrate Level Phosphorylation
Phosphoglycerate Kinase’s Energy
Exergonic due to the phosphoryl ester becoming a carboxylate
-4.5 kcal/mol
Phosphoglycerate Kinase’s Formula
BPG → 3 PG + Pi
ADP + Pi → ATP
In red blood cells, ~20% of glycolysis is used to make
2,3 BPG
This is an example of how cells like to use what they already have
Phosphoglycerate Mutase is what enzyme class
isomerase
Phosphoglycerate Mutase refers to what step
step 8
Phosphoglycerate Mutase’s Reagent
3- Phosphoglycerate
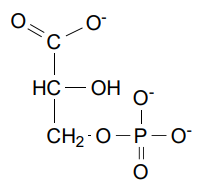
Phosphoglycerate Mutase’s product
2-Phosphoglycerate (2PG)
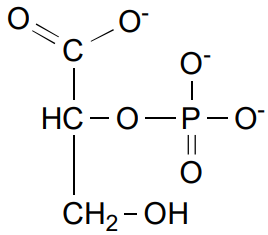
Phosphoglycerate Mutase’s Energy
Endergonic due to closer negative charges
+1.0 kcal/mol
Enolase is what enzyme class
synthase/lyase
Enolase refers to what step
step 9
Enolase’s reagent
2 Phosphoglycerate (2PG)
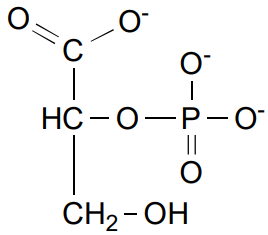
Enolase’s product
Phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP)
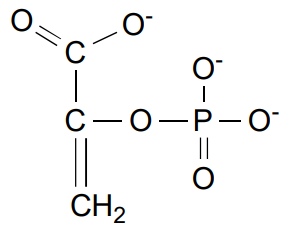
Enolase (step 9)’s energy
Endergonic due to pi bond alkene formation
+0.4 kcal/mol
Pyruvate Kinase is what enzyme class
Transferase
Pyruvate Kinase refers to what step
step 10
Pyruvate Kinase (step 10) reagent
Phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP)

Pyruvate Kinase (step 10) products
Pyruvate and 2 ATP!S
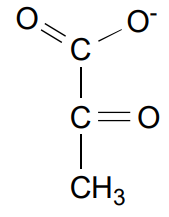
Pyruvate Kinase (step 10) Energy
Exergonic due to enol becoming a keto and removal of the negative repulsion (closeness of the negative charges)
-7.5 kcal/mol
Pyruvate Kinase (step 10) involves
Substrate Level Phosphorylation
Pyruvate Kinase (step 10) Formulas
PEP → Pyruvate + Pi
ADP + Pi → ATP
Which steps involve substrate level phosphorylation (make ATP)
Step 7 (Phosphoglycerate Kinase) and Step 10 (Pyruvate Kinase)
Which steps involve oxidation/reduction (make NADH)?
Step 6 (GAP DH)
What is the net energy carriers made from 1 Glucose to 1 Pyruvate?
2 ATP and 2 NADH
Which steps are exergonic steps?
1,3,7,10
Which steps are endergonic?
2,4,5,6,8,9
Which steps are regulated?
1,3,10
What inhibits Hexokinase?
Its product (G6P) inhibits it.
This controls the amount of G6P in the cell
classical feedback inhibition
Which step is committed?
Step 3
Why is step 3 the committed step?
It’s the earliest irreversible step exclusive to glycolysis. Step 1 is too early because other sugars feed into glycolysis after this step. Step 10 is too late in the pathway.
PRK-1 is inhibited by
ATP
stabilizes the T-state (right shift)
PRK- 1 is activated by
Fructose-2,6-Biphosphate (F2,6BP)
stabilizes the R state (left shift)
indirect feedback activation
Pyruvate Kinase is inhibited by
ATP
Pyruvate Kinase is activated by
Fructose 1, 6, Biphosphate (Step 3 product)
classic feedback activation