Introduction to Host Response
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Learning objectives
Describe the function of the immune system
Compare & Contrast innate immunity and adaptive immunity
Describe the role of B-cells and T-cells in the immune system
List the five classes of antibodies (immunoglobins) and describe the functions of each antibody class
Describe the complement system and explain the role it plays in the immune response
Define the term host response and describe its primary function
Purpose of the immune system
Protect and defend the life of the individual (the host), by identifying foreign substances in the body and developing a defense against them
The way an individual’s body responds to an infection is known as host response.
Two parts of the immune system
innate
adaptive
Innate immunity
Present at birth
Always present
Does not improve with repeated exposure to an infectious agent
Cells include: Neutrophils, Monocytes, Macrophages, Eosinophils, Basophils, Mast Cells, NKT-lymphocytes
Adaptive/acquired immunity
Develops throughout life after exposure to antigen
Acquired= process of repeated exposure
Memory develops, which may provide lifelong immunity to reinfection to the same infectious agent
Cells include: T-lymphocytes, B-lymphocytes
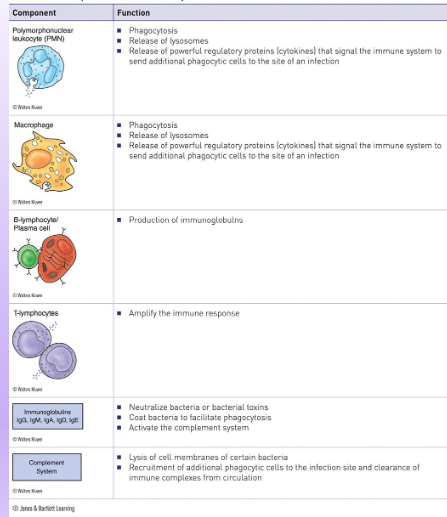
Components of the immune system
cellular defenders
complement system
Lymphocytes
play an important role in recognizing and neutralizing foreign invaders
belong to adaptive immunity
3 types: B, T, NK-lymphocytes
B-lymphocytes
originate from bone marrow
B-cells
• Plasma B-Cells (produce antibodies)
• Memory B-Cells (remember exposed pathogens)
Plasma B cells (produce antibodies/remember exposed antigens)
produce antibodies
Memory B cells (produce antibodies/remember exposed pathogens)
remember exposed pathogens
Antibodies
Collaborate with other leukocytes and complement system to eliminate the offending agent
Also known as immunoglobins: IgM, IgG, IgA, IgE, IgD

IgM
• Found on B cells (circulates in bloodstream)
• Largest therefore, cannot exit the circulatory system easily
• Earliest to appear at a site of infection
• Indicates a recent infection
IgG
• 4 types
• Most abundant of all immunoglobulins
• Found in blood and tissue
• Effective against bacteria, viruses, and fungi
• Only one that can pass through the placenta
IgA
• 2 types serum and secretory
• Found in tears and saliva
• Most important for us
• Prevents bacteria and viruses from adhering to mucous membranes
Which immunoglobulin most pertains to us as dental hygienists?
IgA
IgD
Secreted in the smallest concentrations
• Function is a mystery
IgE
• Only found in mammals
• Major defense against parasites
• May defend against cancer
• Responsible for most allergic reactions and anaphylaxis
T-lymphocytes
mature in thymus
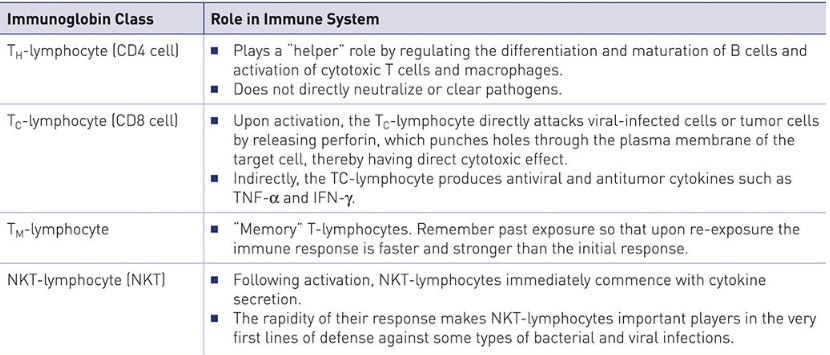
T helper cell (CD4)
regulates differentiation and maturation of B cells and activation of cytotoxic T cells + macrophages
doesn’t directly neutralize or clear pathogens
T cytotoxic cell (CD8)
directly attacks viral infected cells or tumor cells by releasing perforin (punches holes through plasma membrane of target cell)
indirectly attacks by producing antiviral and antitumor cytokines such a TNF-a and IFN-y
Tm lymphocyte
memory
remembers past exposure so immune response is faster and stronger
NKT-lymphocytes (NKT)
cytokine secretion
very first lines of defense against some types of bacterial and viral infections
Complement system
Offers an added layer of defense that is needed against pathogens
Ability to evade and outwit the cellular defenders
Made up of proteins
Lyse bacteria
4 functions: opsonization, membrane attack complex, phagocytosis, clearance