lect8 amines part 1
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
What are the main amine neurotransmitter systems in the CNS?
Noradrenaline (NA), Dopamine (DA), 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), Acetylcholine (ACh), and Histamine.
Name five important amine neurotransmitters that function in the central nervous system.
Dopamine, Noradrenaline, Serotonin (5-HT), Acetylcholine, and Histamine.
What is the role of Noradrenaline (NA) in the CNS?
It is involved in alertness, arousal, and the stress response.
Which neurotransmitter regulates arousal and the fight-or-flight response in the brain?
Noradrenaline (NA).
What are the main functions of Dopamine (DA) in the brain?
It plays a key role in movement, reward, motivation, and is linked to Parkinson’s and schizophrenia.
Which neurotransmitter is essential for reward and motor control, and is disrupted in Parkinson’s disease?
Dopamine (DA).
What is 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) more commonly known as, and what does it regulate?
It is serotonin and regulates mood, sleep, and appetite.
Which neurotransmitter, also called serotonin, helps control emotions and sleep cycles?
5-HT (5-hydroxytryptamine).
What cognitive functions is Acetylcholine (ACh) associated with in the CNS?
Learning, memory, and attention.
Which neurotransmitter involved in memory and attention declines in Alzheimer’s disease?
Acetylcholine (ACh).
What is the role of Histamine as a neurotransmitter in the CNS?
It modulates wakefulness, arousal, and also immune responses in the brain.
What is 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), and what is it derived from?
5-HT, also known as serotonin, is an indoleamine neurotransmitter derived from the amino acid tryptophan. It contains an indole ring and a primary amine group (–NH₂) important for receptor binding.
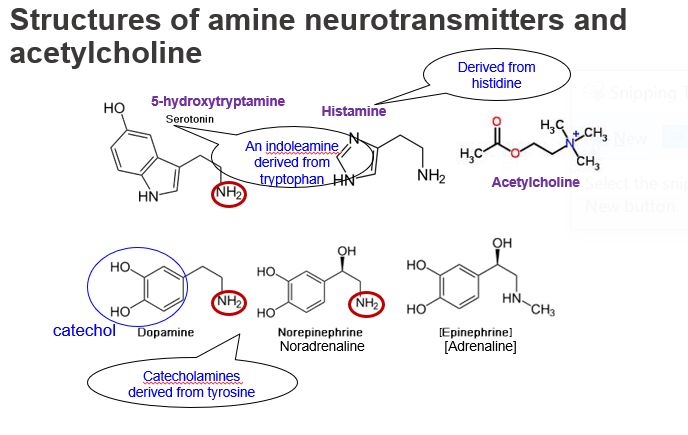
Serotonin is chemically classified as what kind of neurotransmitter, and what amino acid is it made from?
It is an indoleamine, synthesized from tryptophan, and contains an NH₂ group on its side chain.
What is histamine, and what amino acid is it derived from?
Histamine is a biogenic amine neurotransmitter derived from histidine. It contains an imidazole ring and a primary amine (–NH₂) group, which forms during decarboxylation.
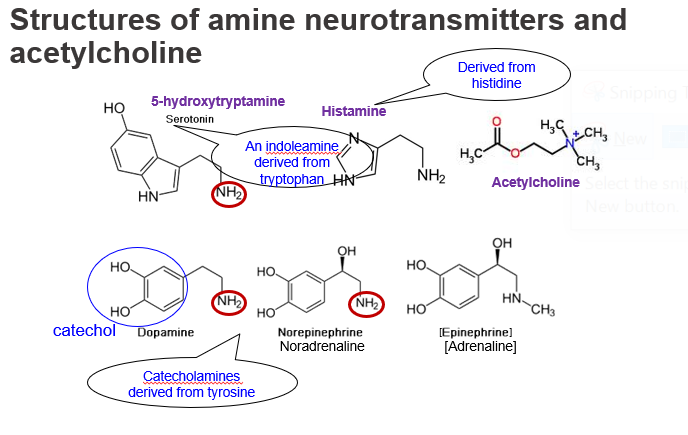
Which neurotransmitter is made from histidine and contains both an imidazole ring and an amino group?
Histamine, which has an –NH₂ group and is active in brain and immune responses.
How is dopamine structurally classified and what is it derived from?
Dopamine is a catecholamine made from the amino acid tyrosine. It includes a catechol ring and a side chain ending in an –NH₂ group, making it a primary amine.
Dopamine contains which structural features and is synthesized from what amino acid?
It has a catechol group and a primary amine (–NH₂) side chain, and it's derived from tyrosine.
What is a catechol, and does it contain an –NH₂ group?
Catechol is a benzene ring with two hydroxyl (–OH) groups in adjacent positions. It is not a neurotransmitter itself and does not contain an –NH₂ group. dopamine which is a catecholamine contains a catechole ring and an amine group.
Is catechol a neurotransmitter and does it have an amino group?
No, catechol is just a ring structure found in catecholamines and does not have an –NH₂ group on its own.
What are catecholamines, and how are they structurally related to tyrosine?
Catecholamines like dopamine, noradrenaline, and adrenaline are derived from tyrosine and contain a catechol ring plus an ethylamine side chain (–CH₂–CH₂–NH₂), giving them an amino group.
Name three catecholamines and describe their structural features.
Dopamine, noradrenaline, and adrenaline all have a catechol ring and an NH₂ group on their side chain, and are made from tyrosine.
What is noradrenaline (norepinephrine) and how does its structure differ from dopamine?
Noradrenaline is a catecholamine like dopamine but has an additional hydroxyl (–OH) group on the β-carbon. It still retains the –NH₂ group, important for its biological activity.
How is noradrenaline structurally different from dopamine?
It has the same catechol and NH₂ group, but adds a β-hydroxyl group, making it more polar and affecting its receptor binding.
What is adrenaline (epinephrine), and what functional group distinguishes it from noradrenaline?
Adrenaline is similar to noradrenaline but has a methyl group attached to the amine, forming a secondary amine (–NHCH₃) instead of a primary one.
: Which neurotransmitter has a methylated amine group and how is it derived?
Adrenaline, derived from tyrosine, has a –NHCH₃ group, making it a secondary amine.
What is acetylcholine (ACh), and does it contain a typical –NH₂ group?
Acetylcholine is a quaternary amine, not derived from an amino acid. It has a positively charged nitrogen (–N⁺(CH₃)₃) but does not contain a free –NH₂ group.
Does acetylcholine have an –NH₂ group like other neurotransmitters?
No, it has a quaternary ammonium group (–N⁺) and is structurally distinct from monoamine neurotransmitters.
Where are the cell bodies of amine neurotransmitter neurons typically located?
In a small number of specific brainstem nuclei, such as the raphe nuclei (serotonin), locus coeruleus (noradrenaline), and substantia nigra (dopamine).
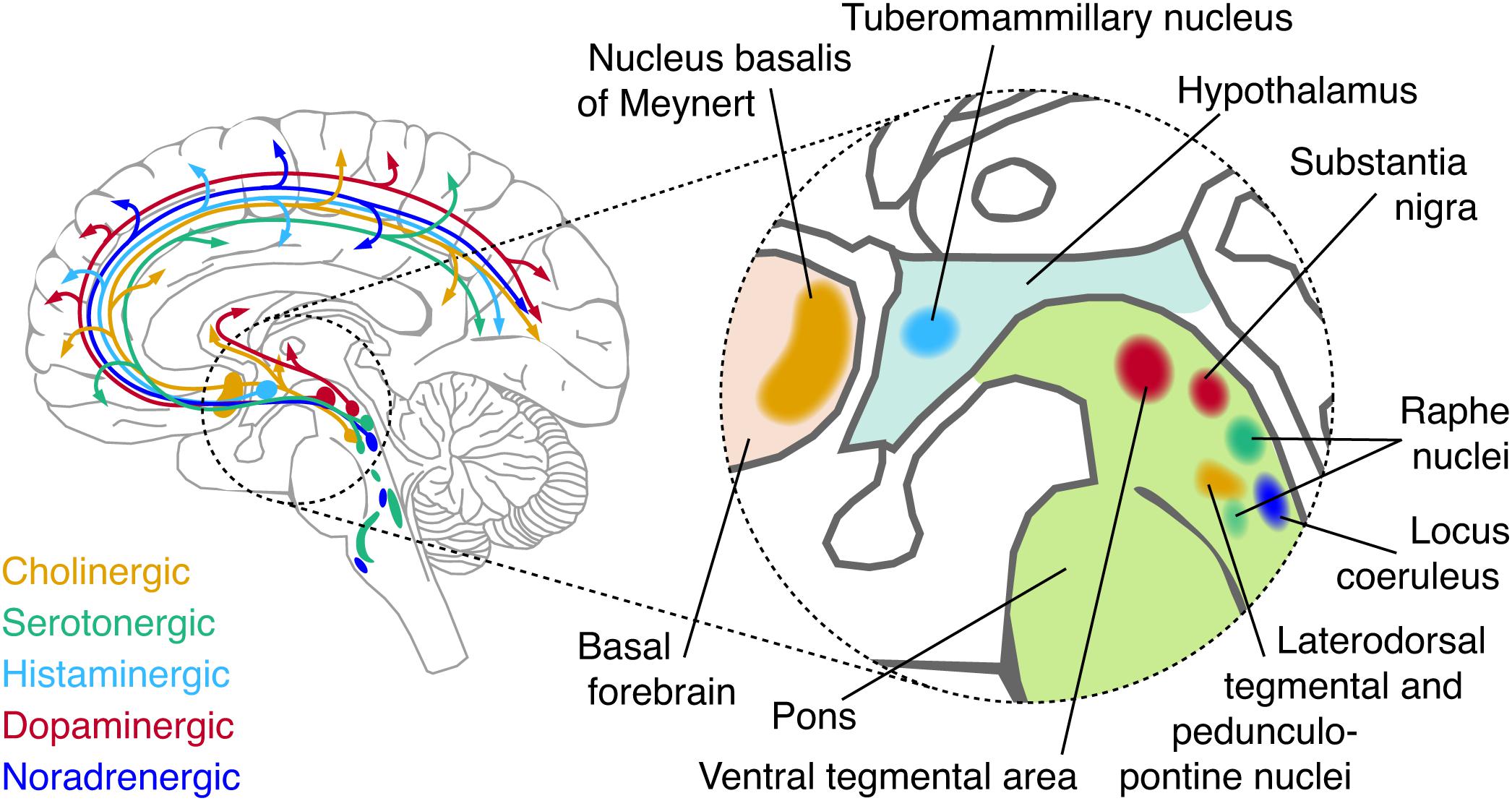
Which part of the brain mainly houses the neurons that produce dopamine, serotonin, and noradrenaline?
A few small nuclei in the brainstem.
How do the axons of amine neurotransmitter neurons behave in the nervous system?
Their axons project widely, allowing them to influence many areas of the CNS from a localized source.
Do amine neurotransmitters produce fast excitatory or inhibitory effects directly?
No, they modulate the activity of other fast neurotransmitters like glutamate or GABA, either enhancing (+) or reducing (–) their effects.
Through what kind of receptors do amine neurotransmitters usually act?
Mostly through G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), leading to slower but longer-lasting effects.
Are the receptors for amine neurotransmitters ion channels or metabotropic?
Metabotropic (GPCRs) — they produce modulatory effects rather than fast transmission.
Do amine neurotransmitters act at specialized synapses like glutamate or GABA?
No, they often act via diffuse release (volume transmission), not at well-defined synaptic contacts
what are the key brain functions regulated by diffuse modulatory systems?
arousal, attention, sleep, motivation, and survival behaviors.
Which essential processes in the brain are controlled by amine neurotransmitter systems?
Sleep-wake cycles, alertness, focus, and stress responses.
Why are amine neurotransmitters well-suited for global brain state regulation?
Their widespread projections and diffuse release allow them to modulate entire brain networks simultaneously.
What feature of amine systems allows them to influence large-scale brain activity?
Their diffuse modulatory nature, reaching multiple brain areas at once.
Where do central noradrenaline pathways originate in the brain?
From the Locus Coeruleus, a nucleus in the brainstem (pons).
What is the main brainstem nucleus that produces noradrenaline for the CNS?
the Locus Coeruleus (LC).
What neurotransmitter is used by the C1 group of neurons in the medulla?
The C1 group may use adrenaline (epinephrine) instead of noradrenaline.
Which catecholamine is associated with the C1 neuron group in the brainstem?
Adrenaline (epinephrine).
What areas of the forebrain are major targets of noradrenaline projections?
The cerebral cortex and hippocampus receive diffuse noradrenergic innervation.
Which forebrain regions receive widespread input from the Locus Coeruleus?
The cortex and hippocampus.
Do noradrenergic pathways only go upward in the brain?
no, they also have descending pathways to the spinal cord, modulating pain and autonomic function.
Apart from the forebrain, where else do noradrenaline axons project?
They also descend to the spinal cord.
Why is noradrenaline often called the “arousal chemical”?
Because it plays a key role in wakefulness, alertness, and stress-related responses.
What is the function of noradrenaline that gives it the nickname "arousal chemical"?
It promotes arousal, attention, and helps the brain respond to stress.
: What types of receptors does noradrenaline act on in the CNS?
It acts on α1, α2, β1, and β2 adrenergic receptors, all of which are GPCRs.
Noradrenaline binds to which receptor families in the brain?
Adrenergic receptors (α1, α2, β1, β2), which are all G-protein-coupled.
What is noradrenaline's role in the brainstem related to blood pressure?
It helps regulate blood pressure via the baroreceptor reflex.
Which brain function involving blood pressure does noradrenaline help control?
The baroreceptor reflex in the brainstem.
What functions are modulated by descending noradrenergic pathways?
they influence movement and pain modulation in the spinal cord.
What does noradrenaline do in its descending pathways to the spinal cord?
It helps regulate motor control and inhibits pain signals.
What is the role of ascending noradrenergic pathways?
They regulate arousal and mood, especially via the cortex and limbic areas.
Which functions are controlled by noradrenaline’s ascending projections?
Wakefulness and emotional mood regulation.
what cognitive processes does noradrenaline influence in the brain?
it supports attention, learning, memory, and aspects of movement.
How does noradrenaline contribute to cognitive performance?
It boosts focus, learning, and executive function.
What condition is associated with noradrenaline depletion in the cortex and hippocampus?
Depression, due to reduced noradrenaline levels in the forebrain.
A lack of noradrenaline in which brain areas is linked to depression?
The cortex and hippocampus.
What mental health condition is linked to noradrenaline overactivity?
Mania, often seen in bipolar disorder.
When noradrenaline activity is too high, what condition can result?
Mania (excessive energy, euphoria, hyperactivity).