Ped Emergencies
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Large occiput, floppy tongue, Larynx is more superior (C3), Larynx funnel shaped, narrowest at subglottic area, vocal cord slant anteriorly to trachea
What is different about pediatric airways?
(age + 16)/ 4 (if older than 1)
Estimation for pediatric ET tube size
Anybody under 10-12 (enlarged thymus and thyroid)
Which patient is NOT getting a crike?
A bridge for open tracheostomy (can support a 30 kg thing for 30 min), CO2 will build up
Describe needle translaryngeal ventilation
Straight blade if under 2 (Miller), uncuffed tubes if below 6-8
Tips on blade and tube choice in kids
Just enough for the chest rise, DO NOT hyperventilate (barotrauma or air in the stomach)
Tips for maintaining breathing in peds
IO is better than nothing, fluid bolus is 20 for peds, 10 for infants; If bolus (20 min max), reassess patient after each bolus
Tips for circulation
secondary to respiratory and shock (primary cardiac arrest is NOT a good sign)
In peds, cardiac arrest is usually
Airway, oxygenation, ventilation
Ped resuscitation priorities
Stridor, epiglottis, croup, FBA, peritonsillar/retropharyngeal abscess, bronchiolitis
Airway emergencies in Peds
Stridor, intercostal and suprasternal retraction, tachypnea, cyanosis (might be the baseline)
Signs of airway/breathing difficulties
Get a quick hx from the parents, keep the baby chill (try blow by oxygen), begin interventions ASAP, prepare to secure the airway
Gameplan for stridor
Dysphagia, drooling, distress
What are the 3Ds of epiglottis
Oxygen supplementation (protect the airway), IV steroids and abx; DO NOT USE A SUPRAGLOTTIC airway!!
Treatment plan for Epiglottis
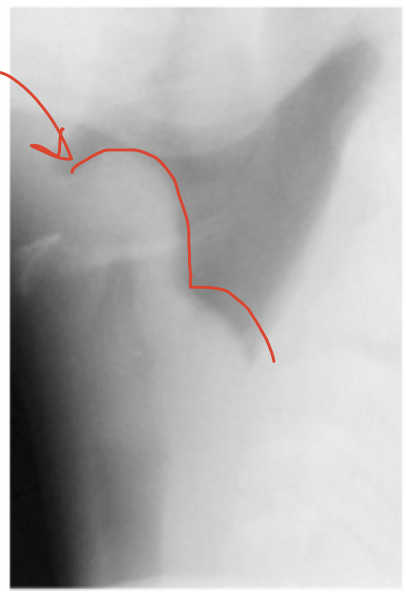
Thumb sign
Xray sign for epiglottis
nasal congestion, rhinorrhea, harsh barking cough, low-grade fever; (tends to be worse at night and related to the edema)
What are the classic symptoms of Croup?
Parainfluenza
What is the most common cause of Croup (AKA viral laryngotracheobronchitis)?
corticosteroids for everybody, nebulized epi, cold air may reduce symptoms
Treatment plan for croup - depends on severity (Westley Croup score)
Level of consciousness, cyanosis, stridor, air entry, retrations
What are the parts of the Westley Croup Score?
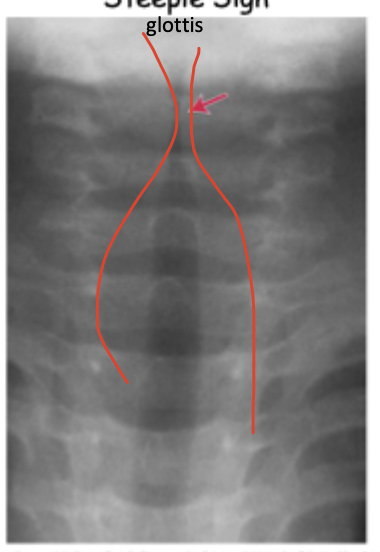
Steeple sign
Xray sign for Croup
RSV (50-70%)
Most common cause of Bronchiolitis?
3 months - 3 y/o (most commonly less than 2)
Bronchiolitis tends to affect…
URI symptoms, wheezing, fever, apneic episodes, cyanosis, poor feeding
Symptoms of Bronchiolitis (normally worse in the 1st week)
Nebulized epi (1x trial), corticosteroids, nebulized hypertonic saline (1x trial)
Treatment plan for Bronchiolitis
valvular dysfunction, septal defects, vascular anomalies
Pediatric heart diseases are usually causes by
Punt to pediatric cardiology (NICU, or whatever), Oxygenation in a PDA or ductal dependent lesion (CoA, ToF, pulmonary atresia) will worsen condition
Gameplan for pediatric heart diseases - general

imaging
Gameplan for a limping child with a hx of trauma/overuse
imaging
Gameplan for a limping child with NO hx of trauma/overuse and NO systemic symptoms
imaging, CBC, ESR, CRP
Gameplan for a limping child with NO hx of trauma/overuse and systemic symptoms
fractures, SCFE, AVN, osteomyelitis, septic joint, cancer, deep abscess
DDX for a limping child
infections, corneal abrasion, eye FB, hair tourniquet, insect bites, burns, recent vaccines, food intolerance, otitis, abuse, anal fissure, intussusception, incarcerated hernia, testicular torsion, drug exposure/withdrawal, congenital abnormality, medication overdose
DDX for a crying child
3 hrs a day, 3 days a week, 3+ weeks
Rule of 3s for Colic
bruising in different stages of healing, fractures in different stages of healing, odd story
Red flags for child abuse