Introduction to Invertebrates: Phyla and Features, Chordate Phylogeny and Vertebrate Characteristics, Introduction to Invertebrates and Chordate Evolution
1/343
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
344 Terms
What percentage of all animal species do invertebrates represent?
~95%
How many phyla of invertebrates are there?
~35 phyla
What is the primary habitat of most invertebrates?
Aquatic (freshwater or marine)
What is the notable exception to the aquatic habitat of invertebrates?
Arthropods have many land species.
What are the size extremes of invertebrates?
Very small (e.g., rotifer, <2mm) to very large (e.g., squid, >12m).
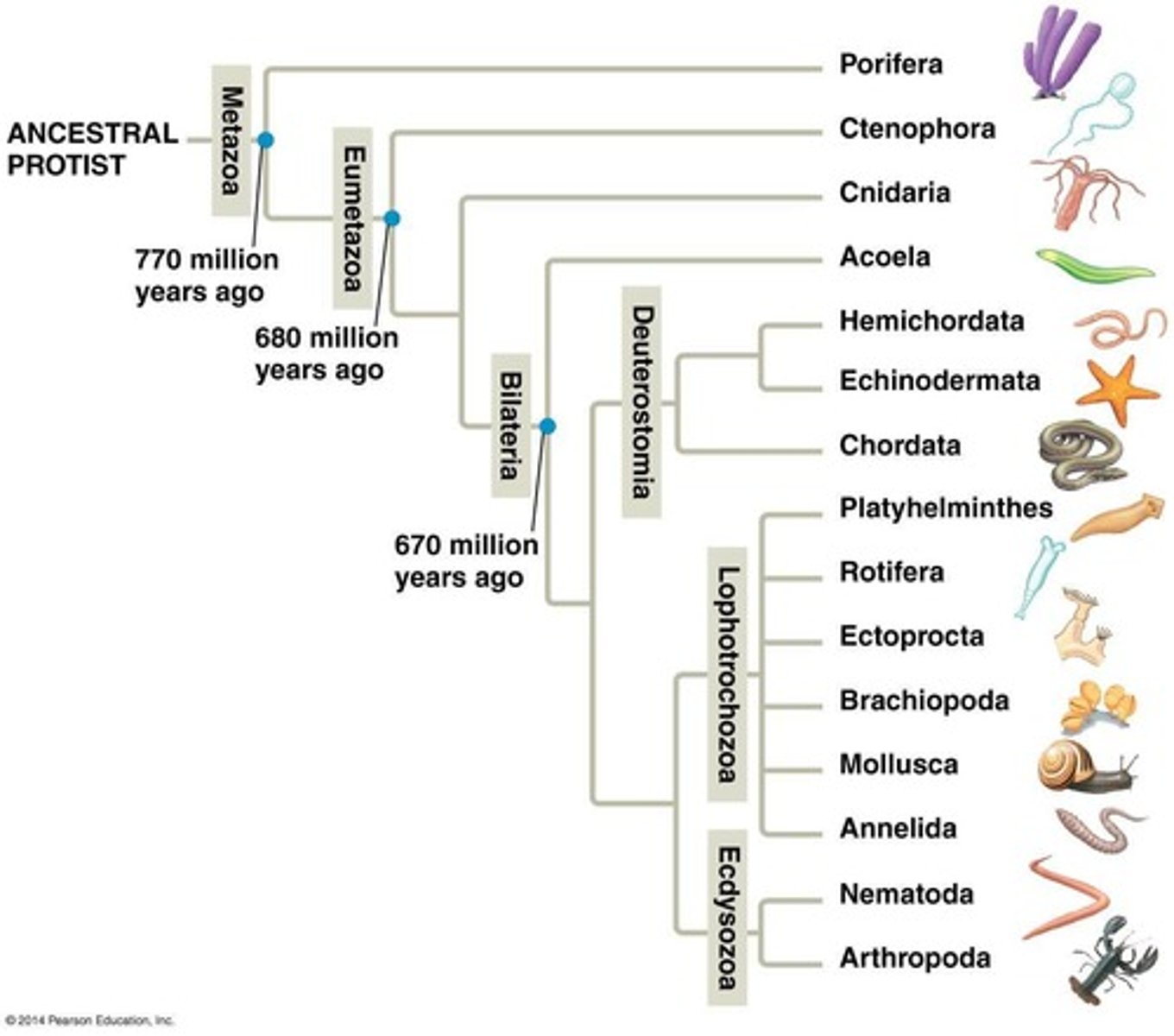
What are the two categories of basal animals?
Porifera (Sponges) and basal eumetazoans (Cnidaria, Ctenophora).
Name the phyla included in Lophotrochozoans.
Platyhelminthes, Rotifera, Ectoprocta, Brachiopoda, Mollusca, Annelida.
What phyla are classified as Ecdysozoans?
Nematoda, Onychophora, Tardigrada, Arthropoda.
Which phylum is classified as Deuterostomians?
Echinodermata.
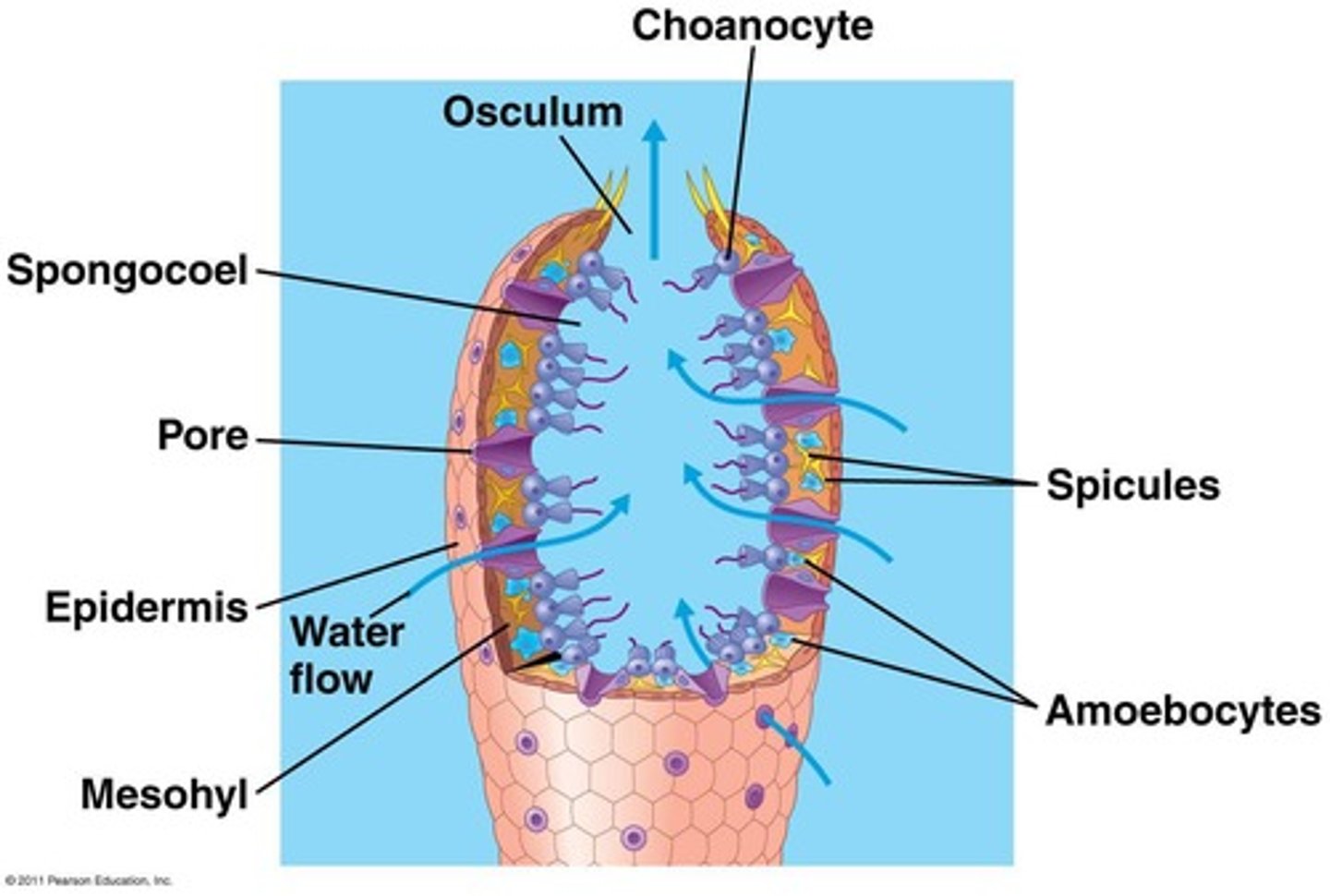
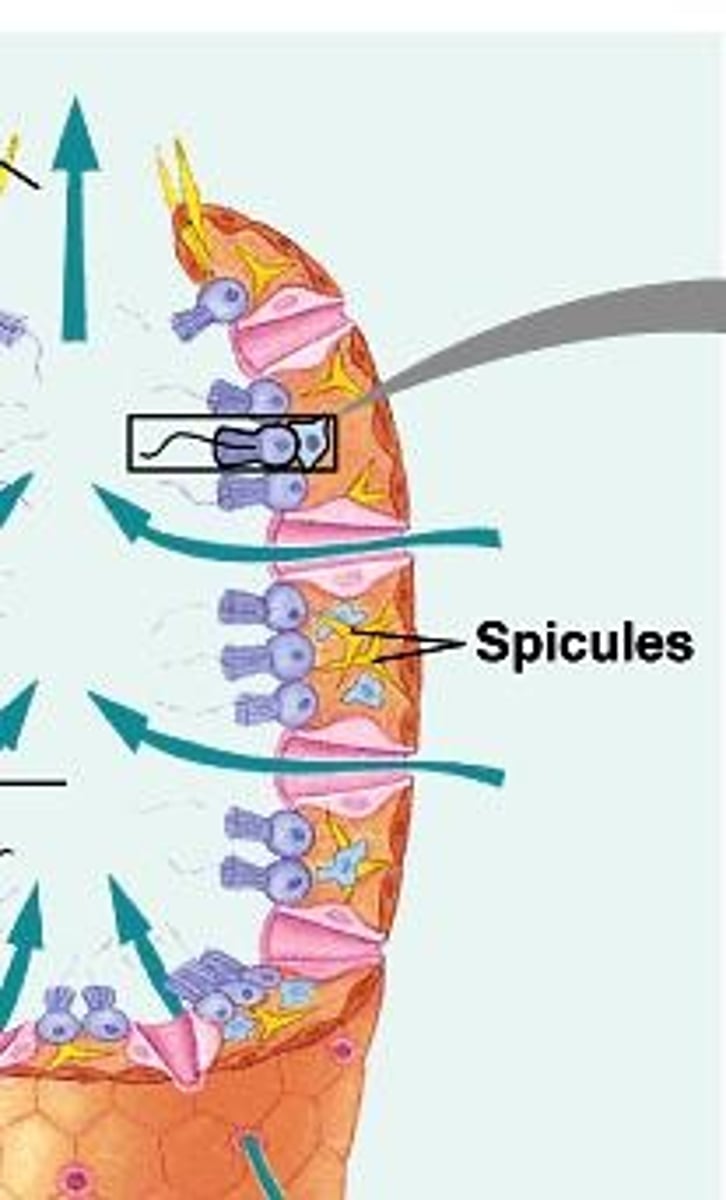
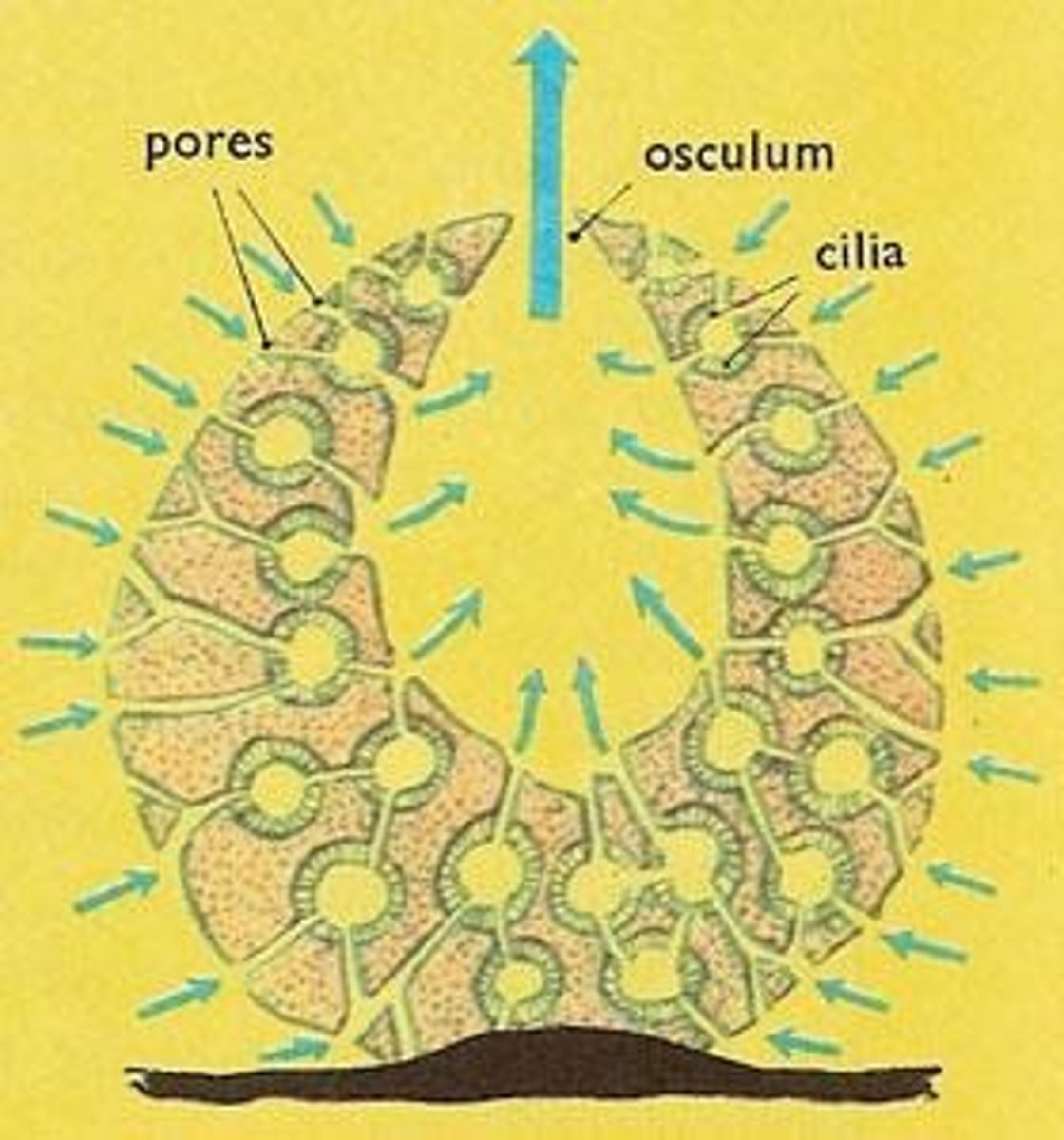
What is the defining characteristic of Porifera (Sponges)?
They lack true symmetry and are sessile as adults.
How do sponges feed?
By passing water across structures that trap tiny food bits (filter feeding).
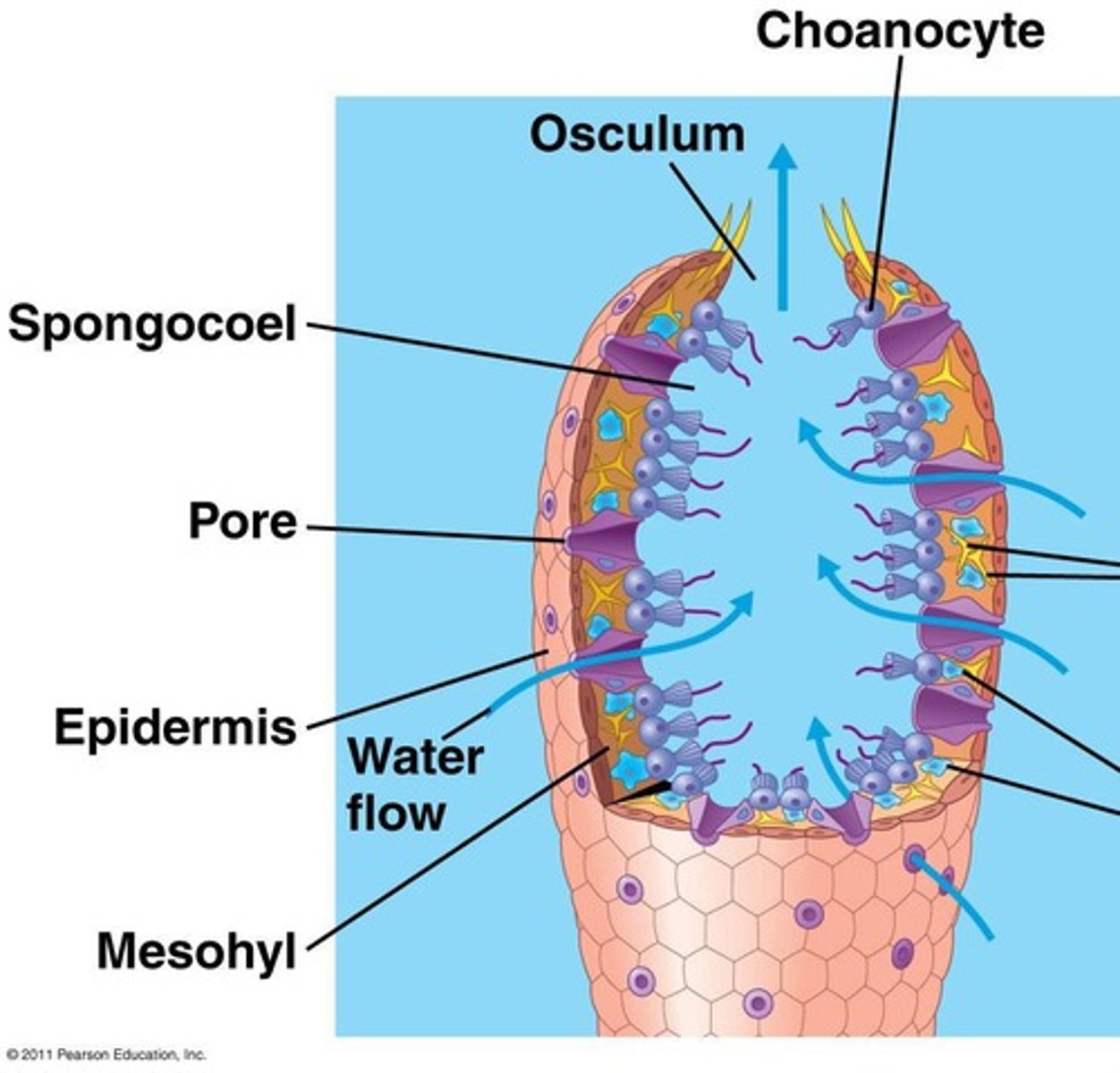
What are choanocytes and their function in sponges?
Choanocytes create currents and trap & ingest food bits through phagocytosis.
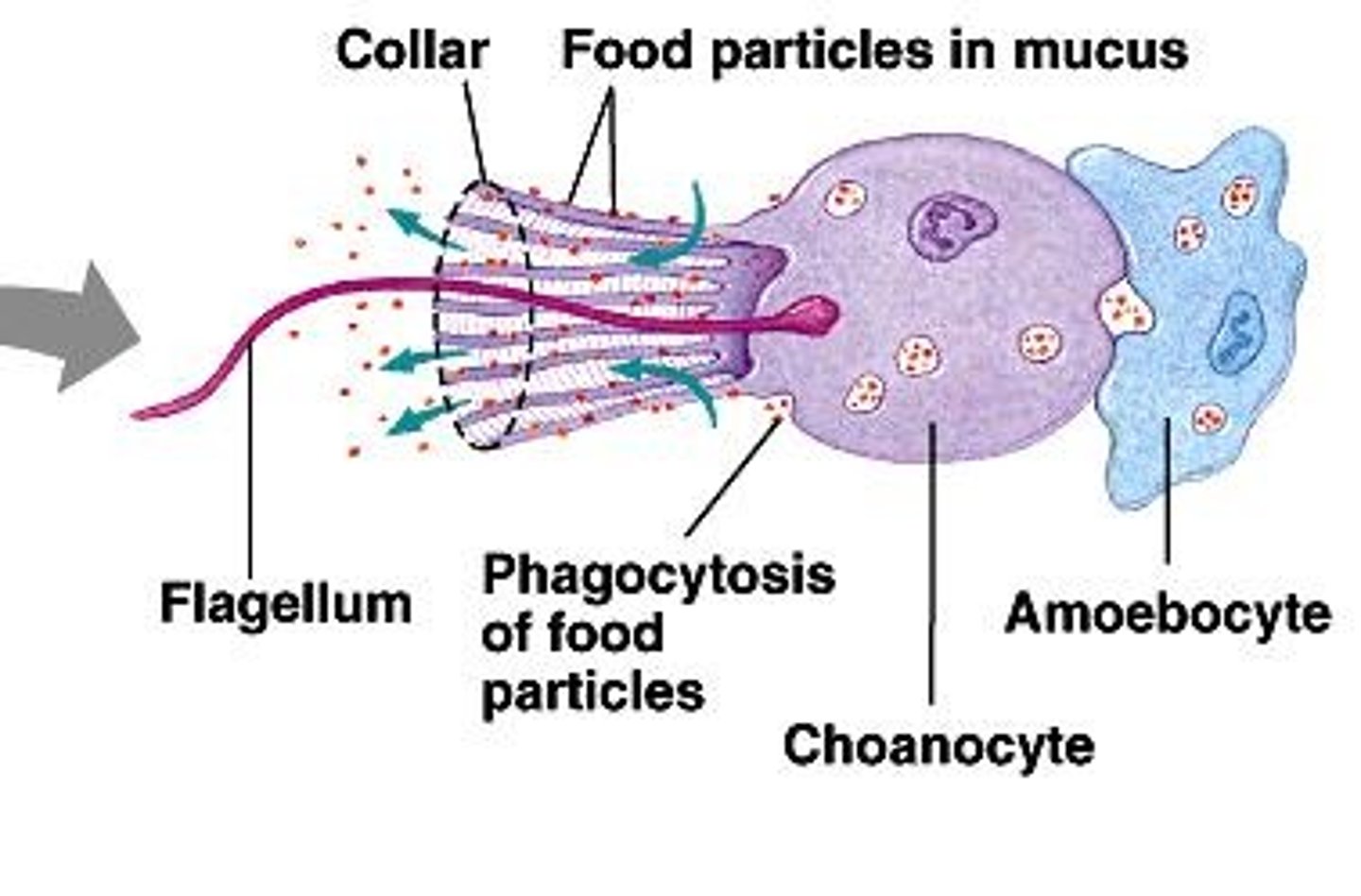
What role do amoebocytes play in sponges?
Amoebocytes distribute food and can change roles.
How do sponges reproduce?
By fragmentation and sexually as hermaphrodites (gametes form in mesohyl).
What is the body structure of Cnidaria?
They have a sac-like body with a gastrovascular cavity.
What are the two adult body forms of Cnidaria?
Sessile polyp and drifting/free-swimming medusa.
What type of symmetry do Cnidarians exhibit?
Radial symmetry.
How do Cnidarians capture prey?
With stinging tentacles that contain cnidocytes.
What is the function of the gastrovascular cavity in Cnidarians?
It distributes nutrients to the entire body and facilitates digestion.
What type of tissue organization do Cnidarians have?
Diploblastic with gel (mesoglea) between tissue layers.
How do Cnidarians perform gas exchange?
Direct O2/CO2 exchange between cells and water.
What is the reproductive strategy of many Cnidarians?
They reproduce sexually and/or by budding, cycling through polyp and medusa forms.
What is an example of a freshwater Cnidarian?
Hydra.
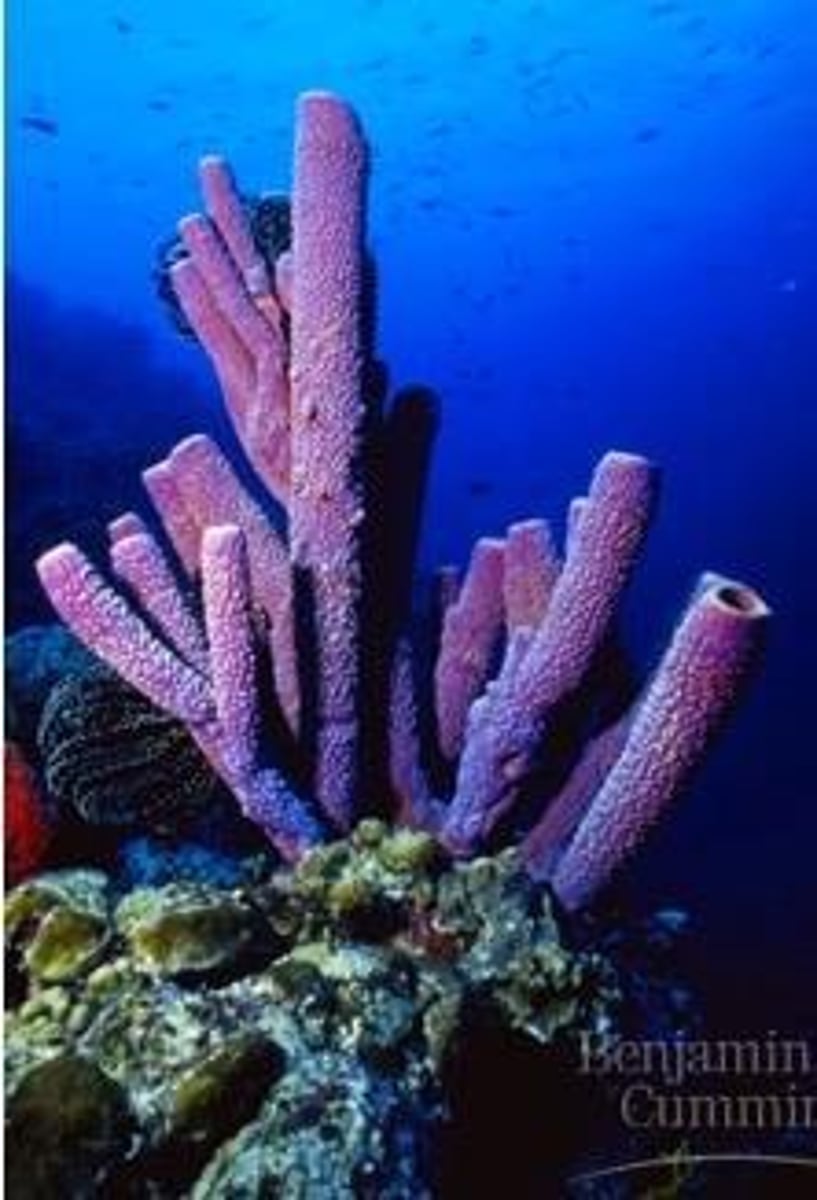
What is the ecological importance of coral reefs?
They are highly diverse ecosystems and important nurseries for economically important fish.

What are the two main types of basal eumetazoans discussed?
Cnidaria and Ctenophora.
What structures do 'soft corals' secrete?
Protein-based support structures.
What are 'comb jellies' scientifically classified as?
Phylum Ctenophora.
What type of symmetry do comb jellies exhibit?
Radial symmetry.
What is a key feature of the movement of comb jellies?
They move with cilia, which are fused into 8 comb-like plates.
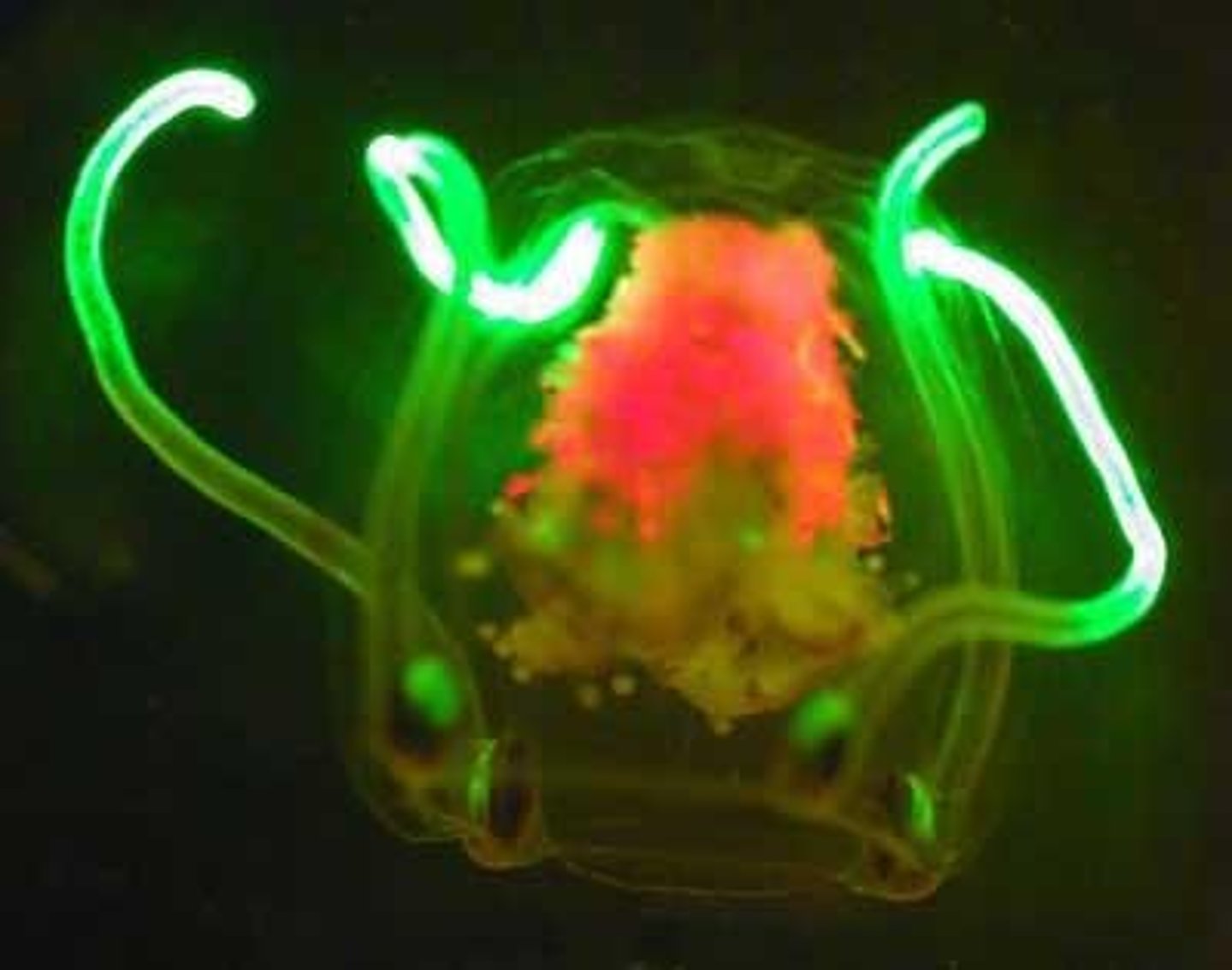
What type of diet do comb jellies have?
They are marine carnivores.
How do comb jellies capture their prey?
They eject a sticky thread from their cells or engulf prey.
What is the scientific classification for flatworms?
Phylum Platyhelminthes.
What are the three germ layers present in flatworms?
Ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm.
What is the body structure of flatworms?
Flat, triploblastic, acoelomate with bilateral symmetry.
What is the function of the gastrovascular cavity in flatworms?
It has one opening and is highly branched to distribute nutrients.
What type of nervous system do flatworms possess?
A simple nervous system with ganglia, ventral nerve cords, and eyespots.
What are protonephridia and their function in flatworms?
They are structures with flame bulbs that remove excess water and some wastes.
What are planarians and where do they live?
Free-living carnivores or scavengers that live in freshwater.
What are trematodes and their life cycle characteristic?
Parasitic flatworms with complex life cycles, such as the Chinese liver fluke.
What disease is caused by Schistosoma?
Schistosomiasis.
What are tapeworms and where do they typically reside?
Parasitic flatworms that mostly reside in vertebrate intestines.
How do humans typically become infected with tapeworms?
By eating undercooked infected beef, pork, or fish.
What is a unique feature of tapeworms regarding their digestive system?
They have no mouth or digestive system and are absorptive feeders.
What are proglottids in tapeworms?
Repeated reproductive segments that fill up with eggs.
What is the scientific classification for rotifers?
Phylum Rotifera.
What is a key characteristic of rotifers?
They are free-living, aquatic, and have a microscopic, cylindrical body.
What is the function of the cilia in rotifers?
They create a rotating wheel to bring plankton to the mouth.
What type of reproductive strategy do many rotifer species use?
Parthenogenesis.
What is the scientific classification for bryozoans?
Phylum Ectoprocta.
What type of feeding mechanism do bryozoans use?
They are sessile suspension-feeders using a lophophore.
What is the Phylum Brachiopoda commonly known as?
Brachiopods or lampshells.
What type of environment do Brachiopoda inhabit?
Marine environments.
What are the key features of Brachiopoda?
They have two shells and a pedicle for attachment, and they suspension-feed using a lophophore.
How diverse is the fossil record of Brachiopoda?
Very diverse, but there are few species today.
What is the estimated number of species in the Phylum Mollusca?
Approximately 93,000 species.
What is the second most diverse phylum in the animal kingdom?
Phylum Mollusca.
What are the main components of the common body plan of Mollusca?
Muscular foot, visceral mass, and mantle.
What is the function of the muscular foot in Mollusca?
Locomotion and digging.
What does the visceral mass contain in Mollusca?
Internal organs and well-developed organ systems.
What type of circulatory system do most mollusks have?
Open circulatory system.
What is the role of the mantle in Mollusca?
It covers the visceral mass, makes the shell (if present), and forms the mantle cavity for gas exchange.
What is the composition of most mollusk shells?
Calcium carbonate (CaCO3) in a protein matrix.
What is a radula and its function in Mollusca?
A radula is a feeding organ used for scraping up food.
How do most aquatic mollusks reproduce?
Most have separate sexes and produce trochophore larvae.
What adaptation do land snails have for reproduction?
They produce shelled eggs with a calcified shell.
What class does the largest group of mollusks belong to?
Class Gastropoda.
What are the characteristics of Class Gastropoda?
Includes land, freshwater, and marine species; may have a single shell or no shell.
What is the significance of the twisting of the viscera in gastropods?
It allows the mantle cavity to lie over the head-end, facilitating retraction into the shell.
What types of feeding behaviors are observed in gastropods?
Some graze on plants, algae, and bacteria, while others are predators.
What are some examples of marine gastropods?
Venomous cone shells, nudibranchs, and various edible snails.
What is the structure of Class Bivalvia?
Bivalves have a two-part shell joined by a hinge and lack a distinct head.
How do bivalves feed?
They are suspension-feeders that filter-feed using ciliated gills.
What are the two main lifestyles of bivalves?
Burrowing or sessile.
How do scallops move?
They move by clapping their valves.
What are bivalves and how have human cultures utilized them?
Bivalves, such as mussels and oysters, have been cultivated and depended upon for food by human cultures for thousands of years.
What is the significance of pearls in relation to bivalves?
Pearls are secreted by the mantle of pearl oysters and are used for jewelry and buttons.
What are the defining characteristics of cephalopods?
Cephalopods are mostly active marine predators with a modified foot into arms and tentacles, beak-like jaws, well-developed eyes and brain, and use water-jet propulsion.

What unique feature does the nautilus possess among cephalopods?
The nautilus is the only living cephalopod with an external shell.
How do squid and cuttlefish differ in terms of shell structure?
Squid and cuttlefish have reduced internal shells, known as the squid 'pen' and cuttlebone.
What is a notable feature of octopuses in terms of anatomy?
Octopuses have no shell and possess the largest brain among invertebrates.
What are the common features of segmented worms in the Phylum Annelida?
Common features include segmentation of external and internal structures, a soft body, and a true coelom that acts as a hydrostatic skeleton.
What type of circulatory system do annelids have?
Annelids have a closed circulatory system where blood and tissue fluid are separate.
Describe the alimentary canal of annelids and its specialized areas.
The alimentary canal includes the mouth and pharynx for intake, a crop for storage, a gizzard for mechanical processing, an intestine for chemical digestion and absorption, and an anus for waste expulsion.
What is the role of metanephridia in annelids?
Metanephridia expel metabolic waste, osmoregulate, and reabsorb useful solutes into the blood.
How do annelids reproduce?
Annelids can have separate sexes or be hermaphroditic, with marine species producing trochophore larvae and earthworms undergoing direct development.
What are bristle worms and their ecological role?
Bristle worms are active marine predators with jaws, characterized by fleshy parapodia and chitinous bristles.
What distinguishes tube worms from other annelids?
Tube worms are sedentary marine suspension- or deposit-feeders that live in tubes or burrows and often have feathery tentacles.
What are the characteristics of earthworms?
Earthworms have few bristles, no parapodia, a reduced head, and are terrestrial or freshwater deposit-feeders that aerate soils.
What are the features of leeches?
Leeches lack bristles and parapodia, have suckers at both ends, and can be freshwater predators or blood-sucking parasites.
What is the Phylum Nematoda known for?
Phylum Nematoda, or roundworms, is characterized by a colorless cylindrical body with tapered ends and lacks segmentation.
What are the ecological roles of annelids?
Annelids play important ecological roles such as aerating soils, recycling nutrients, and serving as prey for various animals.
What adaptations do cephalopods have for camouflage?
Cephalopods can change skin color and use protective ink for camouflage and disguise.
How do cephalopods utilize water-jet propulsion?
Cephalopods use an excurrent siphon and mantle cavity to expel water, allowing for rapid movement.
What is the visual acuity of cephalopods compared to vertebrates?
Squid and octopus eyes are second only to vertebrate eyes in visual acuity.
What is the significance of the term 'mother of pearl'?
'Mother of pearl' refers to the iridescent inner layer of some bivalve shells, often used in jewelry.
What is the ecological importance of bivalves in marine environments?
Bivalves filter feed and help maintain water quality in marine ecosystems.
What is the significance of Coenorhabditis elegans in research?
It is an important research animal.
What type of cuticle do Ecdysozoans in the Nematoda phylum have?
A tough, flexible cuticle that is shed as it grows (ecdysis).
What are the main components of the Nematoda's anatomy?
Well-developed alimentary canal, nerve cords, gonads, anus, intestine, mouth, and pharyngeal bulb.
How does the pseudocoelom function in Nematoda?
It distributes nutrients and acts as a hydrostatic skeleton.