An Introduction to Crime Scene Investigation week 1 power pont
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
•Important to note that criminalistics and CSI are not the same
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Investigate
make a systematic examination or to conduct an official inquiry
Crime
act or commission of an act that is forbidden by a public law and that makes the offender liable to punishment by that law
Crime Scene Investigation (CSI):
process associated with the investigation of a criminal event, which involves a systematic process of documenting, collecting, preserving and interpreting physical evidence.
Trier of fact
•the determination of guilt or innocence left up to the judge/magistrate or jury of peers
Criminalistics
•the analysis of physical evidence. (not at the seen)
Song Ci (1186-1249):
•Wrote book entitled Collected Cases of Injustice Rectified.
Sir Robert Peel (1788-1850):
•Created a force known as “bobbies,” and defined the ethical requirements of police officers known as the “Peelian principles”
Auguste Ambroise Tardieu (1818-1879):
Preeminent forensic medical scientist of the mid-nineteenth century.
Allan Pinkerton (1819-1884):
•Appointed as Chicago’s first detective. This was the first known functional separation of investigations from patrol.
Sir Arthur Conan Doyle: (1859-1930):
Known for his advancement in the work of crime scene investigation. Creator of Sherlock Holmes, the fictional private detective.
Hans Gross (1847-1915):
•Author of the first dissertation concerning the application of scientific disciplines to the field of criminal investigation.
Edmond Locard (1877-1966):
Credited for starting the world’s first crime laboratory. Famous for Locard’s Exchange Principle
Locard’s Exchange Principle:
whenever two objects come in contact with one another, there is a cross transfer of evidence that occurs
–This process stated that every crime scene could be connected to a criminal, witness, and victim, & vice versa
Paul Leland Kirk (1902-1970):
Chemist and forensic scientist known for his work on blood spatter evidence.
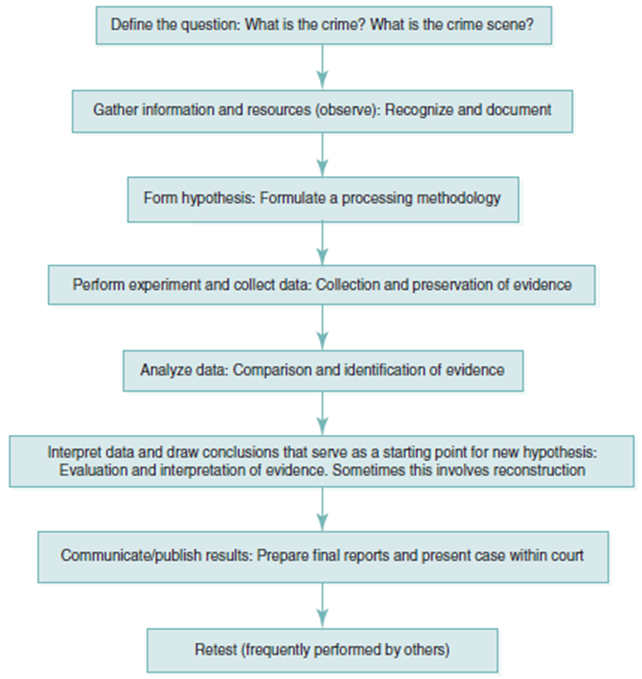
Scientific Crime Scene Investigation
Legally before any evidence is seized, the investigator must decide 3 things
-
-
-
if the case law is pertinent, if a search warrant is required, and if a court order is required
•Swofford vs. Eslinger case
•Courts have enacted civil and criminal penalties for failure to properly preserve evidence
Chain of custody: what is needed?
•Name/initials of the individual collecting the evidence
•Dates the item was collected and transferred
•Agency, case number, and type of crime
•Brief description of the item
•Evidence must be properly booked and stored as well