Nervous System and Brain Quiz Review
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Autonomic division
Involuntary muscle control
Efferent division
Sends impulses from the CNS to the muscles glands
Parasympathetic division
Reduces sympathetic response + provides resting functions such as digestion + urination
Sensory division
Sends impulses from the senses to the CNS
Somatic division
Voluntary muscle control
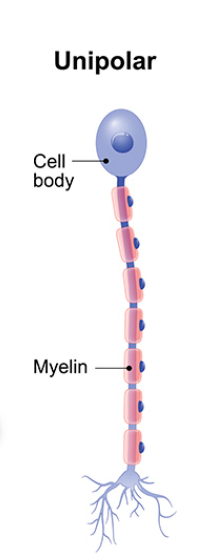
Unipolar neurons
Have ONE process
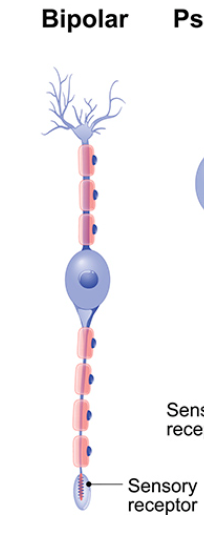
Bipolar neurons
Has 2 processes
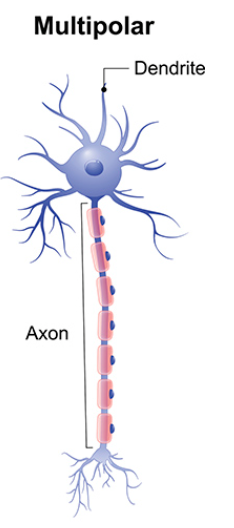
Multipolar neurons
Has many processes
Afferent neurons
Carry impulses toward the CNS
Efferent neurons
Carry impulses away from CNS
Interneurons
Connect afferent z+ efferent neurons
Neuroglia
Supports, insulates, and protects neurons
Pathway of an impulse
Nerve impulse: is an electrical signal that travels along the neuron
Arises from the movement of ions causing a change in electrical charges
What happens when the impulse reaches the end?
It causes a release of neurotransmitters across the synaptic cleft
What charges are as the impulse travels through the neuron?
Potassium diffuses out of the neuron (repolarization)
The sodium-potassium pump then restores the ion concentrations to normal and the resting potential returns
The meninges of the brain:
Dura mater: thick, tough layer
Arachnoid membrane: thin cobweb layer
Pia mater: thin layer containing lots of blood vessels

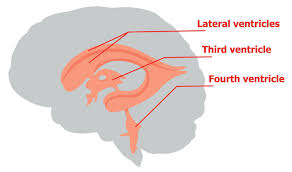
Ventricles of the brain
Lateral ventricles: Connected to the third ventricle by thin interventricular formanen
2 lateral v in each hemisphere
Third ventricle:
diencephalon
Fourth ventricle:
hindbrain
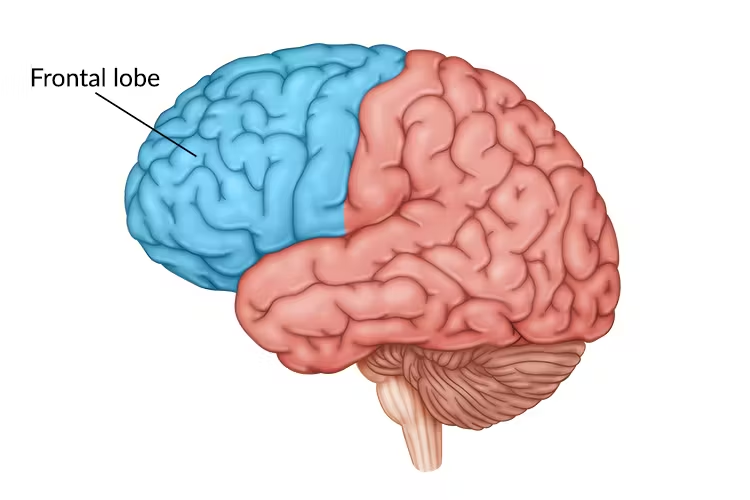
Frontal lobe
Voluntary movements (walking)
Reasoning + decision making
Memory
Ability to predict consequences of actions
Planning
Verbal communication (specifically in the Broca’s area)
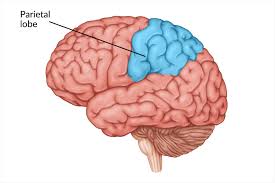
Parietal lobe
Sensations (pain, temperature, touch)
Visual-spatial processing
Body position
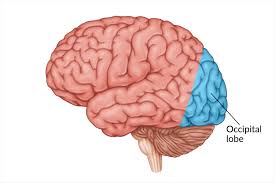
Occipital lobe
Visual processing vision and memory of objects
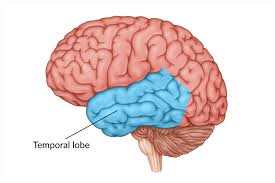
Temporal lobe
Memory
Comprehension and pronounciation of words
Sensations of smell and sound
Emotional association of memories
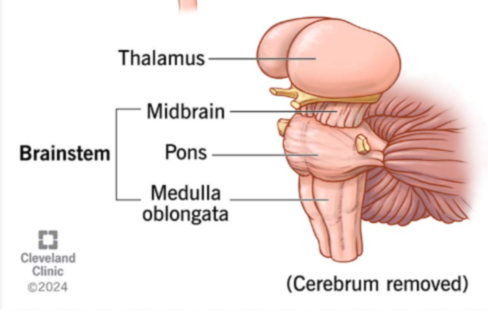
Thalamus
Relays sensory impulses to the cerebral cortex for the processing and sorting
Hypothalamus
Responsible for autonomic processes (body temp, metabolism, blood volume)
Controls hormones released by the pituitary gland
Part of the limbic system, which regulates emotions + feelings of pleasure (thirst, hunger, pain, sex)
Cerebellum
Responsible for coordinating the movements directed by the cerebrum so they’re graceful and efficient (involuntary)
Brain stem
Has 3 regions that relay information to the cerebrum and controls autonomic processes like breathing and heart rate
What happens in a reflex arc?
Pre-programmed responses are called reflex and the pathway they travel through is the reflex arc
Sensory neurons send electrical impulses to relay a neuron