M1 - Introduction to Medicinal Organic Chemistry
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
MEDICINAL CHEMISTRY
Branch of chemistry involved in identification, design, synthesis, and development of biologically active compounds.
interdisciplinary science
Organic Chemistry
Biochemistry
Computational Chemistry
Pharmacology
Pharmacognosy
Molecular biology
Physical Chemistry
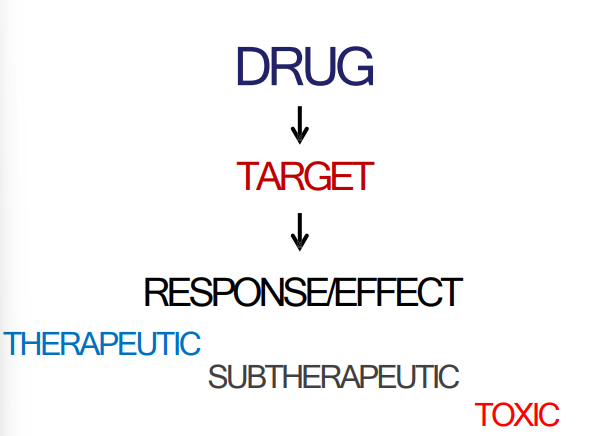
DRUGS
are low MW chemical substances that interact with macromolecular targets in the body to produce effect
Pharmacodynamics
What the drug does to the body
Design a drug that will interact as powerfully and selectively as possible for the target
ENDOGENOUS COMPOUNDS
body’s own natural chemicals
EXOGENOUS COMPOUNDS
foreign substances (XENOBIOTICS)
XENOBIOTICS
EXOGENOUS COMPOUNDS also known as?
Pharmacokinetics
What the body does to the drug
Design the drug so that it is capable of reaching that target
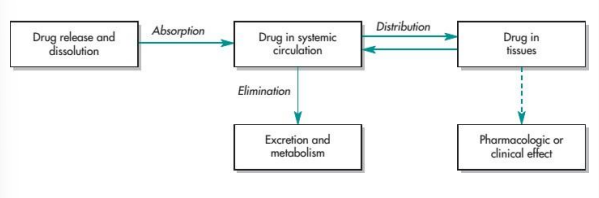
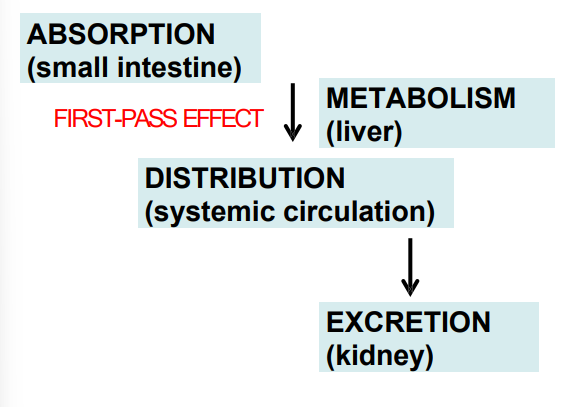
ADME
ABSORPTION DISTRIBUTION METABOLISM EXCRETION
LIBERATION
When the conventional dosage forms are administered orally or topically, the active drug in the dosage form is immediately released and absorbed into the systemic circulation.
Diffusion is the most common mechanism controlling drug release.
LUNA
LIPOPHILIC UNIONIZED NON POLAR ABSORBED
HIPE
HYDROPHILIC IONIZED POLAR EXCRETED
Oral Administration
Parenteral Administration
BLOOD BRAIN BARRIER
DRUG ABSORPTION
Oral Administration
The most common and popular route
Stomach
pH 1.5-2 fed state; pH 2-6 fasting state
pH 1.5-2
fed state
pH 2-6
fasting state
Small Intestine
main site of absorption
→ UNIONIZED
Acidic drug +Acidic medium
Basic drug +Basic medium
→ IONIZED
Acidic drug +Basic medium
Basic drug +Acidic mediu
More absorbed >UNIONIZED → A +A
At what medium are acidic drugs readily absorbed?
More excreted >IONIZED → A +B
At what medium are acidic drugs readily excreted?
Parenteral Administration
Direct to Systemic Circulation
Rapidly distributed
IV, IM, SC,Intraspinal, Intracerebral
BLOOD BRAIN BARRIER
Protects the brain from exposure to chemicals and metabolites, due to the presence of tightly joined epithelial cells lining the cerebral capillaries
DRUG DISTRIBUTION
Drug movement from the systemic circulation going to different organs and tissues
Blood Flow
PERFUSION
Delivery of drug to the tissue is controlled by the specific blood flow to a given tissue
DRUG METABOLISM (BIOTRANSFORMATION)
All substances in the circulatory system, including drugs, metabolites, and nutrients, will pass through the liver.
Most molecules absorbed from the GIT enter the portal vein and are initially transported to the liver.
Azathioprine
Acyclovir
Bioactivation
Azathioprine
immunosuppressant
6-mercaptopurine
Acyclovir
antiviral
Acyclovir triphosphate
First-Pass Effect
a significant proportion of a drug is metabolized by hepatic enzymes during the initial trip through the liver
Drug removal by the liver after absorption
LIDOCAINE
example of First-Pass Effect
antiarrhythmic (60% is metabolized when given orally)
ENZYME INDUCTION
ENZYME INHIBITION
Alteration of Enzymic Action
ENZYME INDUCTION
increased metabolism = low Cp
ENZYME INHIBITION
decreased metabolism = high Cp
Enzyme Inducers

Enzyme Inhibitors

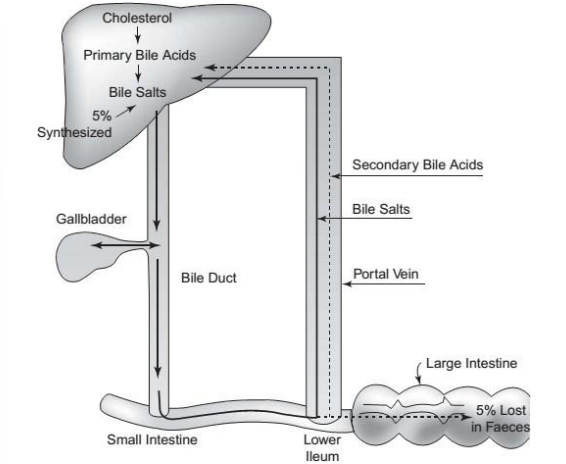
ENTEROHEPATIC CIRCULATION
drug reenters the intestinal tract from the liver through bile duct
BILIARY RECYCLING
Drug elimination
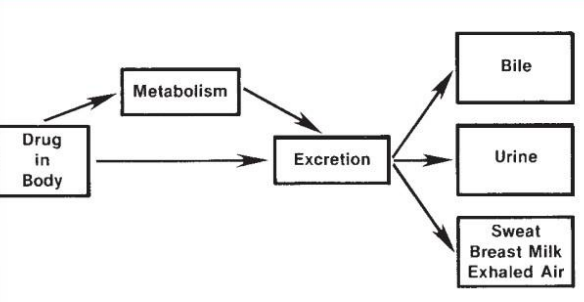
DRUG EXCRETION
____ into the urine is a major route of elimination for metabolites and unchanged drug.
Glomerular Filtration
Tubular Secretion
Tubular Reabsorption
RENAL CLEARANCE
Glomerular Filtration
unbound drug is passively filtered by the glomerulus.
Tubular Secretion
drug is actively secreted.
Tubular Reabsorption
drug is passively reabsorbed back into the blood.