Paper 2 - Computational thinking, algorithms and programming
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Give the characteristics and purposes of the different types of programming languages
Low level languages and high level languages.
Low level languages do not resemble natural human language, making it harder to read, write, understand and learn.
Purpose:
Used when a program must be executed quickly (as the computer doesn’t have to translate it; can be directly understood)
Provides direct control over hardware
High level languages use code written in a way that is similar to a natural human language, making it easier to read, write, understand and learn the language.
Purpose:
leads to fewer errors, easier to debug
easier to write, read, understand and learn
allows for more complex and powerful commands
However, high level languages must be converted into machine code before it can be run, as high level languages cannot be executed directly by the CPU, making it slower to execute.
What does a translator do?
Changes (translates) a program written in one language into a program written in another language (usually machine code)
Explain the two different types of translators
Interpreters: converts high level languages into machine code and executes them one line at a time
Compilers: converts a high level language into machine code for execution at a later time by creating an executable file; the entire program is converted at once
Compare interpreters and compilers
Execution method:
Interpreters: translates source code and executes it one line at a time
Compiler: translates all of the source code all in one go and produces an executable file that will run on other machines without the compiler needing to be installed
Execution speed:
Interpreters: slower as the code must be retranslated each time the program is run
Compiler: when it creates the executable file, it produces much more efficient code, making the compiled programs run faster
Complexity:
Interpreters are much smaller, simpler programs
Compilers tend to be large, complex programs
Error reporting:
Interpreters: the interpreter translates one line at a time, so when it encounters an error in a line it will stop the program from running and report it to the user immediately
Compilers: the compiler analyses the entire program taking note of where errors have occurred and records them in an error file, and provides this to the user
Repetition:
Interpreters: can be edited and run without translating the whole program; the entire program must be retranslated every time
Compilers: requires analysis and generation of the code and executable file only once; however compiled programs have to be recompiled after any changes have been made
What does an integrated development environment do? What does it provide?
IDEs provide programmers with the facilities needed to help create programs.
Editors (allows programmers to enter code, automatic formatting (indentation), line numbering, colour coding, statement completion) to allow programmers to write code
Error diagnostics (displays information about an error (eg. error type, line number it occurs on) to help programmers to debug
Run-time environment (allows a program to run on a computer system, allowing the programmer to test the program)
Translators (converts the source code into machine code to be executed by the CPU to allow the program to be run and tested)
What are defensive design considerations? List them
Defensive design considerations are considerations when creating a program that is secure and robust
Anticipating misuse (planning ahead to take steps against potential misuse)
Input sanitation (eg. removing special characters to prevent an SQL injection)
Validation (checking whether data follows specific criteria that should be accepted)
Verification (checking data entered is correct)
Maintainable code (allow others to be able to quickly and read and understand code that has been written)
Authentication (to confirm the identity of a user)
What is validation?
A process to check that data is reasonable or sensible before it is accepted
Give types of input validation
Length check (length of input is within a range)
Range check (data is within a certain range)
Type check (data is of a certain data type)
Format check (data is entered in a certain way)
Presence check (data has actually been entered and not left blank)
Give methods of making a program maintainable
Commenting (enables programmers to understand the purpose of the code)
Indentation (improves readability)
Subprograms (reuse code and make them easier to test)
Appropriate variable names (purpose of a variable is understood)
Using constants (keeps programs consistent, easy to read and debug)
What is the purpose of testing programs?
To ensure that a program works correctly no matter what input has been entered by the user
Explain the two types of testing
Iterative: repeatedly testing the small parts of the program (modules) during the development of the program (until it works as expected)
Terminal: testing the program after it has been developed and before the program is released to the end user. Takes place once all of the modules have been individually tested to ensure the whole program works all together as expected
Explain the two types of errors:
Syntax: errors where the code doesn’t follow the rules of the programming language, so the computer cannot compile and execute it
Logic: the program can be run but does not work as intended, producing an unexpected output
Explain the four types of test data
Normal test data: test data which should be accepted by a program without causing errors
Boundary test data: test data that is data of the correct type but is at the edge of the data range/ not being valid
Invalid test data: test data that is data of the correct data type which should be rejected by the computer (does not meet the validation rules)
Erroneous test data: test data is data of the incorrect data type which should be rejected by a computer system
What are the three principles of computational thinking?
Abstraction
Decomposition
Algorithmic thinking
What is abstraction and how is it used to solve problems?
Abstraction is a principle of computational thinking that involves removing unnecessary details from a problem to focus on the key information needed to solve it.
It simplifies a problem and makes it less complex; this makes it easier to understand the problem and create a solution.
What is decomposition and how is it used to solve problems?
Decomposition is a principle of computational thinking that involves the breaking down of problems into smaller, simpler steps or stages.
Each individual step can be separately tested and solved, making it easier to solve the problem as each smaller part acts as an easier, manageable sub-problem.
It also enables different people to work on different parts of the same problem simultaneously, allowing problems to be solved more quickly.
What is algorithmic thinking and how is it used to solve problems?
Algorithmic thinking is a principle of computational thinking that involves working out the steps needed to be taken to solve the problem and producing an algorithm (set of instructions) that needs to be followed to solve the problem.
It is used as it helps programmers to understand and breakdown the problem so that they know what they need to do and how to do it, making it easier to solve the problem.
It involves both abstraction and decomposition.
What is an algorithm and why are they created?
A set of instructions presented in a logical sequence
Programmers create algorithms as a method of planning a program before writing any code; this helps them to consider potential problems in the program and easier to begin to create source code.
What are flowcharts?
A tool that can be used to visually represent an algorithm (set of instructions presented in a logical order to plan a program)
What flowchart symbol is used at the beginning and end of a flowchart?
A terminal
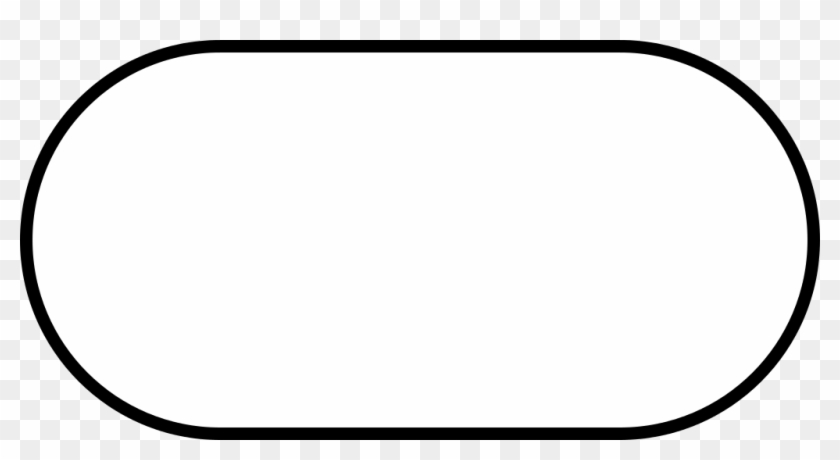
What flowchart symbol is used for an if statement?
A decision

What flowchart symbol would be used for
sum = sum + number
password = 1234
A process

What flowchart symbol would be used for:
print(name)
temperature = input
Input and output
Give the flowchart symbols for:
a line
input and output
process
decision
subprogram
terminal
What are trace tables used for?
To track the value of variables as a program is run
They can be used to manually track the value of variables to investigate why the program isn’t working as intended
Each row in the trace table presents another line, each column stores the value of variables as they change.
Name the standard searching algorithms
Linear search
Binary search
Name the standard sorting algorithms
Bubble sort
Merge sort
Insertion sort
State the main steps of a linear search algorithm, any pre-requisites and give the key features of the code/algorithms
Each value is searched in order from the first value to the last
Pre-requisites:
No pre-requisites; can be used on any dataset, even unsorted ones
For large lists this is not very efficient and takes a long time
Key features:
A loop is used to check the first value in a list and increment by 1, checking each value for a match to the target
Reaching the last element without finding a match means the value is not included
State the main steps of a binary search algorithm, any pre-requisites and give the key features of the code/algorithms
The midpoint of the data set is selected and compared to the target value
If the midpoint is greater than the value, the right half of the dataset is discarded and the midpoint of the remaining dataset is selected etc. If the midpoint is less than the value, the left half of the dataset is discarded and the midpoint of the remaining dataset is selected etc
Pre-requisites:
Data must already be sorted!
Much quicker and more efficient, especially for large datasets.
Key features:
A midpoint, low point and high point are all calculated
A while loop is used to repeatedly compare the midpoint to a target value
The upper half or lower half of the data is completely ignored if the midpoint does not equal the target
State the main steps of a merge sort algorithm
Merge sorts separates and then merges data together again in the correct order.
A merge sort list divides a dataset into half again and again until each data item is separate
The items are then compared and combined until there is one dataset in the correct order
Efficient and quick for large lists
State the main steps of a bubble sort algorithm
The algorithm repeatedly bubbles through the data set comparing each item each time.
The algorithm iterates through a data set continuously and compares adjacent data elements and swaps them if they are not in the correct order
The algorithm will only stop when a complete iteration has been made through the dataset and no swaps have been made
Not suitable for large sets of data
State the main steps of an insertion sort algorithm
The list is logically split into sorted values (on the left) and unsorted values (on the right)
Starting from the left, values from the unsorted part are checked and inserted into the correct position on the sorted part
This continues through all of the elements in the list until the last item is reached and sorted
Efficient for small datasets but slow for large datasets.