Routes of administration- ENT + eye
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
How are drugs usually delivered to the ear?
Topically, where the drug penetrates the middle ear through the tympanic membrane
What instructions should be given to patients when applying medicines topically to the ear?
To lie down or remain still after application, or the product will just pour out
What is corneal angiogenic privilege?
The active maintenance of a transparent state in the eye, preventing blood and lymphatic vessel growth
Why don’t drugs reach the cornea of the eye via systemic circulation?
In a healthy cornea there is little blood supply to the cornea to maintain transparency of the eye/sight
How are the majority of drugs applied to the eye?
Topically
what is the role of the meibomian glands?
To secrete a lipid layer to keep the eye moist (by stopping water evaporating)
What can cause a dry eye?
Very small meibomian glands that produce insufficient lipid layer
What happens after liquid drugs are applied to the eye?
They drain through the nasolacrimal tube within 60s
What determines a drop detaching from its dropping tip?
when the weight of the drop overcomes surface tension
What do eye drops for dry eyes aim to mimic?
tears
Why is it important to have a preservative in multi-use eye drops?
No preservative means risk of bacteria in eye which has potential to blind a patient
Why can eye drops still cause side effects systemically?
The drug is drained through the nasolacrimal tube and will reach back of throat and eventually the stomach
Even if eye dose is lower than oral dose, can still result in enough drug in body to cause side effects
Eg, if 1 eye drop = 0.2mg, 3x drops = 0.6mg where oral dose is 5mg, still enough to cause side effects
What is the pH of tears?
6-7
Why might a drug with pH 4.5 administered to eye cause a white cast?
Eye has pH 6-7 so drug precipitates
Why might nasal route be chosen over oral?
Avoids first pass metabolism
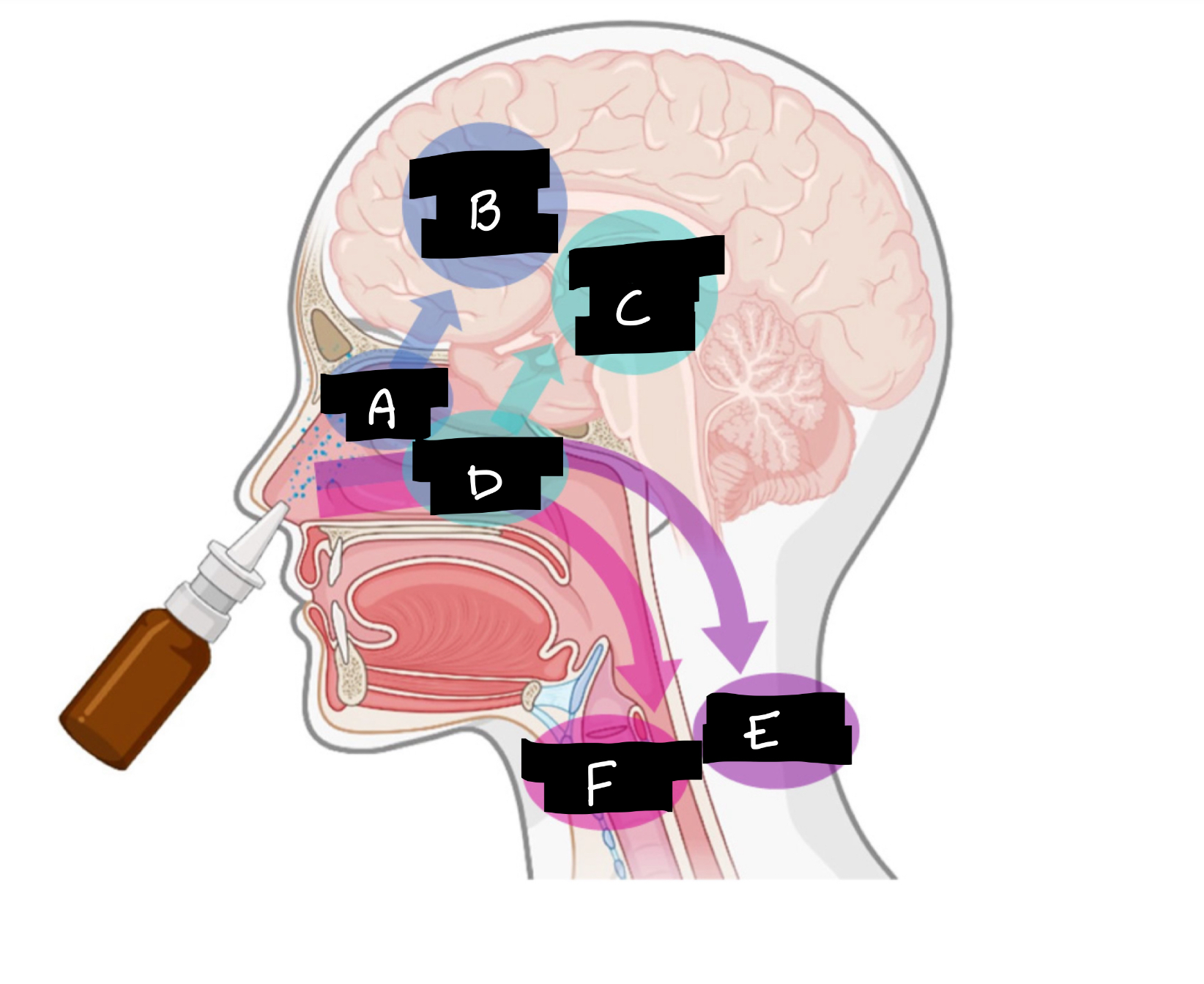
A
Olfactory region

B
Olfactory nerve pathway
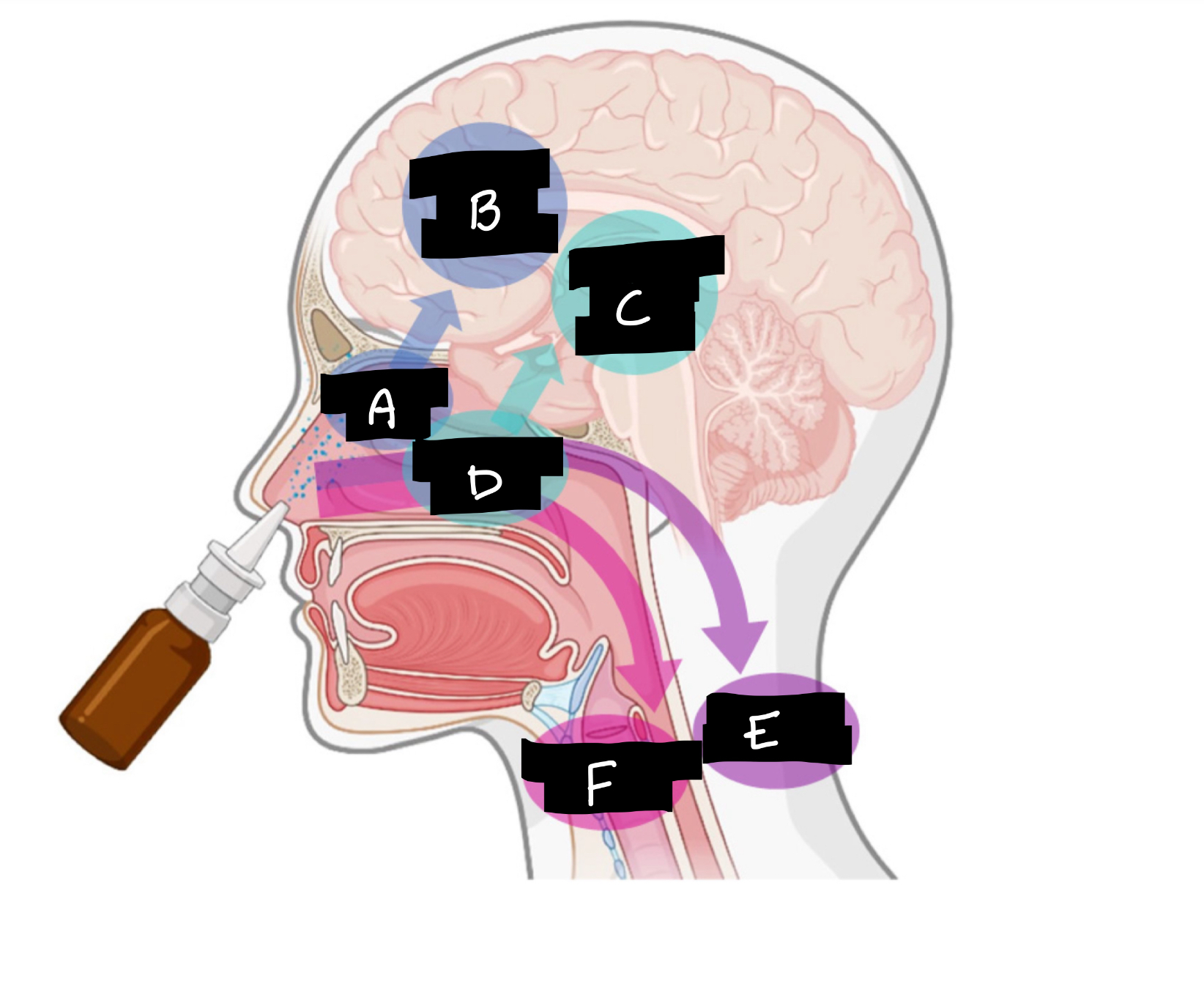
C
Trigeminal nerve pathway
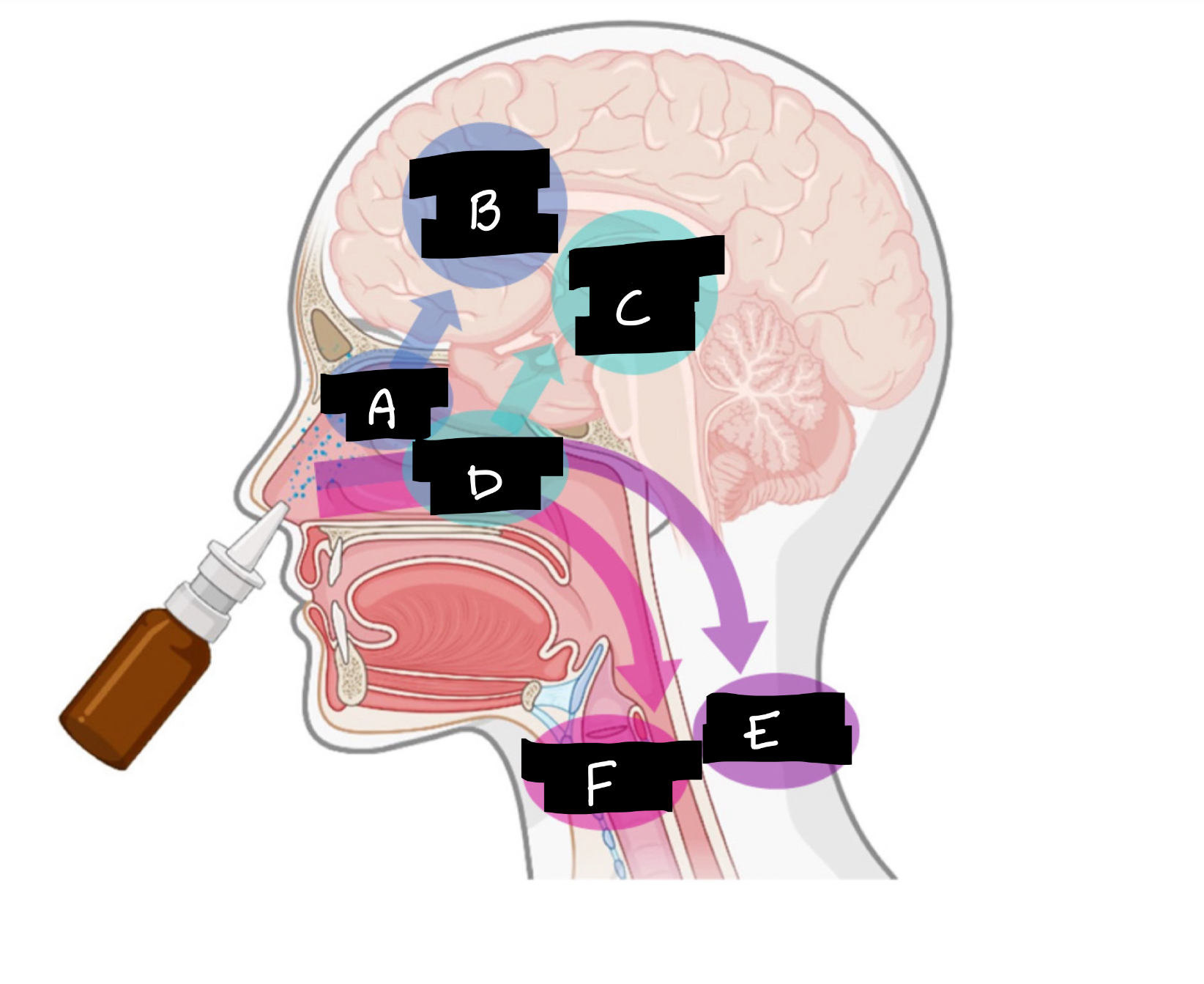
D
Respiratory region

E
Systemic distribution
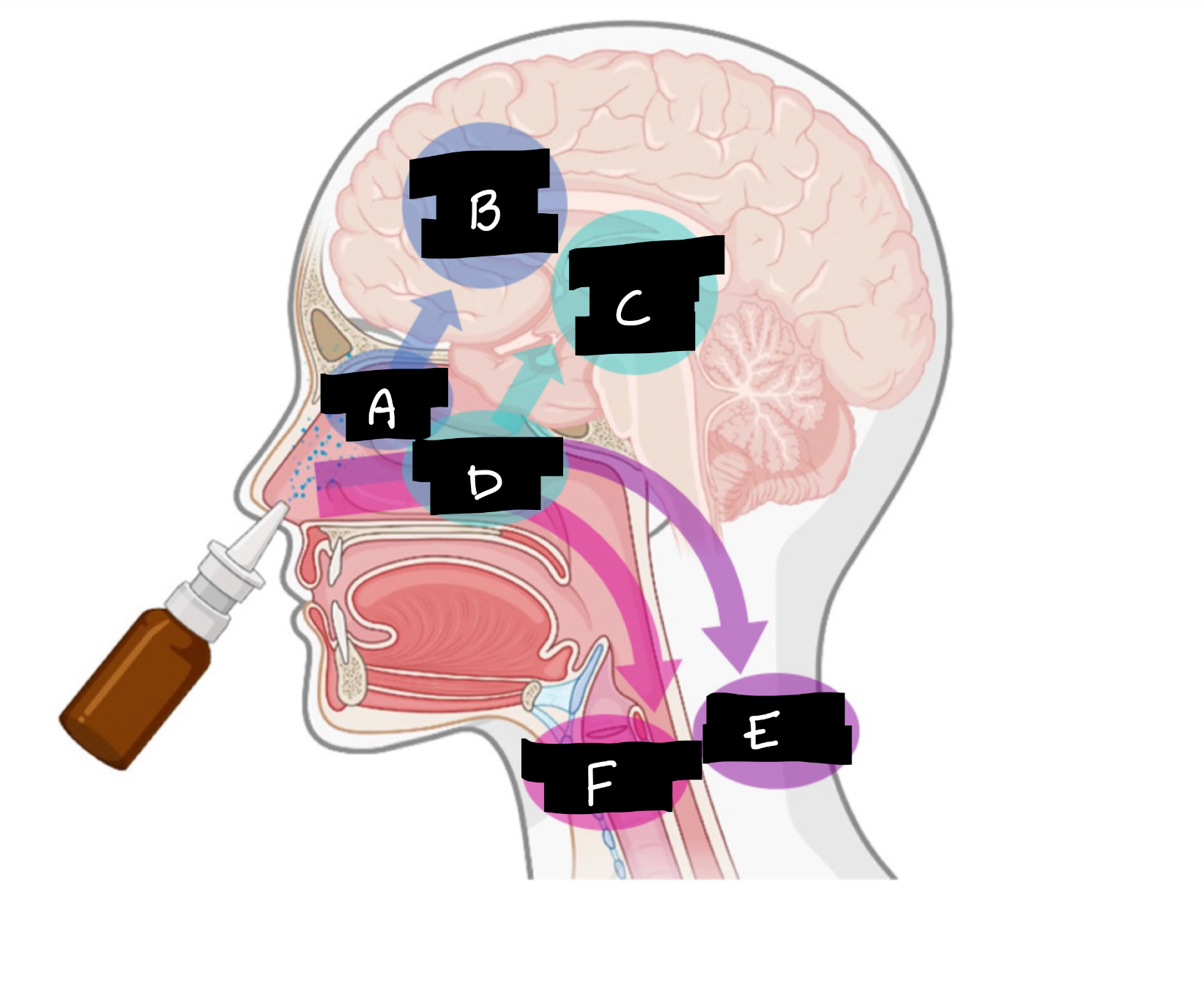
F
Mucociliary clearance
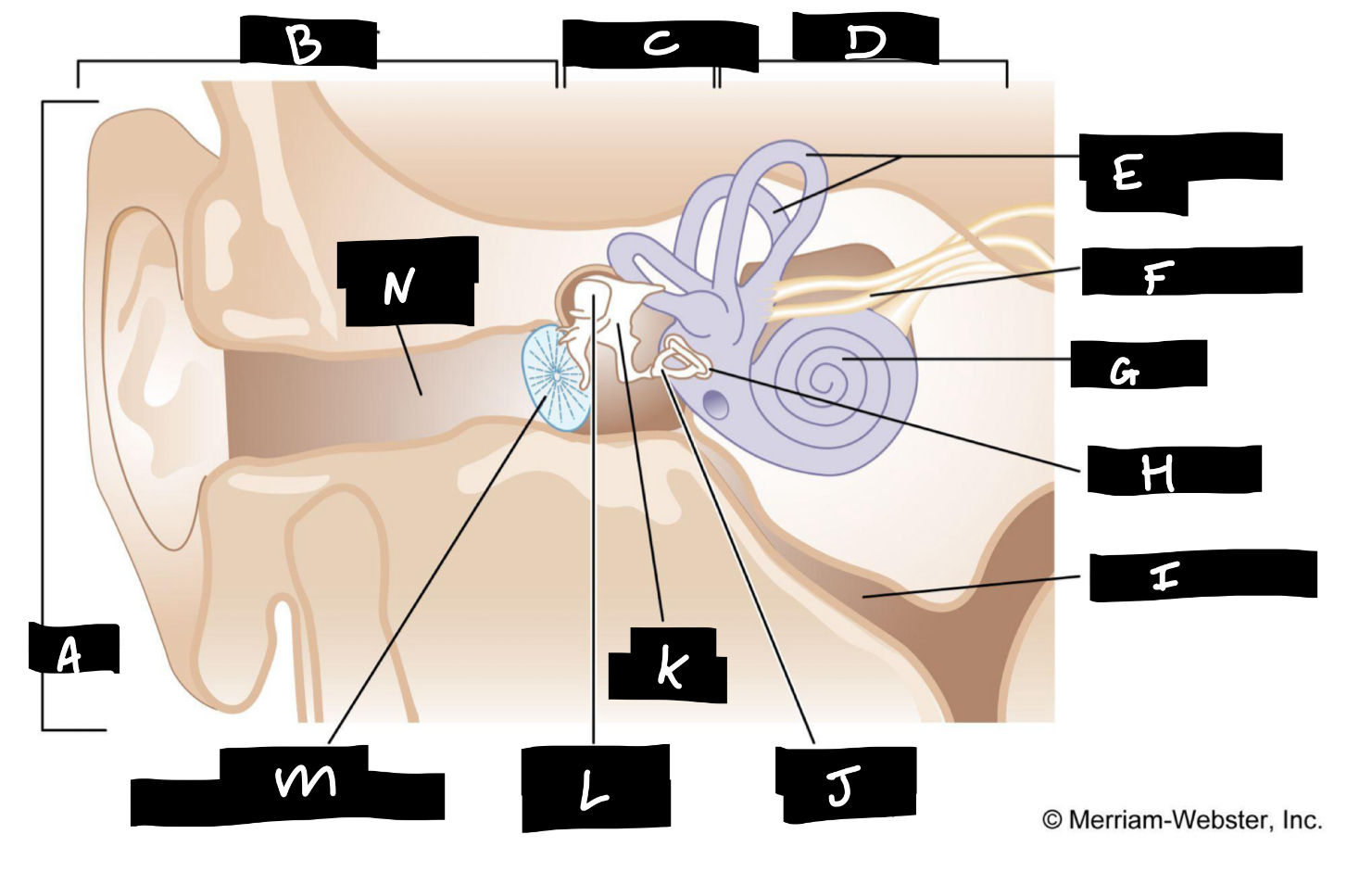
A
Auricle
B
Outer ear
C
Middle ear
D
Inner ear
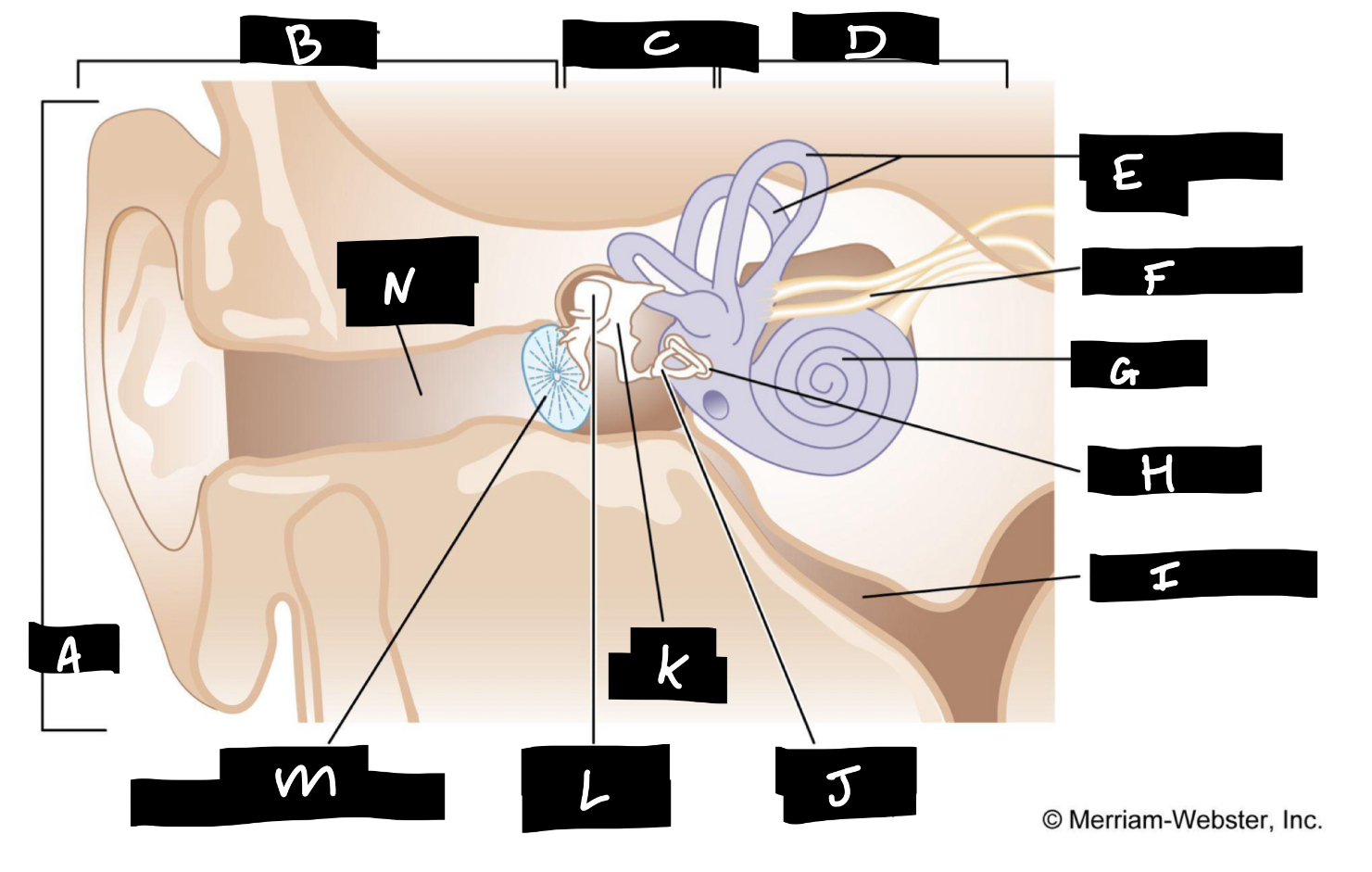
E
Semicircular canals
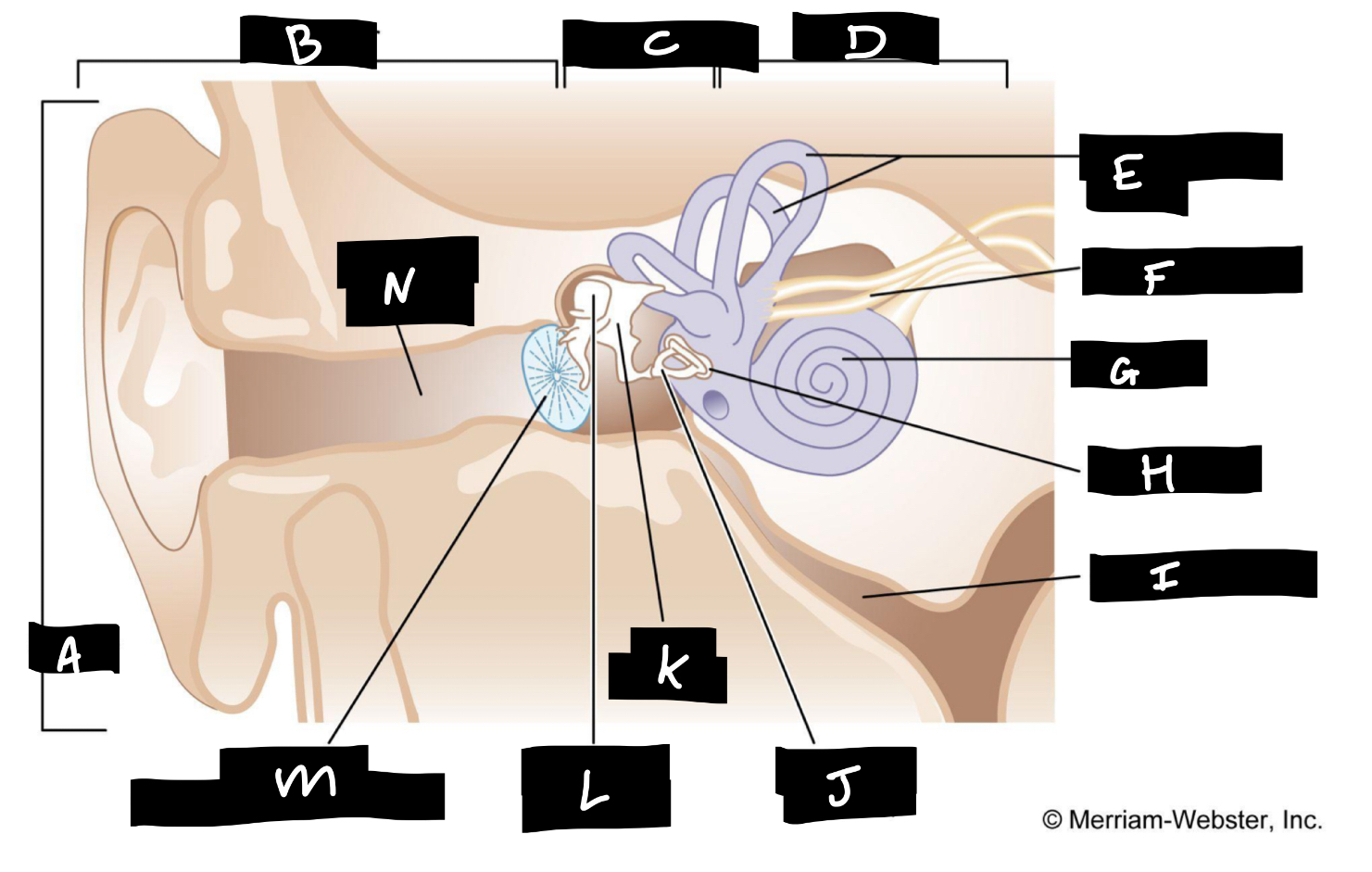
F
Auditory nerve
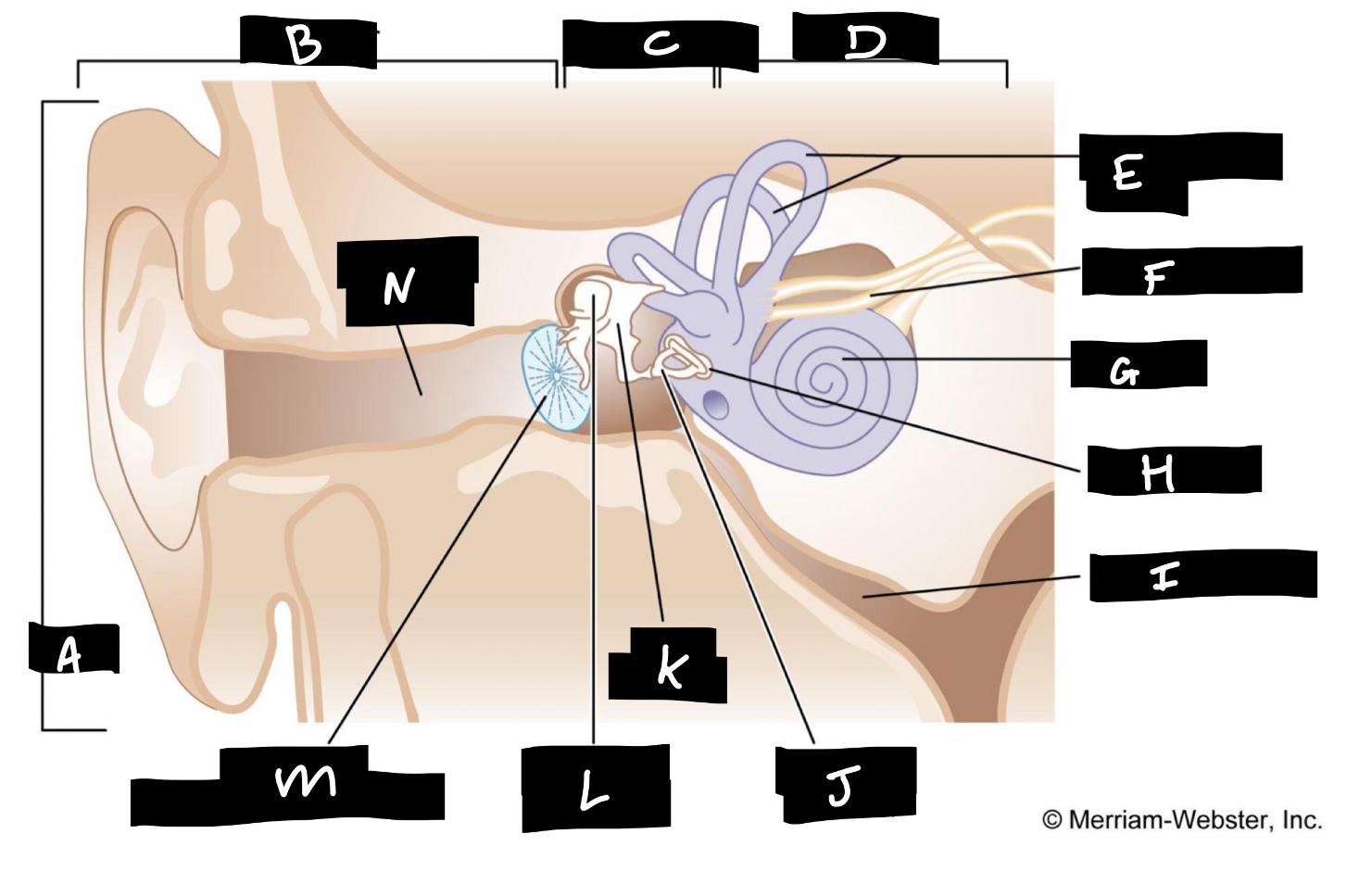
G
Cochlea
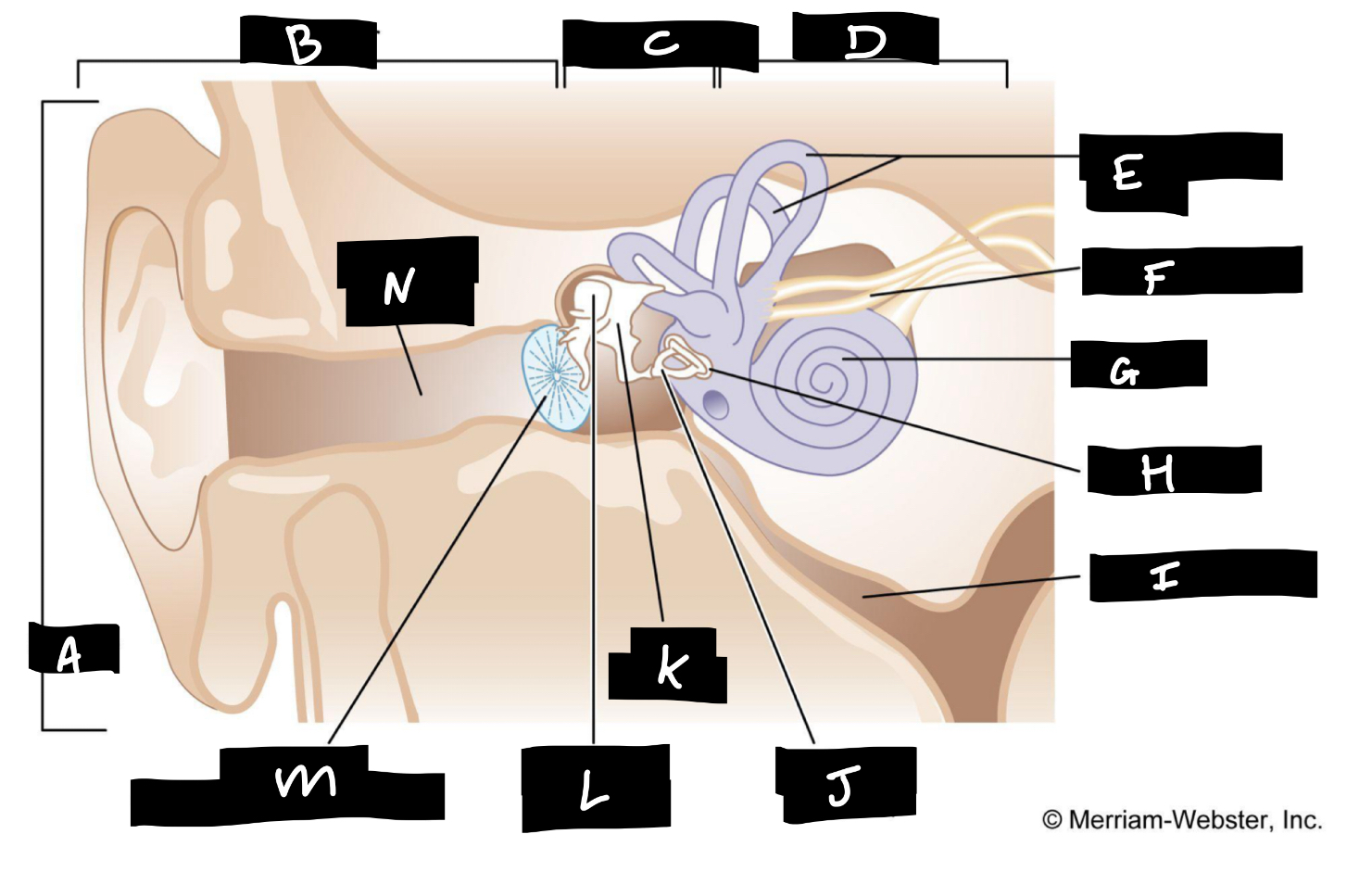
H
Oval window
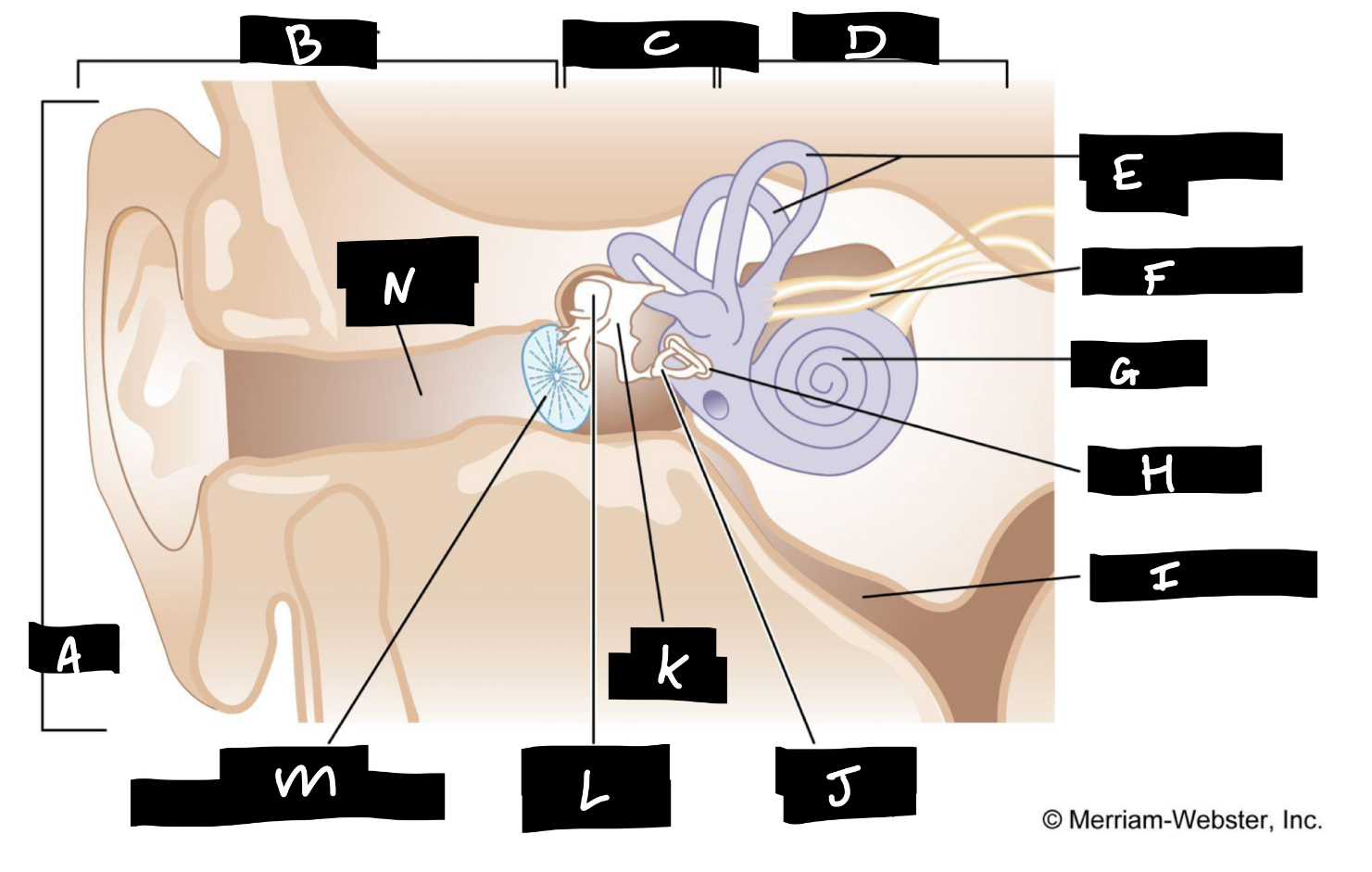
I
Eustachian tube
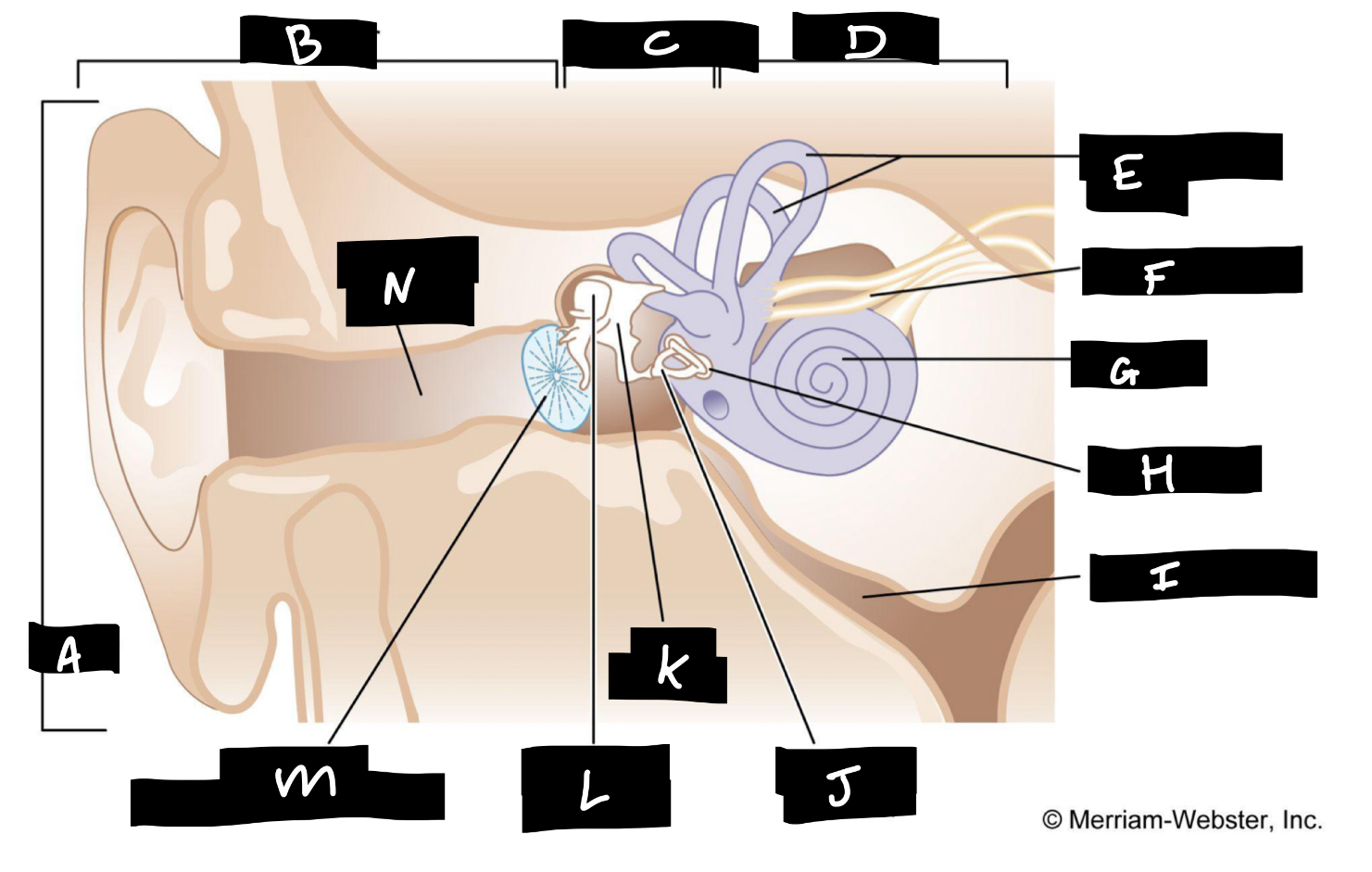
J
Stirrup

K
Anvil
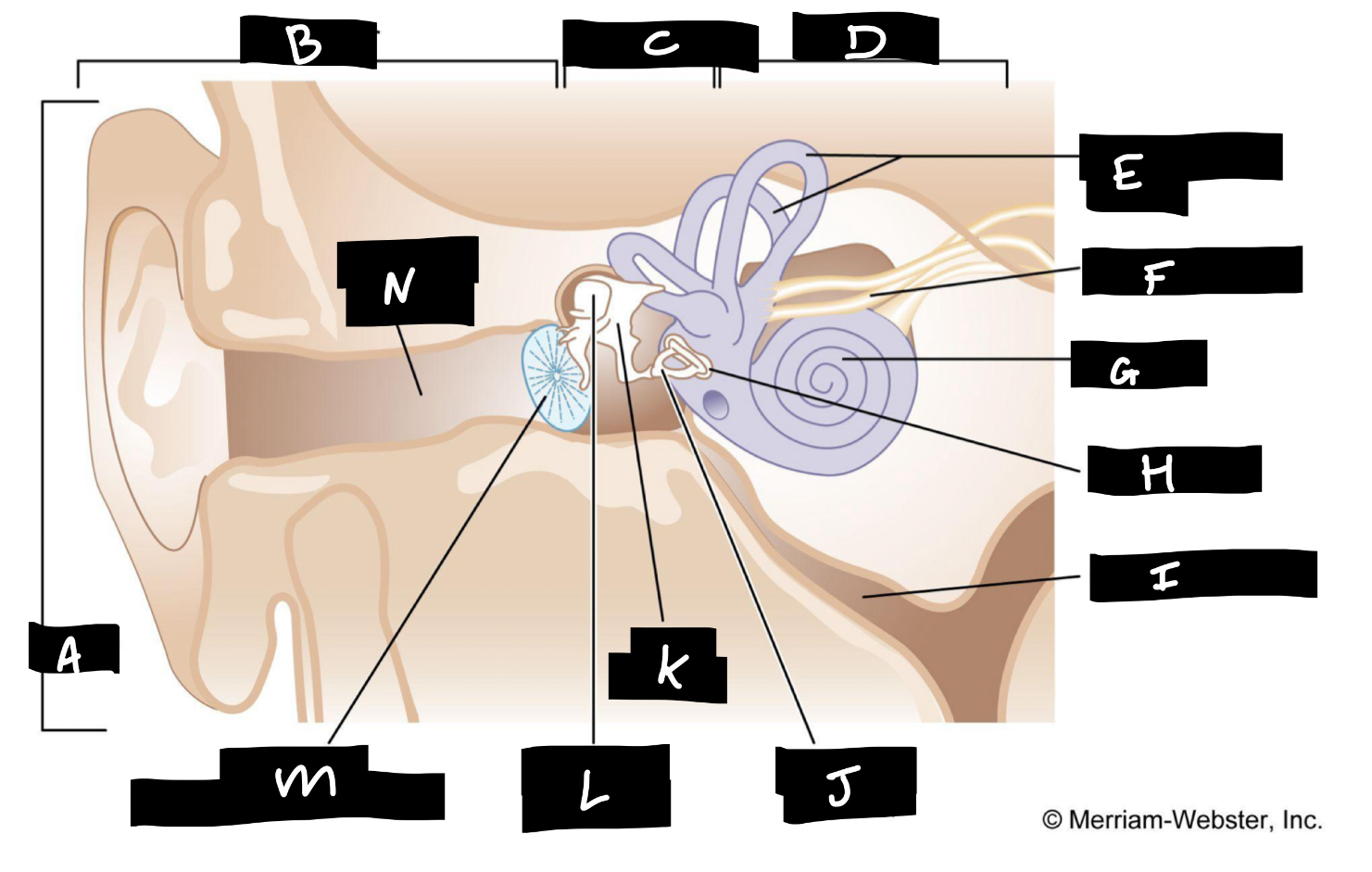
L
Hammer
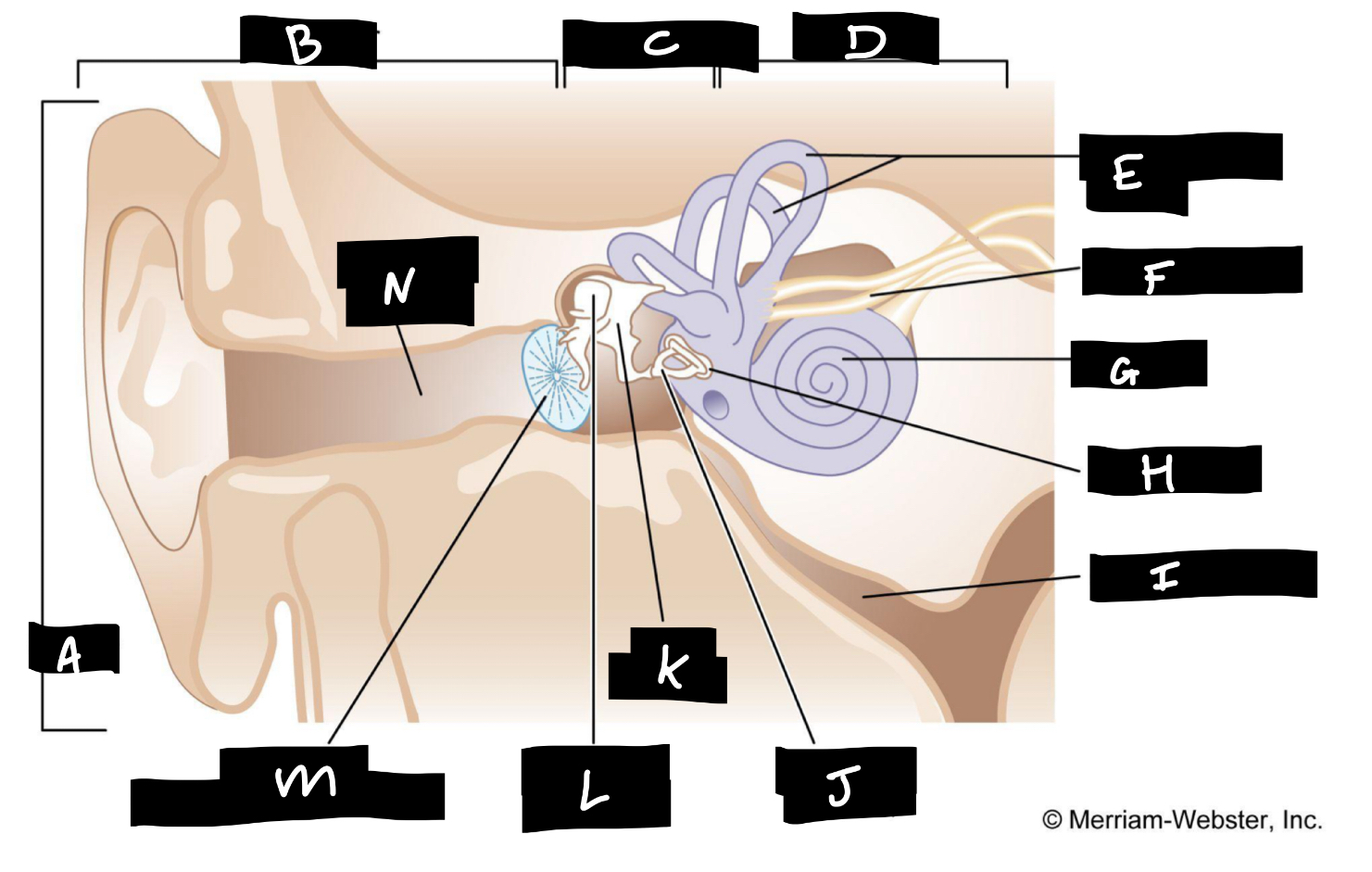
M
Eardrum

N
Auditory canal