Forces & Momentum
1/142
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
143 Terms
When drawing free-body force diagrams
objects can be represented as point particles placed at the object's centre of mass.
Free-body force diagrams show forces acting on multiple objects or systems.
False
State two quantities that a force arrow represents.
The two quantities that a force arrow represents are: the magnitude of the force and the direction of the force
Define the term resultant force.
A resultant force is the vector sum of all the forces exerted on an object
When forces are balanced
they produce a non-zero resultant force.
When two forces in different planes act on an object
how can the resultant force be found?
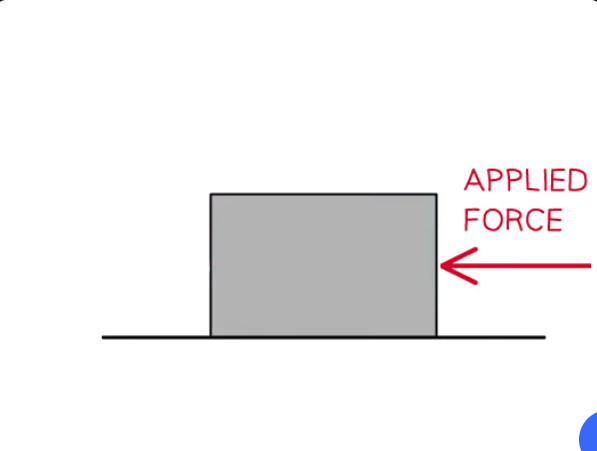
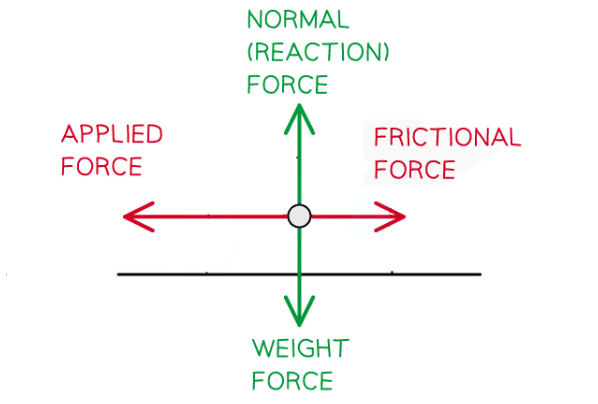
Draw a free-body force diagram for the object on Earth in this situation.
Free-body force diagram showing the applied force acting to the left which is larger than the frictional force acting to the right
A car accelerates in the positive direction. The thrust force from the engine on the car is 1000 N
the air resistance on the car is 50 N and the friction from the road on the car is 500 N. What is the resultant force on the car?
An object moving at a constant velocity has no resultant force acting on it.
True
Define Newton's first law of motion.
Newton's first law of motion states that a body will remain at rest or move with constant velocity unless acted on by a resultant force
According to Newton's first law of motion
an object at rest will remain at rest unless acted upon by a resultant force.
Define the term translational equilibrium.
An object is in translational equilibrium if the vector sum of all the forces acting on it are zero
According to Newton's first law
what would happen to a body that is travelling at a constant velocity if no resultant force acted on it?
What are the three ways that a resultant force can change an object's motion?
The three ways that a resultant force can change an object's motion are: speed it up (accelerate)
Define Newton's second law of motion.
Newton's second law of motion states that the resultant force on an object is directly proportional to its acceleration
State the equation for Newton's second law of motion.
F = m a
A resultant force acts in the direction of motion of an object. Describe the change in the object's motion.
The object will speed up / accelerate in the direction of motion
A resultant force opposes the direction of motion of an object. Describe the change in the object's motion.
The object will slow down / decelerate
A resultant force acts at an angle to the direction of motion of an object. Describe the change in the object's motion.
The object will change direction
Acceleration always acts in the same direction as the resultant force.
True
If no drag forces are present
then the acceleration of a falling object is independent of its mass.
State Newton's second law of motion in terms of momentum.
Newton's second law
Newton's first and second laws of motion can involve multiple forces acting on one object.
True
Newton's third law of motion involves two objects exerting the same type of force on each other.
True
State Newton's third law of motion.
Newton's third law states that if one body (Object A) exerts a force on another body (Object B)
Name four characteristics of a Newton's third law force pair.
The four characteristics of a third law force pair are: the same type of force
Weight and normal contact force are an example of a third law pair.
False
According to Newton's third law of motion
if two forces are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction
A car drives at a constant velocity on a road. Name a third law force pair in this situation.
Two examples of third law force pairs for a car driving at a constant velocity on a road are: normal contact forces due to the car pushing on the road and the road pushing back on the car
Define the term contact force.
A contact force is defined as a force that acts between objects that are physically touching
Give one example of a contact force.
Examples of contact forces are: surface friction
What is surface friction?
Surface friction is a force that opposes the motion of an object moving over a solid surface
What is viscous drag?
Viscous drag is a type of frictional force that occurs when an object moves through a fluid (a liquid or a gas)
Define tension force.
Tension is a force that occurs within an object when a pulling force is applied to both ends
What is the normal reaction force?
The normal reaction force is the component of the contact force acting perpendicular to the surface
Define the term fluid in relation to physics.
In physics
Define a non-contact force.
A non-contact force is a force which acts at a distance without any physical contact between bodies due to the action of a field
State one example of a non-contact force.
Examples of non-contact forces are: gravitational force (weight)
What is the gravitational force?
The gravitational force
What is the electrostatic force?
The electrostatic force is an attractive or repulsive force experienced by charged objects in an electric field
What is the magnetic force?
The magnetic force is an attractive or repulsive force experienced between magnetic poles in a magnetic field
Air resistance is a non-contact force.
False
When a frictional force is exerted on an object
energy is transferred.
When a frictional force is exerted on an object
the temperature of the object decreases.
What causes surface friction?
Surface friction is caused by imperfections in the surfaces of two objects that rub against one another
Define the term static friction.
Static friction is a type of surface friction that occurs when an object is stationary on a surface
Define the term dynamic friction.
Dynamic friction is a type of surface friction that occurs when an object is moving across a surface
Surface friction always acts parallel to the plane of contact between the object and the surface.
True
Static friction decreases in magnitude until movement begins.
False
For any given situation
static friction will reach a maximum value that is larger than that of dynamic friction.
For a constant pushing force
dynamic friction will be constant.
State the equation for static friction.
Ff ≤ μs F_N
State the equation for dynamic friction.
Ff = μd F_N
State Hooke's law.
A material obeys Hooke’s law if the extension of the material is directly proportional to the applied force up to the limit of proportionality
State the equation for Hooke's law.
F_H = -k x
Define the term spring constant.
The spring constant is a property of the material being stretched and describes the stiffness of the material
The stiffer the spring
the smaller the spring constant.
Hooke's law applies to extensions and compressions.
True
What does the linear portion of a force-extension graph represent?
The linear portion of a force-extension graph shows that the force applied is directly proportional to the extension
What does the gradient of the linear region of a force-extension graph represent?
The gradient of the linear region of a force-extension graph represents the spring constant
What does the gradient of the linear region of an extension-force graph represent?
The gradient of the linear region of an extension-force graph represents 1/k
State the equation for Stokes' law.
F_d = 6πηrv
Define the term viscosity.
The viscosity of a fluid is its resistance to movement
The rate of flow of a fluid is inversely proportional to its coefficient of viscosity.
True
The magnitude of the viscous drag force is dependent on the speed of the object moving through the fluid.
True
The magnitude of the viscous drag force is independent of the volume of the object moving through the fluid.
False
The magnitude of the viscous drag force is dependent on the shape of the object moving through the fluid.
True
The force of buoyancy is only exerted on objects that are immersed in liquids.
False
The buoyancy force is exerted on a body due to the displacement of the fluid it is immersed in.
True
State the equation for the buoyancy force.
F_b = ρ V g
State the equation for the weight of a sphere of volume V and density ρ.
Ws = ρs V_s g
The terminal velocity of a sphere falling through a fluid is indirectly proportional to the square of the radius of the sphere.
False
The terminal velocity of a sphere falling through a fluid is directly proportional to the viscosity of the fluid.
False
Define linear momentum.
Linear momentum is the momentum of an object that is moving in only one dimension
The linear momentum of an object remains constant
unless the system is acted upon by an external resultant force.
State the equation for linear momentum.
p = m v
Linear momentum is a vector quantity.
True
State the principle of linear momentum.
The principle of linear momentum states that the total linear momentum before a collision is equal to the total linear momentum after a collision. Unless the system is acted on by a resultant external force
Linear momentum is always conserved.
True
A toy car of mass 0.2 kg travels with a velocity of 0.1 m s–1. What is the linear momentum of the toy car?
0.02 kg m s–1
Moving object A collides with stationary object B. After the collision
they move in opposite directions. Write equations for the momentum before and after the collision.
pafter = -mA vA + mB v_B
Define impulse.
Impulse is when an external resultant force acts on an object for a very short time and changes the object's motion
What is the symbol for impulse?
J
State the equation for the impulse of a force.
J = F Δt
Impulse is equal to change in momentum.
True
Impulse always acts in the opposite direction to the external resultant force.
False
A larger force exerted for a short time has the same effect as a smaller force exerted for a longer time.
True
Increasing the time over which a change in momentum occurs reduces the force applied to the object.
True
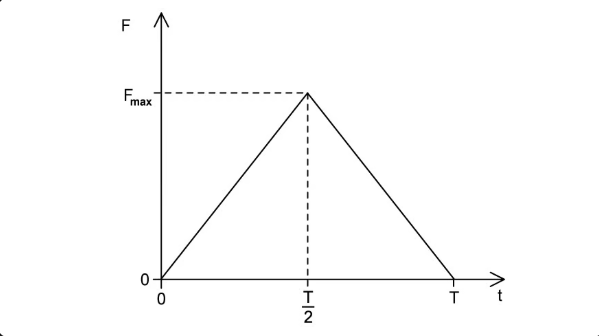
Write an expression for the impulse of the force acting for a time T.
J = (1/2) F_max T
The equation F = Δp / Δt can only be used when mass is constant.
False
A toy car collides with a skirting board. The toy car exerts a force of 4.5 N on the skirting board. State the magnitude and direction of the force exerted by the skirting board on the car.
-4.5 N
A student of mass 50 kg sits on a chair. State the magnitude of the force exerted by the chair on the student.
490 N
The equation F = m a can be used when mass is not constant.
False
How can force
as the rate of change of momentum
Define the term collision.
A collision is when two or more moving objects come together and exert a force on one another for a relatively short time
Define the term explosion.
An explosion is when two or more objects that are initially at rest
Momentum is conserved in all collisions and all explosions.
True
Kinetic energy is conserved in all collisions and all explosions.
False
Define the term elastic collision.
An elastic collision is a collision in which both the momentum and kinetic energy are conserved