Module 5: Cities and Citadels of Bronze Age Greece
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Apotropaic
An object is believed to have the power to turn away evil
Metonymy
when a piece of something us used to represent the whole
Ashlar Masonry
Blocks of cut stone with crisp edges; Rubble wall construction
Citadel
A fortified city/town
Cyclopean masonry
massive, irregular stone fitted together without the use of mortar
Megaron
A square or oblong room with a central heart and usually four columns to support the roof
Minian
Early Greek civilization known for extensive trading networks across the Mediterranean Sea; The first maritime empire, 3000-1200 BCE; Temple/Palace at Knossos, Crete, Greece, 1600 BCE
Mycenaean
Warring civilization, rising after the fall of Minoans; mythologized in the epics of Homer; Lion Gate, Citadel of Mycenae, Greece, 1300 BCE; Tomb of Atreus, Mycenae, 1250 BCE
Palace at Knossos
Greece, 1600 BCE

Citadel of Mycenae
Greece, 1300 BCE
Lion Gate at the Citadel of Mycenae
Greece,1300 BCE

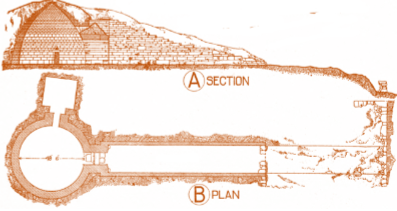
Tomb of Atreus
a bee-hive shaped tholos tomb that exemplifies the architectural sophistication of Mycenean royal burials; Mycenae, Greece,1250 BCE
King Minos
Ruler of ancient Crete, associated with Minoan civilization, famed in Greek mythology for commissioning the Labyrinth to imprison the Minotaur
Homer
ancient Greek poet; believed to have lived around 750-700 BCE; composed the epic poems The Iliad and The Odyssey
Virgil
a Roman poet; wrote the Aeneid, an epic that links Rome's origins to the heroic legacy of Troy
Odysseus
Legendary Greek hero and kind of Ithaca, mythical figure, cantral role in Homer's Odessey
Polyphemus
One eyed cyclops from Greek mythology, from Homer's Odyssey as the giant who traps and is eventually outwitted and blinded by Odysseus
Atreus
legendary king of Mycenae and father of Agamemnon; associated with the monumental "Tomb of Atreus"
Who excavated the Minoan city of Knossos?
Sir Arthur Evans
What did the ancient Greeks guess the ruins of the palace of Knossos might have been?
The palace of king Minos and the labyrinth that housed the Minotaur
What took place in the central court of Knossos?
Public ceremonies and social gatherings
What took place in the “throne room” of Knossos?
Religious ceremonies
Mycenaean society was known for being peaceful?
False
What was the central feature of Mycenaean citadels?
the megaron
What kind of tomb is the Tomb of Atreus?
Bee-hive tomb: tholos shaped like beehive; grave goods placed in tholos
How was the interior space of the Tome of Atreus created?
corbelling: blocked stone to form arcs/dome