Rnr Great Lakes
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
Lacey Act
prohibits interstate transport of wild animals dead or alive without federal permit.
Kelso also believes that the act should be revisited to to require screening of imported species for diseases, parasites.
- Specifically the invasive Asian Carps
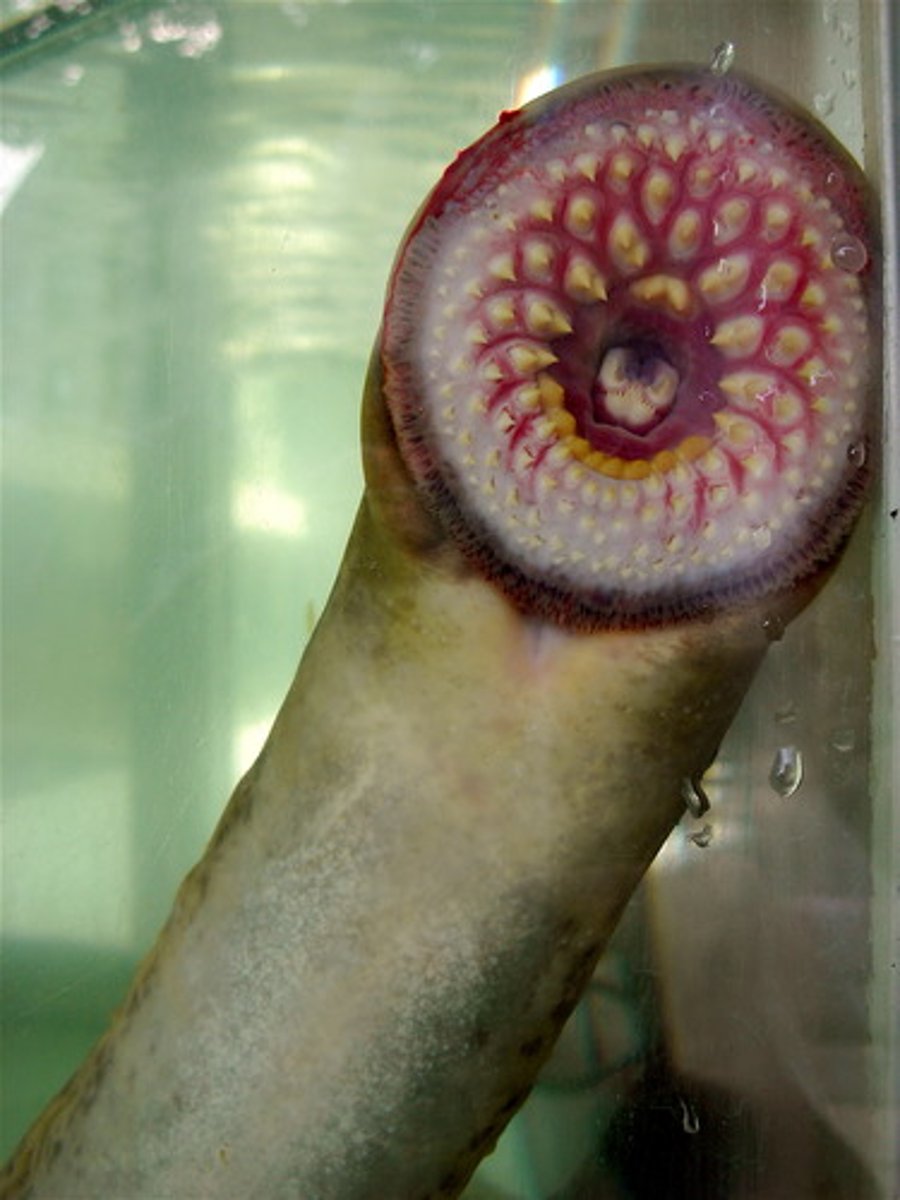
Ammocete Larvae
. the young Larvae of Sea Lamprey
. they are stream spawners
. they stay in streams for around 3-14 years and then swim into lakes
. when they get old they swim back to streams to spawn and then die

. Silver Carp
. Bighead Carp
. Black Carp
. Grass Carp
What are the 4 invasive Asian Carps inhabiting the great lakes?
Control of Sea Lamprey attempts
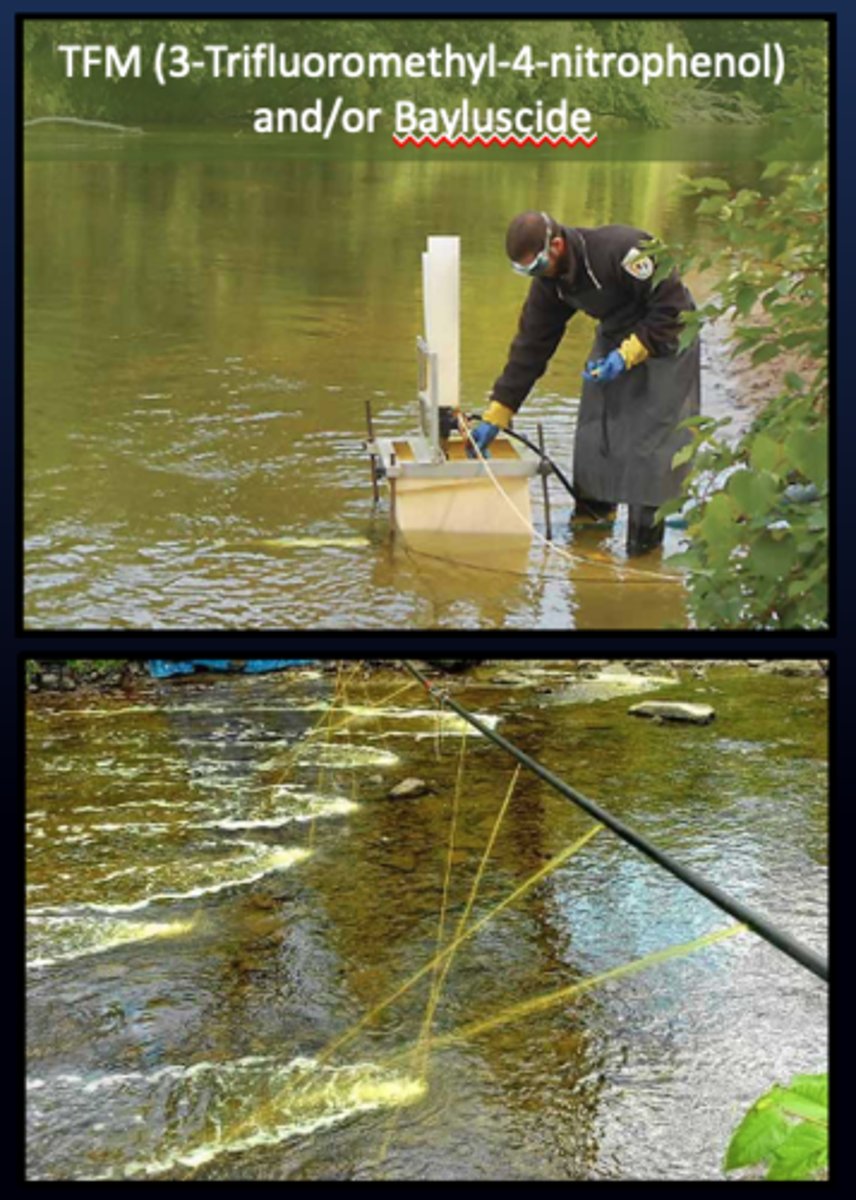
. TFM (3 Trifluoromethly - 4-nitrogphenol) and/ or Bayluscide
. Barrier traps
. Pheromone Traps
. Electrified weir

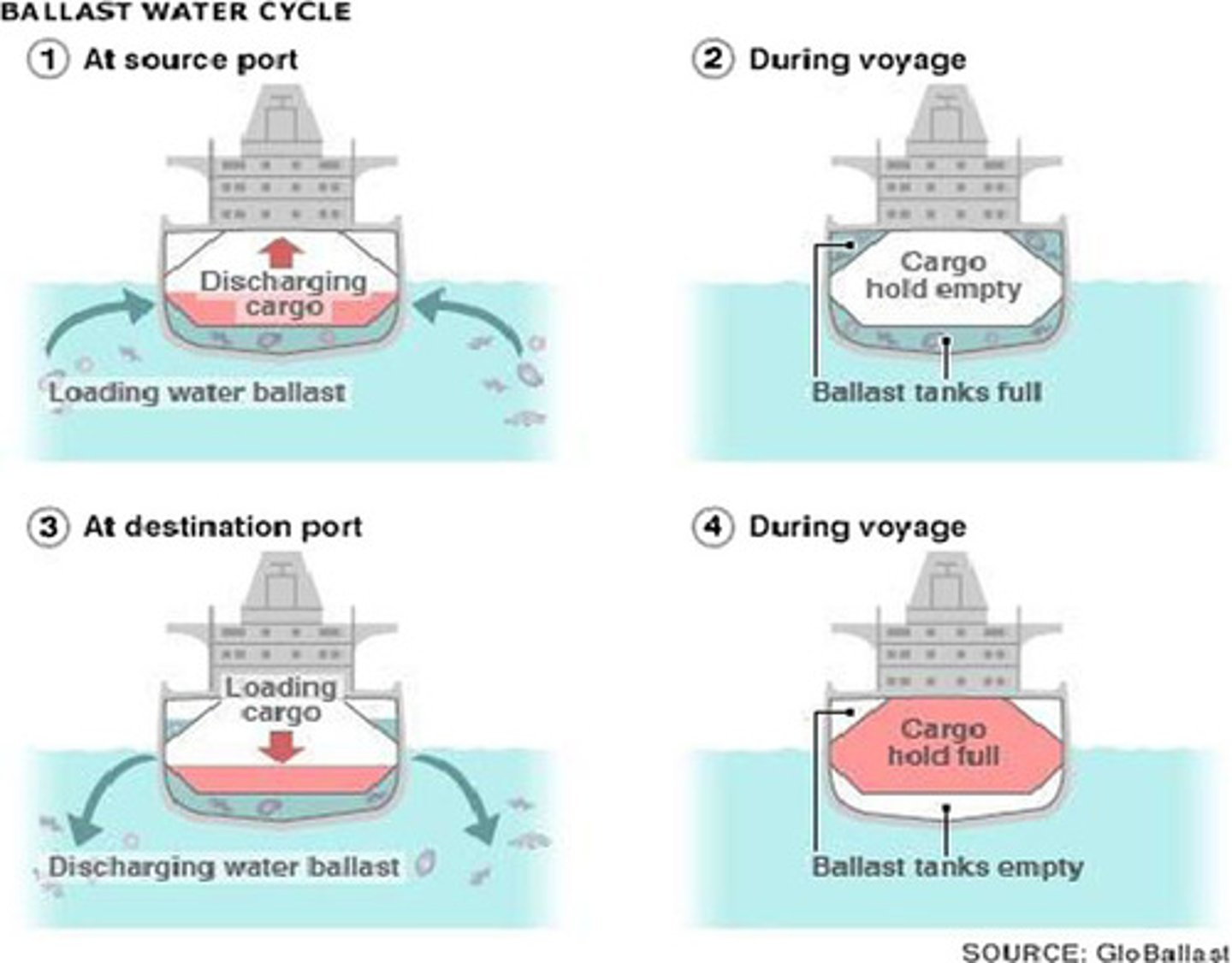
Ballast Water
water filled into an empty ship in place of heavy cargo to stabilize it until it reaches its port. Then releasing the and all the organisms in it to the new location. Introduced 60% - 70% of all Great Lake invasive species
Bioaccumulation/ Biomagnification
The accumulation of a substance, such as a toxic chemical, in various tissues of a living organism as they move up the trophic web
- a bear to bioaccumulate to a greater extent than a mouse, and a 15-pound largemouth bass to bioaccumulate more than a topminnow.
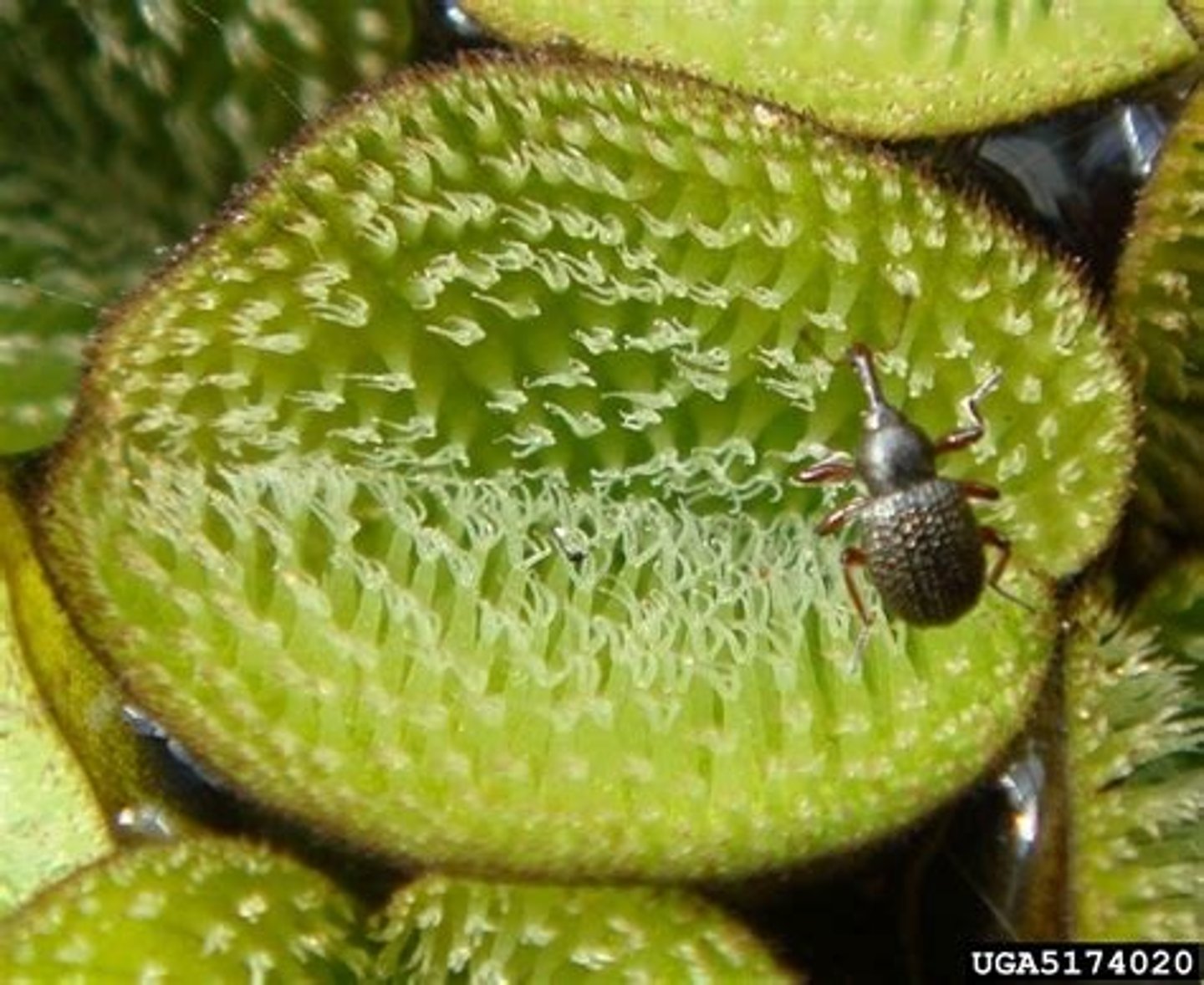
Biological Control
the intentional release of a natural enemy to attack a pest population
- Think of salvinia eating weavels

Chemical Control
Use of pesticides or herbicides to manage an unwanted organism(s) and invasive species
Chlorophyll a
A photosynthetic pigment that participates directly in the light reactions, which convert solar energy to chemical energy.
Competition
simultaneous demand for limited resources that impacts the fitness of the interacting species
- Interference competition
- Exploitation competition
Cyanobacteria/ cyanotoxins
(formerly blue-green algae) produce toxins that are lethal to fish, invertebrates, and even humans
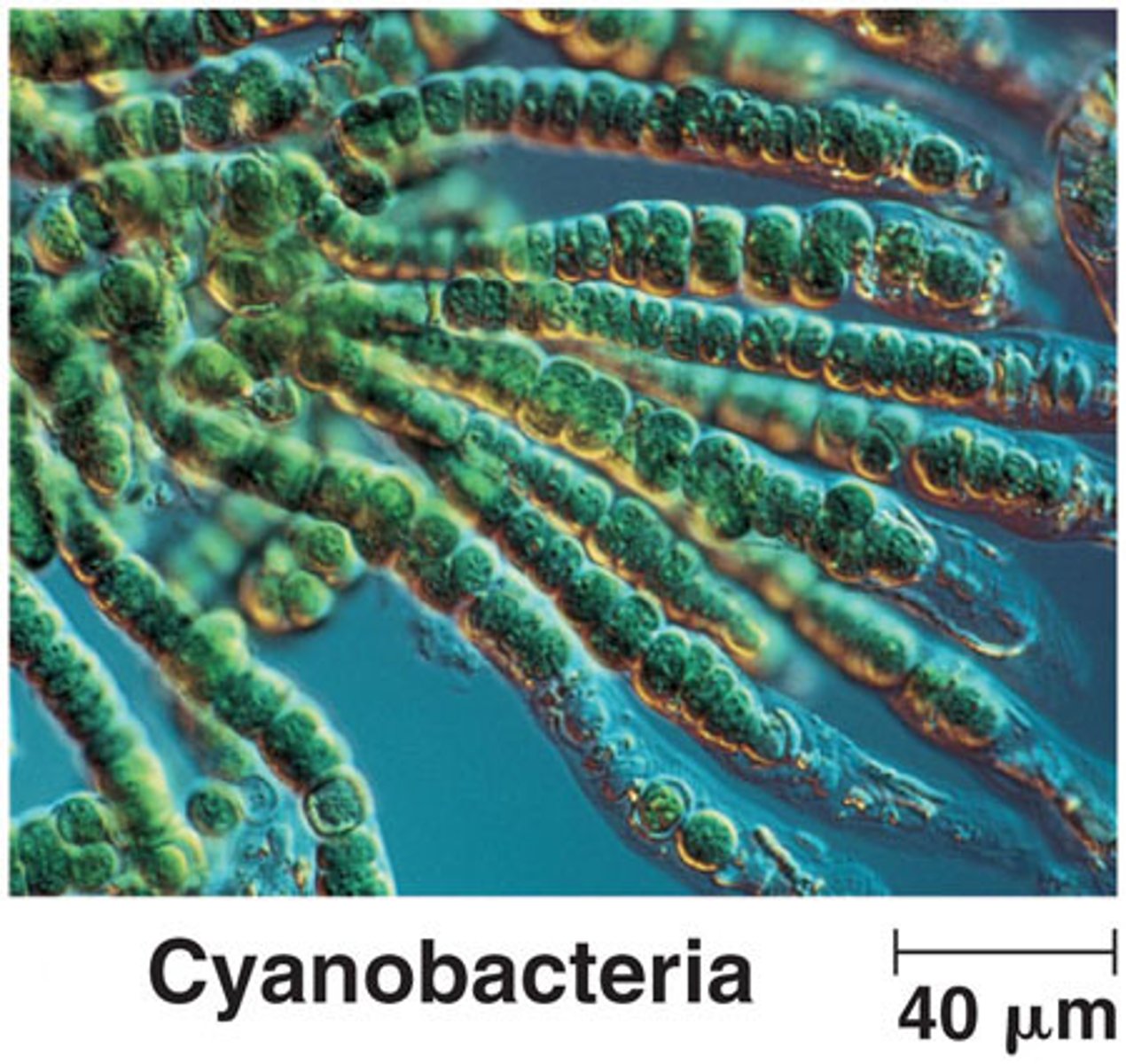
- hepatotoxin
- neurotoxins
Example of an microcystin and an anatoxins
Hepatotoxins attack to liver
Neurotoxins attack the nervous systems
Which toxin attacks the liver and which attacks the nervous system?
Dirunal
active during the day
- usually when algae densities are high
Dynamic equilibrium
eventually the concentration of a chemical in the environment will be equal to that in an organism. If an organism moves to a "clean" environment, it will eventually eliminate the chemical from its tissues
Dead zones
In a body of water, an area with extremely low oxygen concentration and very little life
- happened in the Gulf of MEXICO because farmers in Midwestern states apply high levels of nitrogen and phosphorus to fertilize crops
Interference competition
direct interactions between individuals
Exploitation competition
indirect competition through use of shared resources
Cultural Eutrophication
an increase in fertility in a body of water, the result of anthropogenic inputs of nutrients. Nutrients from agriculture and livestock production in the watershed
eDNA
environmental DNA
genetic material from organisms that has been shed into the environment. It can be found in water, soil, air, and other places.
eDNA can help detect invasive species that might be hard to find because they are present in low numbers. Specifically the presence of Silver and Bighead Carp in the lower Des Plaines River below the electric barriers, also positive hits in Lake Erie
Elimination
removes chemicals from organisms, and the breakdown of chemicals into excretable forms (metabolites) is part of our metabolism.
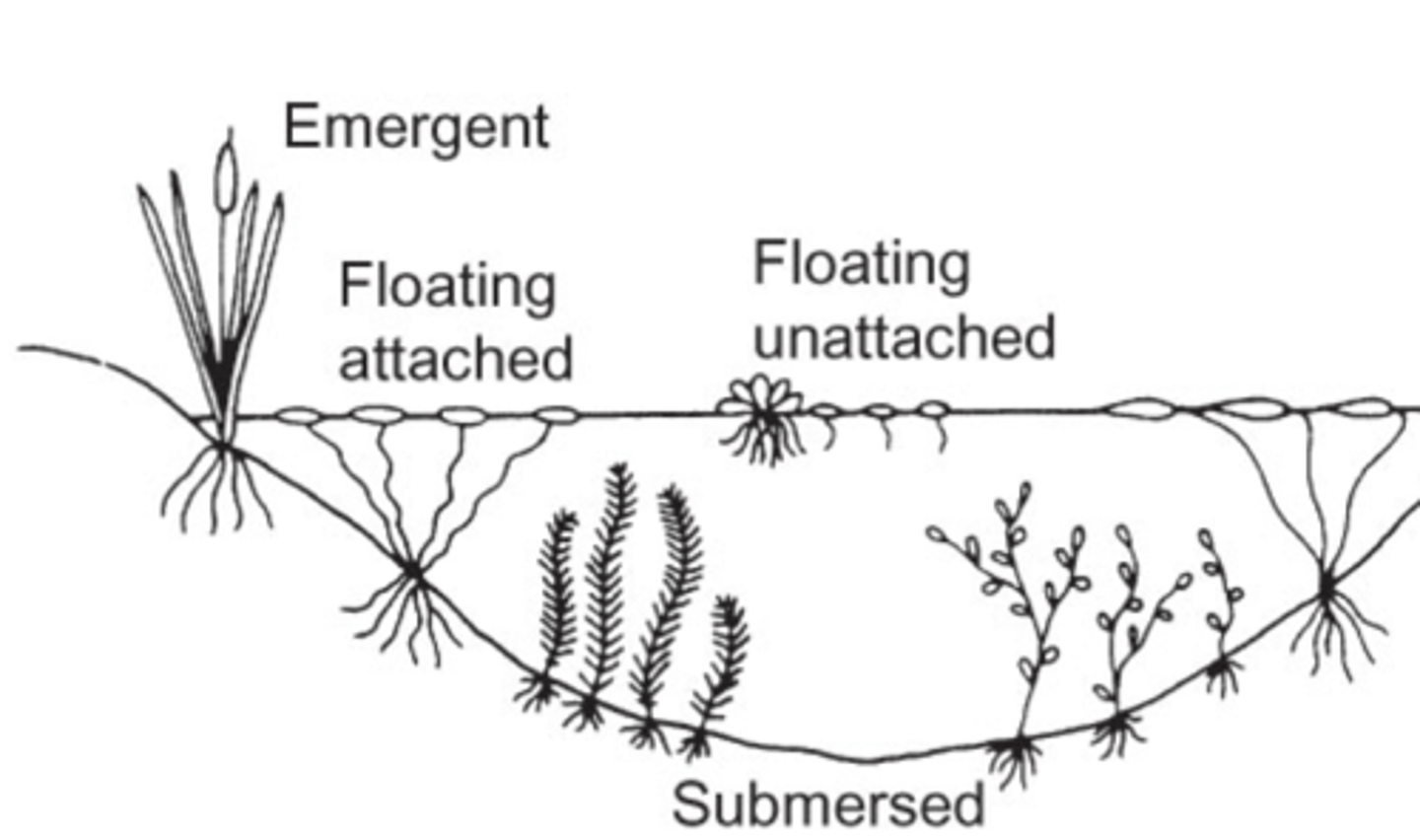
Emergent Plants
Aquatic vegetation that is rooted on the bottom but has leaves that float on the surface or protrude above the water.
- purple loosestrife
- Lotus

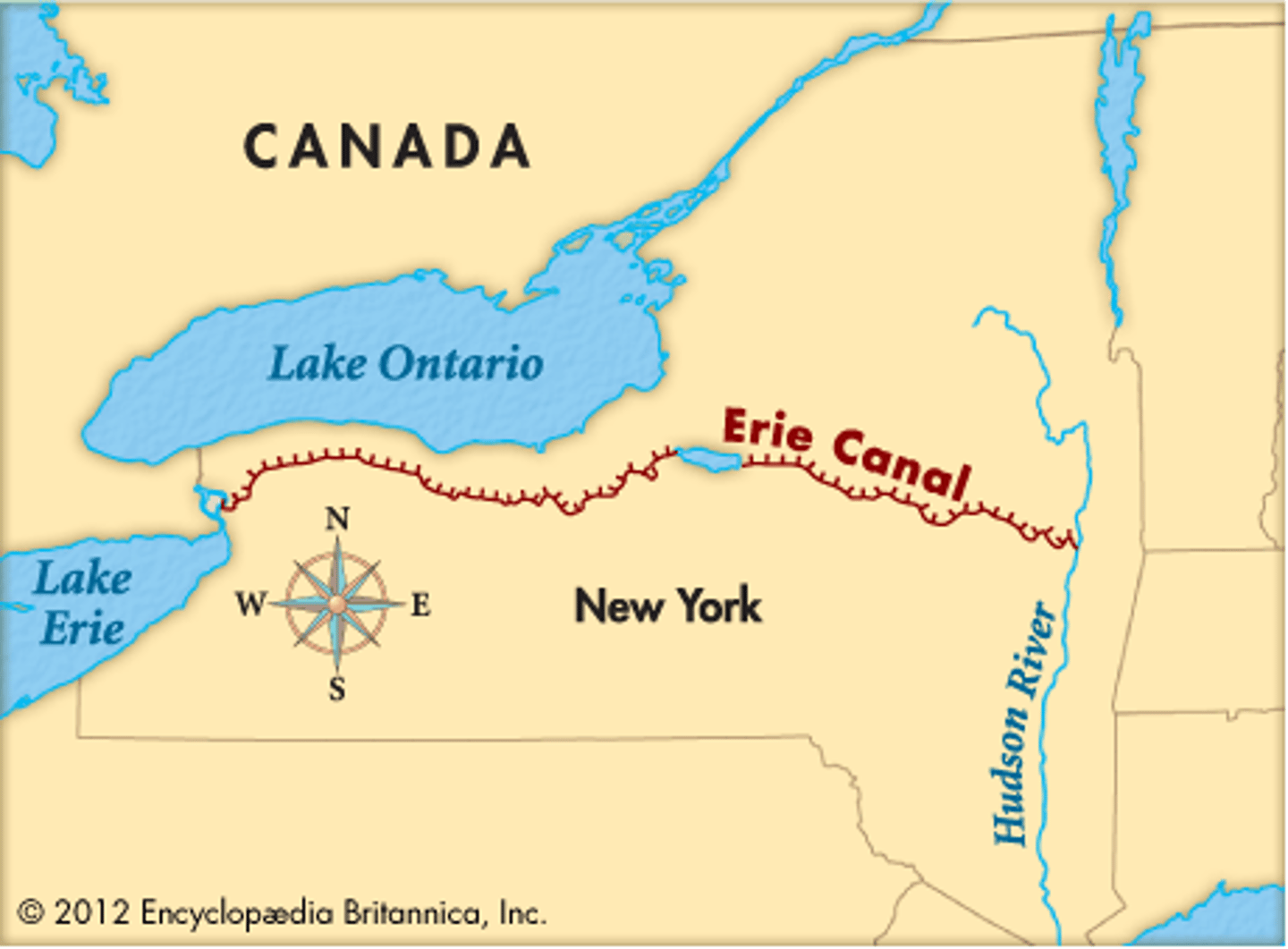
Erie Canal
an artificial waterway connecting the Hudson river term-0at Albany with Lake Erie at Buffalo
Eutrophic
Describes a lake with a high level of nutrient productivity

Generalist Species
species with a broad ecological niche
- deer
- apple snails
- phythons
- raccoon
- peigons
Hydrology
the study of water and its effects on and in the earth and in the atmosphere
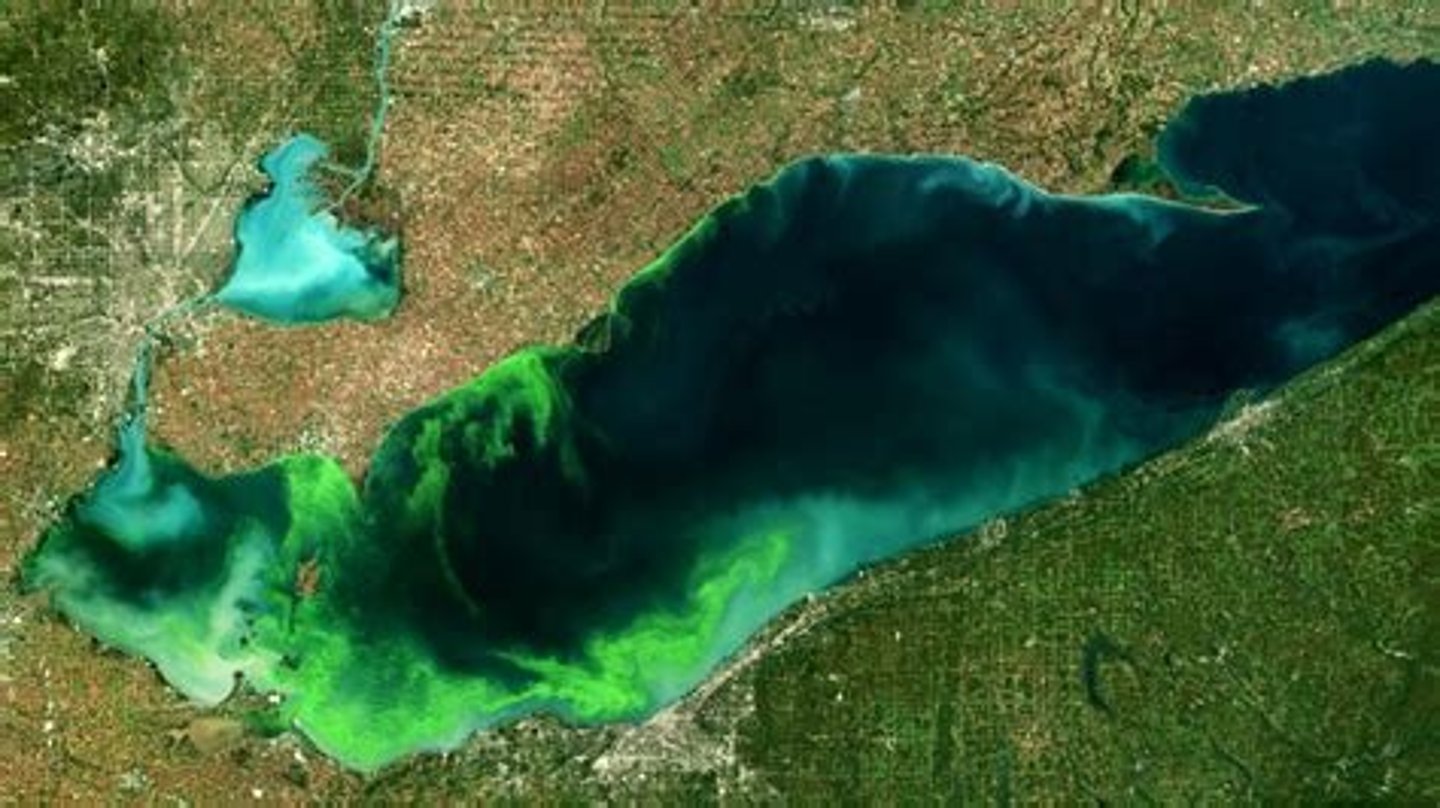
Hypereutrophic
Hypereutrophic lakes are very nutrient-rich, with high levels of algae and chlorophyll.
- best seen in Lake Erie
Hypoxia
Low oxygen saturation of the body, not enough oxygen in the blood
- what fish in eutrophic lakes experience as more oxygen is taken up by algae, leaving the water with less oxygen
Apoxia
no oxygen, zerooooooo
Instar
The larval insect developmental stage, one of the three larval stages of insect development
- Sea Lamprey
- Purple Loosestrife
- Curly pondweed
- water chestnut
- watermilfoil
Invasive (alien) species examples in the Great Lakes
Lacustrine
another word for lakes
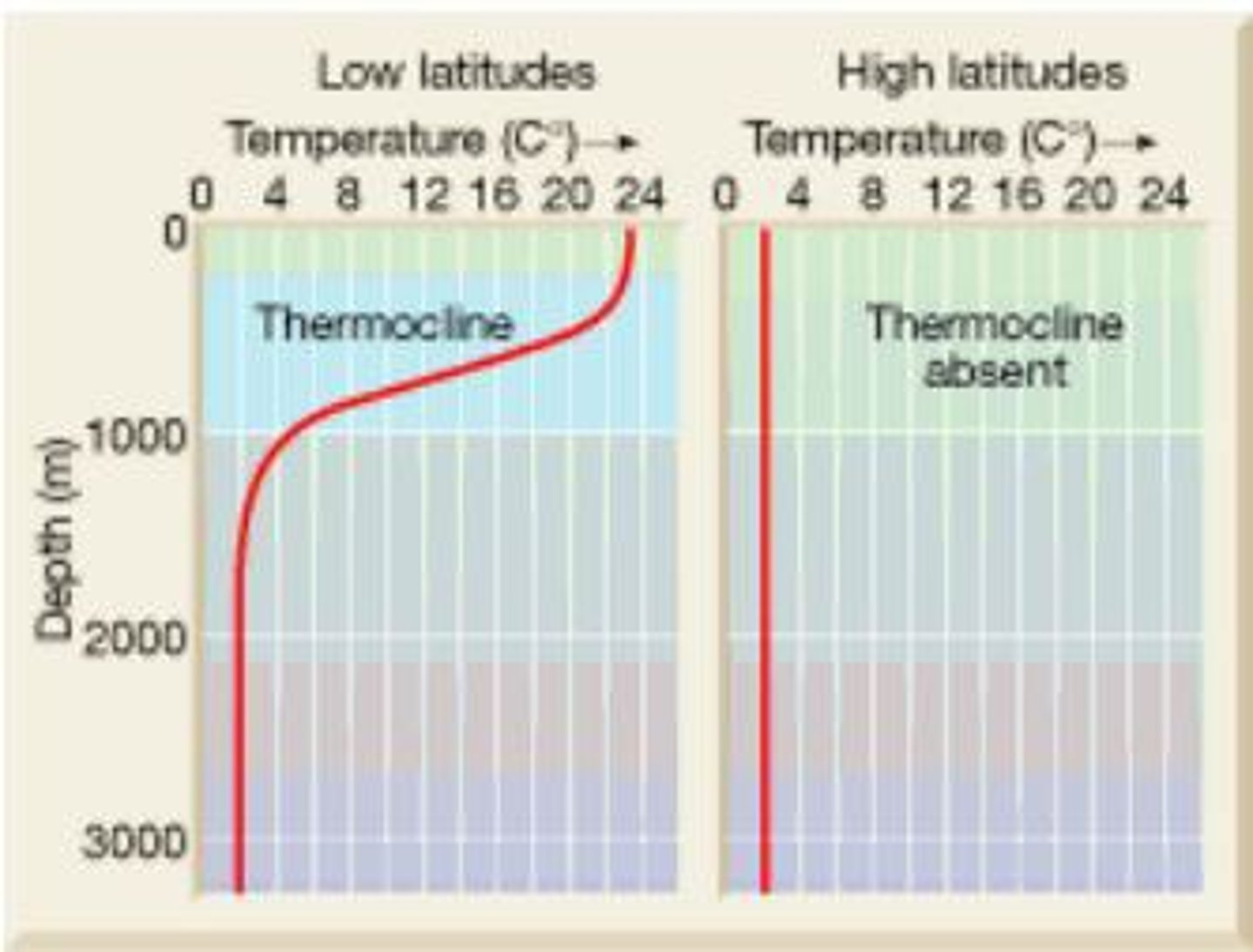
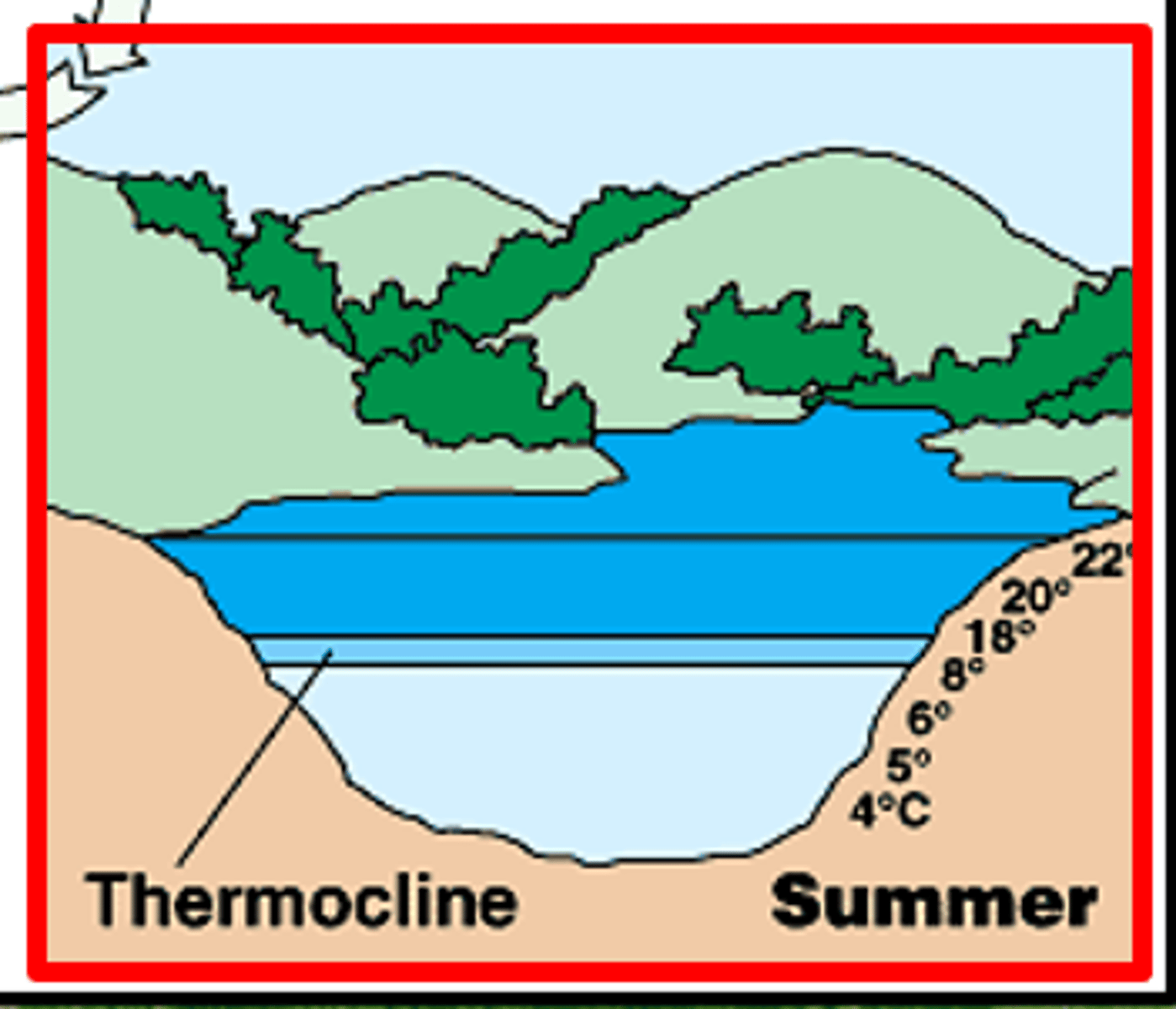
Lake Mixing Cycle
an annual process dependent on water temperature (density) and wind strength; turnover, stratification
https://youtu.be/2ONLSxqVtP0?si=nZ2GAtuMOS0WMj3V
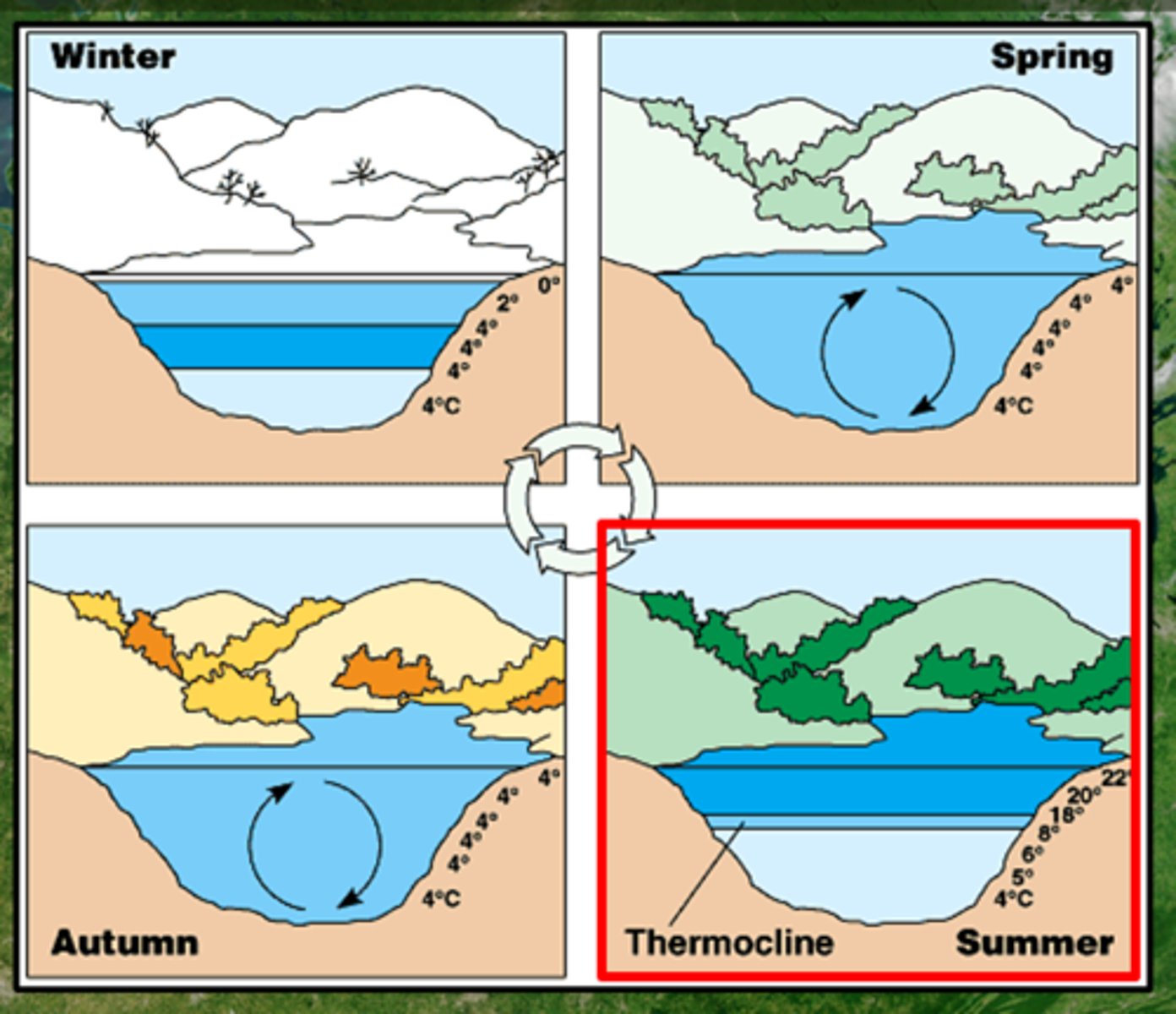
Stratification
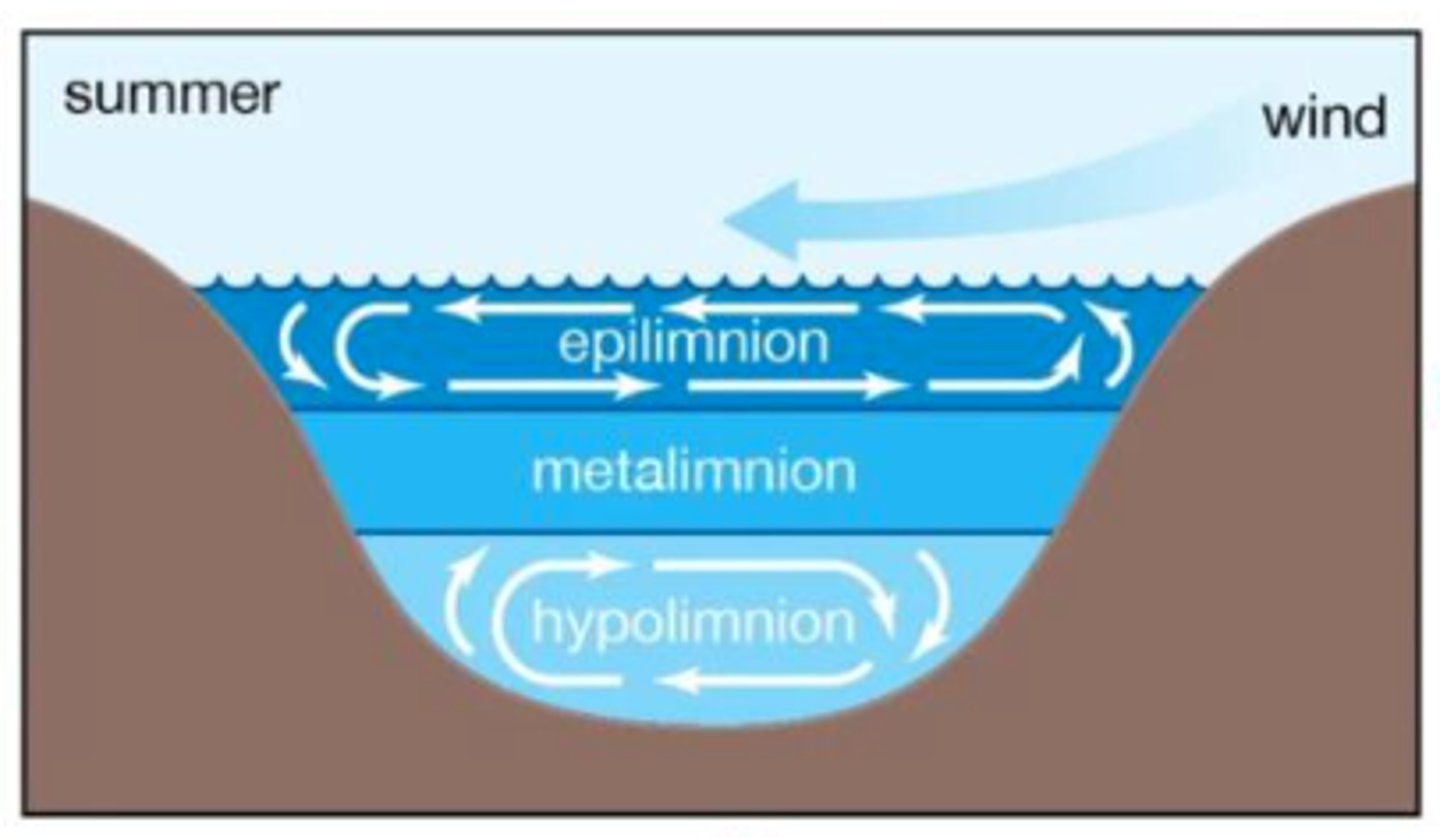
During summer and winter, where the different layers of a lake have different temperatures
high P loading → algal blooms → decomposition → hypoxia
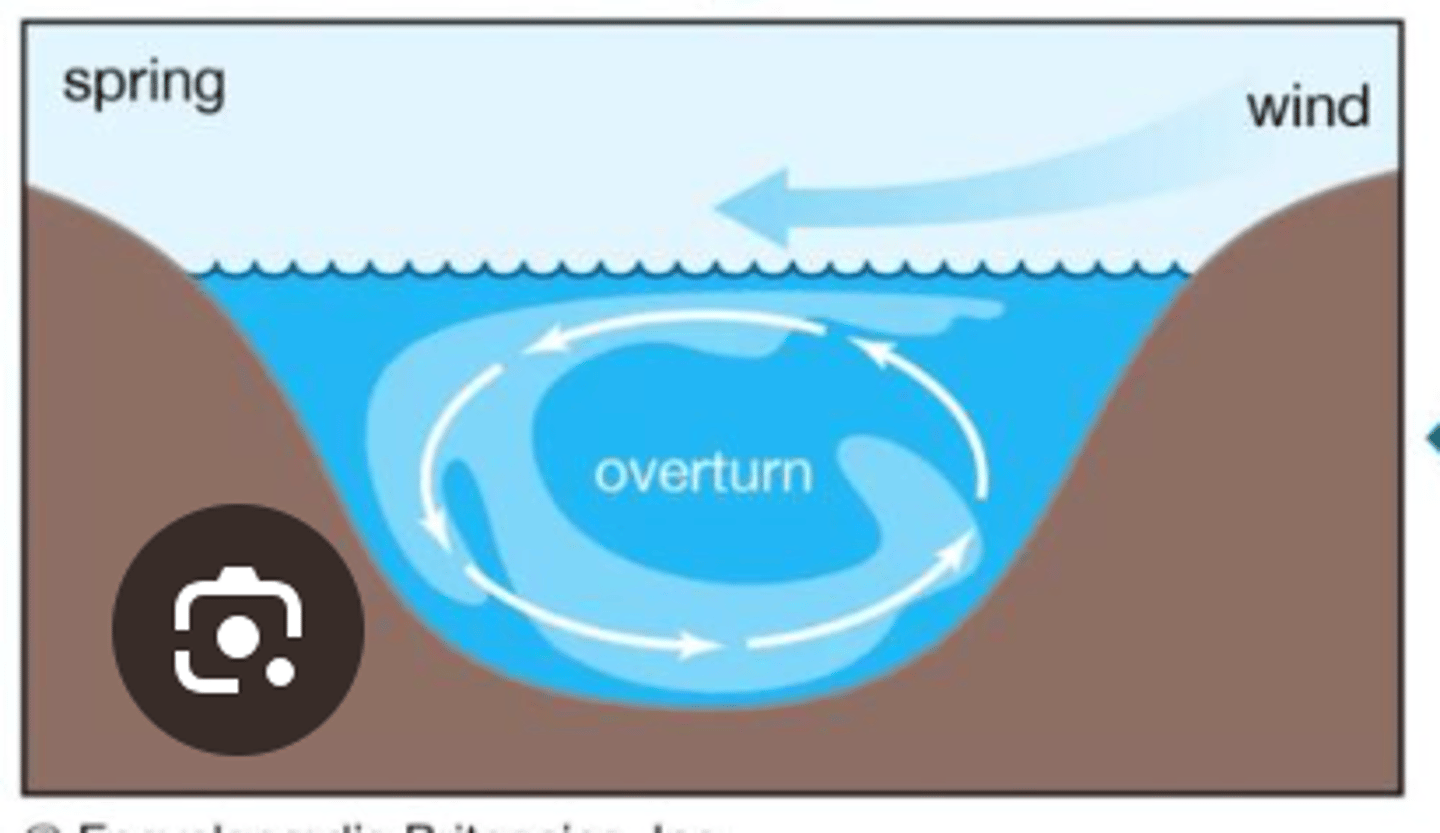
Turnover
In Fall and Spring when all of the layers of the lake are similar to identical temperatures, which allows the sediments at the bottom of the lake to mix with the sediments from the top layer
- epilimnion
- metalimnion (thermocline)
- hypolimnion
- monimolimnion
Lake Zones
Amictic
lakes that never mix
- Particularly in the Arctic
Meromictic
Describing a lake that doesn't mix completely, only partially
Monimolimnion
Bottom layer of stagnant water in a meromictic lake that never is completely mixed, because winds are not strong enough to mix it
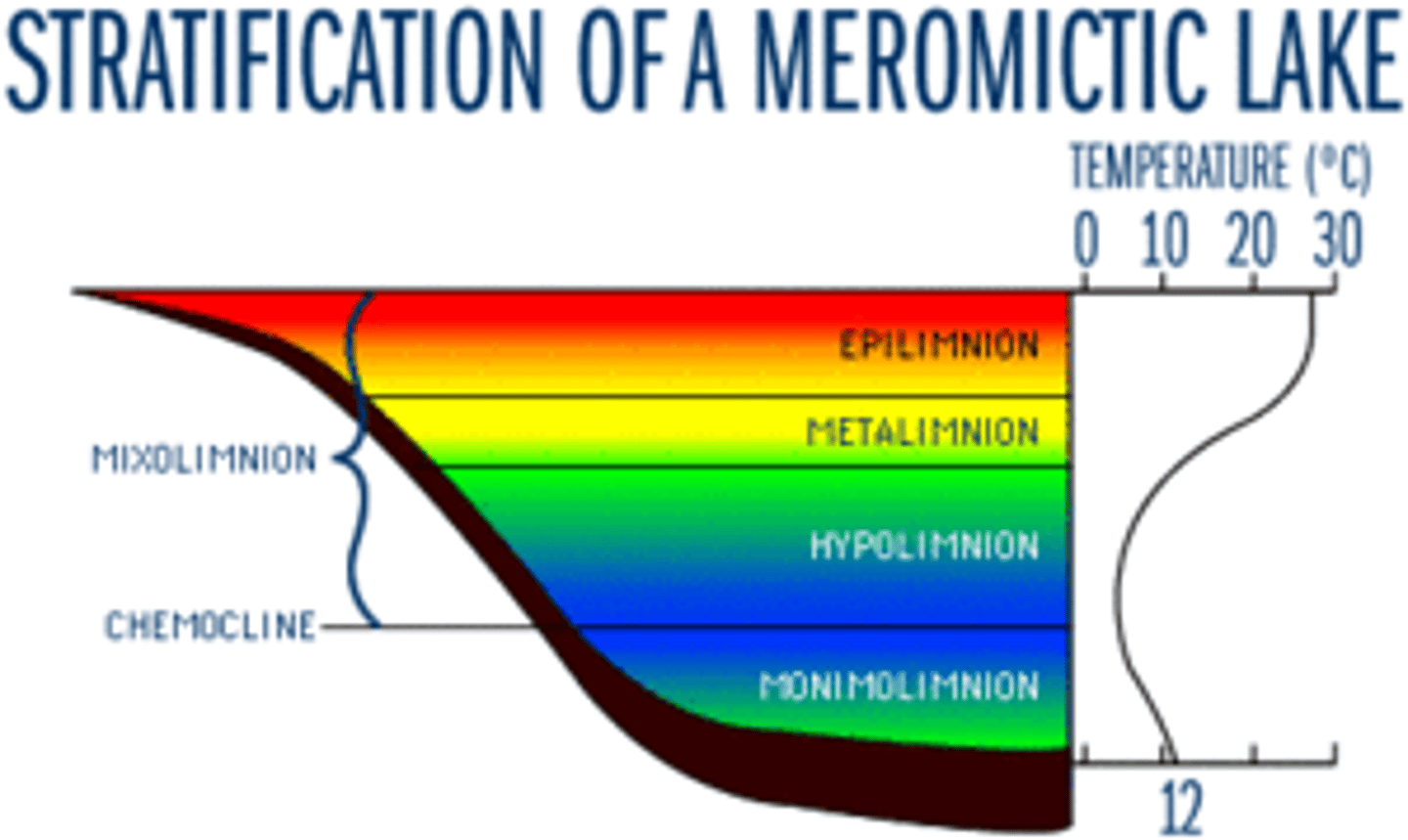
Holomictic
Lake mixes entirely at least once a year
Hydrologic divide
a body of water that separates the different land masses
Dimitic lakes
lake mixes twice a year
Limnology
study of freshwater ecosystems
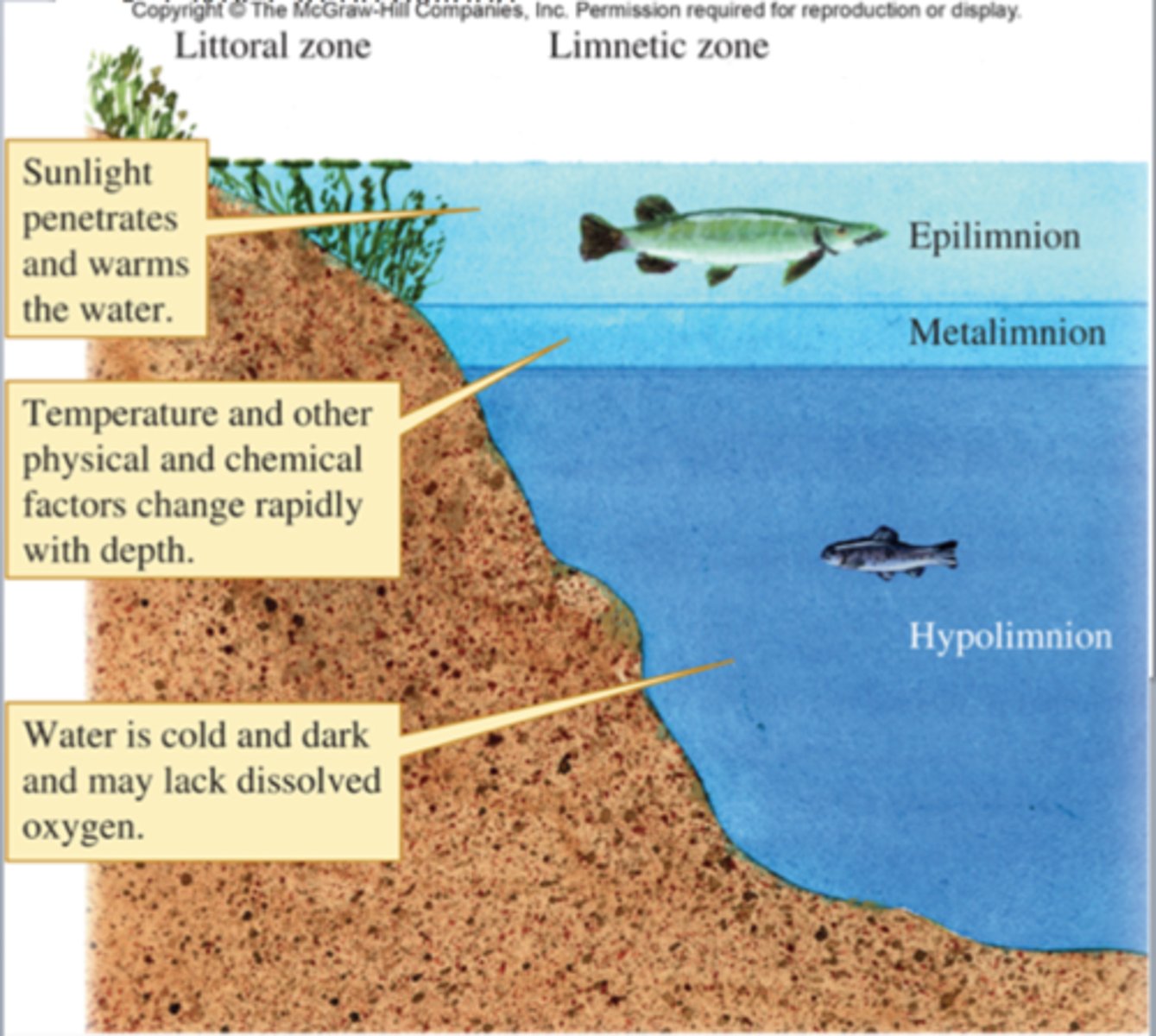
Epilimnion
An upper layer of warm water with high levels of dissolved oxygen
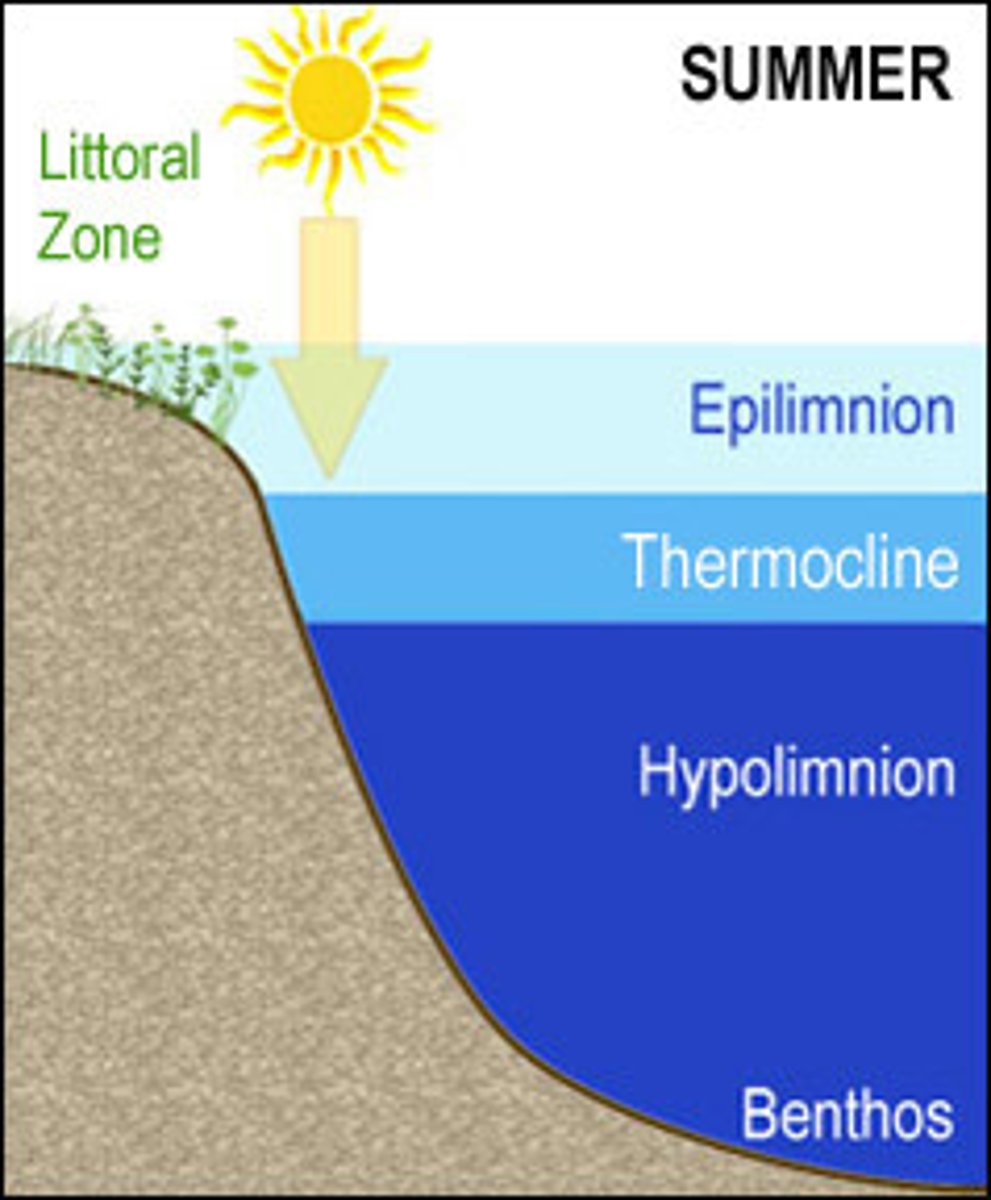
Metalimnion
middle layer in a stratified lake or other body of water where temperature changes most rapidly with depth, also known as the thermocline.
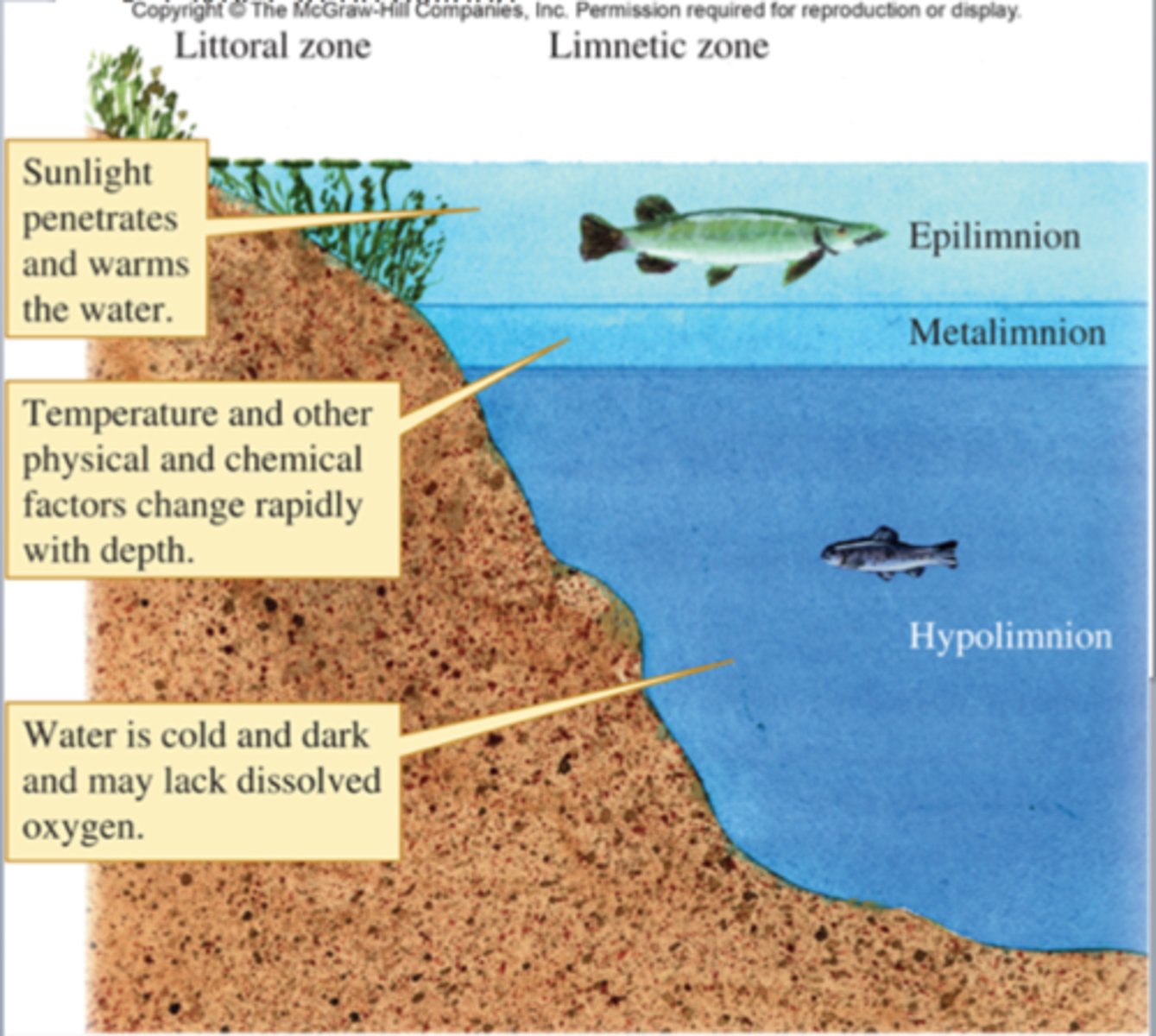
Thermocline
a layer in a large body of water, such as a lake, that sharply separates regions differing in temperature, so that the temperature gradient across the layer is abrupt.
Hypolimnion
the lower layer of water in a stratified lake, typically cooler than the water above and relatively stagnant.
John Muir
(1838-1914) Naturalist who believed the wilderness should be preserved in its natural state. He was largely responsible for the creation of Yosemite National Park in California.
Land-use mosaic
a landscape where different types of land use, like agriculture, forestry, urban development, and natural areas, are intermixed in a patchwork pattern, creating a diverse mix of land cover within a single region

Lipophilic
attracted to fats and lips such as oil
Littoral zone
the shallow edge areas that provide enough light for rooted plants to grow
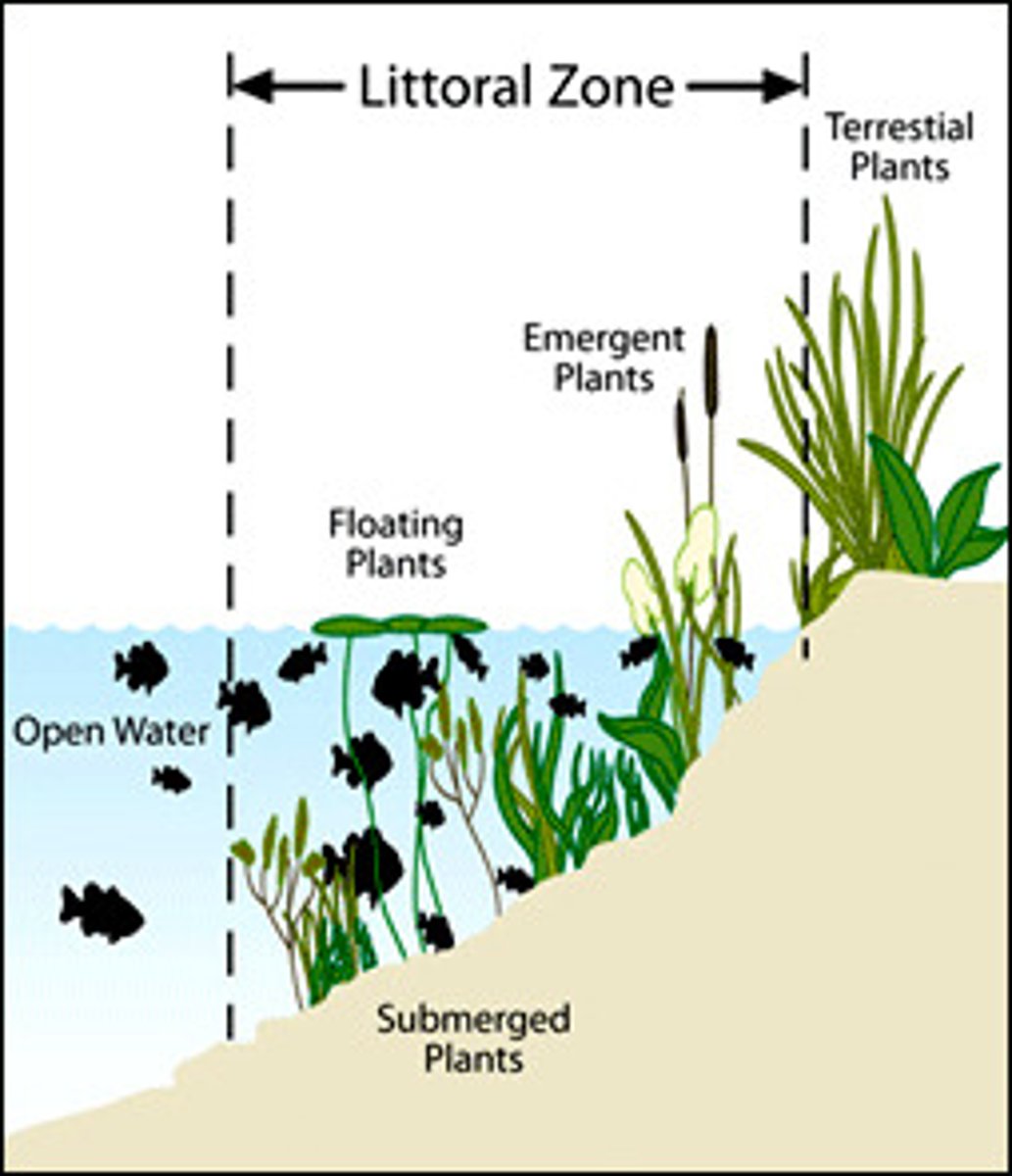
Macroinvertebrate
an organism without a backbone that can be seen without a microscope.
- a negative decline is seen in the great lakes as Typha x glauca water plants continue to invade the borders of streams and lakes
Macrophyte
A rooted or floating aquatic vascular plant.
- The invasive Curly pondweed
- Many fishes use macrophytes as cover, either to hide from predators, or to ambush prey.
Metabolite
a specific product of a substance, formed by chemical processes in the body that is water soluble and much more excretable.
- amino acids
- lactic acid
- ethanol (alcohol)
- carbon dioxide
quickly
If a chemical is water soluble (hydrophilic) it tends to be excreted _________ by organisms.
This is because it is not stored to a great extent in tissues
Mesotrophic
Describes a lake with a moderate level of productivity
Niche
an organism's particular role in an ecosystem, or what it does/needs to survive
N-dimensional hypervolume (G. E. Hutchinson)
Analytical model that shows multiple dimensions to a species niche
- helps determine what conservation focus is needing to conserve a species

Oligotrophic
a condition of a lake or other body of water characterized by low nutrients, low productivity, and high oxygen levels in the water column.
Periphyton
The film of algae, diatoms, bacteria, and organic material that coats most hard surfaces underwater, that is an important macroinvertebrate food source.

Pheromone
A chemical released by one animal that affects the behavior of another animal of the same species.
- Pheromone traps are used to catch Sea Lamprey
P Loading
The amount of phosphorus that enters a body of water over a specific period of time. It can come from external sources, like rivers and streams, or internal sources, like sediment in the lake.
- allows for algal blooms to grow excessively
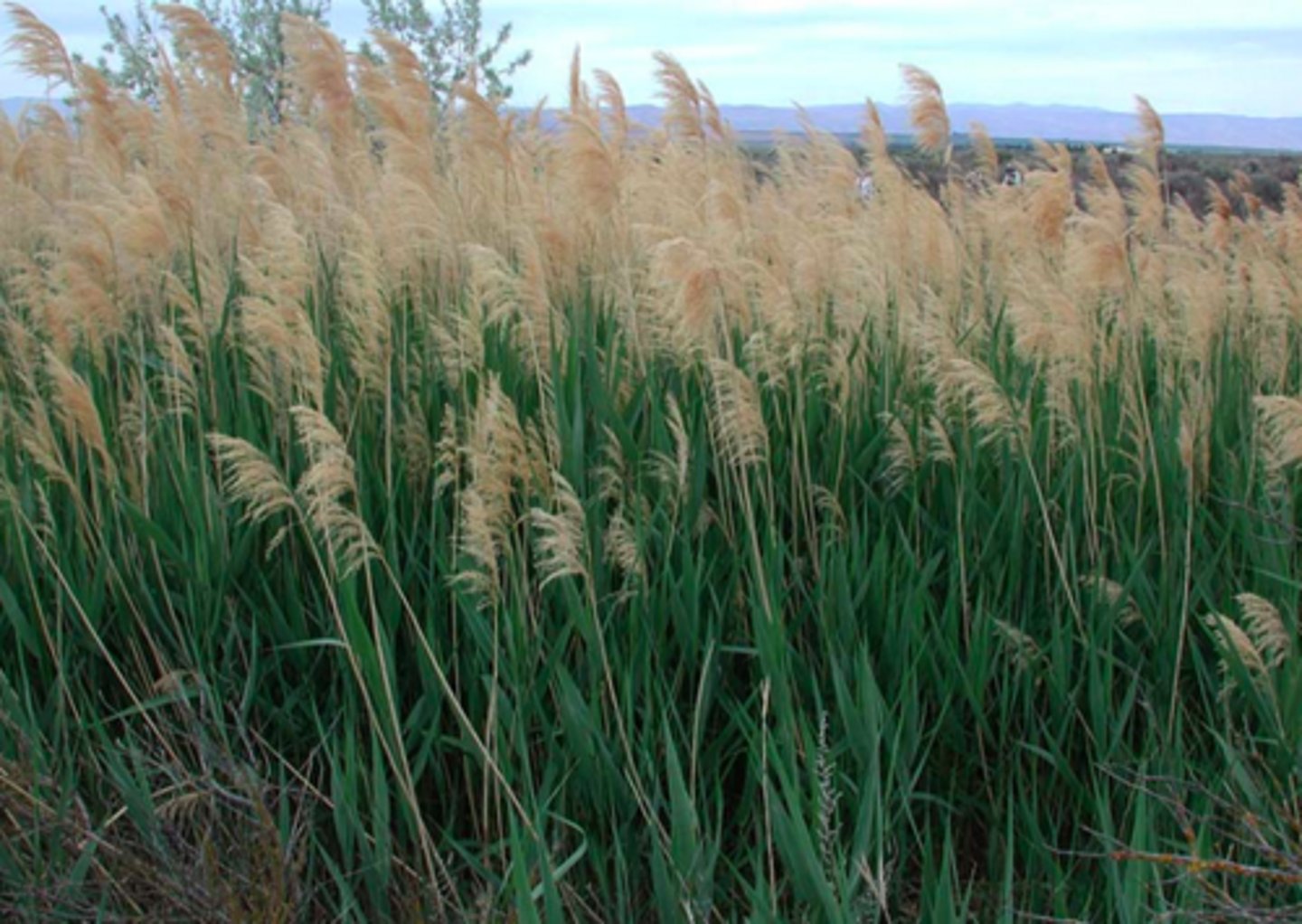
Phragmites australis
The invasive common reed, likely introduced with soil ballast; highly aggressive, multiple reproductive modes, extirpation of native Phragmites species

Planktivorous
describes an organism that eats plankton
- the Silver Carp

Piscivorous
fish eating
- Common Loon
- Red-throated
- Ring-bellied Gull
- Red-breasted Merganser
- Horned Grebe
- Lake Sturgeon

Predation
An interaction in which one organism kills another for food.
- used in biocontrol
Point Source
A specific source of pollution that can be identified
- a pipe
Non-point source
pollution that does not have a specific point of origin
- agricultural run off
- individual cars driving
R-selective species
Live short amount of time, adapt easier, lots of offsprings, die younger, small body size, bad parental care
- invasive species are usually R-selective species
- they usually live in unstable environments
K-selective species
A species with a low growth rate due to small number of offspring; provides high parental care and most offspring are expected to survive to maturity
- usually negatively effected by r-selective invasive species
- thrives on stable environments
dN/dt = rN (K-N)/K
What is the model of population growth formulas?
Density-independent mortality
mortality is independent of population density (random/stochastic). Like bunnies or raccoons, tje death rate can be super high because they reproduce more quickly to replace the ones lost.
Density-dependent mortality
as population density increases, the rate of mortality increases. Like elephants or whales that have fewer young because they tend to live longer.
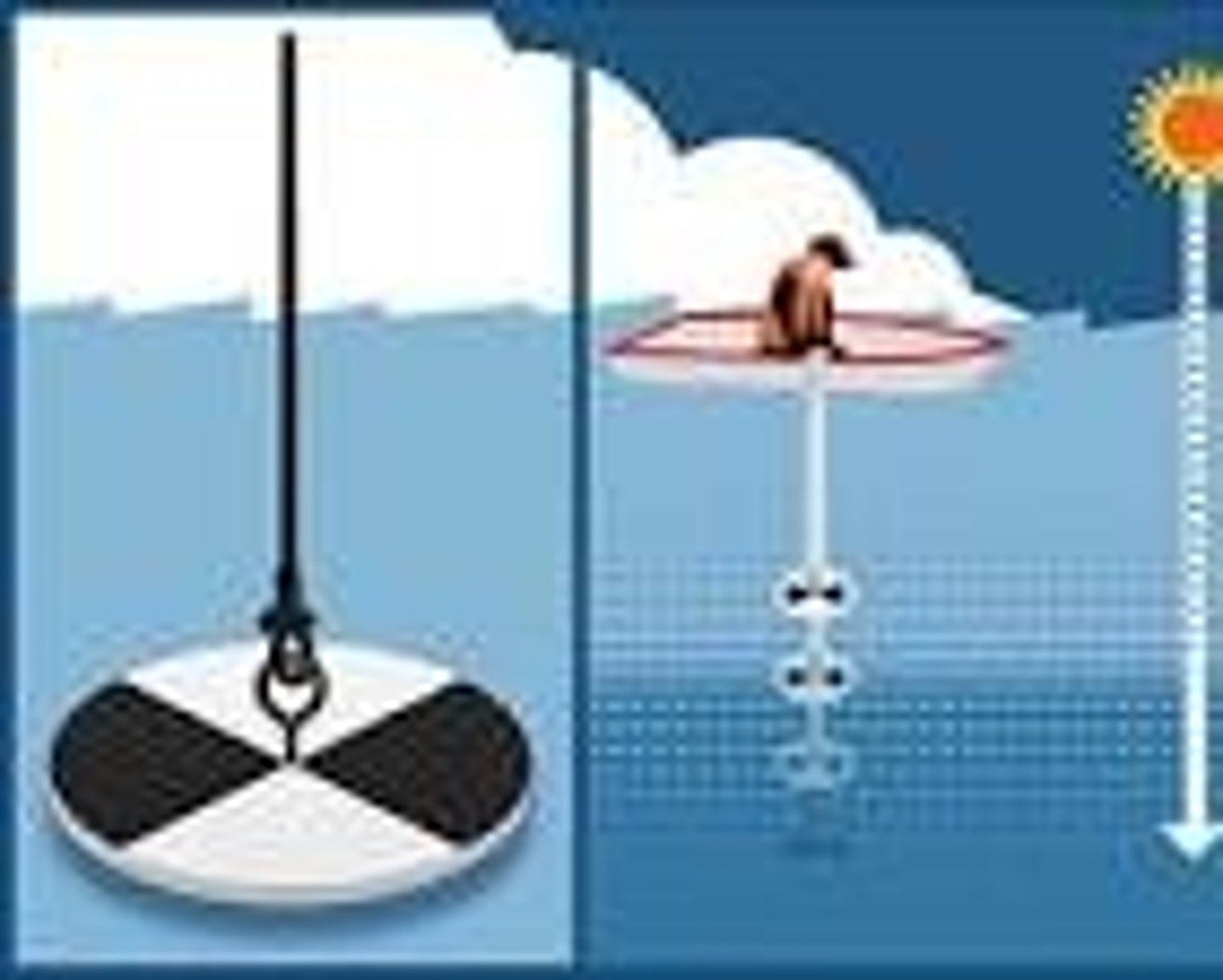
Secchi depth
a measurement of water clarity, or turbidity, that indicates how far light can penetrate into water. It's measured by lowering a weighted disk into the water until it's no longer visible
Summer Stratification
warm temps in spring and summer create stratification because warmer lighter water stays on top
high P loading → algal blooms → decomposition → hypoxia
TFM and Bayluscide
Chemical Control of Sea Lamprey
TFM = 3-Trifluoromethyl 4 nitrophenol

Trophic State
The total weight of biomass in a given water body at the time of measurement.

Uptake
rate of absorption of a radionuclide into an organ or tissue through the process of Biomagnification
Vectors
An organism that transmits disease by conveying pathogens from one host to another
Watershed
An ecosystem where all water runoff drains into a single body of water
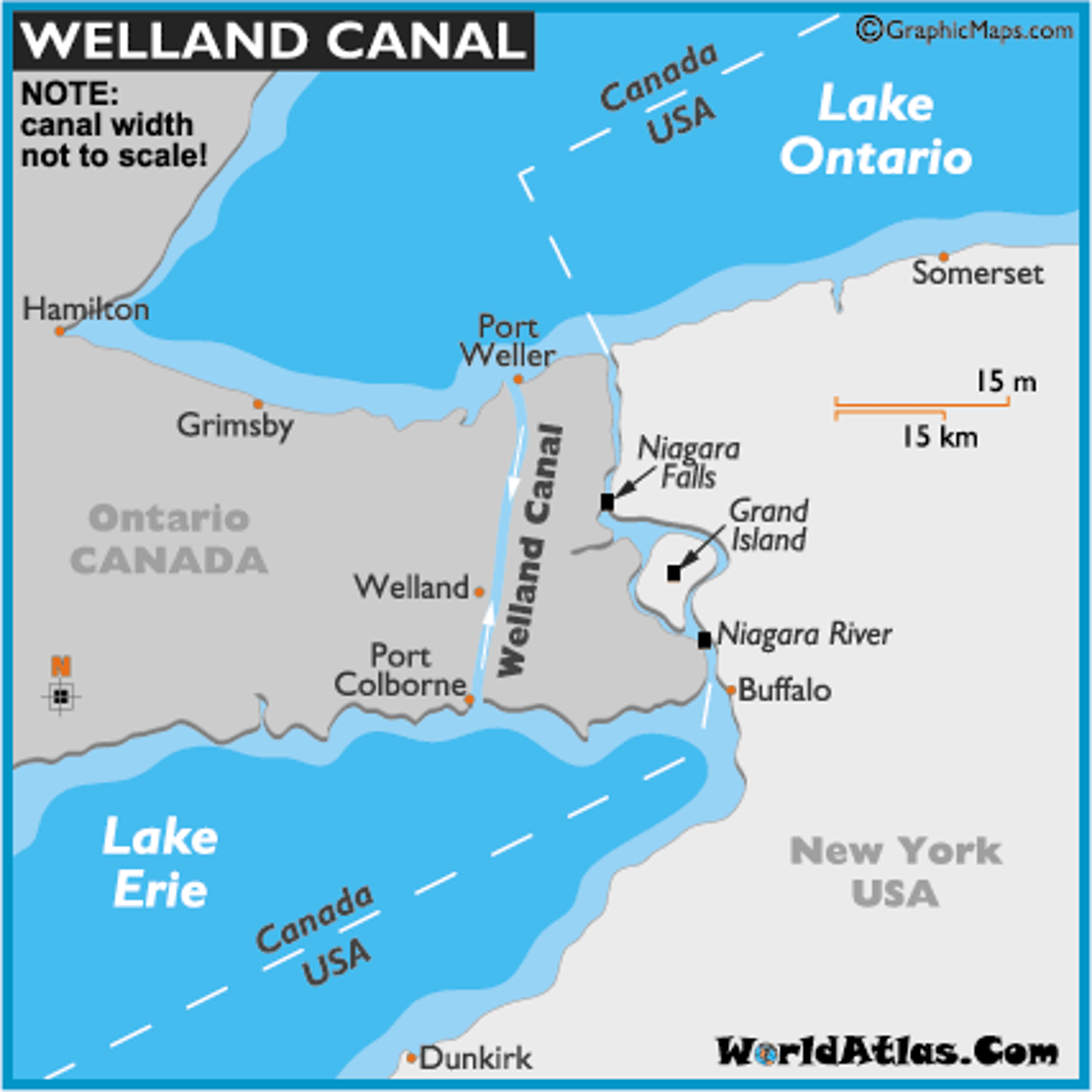
Welland Canal
Connects all the Great Lakes with the Atlantic Ocean; part of the St. Lawrence Seaway
Zooplankton
microscopic animals that swim or drift near the surface of aquatic environments
- bigger than photplankton
- is prey for:
. fish
. whales
. jelly fish
. arrow worms

Parthenogenetic
asexual reproduction of populations that exists entirely of females that produce more females from unfertilized eggs
- bees
- wasps
- ants
Corona
has hairs (cilias) that they trash around to create a current that brings food particles to their mouths
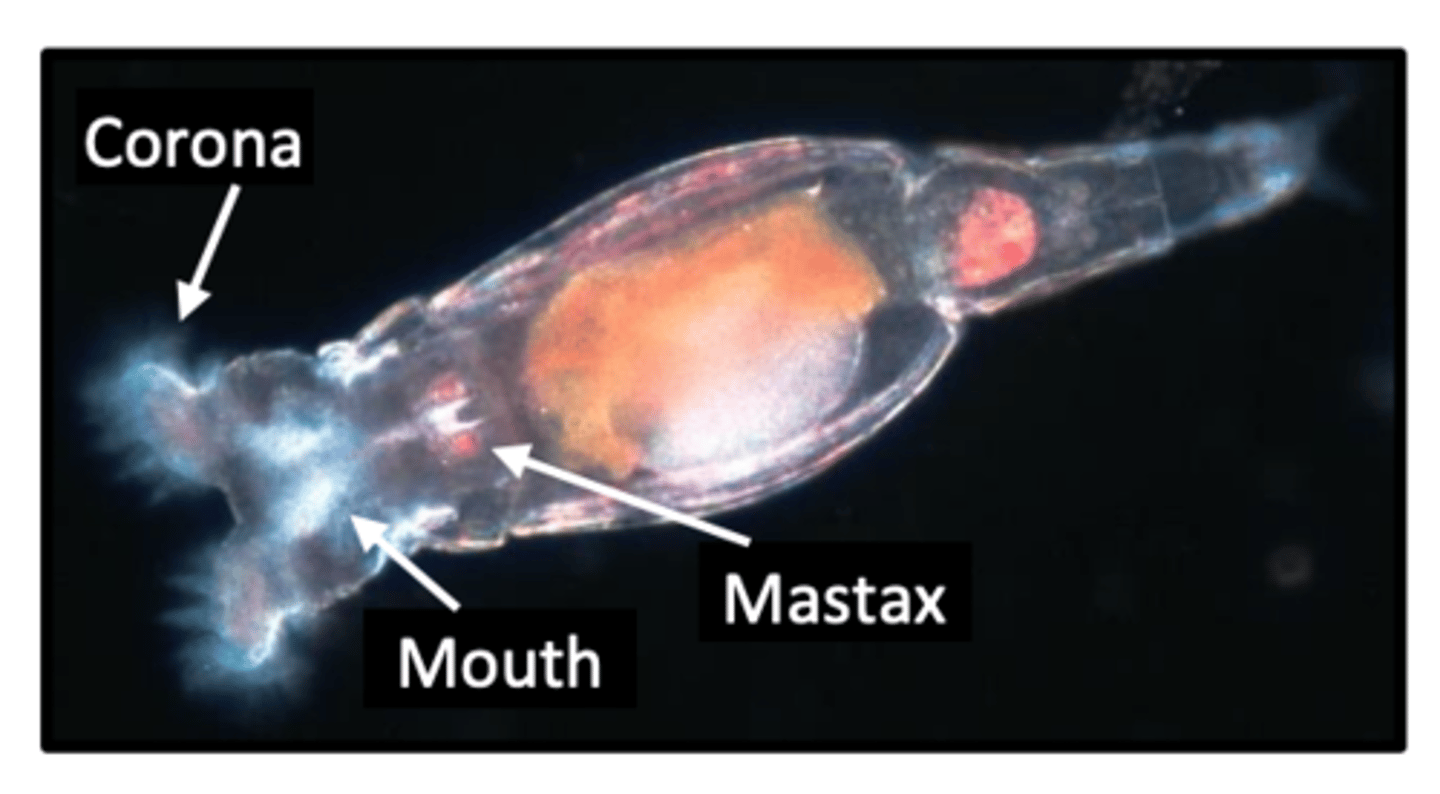
Mastax
the stomach of parthenogenetics
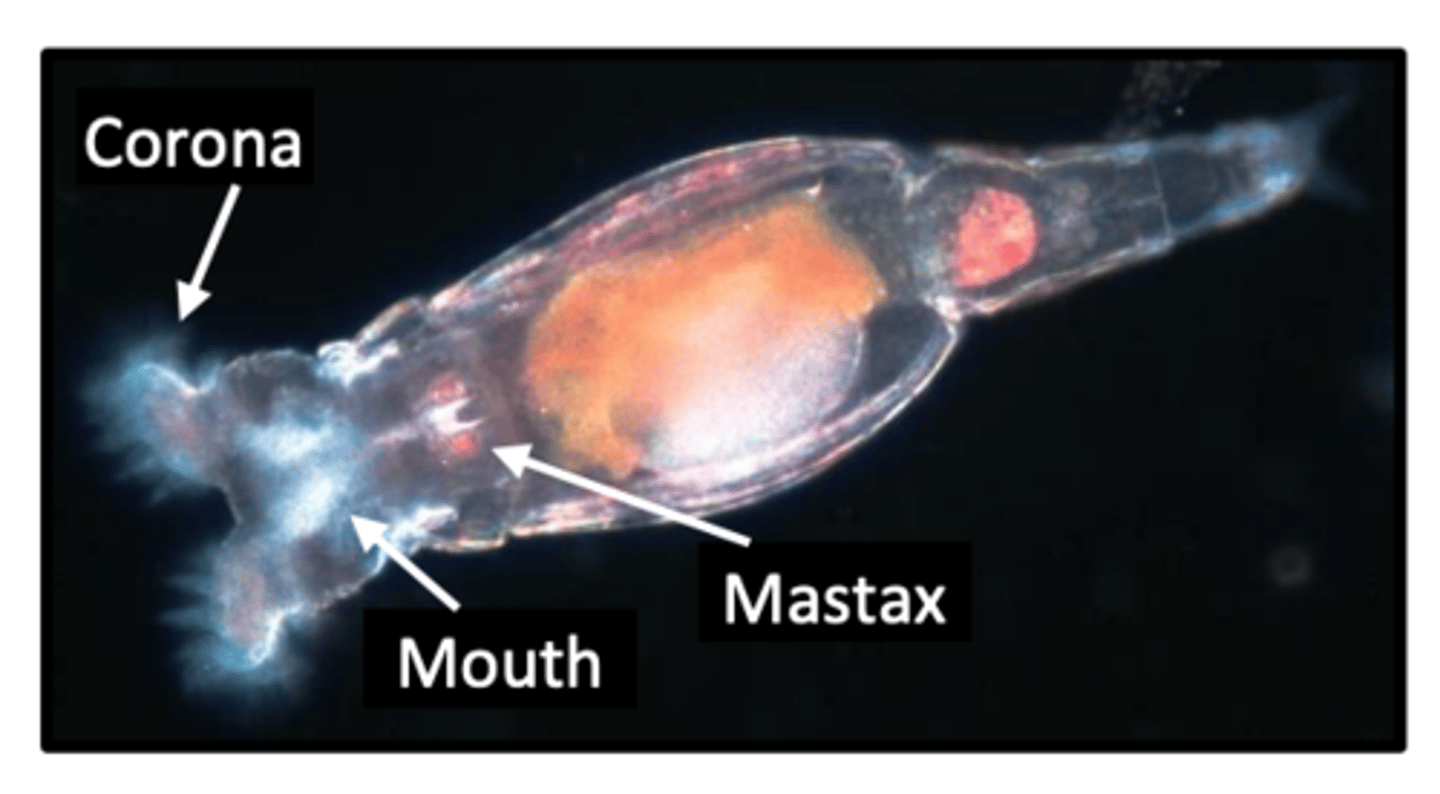
Trophi
the teeth of parthenogenetics
Detritus
Dead organic matter
Ephippia
1-3 eggs and sink to the bottom when they are released by the female with an extra shell layer.
Copepods
minute shrimp-like crustaceans; often they are the most common zooplankton in estuarine waters
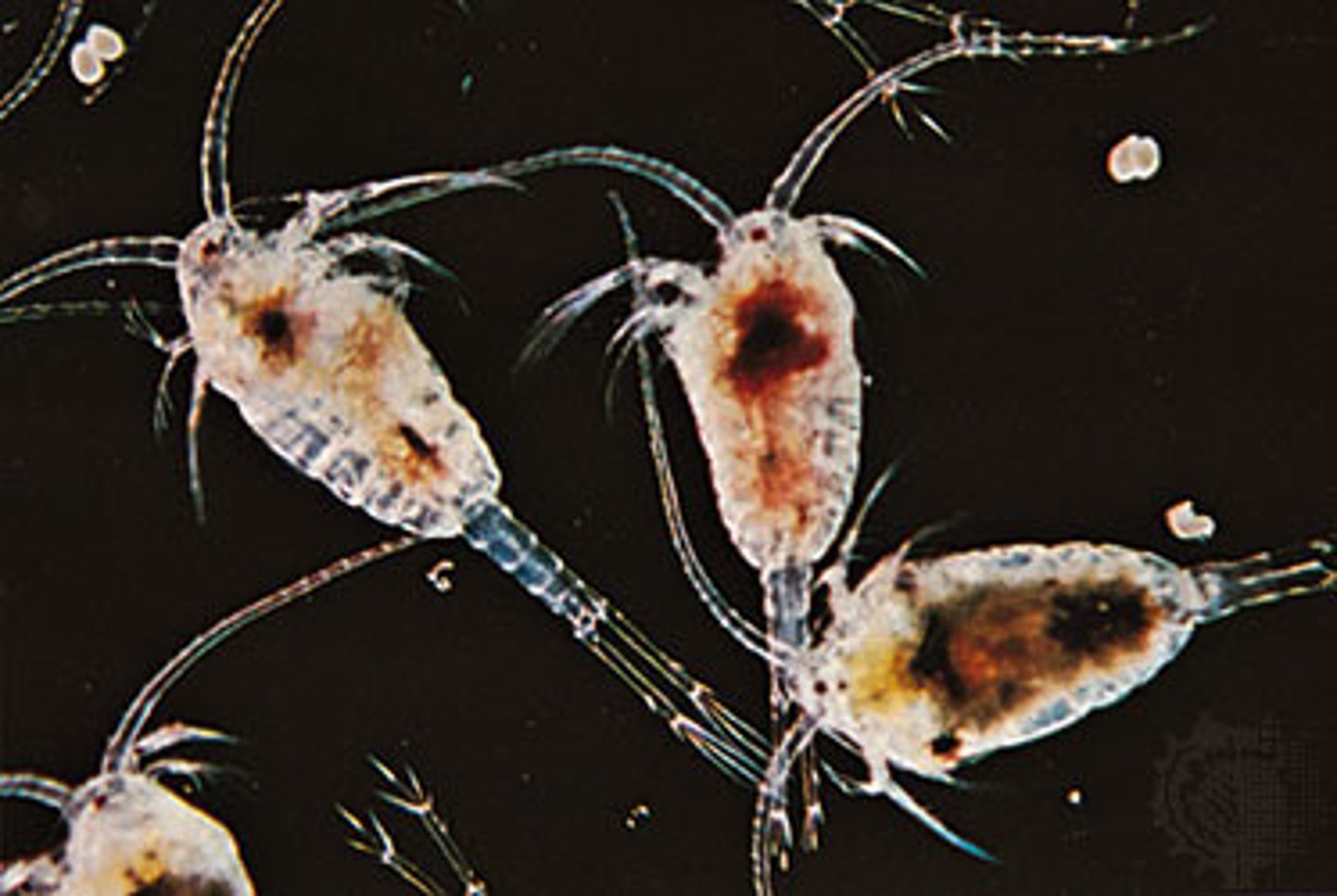
1st antennae
allows copepods to be strong swimmers