07 - Reproductive Systems
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
sexual differentiation
causes sex difference and specificity of reproductive systems
formed during fetal development
puberty to establish its functional and structural maturation as a function of hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis
sex hormone synthesis and control mechanisms
menstrual cycle
genetic sex → determined by sex chromosomes
Y chromosome is determinant for male gonadal and phenotypic sex, since testis-determining gene is located on Y chromosome
gonadal sex → testes or ovaries
phenotypic sex → physical appearance of internal and external genitalia
differentiation of male phenotype determined by presence of testes and the hormones they produce
differentiation of female phenotype is independent on presence of ovaries, but is dependent on absence of testes and the hormones they produce
gonads and hormones
testes
Leydig cells → secretes testosterone for male differentiation
Sertoli cells → secretes antimullerian hormone for regression of Mullerian ducts, converts testosterone to estrogen
ovaries
theca cells → produce progesterone and androgen precursors
granulosa cells → converts progesterone to estrogen
duct development
before differentiation, both Mullerian and Wolffian ducts are present
testosterone → stimulates Wollfian duct
antimullerian hormone → regresses Mullerian duct
no testosterone/AMH → Wolffian duct regresses, Mullerian duct develops
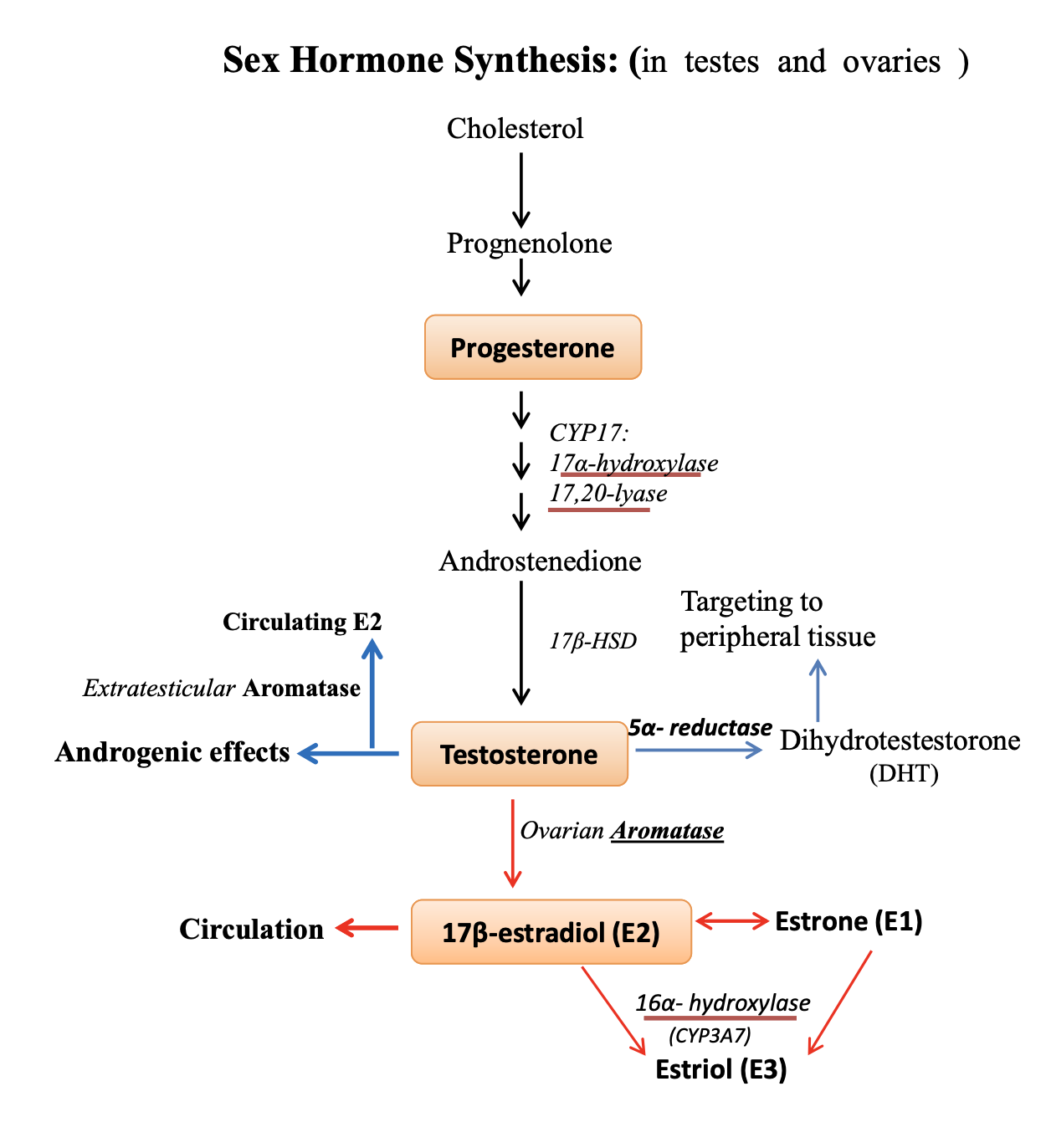
sex hormone synthesis
cholesterol → progesterone → testosterone → estrogen (E2) → estriol (E3)
17⍺-hydroxylase and 17,20-lyase → progesterone to testosterone
5⍺-reductase → testosterone to potent dihydrotestosterone (DHT)
deficiency alters development of targeting organs
aromatase → testosterone to estrogen (E2)
located in gonads and peripheral tissues
in males, E2 functions in spermatogenesis in testes
in females, E2 circulation released from ovaries
estrogen promotes survival of osteoblasts and inhibits osteoclasts, where deficiency causes osteoporosis
16⍺-hydroxylase → E2 to E3
major product in placenta
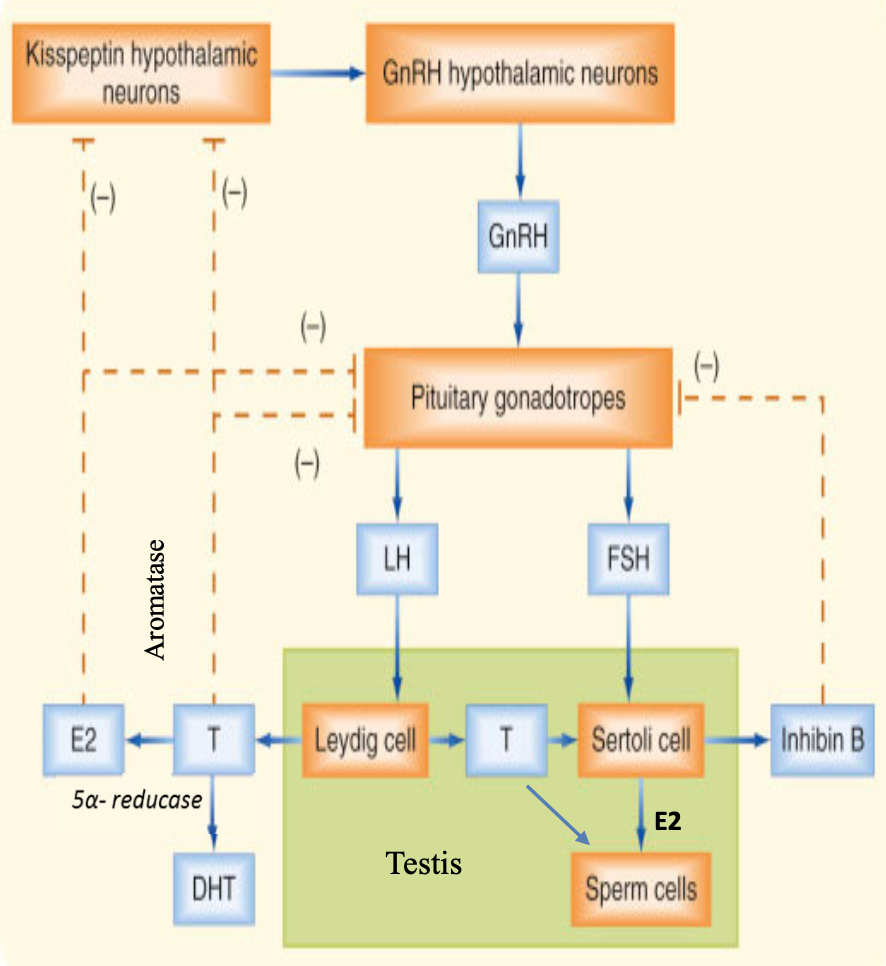
male — hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis
hypothalamic neurons secrete GnRH in a pulsatile manner that stimulate pituitary gonadotropes to secrete LH and FSH
LH acts on Leydig cells to produce progesterone and then testosterone
degerming male phenotype in embryogenesis
spermatogenesis
all androgenic responses
FSH acts on Sertoli cells
provide antimullerian hormone for male phenotype development in embryogenesis
provide structural support and nutritional support for germ cell development
convert testosterone to estrogen via aromatase for spermatogenesis
produce inhibin to control/inhibit pituitary release of FSH
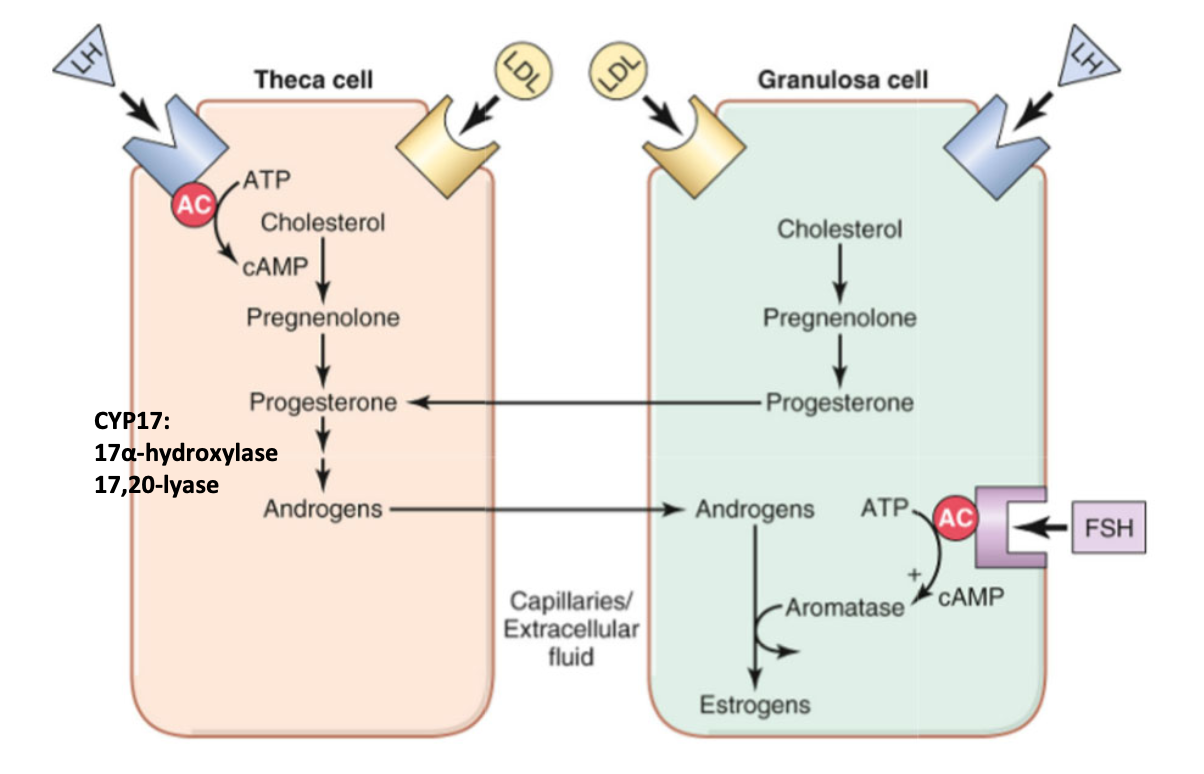
female — hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis
LH acts on both theca and granulosa cells to produce progesterone
theca cell → progesterone converted to androgens via 17⍺-hydroxylase and 17,20-lyase
androgens diffuse from theca cell to granulosa cell
granulosa cell → progesterone diffuses into theca cell
FSH acts on granulosa cells to produce estrogen
aromatase → converts androgens to estrogens
produce inhibin and activin
GnRH during puberty
secretion of GnRH begins at gestational week 4, with secretion of FSH and LH around 10-12 weeks of gestation at low levels until puberty
puberty starts with predominant release of GnRH in pulsatile manner during child sleeping
allows for time frame for receptor replenishment
stimulates FSH and LH release from pituitary
feedback mechanisms
negative feedback (both sexes) → testosterone, estrogen, progesterone, and inhibin decrease GnRH, LH, and FSH levels
Leydig cells feedback on LH and FSH
Sertoli cells feedback on FSH
estrogen feedbacks on hypothalamus and pituitary
positive feedback (females only) → high estrogen will increase GnRH and LH levels, leading to LH surge
estrogen feedforwards to hypothalamus and pituitary
ovarian cycle
follicular phase → days 1-14
increased FSH promotes estrogen synthesis
activin released to convert all androgens to estrogen via aromatase
follicle growth, endometrial proliferation
ovulation phase → day 14
LH surge, triggered by increased estrogen
positive feedback of estrogen
theca and granulosa cells become luteal cells
luteal phase → days 14-28
increased progesterone from corpus luteum
low levels of 17,20-lyase and release of inhibin to lower estrogen
luteal cells regress from having lowered LH and FSH
high progesterone and estrogen for negative feedback
uterine/endometrial cycle
proliferative phase → 11 days
high levels of estrogen
endometrial growth
cervical mucus is thin and alkaline
secretory phase → 12 days
high levels of progesterone
glandular secretion and vascularization
cervical mucus is thick and acidic for sperm-blocking
menstrual phase → 5 days
endometrial necrosis and shedding
prostaglandins (PGs) cause vasoconstriction in uterus and vasodilation in systemic circulation
gonadal cells summary
in males:
Leydig cells → secretes testosterone
LH receptor
drives spermatogenesis and male phenotype
Sertoli cells → secretes estrogen and inhibin
FSH receptor
supports spermatogenesis, inhibits FSH
in females:
theca cells → converts androgens to progesterone
LH receptor
substrate for granulosa conversion
granulosa cells → secretes estrogen, inhibin, and activin
FSH and LH receptors
promotes follicle maturation
positive feedback mechanism for estrogen