HOSA behavioral health
1/297
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
298 Terms
amygdala
“angry almond” - fear and aggression/other emotions
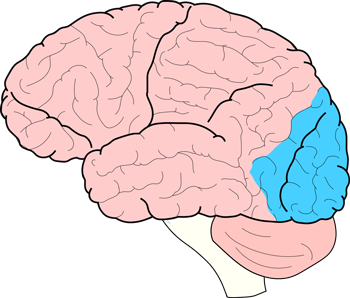
which lobe of the brain is pictured?
occipital lobe
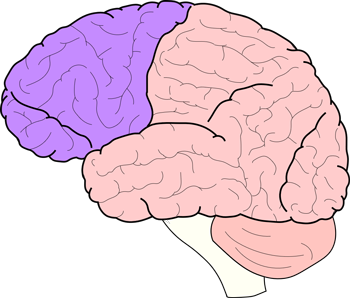
which lobe of the brain is pictured?
frontal lobe
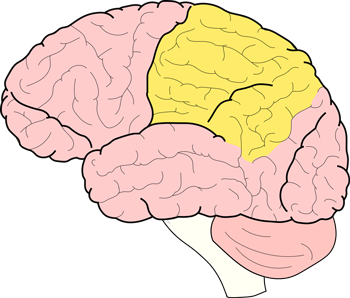
which lobe of the brain is pictured?
parietal lobe
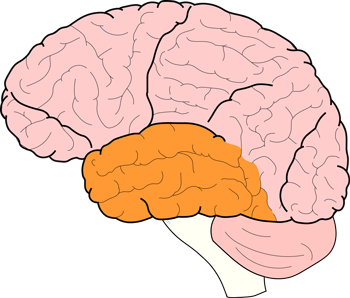
which lobe of the brain is pictured?
temporal lobe
what is the function of the parasympathetic nervous system?
rest and digest
what is the function of the sympathetic nervous system?
fight or flight
what is neuroleptic malignant syndrome
a potentially fatal emergency caused by high doses of numerous neuroleptics
what is a common side effect of clozapine?
hypersalivation
what are characteristics of tardive dyskinesia?
bizarre facial and tongue movements that are potentially irreversible
what are the causes of tardive dyskinesia?
long term use of neuroleptics
what are some common neuroleptics?
haloperidol, risperdal, clozapine, olanzapine, aripiprazole
what are some characteristics of neuroleptic malignant syndrome?
BP changes, tachycardia, hyperpyrexia, parkinsonian symptoms
what is the abbreviation for neuroleptic malignant syndrome?
NMS
what is the abbreviation for dopamine?
DA
what is the abbreviation for serotonin?
5-HT
what is the abbreviation for norepinephrine?
NE
anxiolytics MOA
potentiate effects of GABA (except buspar)
typical antis
atypical antipsychotics MOA
block DA receptors
norepinephrine (NE) - function:
mood, stimulates ANS for fight or flight, cognition, sleep, arousal, locomotion, CV functioning
NTs involved in anxiety
Inc. DA
Inc. NE
Inc. 5-HT
Dec. GABA
NTs involved in depression
Inc. ACh
Dec. DA
Dec. NE
Dec. 5-HT
NTs involved in schizophrenia
Inc. DA
Inc. NE
Dec. GABA
NTs involved in parkinson’s
Dec. DA
Inc. ACh
NTs involved in alzheimer’s
Inc. DA
Inc. NE
Dec. ACh
what are psychotropics?
medications that affect psychic function, behavior, or experience
what are 3 common antipsychotics?
Haldol
Thorazine
Compazine
is GABA inhibitory or excitatory?
inhibitory
is GLUTAMATE inhibitory or excitatory?
excitatory
how can children with depression can present with depression?
irritable or cranky
how should major depressive disorder (MDD) be treated?
antidepressants and cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT)
what is the goal of intrapersonal therapy?
reduce depressive symptoms and develop effective strategies in coping with social and interpersonal relations
what is bipolar disorder treated with?
lithium
what are the four theories of emotion?
James-Lange, Cannon-Bard, Schachter-Singer, Lazarus
bipolar disorder
mood disorder characterized by alternating periods of mania and depression
abnormalities in what neurotransmitter are associated with schizophrenia?
dopamine
what course is major depressive disorder treated with?
cyclic course
what is the cyclic course of treatment for major depressive disorder?
first, the acute symptoms are treated, then continued treatment is provided to prevent early relapse, and lastly, maintenance therapy is given to make relapse less likely
masked depression
a term for people who do not report a depressed mood but suffer from major depressive episodes
when is a depressed individual at the highest risk for committing suicide?
after the initiation of treatment, during the 6-9 month period of symptom recovery
who are antidepressants most effective with?
elderly pt, individuals who have dosage requirements reduced due to the need for hepatic clearance and protein binding.
the two main endocrine systems studied in psychology are:
Hypothalamus-pituitary-thyroid (HPT) axis and Hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis
hypothalamus-pituitary-thyroid (HPT) axis changes noted in a person with bipolar disorder include…
nocturnal TSH peak, blunted TSH response to TRH administration, and high prevalence of hypothyroidism
James-Lange Theory (of emotion)
Event -> Physiological response -> Emotion
example of James-Lange Theory (of emotion)
stimulus/event:
arousal/physiological response:
emotion:
stimulus/event: a threatening grizzly bear approaching
arousal/physiological response: heart pounding, trembling, sweating, running away
emotion: fear
Cannon-Bard Theory (of emotion)
Event -> Physiological response AND emotion (simultaneous)
example of Cannon-Bard Theory (of emotion):
stimulus/event:
arousal/physiological response and emotion:
stimulus/event: a threatening grizzly bear approaching
arousal/physiological response and emotion: heart pounding, trembling, sweating, running away and fear
Schlachter-Singer Theory (of emotion)
Event -> Physiological response -> Identify REASON for physiological response -> emotion
example of Schlachter-Singer Theory (of emotion):
stimulus/event:
arousal/physiological response:
cognitive label/identify reason:
emotion:
stimulus/event: a threatening grizzly bear approaching
arousal/physiological response: heart pounding, trembling, sweating, running away
cognitive label/identify reason: “That is one scary bear! I’m afraid of it!”
emotion: fear
Lazarus Theory (of emotion)
Event -> APPRAISAL of event -> emotion and physiological response (two factor theory but reversed)
buprenorphine
opioid agonist (first line)
agonist
mimic and increase effects of NTs
antagonist
blocks and decreases effects of NTs
naloxone
life saving opioid antagonist
what is naloxone used for?
subdue cravings and in emergencies
disulfiram
alcohol antagonist
what does disulfiram do?
will create unpleasant reaction to alcohol
modafinil
non-amphetamine CNS stimulant and wakefulness promoting agent
what does modafinil do?
treats narcolepsy
clozapine
antipsychotic
what does clozapine treat?
schizophrenia
what is one major side effect of clozapine?
agranulocytosis
what is agranulocytosis?
low levels of granulocytes in blood
what are people with agranulocytosis prone to?
infection
what is a granulocyte?
white blood cell type containing small granules with protein in them
intramuscular haloperidol
drug used to treat schizophrenia inserted into muscle
who is intramuscular haloperidol NOT for?
older patients with dementia-related psychosis
what do selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) do?
blocks reuptake of serotonin
fluoxetine
first line SSRI
what does fluoxetine treat?
depression, anxiety, eating disorders, panic attacks
what are tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs)?
drug class first released in 1959 as a pharmacotherapy for MDD
why aren’t tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) used much anymore?
due to SSRIs and SNRIs having less side effects and being safer in overdose
amitriptyline
TCA
what does amitriptyline do?
increases serotonin, nerve pain med
what should be monitored in lithium usage?
EKG, thyroid + renal functions, lithium levels, electrolyte (blood / urine) + creatinine (renal) levels
where is the first psychology lab?
germany
first experimental psychologist
wilhelm wundt
opioids increase the release of what neurotransmitter?
dopamine
what neurotransmitters do TYPICAL antipsychotics affect?
block dopamine receptors
what do ATYPICAL antipsychotics affect?
lower affinity and occupancy for the dopaminergic receptors, HIGHER degree of occupancy of the SEROTONINERGIC receptors
what neurotransmitters do benzodiazepines affect?
they enhance the effects of GABA (Gamma Aminobutyric acid)
what neurotransmitters do SSRIs (Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors) effect?
increases serotonin by blocking reuptake
what neurotransmitters do SNRIs (Serotonin Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors) effect?
increases serotonin and norepinephrine by blocking reuptake
what does histamine do?
causes many symptoms of allergies
retina
the light-sensitive inner surface of the eye, containing the receptors called RODS and CONES plus layers of neurons to process visual information
optic nerve
carries neural impulses from the eye to the brain
macula
round darker area of the ocular fundus that mediates vision only from the CENTRAL VISION FIELD
retinal blood vessels
the blood vessels that supply oxygen to the rods and cones of the retina
vitreous body
a transparent, jellylike substance filling the interior of the eyeball
what does the vitreous body do?
help stabilize the eye and give physical support
conjunctiva
delicate membrane lining the eyelids and covering the eyeball
sclera
white part of eye
ciliary body and muscle
a muscle that controls the shape of the lens to better focus the light onto the retina of the inner eye
lens
the transparent structure behind the pupil that CHANGES SHAPE to help focus images on the retina
pupil
the adjustable opening in the center of the eye through which light enters (the black dot)
cornea
the transparent layer forming the front of the eye
iris
a ring of muscle tissue that forms the colored portion of the eye around the pupil
what does the iris do?
controls the size of the pupil opening
rods
retinal receptors that detect black, white, and gray